Official business style (ODS) serves the sphere of official relations, in which communication participants perform certain social functions. Situations during such communication are as typical as possible, which gives rise to the standard speech behavior their participants, therefore many documents are ready-made forms in which you only need to enter the passport data of the document submitter.
The term “official business style” is usually used to denote the peculiarities of the language of official (organizational and administrative) and diplomatic documents. The main function of the official business style is that it requires known form when presenting the content in writing, it gives the text the character of a document and transfers the various aspects of human relations reflected in this text into the category of official business documents.
The main features of ODS are precision of formulation, standard arrangement of material, regulation (limited set of linguistic means), rigor and simplicity, information richness, written form of presentation and impersonality of the statement.
ODS is divided into three substyles - legal, diplomatic and clerical and business. Each of them is reflected in a number of genres. The genres of the legal substyle include the constitution, code, law, charter, resolution; the genres of the diplomatic substyle include a credential, note of protest, declaration, communiqué; the genres of the clerical and business substyle include orders, contracts, notices, orders, as well as all types of documents. of a personal nature (application, complaint, receipt, power of attorney, letter, report / official / explanatory note, autobiography, etc.).
Among the linguistic features of the official business style, the following should be highlighted. TO lexical features UDF refers to the presence of stable expressions and terms denoting the realities of social life, as well as clericalisms that immediately catch the eye, are imprinted and later emerge in a spontaneous and unprepared form in colloquial speech (proper, undersigned, hear, plaintiff, individual, consumer and etc.). ODS texts lack emotionally expressive vocabulary, evaluative and introductory modal words ( good, bad, like, want, probably, maybe, etc.). The words used in the texts are characterized by limited lexical compatibility, for example, official letter not written, A is being compiled.
In morphological terms noted use short forms adjectives with the meaning of obligation ( obliged, responsible, accountable) and participles ( the decision was made, the candidacy was supported), an abundance of denominate prepositions and conjunctions ( accordingly, in continuation, for the purpose, due to the fact that). To express imperativeness, infinitive constructions are used, reinforced by adverbs and modal words ( repairs must be made, I order that measures be taken, it is necessary to begin... etc.).
On syntactic features ODS texts include the active use of passive constructions ( the order is completed, it is not possible, negotiations are completed) and an abundance of sentences with homogeneous members and isolated phrases, various kinds stamps and cliches with archaic elements ( according to the act, the punishability of the act).
ODS texts are characterized by sentences with inversion - the subject with an objective meaning follows the predicate ( Everyone is guaranteed freedom of conscience). Sentences with participles and participial phrases allow you to make the text information-rich. The texts are dominated by constructions with “stringing” of genitive cases of nouns without prepositions ( Any form of restriction of the rights of citizens is prohibited Russian Federation ).
Official business texts are characterized by a high degree of segmentation, which allows you to clearly structure the text, dividing it into articles, paragraphs, paragraphs, and subparagraphs. The text is built according to a template (form), which includes all the elements required for a given genre.
ODS texts, or documents, occupy a significant place in life modern man. They regulate our social life, so we feel the need for them every day. That is why each of us must be able not only to correctly interpret a document, but also to draft it correctly. The author composing this or that document must use in it those linguistic means that the genre of the document requires of him, and not “invent” his own phrases that differ from the standard ones.
The document is created in accordance with the genre model of the text with a constant composition, which includes mandatory thematic blocks, i.e. details.
For example, a job application contains the following details:
1) indication of the addressee (name of the manager and enterprise);
2) indication of the addressee;
3) name of the genre of the document (statement);
4) the main content of the request (please accept me...);
5) indication of the date of preparation of the document;
6) signature (handwritten signature).
It is necessary to strictly observe the requirements for the location of details in relation to each other. In the application, the addressee and addressee are indicated in the upper right corner of the sheet. Document title (with capital letter and without a dot at the end, if the addressee is with the preposition “from”, or with a lowercase letter and with a dot at the end, if the addressee is without the preposition “from”) is located in the middle, and the main content is along the width of the sheet. The date is placed at the bottom left, and the signature is placed at the right, on the same line as the date. In this case, empty lines are left between the details. Below the date and signature, free space is left for the resolution. Resolutions are also in the top left corner.
The official business style is the most common style, which functions not only in clerical work and diplomacy, but also in any official relations, for example, in production, at a university, in medical institutions, in the newspaper, etc.
