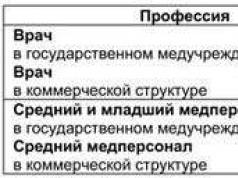
13.12.2016 0
Let's talk about how to draw your own conclusions queen bees: basic techniques and how to work with the calendar. Sooner or later, any beekeeper has to purchase or independently breed new queens for bee colonies. After all, the old ones may die, fly away, or stop producing the desired brood.
Life of bees
Different types of bees in the hive perform their own type of work. And the queen bee is the center of the hive, without which it will not last long. After all, it is she who lays the larvae, from which both worker bees and drones emerge. Depending on what the young brood is fed, certain types of individuals will appear.
So, if you feed them only royal jelly, a new queen bee will appear. And if you feed them with honey, then worker bees will grow. In nature, a new queen appears as a result of swarming bees and new queen bees fly away with part of the hive, creating their own separate colony.
This natural method is not suitable for people, since it does not provide for any control over the family and you can lose most of the bee colonies just before the honey harvest season. Therefore, there are several options for how to breed the number of queens you need exactly when you need it. Thanks to artificial methods, you can learn how to hatch queens from scratch, even without much beekeeping experience.
Different methods mean that the same method may not work in every region. Therefore, a lot depends on the climate, terrain, weather conditions and the bees themselves. Which one is right for your apiary can only be understood over time, by experimenting and trying different methods.
Natural swarming
In nature, a new queen is hatched only when the process of swarming bees begins. This usually happens when there is no longer room in the colony for new worker bees and the hive is ready to split into several new colonies. Similar conditions can also be created artificially.
- To do this, simply remove the empty frames and leave only those completely filled with brood. Then the bees actively begin the process of swarming and laying the so-called queen cells.
- If you decide to use the simplest and in a natural way, borrowed from nature, then you need to compact the colony at a certain moment, take away the extra frames and wait for the bees to lay the queen cell. Now they are being layered.
- But this method is now little used in beekeeping, since you cannot predict the quality of the future queen, nor the number of new individuals. The main danger is that you may not notice the appearance of new queens, and they will leave your hives with most of the worker bees.
Creation of fistulous queen bees
This method is also more natural, created by nature for the emergency restoration of the queen in the hive if she accidentally died.
- V in this case usual laid larvae for breeding working individuals in urgently are converted into queen cells by the bees themselves;
- in the apiary this method is very often used both independently and in addition to others artificial methods. This is an opportunity to very quickly create a large number of new queen bees;
- However, there are also disadvantages. In this case, the honeycombs most often deteriorate when you have to cut them off, because the queen cells are in close proximity to each other.
Emergency method
Artificial breeding of queens was invented by people taking into account the vital activity of bees. Only by understanding what the bees will do in a given case can one predict when and how a new queen will appear. We will describe one of the simplest and fastest methods in beekeeping below.
- We take a frame with ready-made brood from the strongest family. In this case, it is imperative to keep the frame away from the bees, so as not to drag the queen bee along with you.
- We put such a frame in a new home. In this case, you can cut a small hole in this frame and also remove lower walls, leaving only two larvae. You don’t have to do this, but rearrange the entire frame as it is. They move such a frame with larvae to the family that has lost its “queen”.
- Thus, in the first hive, the queen will continue to create new brood, and in the second, from the transferred larvae, the bees will quickly create queen cells and they will have their own queen bee.
- If you do not find fistulous uterus, this can only mean that the uterus is still present there. This means that we need to look for the reason why she stopped producing brood.
Method with insulator
- in this case, a good queen from a strong family is placed in a so-called insulator and installed in a well. The insulator is made of two frames and grilles. A frame with brood and an empty frame for laying new larvae are placed next to it. The main thing is to lay the structure on all sides so that the queen does not have the opportunity to escape;
- When the queen has laid the brood we need, we place her back between the frames with the larvae. And we create the nucleus ourselves. To do this, select a frame with dry food, honey and freshly made brood in the insulator. We throw several bees there, chickening them out from other frames. We place the uterus there;
- then fresh brood at high temperature and moisture content is cut to the lower border and placed in the same body from which the uterus was taken. We cut off the queen cells and place them in the nucleus and wait for the finished specimens to ripen.
A similar method of breeding queens is proposed by Gennady Stepanenko, who often shares beekeeping tips with beginners. With this method, it is important to use a hatching calendar so as not to miss when and what needs to be done.