When drawing up documents, generally accepted stable speech patterns are used: I ask your permission to...; I, who have signed below...; the certificate was given... that... indeed...; let me invite you...; I, who live at the address..., trust...
It is extremely important for documents correct usage verbs like trust, assure, guarantee, declare, notify, insist, confirm, notify, offer, order etc. These verbs are used in the first person plural or singular in sentences without a subject, as well as the third person singular when mentioning the addresser, for example: “I ask”, not “I ask”; “we undertake”, not “we undertake”.
The author of the document must be able to accurately and concisely express his point of view on the issue of interest to him. To do this, he must know linguistic means expressing cause-and-effect and other logical relationships, which, first of all, include complex conjunctions and denominate prepositions: for the reason, for the purposes of, on the basis of, in order to avoid, in accordance with, according to, thanks to, in view of and so on.
In official business papers, you should correctly use etiquette formulas of address, indicating the addressee’s respectful attitude towards the addressee: Thank you for..., We kindly ask you..., Unfortunately... It should be borne in mind that in a business letter the second person pronouns ( You, Your) are written with a capital letter, while in ordinary written speech such spelling contradicts the norms of Russian spelling.
In official business papers, familiar address to the addressee is not allowed ( Expensive…), indication of response time in ultimatum form ( Please answer me immediately...)or refusal to the addressee’s request without specifying reasons.
Typical errors in business speech include the following violations:
1) unmotivated use foreign words (prolong instead of extend; appeal instead of address);
2) the use of archaisms ( which instead of which, this year instead of this year);
3) incorrect use of paronyms ( graduated from university instead of graduated from university; introduce the products instead of introduce the products);
4) violation of the norms of using prepositions ( thanks, according to, despite, according to combined with the dative case; as a result, during differ in their spelling from prepositional-case combinations An experienced detective is involved in the investigation; there are rapids along the river).
Here are two options for writing a statement:.
Option 1 (application from whom):
prof. A.M. Shammazov
from a second year student
Faculty of Technology
Nikolaev Denis Yakovlevich.
Statement
Please transfer me to correspondence form training for family reasons. An extract from the academic certificate about the tests and exams I passed is attached.
07/25/2012 Personal signature
Option 2 (whose statement):
Rector of Ufa State
Petroleum Technical University
prof. A.M. Shammazov
second year student
Faculty of Technology
Nikolaev Denis Yakovlevich
statement.
In connection with the request of the enterprise, which sent me at its own expense for training, I ask you to transfer me to the specialty “Drilling of oil and gas wells”. A letter from the HR department of Burintech LLC is attached.
Officially, the business style of speech is used in the interaction of people in the field of business and management. The focus of the official business style of speech is quite broad: jurisprudence, criminal and administrative law.
The peculiarities are such that it must be built according to certain rules. No free impulses or independent introductions are allowed here. The need to follow clear standards helps to become a successful and respected person.
It may seem to some that the official business style of speech is characterized by excessive rigor in design, but it should be noted that this necessary requirement, which is observed for better delivery and perception of information by the opponent. But, once you have mastered a certain template, you can create several hundred similar requests.
Formal – business style of speech. Signs
The features of the official business style of speech are quite recognizable and easily applicable in any area that involves following established norms and procedures. Learn to compose business letters may seem like a daunting task at first, but by studying the parameters, you can master official appeals much faster than expected.
Ultimate accuracy
Perhaps this is the most main characteristic, which determines the success of the entire enterprise. Main feature The official business style of speech is its stability, consistency in the composition of phrases and figures of speech. Once mastered this Difficult language, you will no longer experience significant difficulties: you will have ready-made templates for various situations, on which you can safely act.
You need to be very attentive and interested in the matter in order to avoid any mistakes when drawing up an important document. Extreme precision completely eliminates the possibility of interpreting written words in two ways. For this reason, the official text can hardly be understood differently, or put into it a different meaning than the one that the interlocutor wants to convey to you.
Strict nature of presentation
In business letters you will not find any individual focus or even interest in the individual. From the outside, the official language looks deliberately dry and pragmatic. Don't expect official document great creativity or strong emotions. A business letter or speech has a clear purpose - to convey specific information to the interlocutor. It is best to do this precisely when there are no lyrical digressions or distractions. The strict nature of the presentation guarantees an extremely accurate understanding of the main meaning.
Stereotypical phrase construction
As a rule, all official papers are somewhat similar to each other. This impression is created because the text is written based on an existing template to facilitate its composition and subsequent perception. If people approached every insignificant document as if they were creating an original work of authorship, they would have neither the energy nor the time to work. In official business documents you can find quite common phrases, such as: “Based on the above”, “It should be noted”, “Please note”
Consistency and logic of presentation
In business speech you will not encounter chaos or any exceptions to the rules. All necessary information is always provided depending on the specific goal and tasks that need to be solved. The chance of getting confused in the presented material is negligible. Official - business style of speech always implies a logical presentation of information and according to a strictly defined template. Perhaps people of creative professions will not really like this, but from time to time they also need to conclude contracts and sign important papers. Knowledge of business communication will never be superfluous!
The information is prescriptive in nature.
To an outside observer, it may sometimes seem that such an overly dry style contains only instructive information and has nothing to do with the real state of affairs. Actually this is not true. It’s just that the official style requires a detailed and scrupulous immersion in the situation, a detailed consideration of all the details.
Genres of official - business style of speech

It is traditional to highlight the following main directions. All of them are strongly interconnected, but each individually also deserves attention.
- Clerical focus. This includes business papers, memos, official letters customers and suppliers of goods. Managers of serious enterprises know from their own experience how much work it sometimes takes to compose such a text and how much effort needs to be put into it. Creating competent, constructive content is the key to the success of the development and prosperity of your business. With the help of business letters, you can advertise your services and expand the boundaries of your activities.
- Diplomatic focus. Drawing up contracts and creating special appeals addressed to other companies also requires serious preparation and knowledge of certain things. It is necessary to present information as accurately, clearly and consistently as possible, highlighting the main thing and identifying the positions of each interested party. Diplomatic orientation often helps people find a way out of difficult situations.
- Legal orientation. This may include rules, laws, criminal and administrative codes. To correctly draw up all these legal and other forms of documents, you must have special knowledge. Drawing up contracts is notoriously difficult. A competent specialist needs time to master this information.
Thus, the official - business style of speech finds wide application in jurisprudence, banking and investment. To a business person you need to be able to correctly draw up contracts, draw up documents, communicate productively with clients, plan work time. And all this cannot be achieved without special knowledge.
OFFICIAL BUSINESS SPEECH STYLE
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 Linguistic features of an official business style of speech. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.1 Lexical features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.2 Morphological and word-formation features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3 Syntactic features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Genre diversity of official business style of speech. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Conclusion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
List of sources used. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Introduction
Official business style is a style that serves the legal and administrative and public spheres of activity. It is used when writing documents, business papers and letters in government agencies, courts, as well as in different types business oral communication.
The most important functions of this style - communication and influence - are implemented in such official documents as laws, regulations, decrees, orders, contracts, agreements, business correspondence, statements, receipts, etc. This style is also called administrative, since it serves the sphere of official, business relations, area of law and public policy. Its other name - business speech - indicates that this style is the most ancient of book styles, its origins are in the business speech of the era of the Kievan state, in which legal documents (agreements, “Russian Truth”, various charters) were created already in the 10th century. century.
The official business style stands out among other book styles for its stability, isolation and standardization. Despite the wide variety of business documents, their language is strictly subject to the requirements of official business presentation: the accuracy of the wording of legal norms and the need for absolute adequacy of their understanding, the composition of the mandatory elements of document design that ensure its legal validity, the standardized nature of presentation, stable forms of arrangement of material in a certain logical sequences, etc.
For all forms of business writing, strict compliance with the literary norm is required at all language levels: the use of lexical and phraseological means of a colloquial, colloquial nature, dialect, professional slang words is unacceptable; non-literary variants of inflection and word formation; conversational syntactic constructions. The official business style does not accept expressive elements: evaluative vocabulary, high or low words (joking, ironic), figurative expressions. The most important requirement for the language of a document is objectivity and “dispassionateness” in the presentation of facts.
The official business style operates primarily in written form, but its oral form is not excluded - speeches by government and public figures at ceremonial meetings, sessions, and receptions. The oral form of business speech is characterized by a complete style of pronunciation, special expressiveness of intonation, and logical stress. The speaker can allow a certain emotional elevation of speech, even interspersing foreign-style language means, without, however, violating the literary norm. Incorrect accents and unliterary pronunciation are unacceptable.