Nicot system for breeding queens
In order to create new queens using the Nicot method, you should have some equipment available. This:
- Cassette made of dividing grid and lid.
- Bowls and holders for them.
- Plinths for attaching to the frame.
- Ready cells for future queen cells.
All this can be purchased ready-made and you can simply use Nicot to hatch queens through the system. Initially, the cassette is installed in the center of the frame. To do this, free space is cut out in it. It must be firmly attached to the frame. Next, you need to make a so-called grafting frame and clean the cassette.
The uterus is transplanted into the finished device. A family-educator is formed separately. Now the grafting frame is moved to this colony and the entire process of maturation of the larvae is controlled, until the appearance of the finished queen bee. The queen hatching calendar will help you with this. In this case, the queens are hatched without transferring the larvae from hive to hive.
Kashkovsky method
According to the method of the scientist Kashkovsky, the following procedure is performed.
- Each bee colony helps the young queen to hatch independently. At the beginning of the honey harvest, a layering is made, where frames with worker bees, an old queen, already sealed brood, honey and beebread, wax and dry land are transferred, and a few workers are also shaken off. Leave such cuttings for a month in a warm place;
- In the old hive, bees actively begin to create fistulous queen cells at this time, since that same emergency period has begun for them. Next, the beekeeper culls and leaves only the best and largest larvae;
- over time, they remove the old queen from the layer and unite the family again into one hive, but with a new young “queen”.
Video: breeding queens from scratch.
Basic requirements for quality breeding
So that your efforts are not in vain, and the result is sure to please you, you should adhere to some rules of beekeeping:
- The first and most important thing is that work is carried out only with strong families in the apiary. After all, only from a strong family can you confidently obtain the same good and high-quality queens.
- Carrying out work to remove queens most often occurs in the spring, early May or summer, when the good temperature, and young bees have the opportunity to fly around.
- To fertilize eggs in an apiary in mandatory drones must be present.
- An important condition is to ensure optimal temperature conditions and air moisture, especially if you move the frame with brood from the hive for some time.
Working with the calendar
The queen hatching calendar is used in almost all artificial methods of breeding queen bees. After all, you need to carefully monitor which day to carry out which procedures, do not forget about the vital activity of bees, the number of days of larval maturation, etc. There are two options for what the queen hatching calendar looks like. This can be a multi-colored table or two cardboard circles connected in the center.

Almost every beekeeper claims that breeding queens in the spring is not a very successful task. According to the literature, such individuals are very weak and are of no use to them, so they are completely discarded. But why is this happening, everyone is silent. However, after lengthy experiments, some beekeepers still managed to achieve very good results. Therefore, we can safely say that successful hatching is possible and even necessary if you want to increase the productivity of your apiary.
Now let's look at the reasons that prevent us from successfully carrying out the withdrawal procedure. This is primarily bad weather. As the textbooks say, successful hatching requires temperature environment not less than +24 degrees Celsius. Where can I get it in early spring, when it’s +20 outside? Of course, such a prospect becomes an unsolvable task for inexperienced beekeepers.
The second reason is the weakness of the queens bred in this way. They will be of little use, but a lot of hassle. Therefore, if you are not confident in your abilities, then it is better not to make early withdrawals. Well, now let's look at how to make this difficult task a reality. So, as already mentioned, this is a troublesome and difficult matter, but if everything works out, then the output will be at least twice as large. The following video shows how to carry out early withdrawal queens
90% of the success of early queen hatching depends on the beekeeper himself and only 10% is due to circumstances that cannot be influenced in any way. It is also worth remembering that the quality of the breeding material must be the highest. This aspect has already been proven in practice many times. It says that even with the correct and timely work of the beekeeper, the quality and quantity of the product depends on him only 50%, and the remaining 50% depends on the quality of the queens.
Then the success of the business also largely depends on the method of breeding the queens. After all, your main task is to get a strong and developed uterus, which, when correct content must make the flight even in bad weather conditions. It is often very difficult to ensure that it flies around in the early spring at its physiological time, and some even claim that it is impossible to do this. But this is far from true. Now a few words about how it is impossible or undesirable to breed queens.