In official papers, the set of linguistic means used is predetermined. The most striking feature of the official business style is linguistic cliches, or so-called cliches (French. clich). A document is not expected to show the individuality of its author; on the contrary, the more clichéd a document is, the more convenient it is to use (see examples of clichés below)
Official business style is the style of documents of different genres: international treaties, state acts, legal laws, regulations, charters, instructions, official correspondence, business papers, etc. But, despite the differences in content and variety of genres, the official business style as a whole is characterized by common and most important features. These include:
1) accuracy, excluding the possibility of other interpretations;
2) locale standard.
These features find their expression a) in the selection of linguistic means (lexical, morphological and syntactic); b) in the preparation of business documents.
Let's consider the features of vocabulary, morphology and syntax of the official business style.
2 Linguistic signs of official business style of speech
2.1 Lexical features
Official business speech reveals a tendency towards extremely generalized semantically vocabulary, where everything that is sharply original, specific, and unique is eliminated, and the typical is brought to the fore. What is important for an official document is not the living flesh of a given phenomenon, but its “legal” essence.
Official business speech reflects not the individual, but social experience, as a result of which her vocabulary is extremely generalized. In an official document, preference is given to generic concepts with broad and poor semantics, with a limited number of semantic features:
premises (cf.: apartment, workshop, hangar, lobby, shelter, monastery, apartments), person (cf.: individual, person, man, girl, guy, small, owner, tenant, passerby), parent (cf.: mother , father, father, mother, ancestor), serviceman (cf.: soldier, lieutenant general, artilleryman, recruit, soldier, serviceman, sailor), punishment (cf.: reprimand, fine, arrest, scolding, reprimand), arrive ( cf.: to come, to arrive, to sail, to gallop, to burst in, to arrive, to arrive) and others.
The lexical (dictionary) system of the official business style, in addition to general book and neutral words, includes:
1) linguistic cliches (clichés, clichés): raise a question based on a decision, incoming and outgoing documents, control over execution is assigned upon expiration of the deadline.
2) professional terminology: arrears, alibi, black cash, shadow business;
3) archaisms: I certify this document.
In an official business style, the use of polysemantic words, as well as words with figurative meanings, is unacceptable, and synonyms are used extremely rarely and, as a rule, belong to the same style: supply = supply = collateral, solvency = creditworthiness, depreciation = depreciation, appropriation = subsidy and etc.
2.2 Morphological and word-formation features
The word-formation and morphological features of the official business style are inextricably linked with its general characteristics: the desire for accuracy, standardization, the impersonal and obligatorily prescriptive nature of the presentation.
The inappropriateness of the expressive coloring of official speech makes it impossible to use interjections, modal words, a number of particles, words with suffixes of subjective assessment, adjectives in the comparative and superlative degrees. Nouns denoting positions are usually used in the masculine form (accountant, director, laboratory assistant, postman, controller and etc.).
IN official business speech the highest percentage of infinitives from other verb forms is observed among all functional styles. This is due to the purpose of most official business documents - to express the will of the legislator. Here is an example from the Convention on the Rights of the Child: "The child has the right to freely express his or her opinions; this right includes the freedom to seek, receive and impart information and ideas of any kind, whether or not granted, whether orally, in writing or in print, in the form of works of art or through other media of the child's choice.".
Of the conjugated forms, the present tense forms are most often used here, but with a different meaning compared to the scientific style. This value is usually defined as the present prescription. The verb form does not denote a permanent or ordinary action, but an action that the law requires to be performed under certain conditions:
"The accused is guaranteed the right to defense."
When designating a person in an official business style, nouns are used that designate a person based on a characteristic determined by some action or attitude, which is intended to accurately designate the “roles” of the participants in the situation: defendant, tenant, tenant, reader, guardian, adoptive parent, plaintiff, witness, etc.
Nouns denoting positions and titles are used in the masculine form even when they refer to female persons: police officer Smirnov, defendant Proshina and the like.
Among the word-formation models of nouns, verbal formations are widely represented, including na-nie, sometimes with a prefix and non-: non-compliance, non-recognition, decision, execution. For example: “Children left without parental care and located in educational institutions, medical institutions, social protection institutions and other similar institutions have the right to: maintenance, upbringing, education, comprehensive development, respect for their human dignity, ensuring their interests.... "(Family Code of the Russian Federation, p. 149).