The first method of hatching that is not recommended is when families are divided and fistulous queens are removed. This method is not suitable for early hatching, since there is no guarantee of the quality of the new queens. The second not recommended option is when we introduce one or a couple of families into a swarm state, and then their queen cells are transferred to other families. But if at the same time we put the queen cells in layering, then we are guaranteed to receive good queens there is none. You can, however, go the other way.
For one fetal uterus, and we place the queen cell itself in the family, which is considered the main one. Then the quality of the product will be high, but the early bribe will be missed. This option is considered more or less acceptable, but it is still not advisable to use it. The hassle will be no less than when breeding queens in warm time, and the result will remain almost the same. Finally, let’s say that a significant share of success depends on the layering where the queen cell or young queen will be placed. Next is the second part of the video about the early hatching of queen bees.
The whole point is that a full-fledged and strong family cares for and feeds the uterus. This helps her develop on time and not lose anything. Of course, some sources may claim that the mother can feed herself just fine. Yes, this is true, but at the same time she also receives additional care from her family. If there is no such care, then it will be poorly developed and not on time, which will negate all early hatching.
Conditions and sequence of withdrawal
To successfully hatch queens, we need to clearly know what and how, and most importantly, in what sequence we need to do it. Then it is necessary to withstand all the conditions for the removal of queens High Quality. Only by observing all these points can you count on success. Now let's take a closer look at what to do, how to do it, and what conditions are needed for success.
What and how should you do?

Conditions for breeding quality queens
- Propagation material must be purchased from proven breeding apiaries and its quality must be undeniable.
- When breeding, it is imperative to give the queen a seven-day rest, isolating her from the main bees. Then her eggs will be large and the offspring strong.
- In the queen cells on the grafting frames, the temperature must be maintained at +32 degrees Celsius. Humidity should be in the range of 75-90%. Experienced experts recommend using aerothermostats when removing queens. Then support the necessary conditions will not be difficult.
- Mandatory even distribution of queen cells among bee colonies. Then they will be fully fed with royal jelly, and their development will be complete and timely. For this rearing process, half of the hives are fenced off, which then become layering.
Video “Hearing queen bees in early spring. Part 3"
In this final video, Vadim Tumanov tells and shows how he carried out the early hatching of queens.
In this article you will learn how to breed bees from scratch and what methods exist for breeding these beneficial insects.
How to raise bees from scratch
In order for the apiary to be profitable, it is necessary not only to follow all the rules of maintenance, but also to correctly select insects for further breeding. In addition, there are certain rules for breeding and breeding queens.
Where to begin
Bees for breeding can be purchased from a variety of places: from large specialized farms and from amateur beekeepers. When purchasing, be sure to check veterinary documents confirming the health of the insects. That is why it is better to buy insects on specialized farms, although non-specialized farms with apiaries also sell queens and families.
Note: A productive family, when purchased in the spring, should have 4-5 kg of food, and in the fall - more than 16, as well as at least 10-12 nesting combs.
 Figure 1. Composition of a bee colony
Figure 1. Composition of a bee colony - It is better to purchase 2-3 families at once that have already survived the winter. In this case, in the new season it will be possible to obtain commercial honey from them;
- It is best to make a purchase in early spring;
- For beginners, to make a profit, it is enough to buy 20-50 families. You can make a profit from them by servicing the apiary yourself. Larger numbers require more time and skill to breed. As experience increases, the number of families in the apiary can be increased to 100-150 per person or 200-300 per two specialists.
To transport insects, you can use ready-made hives, special bags or cages. Transportation is best done in the evening or at night. Examples of transport cages are shown in Figure 2.
 Figure 2. Transport cages
Figure 2. Transport cages The hive entrance is tightly closed and opened only after placement in a new apiary. If transportation is carried out in bags, be sure to check that each container contains about 1.5 kg of bees, a queen, four honeycombs and 3 kg of sealed honey. In summer you can also buy swarms in swarms. In this case, you must make sure that there is a queen in the swarm, since without her the insects will scatter.
What is needed to breed bees?
Reproduction occurs by laying eggs by the queen. Fertilized eggs produce new queens and workers, and unfertilized eggs produce drones, which are subsequently used for mating (Figure 3).
Note: Throughout the year, the number of insects constantly changes due to the death of old ones and the breeding of new individuals. Workers also sometimes lay eggs, but only dwarf drones hatch from them, which cannot mate.
Immediately after wintering, in approximately the first three weeks, the size of the family decreases, since the breeding of new individuals does not yet cover the death of old ones. In the future, the indicators are equalized and the population grows. As the number of young individuals increases, the productivity of the queen decreases and the growth of the young stops. Subsequently, the number of individuals continues to decline during wintering.
 Figure 3. Reproduction of insects by eggs
Figure 3. Reproduction of insects by eggs The strength of the family can be assessed after wintering. If it occupies 8 frames (4 each with food and brood), the family is considered strong. Medium productive ones occupy approximately 5-7 frames, and weak ones - less than five.
Peculiarities
Under natural conditions, bees reproduce by swarming. This process begins after the accumulation of too many young individuals. The future swarm is formed by young workers who do not have enough work in the old hive. Examples of swarming are shown in Figure 4.
The swarming process goes like this:
- In the second half of summer, bees fly out of the hive (from about 10 a.m. to 1 p.m.). The first to leave the hive are the scouts, who are looking for a place for a new family.
- After this, some of the working insects fly out, followed by the queen, and lastly the remaining individuals.
- The new swarm remains close to the mother hive for several days (for example, on a branch). At this time, the beekeeper needs to prepare a place for relocation. If this is not done, the insects will simply fly away.
Typically, after removal new uterus and the departure of the first swarm, the swarming process is repeated: the second leaves the mother hive after 9 days, and the third after another 1-2 days. After this, all young queens in the mother hive are destroyed, since the worker insects leave only the largest individual.
 Figure 4. Swarming process
Figure 4. Swarming process To collect a new swarm you need a special device - a swarm. As a rule, a hook or rope is attached to the top for hanging the device. The swarm is hung under the collected insects and carefully shaken off inside. It is better to keep the collected swarm in the winter hut until the evening and transplant it into the hive at night. Inside the new hive, it is necessary to install frames with honeycombs and fodder honey. You can make a swivel yourself using the diagram and photo in Figure 5.
To move bees into the hive, a small gangway is placed next to the arrival board and the bees begin to pour out a little at a time. Sometimes insects are poured onto the frames from above, treating them with smoke. The top of the hive must be covered.
Note: Young individuals from a new swarm have an increased ability to collect honey, so they are often moved into an old hive, installing a new one next to it.
To limit natural swarming, colonies are propagated artificially. There are several methods of reproduction:
- Using individual layering: To do this, several frames with brood and adults are removed from the hive and moved to a new empty hive, located slightly away from the old one. After the brood appears, the family is strengthened by introducing several new frames.
- Half-flight division: in this case, the family is divided approximately in half. This method is only suitable for strong families, which tolerate wintering well. Half of the frames with brood, food and insects are moved to the new hive and placed about half a meter away from the mother hive. Next, you need to determine which of the families has the queen. This is very simple to do: working individuals from the hive with the queen fussily run around the tray. After this, a young individual is added to the queenless colony.
- Temporary layers: This method can be used only before the start of honey collection. New individuals are placed in the second part of the multi-hull hive, and when the first honey flow is completed, young and old individuals are combined, forming a stronger family.
Separate keeping of families can be practiced only if there is a good honey collection near the apiary. This will not only increase the survival rate of insects, but also improve the quality of commercial honey.
Preparation for breeding
The apiary should always have a supply of queens to replace old, sick or dead individuals. In addition, young queens are needed to expand the apiary and plant new families in the hives.
 Figure 5. Diagram and photo examples for making a swivel
Figure 5. Diagram and photo examples for making a swivel The highest quality and productive queens can be obtained from specialized farms that breed them. To transport or send queens by mail, special cages are used, in which not only the queen is placed, but also several accompanying bees and honey for feeding. After receiving a new individual, it must be immediately transplanted into the hive, since prolonged keeping in a cage will negatively affect its productivity.
Note: Breeding quality breeding queens is difficult. To do this, you need not only to carefully monitor the purity of the breed and brood, but also to create special families in which the queens will be bred. In small apiaries, queens can be bred on their own, using swarming or popular methods of artificial rearing.
For example, a productive family is allowed to release the first swarm. After this, the combs with the maturing larvae of the queens are cut out from the nest and they are rearranged into the cutouts of the combs of the colonies without queens. It is imperative to leave one queen cell in the mother’s nest to breed a young productive queen.
 Figure 6. Artificial removal of the uterus
Figure 6. Artificial removal of the uterus Another method can also be used: the queen is temporarily removed from the productive colony and placed in a nuc. After this, a honeycomb with eggs is selected and all cells are removed, except those from which the larvae have already hatched. The larvae are further thinned out (no more than two larvae should remain per three cells). Next, the frame is moved to the center of the nest, and the workers begin to place queen cells in them. When the time for the larvae to hatch approaches, the cells are cut off and transferred to queenless colonies, and the removed queen is returned to the hive. Figure 6 shows examples of artificial creation of queen cells for breeding productive queens.
The queens are hatched at the end of spring or early summer, when the bees are already stronger after wintering and the honey plants begin to bloom intensively.
Keeping bees for beginners: video
The video shows in detail the features of raising bees at home for beginners. With the help of this video you will be able to properly organize the process of caring for insects in the apiary.
Rotational beekeeping for beginners is considered one of the most effective technologies in beekeeping. This method is also called year-round maintenance.
primary goal this method breeding - to maintain the health of bee colonies during the winter and prevent the development of diseases.
What is this method
Rotational breeding of bees involves the implementation of several mandatory activities. First, the beekeeper must regularly remove drone brood, since drones are most often affected by Varroa mites.
Secondly, their old colonies need to be constantly created with new ones with careful monitoring of insect health. In addition, the hives need to be regularly transported to apiaries where there are more honey plants. With the arrival of winter, you need to provide insects optimal conditions wintering in natural conditions.
By following these rules, breeding and caring for bees will continue without serious difficulties. The beekeeper will be able to constantly form new families that are resistant to diseases.
Peculiarities
If you are interested in how to start breeding bees from scratch using rotational technology, you should know what features and rules need to be taken into account.
Among the main stages of breeding using this method, I highlight t (Figure 7):
- Spring honey collection It is better to carry out in apiaries with a large number of honey plants. Since bees are prone to swarming during this period, excess honey and young bees must be regularly removed from the hive.
- Creation of new families involves moving young insects and queens to a special room. When all the insects have gathered around the queen, the colony is considered created and can be moved to the hive. After a week, the quality of the brood and the degree of acceptance of the queen are monitored. If she does not cope with her task, or the bees do not perceive her, the queen is replaced.
- Monitoring family readiness for winter carried out by weighing. This allows you to determine whether the insects have enough honey to survive the winter.
 Figure 7. Scheme of placement of insects in the hive during rotational breeding
Figure 7. Scheme of placement of insects in the hive during rotational breeding Before the onset of winter, the maternal families are disbanded, and the queens are placed in separate cages to create an artificial swarm. Old families are united with new ones and preventive actions to prevent diseases.
Rotational bee breeding: video
You will find more information about rotational breeding in the video. It describes the main features of the method and the rules for carrying out the necessary activities in the apiary.
The two-queen breeding method is based on the biological ability of these insects to coexist peacefully and productively in one large colony with two queens (Figure 8).
Note: In this case, two dividing grids are installed in the hive, through which bees from one colony can contact the brood of another, and vice versa.
With such maintenance, the theft of honey is reduced, and the bees produce much more products per season, while maintaining the health of the brood, workers and queen.
Peculiarities
Many modern beekeepers prefer to use not the two-queen system itself throughout the year, but only some of its aspects. In particular, families are united immediately before the start of the honey harvest to increase the amount of production.
 Figure 8. Drawing of a hive for two-queen housing
Figure 8. Drawing of a hive for two-queen housing Among the positive features of the method it is worth highlighting:
- Overwintering large joint families allows for more economical consumption of feed and maintains the health of insects;
- Rearing brood requires less feed and labor;
- Large families are less susceptible to disease and are highly productive and active.
However, it should be noted that to use this method bulkier hives will be needed. In addition, insects often begin to swarm, so the beekeeper needs to carefully control this process.
Queen rearing is considered one of the most important skills in beekeeping.
There is even a special branch of science - mother breeding.
Today there are many known effective methods that allow you to achieve good results.
The bee family consists of 3 groups - worker bees and drones. In addition, there are young developing individuals in the hive. Only worker bees collect nectar and pollen. They are sterile and have underdeveloped genitals.
The queen bee is a female insect characterized by well-developed genitals. She is responsible for laying eggs. Drones do fertilization.
The insect is characterized by visual features:
- It is larger than other species. The insect has a wider and longer body.
- The abdomen of the uterus has a pointed end and protrudes forward.
- It has a smooth and straight tip.
- The paws are located almost perpendicular to the body and splayed in different directions.
When to hatch queens
In apiaries it is worth changing the queen bee at intervals of 1-2 years. From the age of two, the queen bee loses her productivity and lays many unfertilized eggs, which become drones. As a result, the colony becomes less strong and produces less honey. To maintain productivity, the queen bee needs to be replaced.
Family choice
For the hatching to be successful, it is necessary to choose the right parent family. The offspring that will be born depends on this.
When choosing a family, you should consider the following requirements:
- high honey productivity;
- endurance throughout the year - this is especially true for winter;
- resistance to diseases.
Launch calendar
Before withdrawal, you should familiarize yourself with the calendar dates of the event. various procedures. In addition, you should worry about the presence of a rich bribe. Nutritional deficiency or adverse climatic conditions will provoke the removal of unproductive queens.
It is best to carry out work on removing queen bees from late spring to the first half of summer. In the middle zone, the procedure begins after the first honey plants bloom.
In September, breeding of queens is done quite rarely. This procedure is carried out by the bees themselves if the old queen is sick. In such a situation, the new individual has time to fly around and prepare for winter. Thanks to this, problems can be avoided in the spring.

Hatching calendar
Mother breeding from the queen cell to the fetal uterus:
Conditions for withdrawal
If you plan to hatch queens, you need to create certain conditions in early spring:
- provide insects with food;
- perform an ultra-early flyby;
- qualitatively insulate the hive;
- provide quality honeycombs;
- use honey-beebread fertilizing;
- create favorable conditions - the temperature should be +28-30 degrees, humidity - 80-90%.
How to remove a queen bee: methods with video
To achieve good results during removal, you need to choose the right method for carrying out the procedure.
The simplest conclusion of queens:
The main method of breeding queens
The queen bee is a large individual that is located in the hive. She is responsible for laying eggs. Therefore, her health affects the condition of the entire family. In nature, an individual lives 8 years. But to maintain productivity in apiaries, it is replaced at intervals of 2 years.
To remove you can use in a simple way, which is popular among novice beekeepers:
- Place 3 frames with brood and close the entrance.
- Make sure that there are no broodless frames in the hive.
- Wait for the queen cells to set. Then layering will appear.
Artificial methods
Today, many artificial methods of removing uteri are known - emergency, using an isolator, the Kashkovsky and Tsebro methods. Such methods are complex, but at the same time they allow you to achieve better results.
The most in a fast way considered emergency:
- Most strong family pick up the frame with brood. Be sure to shake off the bees so as not to displace the queen.
- Remove the bottom walls from the frame with 2 larvae and place it in a new home with a family that has lost its queen bee.
- In the first hive, a new generation of bees will appear, and in the second, the bees will form new queens instead of the transferred one.

Cerebro method
To facilitate the removal of the uterus, an insulator is used. It is a cell with a grid with marked cells. Thanks to this, the queen bee cannot enter the hive ahead of time, and worker bees cannot fly to her. Getting used to the new queen bee lasts 3-7 days.
Kashkovsky’s technique requires compliance with the following rules:
- Strong families are placed on wide streets. Uninhabited honeycombs are not taken out of the hive.
- Inspection and disassembly of hives is performed no more than 7-8 times during the season.
- Fistula uteri are used for production. This helps to significantly reduce the amount of work.

The advantage of the procedure is the possibility of obtaining a large number of unrelated queens. The disadvantages include the need to break out excess queen cells.
The Cebro method is considered one of the most effective. It consists of observing the following rules:
- Bees are kept in three-part hives.
- In the spring, during the growth period, the inserts are not removed, but a second body is made.
- Weak families are rejected.
- On the 14th day, at a late harvest, 2-3 layers are created and a bee colony is formed.
- After the bribe, the formed layers are combined with the main family. In this case, the queen bee is removed.
- To increase honey collection, it is worth providing for a high-quality wintering. To do this, the bees are well fed and the hives are ventilated.
Conclusion in a simple way
To raise an individual, the main bee must be removed for a certain time and the honeycomb must be selected. It must have open brood. It is carefully cut so that young larvae are present on the edges. Place in the central area of the nest. As a result, insects will begin to form queen cells.
This method will give results if there are a sufficient number of larvae in the family. They should be distributed throughout the cell. The technique is not used for large apiaries. This is due to high labor intensity.

Hatching without transfer of larvae
To breed queen bees all year round, you can use the Zander method. The procedure is carried out without moving the larvae. As a result, many individuals will appear, which are used to replace old ones, the emergence of new families and offspring. The method is suitable for large apiaries.
To implement this method, you should cut the frames into strips. There should be 1 larva on each of them. Attach the cells to the block and secure them to the bar. To do this, it is recommended to use liquid wax.

Hatching with transfer of larvae
This is a common method that helps to obtain young queen bees. It is used in small apiaries. First, you should choose the most productive family. Place an insulator with high-quality honeycomb in the center light color. If there is no insulator, the honeycomb is placed in a nest.
When young larvae form on the 4th day after placing the comb, you need to select the queen bee from the colony and replant her layering. It includes young bees and brood obtained from other colonies. After 5-6 hours, the honeycomb is removed and a strip with the youngest larvae is cut off from it with a sharp knife. The cells need to be carefully expanded. Insects will build queen cells on them.
Hatching in a multi-body hive
Will help to grow powerful families multi-body hives. To do this, the formation of queens begins in early May. At the same time, families occupy several buildings. A layer appears at the top. A barren individual and a queen cell are placed in it. At the end of May you can start sowing the honeycombs.
Output from the syringe
This effective method, which helps to get healthy bees and avoid fights. No special equipment is required to isolate a bee. To do this, use an ordinary syringe equipped with a piston. Its volume should be 20 ml.
To do this, do the following:
- Take out the piston and make 4 rows of holes of 6 pieces along the length of the device. The upper ones are done in the area where the piston enters the syringe. They are used for fixation when it is necessary to transport a bee.
- Holes for the bowl should be drilled in the rod. It is made not far from the center.
- The bowl is fixed to the hole. The rest of the piston must be cut off with an ordinary knife.
- Place candy balls at the bottom and let the bees in there. They are responsible for feeding the main individual.

Incubators for hatching queen bees
For breeding queens, it is permissible to use special incubators. At the same time, they must remain constant temperature at 34 degrees for queen cells and 27 degrees for barren queens. Humidity parameters are maintained at 75%. In order for barren individuals to develop normally, they need to be fully fed. Queen bees appear 16 days after laying.
Breeding queens without orphaning the family
This modern method. In this case, the individual is not removed from the hive, but is left behind a special grill. This ensures the bees have access to the queen.
The family raises brood and hatches larvae. An existing individual cannot destroy young ones. After hatching from the cocoons, new families can be obtained.
At the same time, the key disadvantage of the method is that worker bees do not provide enough larvae. They also create too many fistulous queen cells.
Problems often arise after the queen bee is isolated. Early isolation will help avoid this. Only after this is it worth breeding new individuals. The breed of bees is also important. Southern individuals are able to feed more insects compared to highland and northern ones.
Early breeding of queen bees
If you need to obtain several queen bees, it is recommended to use swarm queen cells. You can provoke bees to lay queen cells by dividing the nest. A special board is used for this. There should be a window in the central part. It is covered with bars.
2 frames are attached to the board on each side. They must contain food. Then the frames with brood are fixed. The branches must have at least 1 cell. It must contain eggs and larvae. Each part must have a taphole.
In one part of the hive there will be a queen bee, in the other there will be bees. After 10 days, the queen cells must be carefully cut off and used for layering. In this case, the insert board must be pulled out of the socket.

Natural Methods
The most in an accessible way The reproduction of queens is considered to be the natural reproduction of bees. In this case, the insect family must go into a swarm state. By creating a favorable environment for swarming, it will be possible to significantly speed up the process.
Three frames with brood should be placed in the hive and the entrance should be covered. Then you can expect the formation of queen cells. It is worth forming layering in this area and on the new framework.
One more natural method are considered fistulous queen bees. The key advantage is the breeding of individuals in the required period of time. Bees should be encouraged to lay queen cells.
To do this, you should choose a strong family, find the queen, transfer her and 2 frames with brood to the hive. Shake the bees out there. As a result, it will be possible to form a layer, which is moved to a permanent hive. Individuals from the old hive lay queen cells. At the same time, it is important to ensure that they are present exclusively on formed larvae.
Conclusion with partial orphaning of the family
In this situation, the queen bee is removed from the hive before being adopted. Then it is returned to its original place.
Breeding queens from A to Z:
Conditions for a successful procedure
In order for queen bee breeding to be successful, it is important to follow certain recommendations:
- To get a high-quality queen bee, you should buy it exclusively from well-known beekeepers. This can also be done at breeding apiaries with a good reputation.
- Before breeding, it is recommended that the queen bee rest for a week. To do this, active bees should be removed from the individual. After resting, the bee will produce large eggs.
- In queen cells placed on frames, it is necessary to ensure a temperature of +32 degrees and a humidity of at least 75-90%. For breeding, a special device is used - an aerothermostat.
- Queen cells should be distributed evenly between families. This will help to grow them and ensure a sufficient amount of royal jelly.


Possible problems
Beginning beekeepers may encounter various difficulties when breeding queens. Common mistakes include the following:
- Removal without using clean material.
- Impact on honeycombs with larvae or queen cells.
- Crossing of relatives.
- Incorrect microclimate in the hive.
- Lack of control over the milk, which causes it to dry out.
- Performing crossbreeding of different breeds.
Removing queen bees is a rather complex and labor-intensive procedure that requires certain skills from the beekeeper. To achieve good results, you must strictly follow the basic rules and recommendations.
In order to developed successfully, you should definitely provide your apiary with queen bees that have a stable and highest egg production. The growth rate and productivity of a bee colony depend on the fertility of the queen.
At the same time, removing the queen may seem like an overwhelming task to a novice beekeeper. In this case, a beginner in the field of beekeeping is advised to consider the most simple methods, which can greatly facilitate his task.
Calendar
First, you should create a special calendar, without which there is no point in moving forward for a novice beekeeper. This calendar should display all the work in the apiary and the exact deadlines for their completion. This calendar is divided into two main parts (disks). To begin, cut out the outer disk, on which large numbers should indicate the day and month. Both parts of the calendar should then be glued onto plywood or thick cardboard, and then connected using a bolt. The calendar must indicate the date when the queen bee begins laying eggs. It is recommended to use separate calendars for each individual bee colony.
Methods for obtaining a queen bee
To obtain a good queen bee, the beekeeper should follow certain rules. Firstly, queen bees must be bred in warm weather and only in quiet, strong bee colonies. It is recommended to start hatching after replacing overwintered bees and in the presence of drone printed brood. It is necessary to hatch queens from the larvae of their own queens. Moreover, the breeding process should begin with the formation of a family of drones.
Obtaining queen bees using swarm queen cells
In terms of their live weight and fertility, swarming queens often exceed those queens that were eaten artificially. This is understandable, since swarm queens are initially raised in more comfortable conditions in the presence of a large number of bees, which are called nurses. While still larvae, such queens are provided with full royal jelly, which increases all the quality indicators of the queens. In those bee colonies that are actively preparing for swarming, egg laying is significantly reduced, but larger eggs are laid. About the seventh day after the queen cells are sealed, they can be cut out with a small piece of honeycomb using a knife. You can leave only one queen cell in a bee colony, which is considered the best. Place all the cut out queen cells in cells, where up to ten bees are first released and the candy is laid out. These cells are constantly supported elevated temperature, and place them in the central part of the nest. After this, the smallest queen cells are destroyed, but the straight, largest ones are left for the full rearing of queen bees.
Obtaining queen bees without transferring larvae
This method of obtaining queens is mainly used in small apiaries, and this method is considered the simplest and most widespread.
With this method, the queen bee is temporarily removed from the selected colony, then the beekeeper should select the honeycomb that contains young open brood with eggs and larvae. This comb should be trimmed so carefully that the newly hatched larvae remain at the edges. Next, the cut honeycomb is immediately placed in the very center of the nest, and several queen cells are laid by the bees along the edges of the cuts. This method is considered effective only if young larvae of the same age cover the comb evenly.
Regarding apiaries large sizes, then you need to breed a hundred, or even several hundred queen bees. In this case, beekeepers need to use frames in which larvae from the breeding family and cells cut from the honeycomb are glued together with wax. Instead of such frames, wedges can also be used. Honeycombs with larvae of the same age are selected from the mother colony, then they are very carefully transferred to another room and laid flat on the table. After this, you should cut the honeycombs into strips with a knife, then further cut them into pieces so that each of them contains a larva with a whole cell. Next, the cell is glued with the non-shortened side to the wedge using warmed wax and the teacher is placed in the family.