Stringing nouns with the suffix -nie can be considered a striking sign of an official business style: “Preparation for a crime is the search and adaptation of means or instruments or the deliberate creation of conditions for the commission of crimes...”
The official business style is rich in constructions with a verb that takes on purely grammatical functions. The number of verbs that act as grammatically supporting words and serve to express almost only grammatical meanings amounts to many dozens: conduct (campaigning, installation, observation, negotiations, preparation, searches, development, investigation); make (additions, corrections, clarifications); give (consultation, appointment, justification, explanation, refutation, refusal, assessment, instruction, permission, clarification, order, recommendation, consent, instruction); conduct (voting, meeting, research, testing, search); undergo (examination, training, inspection) and so on.
Extremely characteristic of official speech are the methods of composite word formation - stem and word composition, fusion, as a result of which in the lexicon of a business language two (or more) root formations are represented by a very extensive collection: marriage, offense, taxation, land use, passenger transportation, disability, tenant, landlord, dacha owner, paper holder, cultural and entertainment, material and technical, repair and construction, administrative and economic, autumn-winter, bakery, apartment intermediary, knowledge-intensive, transport-intensive, low-paid , low-income, person-ruble, vessel-day, passenger-seat-mileand many others.
The business style’s predilection for complex words is easily explained: they are transparent in structure and meaning, and have idiomatic effects. To an even greater extent, the need for semantically clear names is met by the phrase; the number of names created in this way in the official business style amounts to many thousands of units: vehicles, wage, official, confectionery, securities, travel document, reception point, executive committee, non-cash payment, work injury, bodily injury, public places, occupational disease, catering establishment, high-demand goods, on-the-job training, right to rest, search warrant, demotion, loss of rights....
The convenience of “analytical” models is expressed with particular clarity in the nomenclature of institutions, professions, positions, etc. that makes up a gigantic layer of official names: chief researcher, deputy regiment commander for engineering service, Moscow State University, St. Petersburg State Mining Institute (Technical University). Transcaucasian Railway, Volyn Household Chemicals Plant, State Duma deputy...
Characteristic for legal, administrative and social activities. For such a phenomenon as the culture of speech, the official business style is very important, because with its help documents and business papers relating to government tasks, court cases and diplomatic communication are drawn up. It is characterized by isolation, stability of many speech patterns, specific vocabulary and special syntactic patterns. Documents written in a formal business manner are compact and filled with cliches and linguistic cliches. These are international treaties, government decrees and acts, legal laws and court decisions, various charters and official correspondence, as well as other types of business papers that differ in the accuracy of presentation and language standard.
This is a special culture of speech. The official business style, in addition to cliches and language clichés, includes an abundance of professional terminology and archaisms. When using this style, ambiguous words are not used at all. Documents also avoid synonyms, and if they are used, their style is also strictly adhered to and the vocabulary is, as it were, shackled within a framework, beyond which it is prohibited.
But the official business style uses nouns in abundance, naming people based on their activities; positions are always called in the masculine gender. Words with a particle are often used not as antonyms for the same words when they are used without a negative particle. Complex and infinitives are also popular in business documents to denote actions performed or being performed. Enough great place In this style of speech, complex words are also used.
Formal business style gives preference to homogeneous members. Passive constructions are also often used, that is, impersonal offers without specifying the person performing the action. The genitive case of nouns forms a chain of syntactic constructions; sentences are often very common and burdened with subordinate clause conditions.
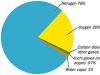
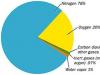
The official business style has two varieties: official-documentary and everyday business. The first group is the language of such legislative acts as the Constitutions of the Russian Federation and its constituent entities, charters and programs of parties, as well as diplomatic documents of international importance, such as communiqués, memorandums, conventions, etc. The second group includes the language used in the process of conducting official correspondence and drawing up private business papers. These include various certificates, business letters, powers of attorney, advertisements, statements, receipts, autobiographies, etc. It is known how standardized the listed papers are, which greatly facilitates their preparation. The information they contain is brief and used in minimal quantities.
It is known that English is a means of international communication. Therefore, formal business style in English used in diplomatic settings when business papers need to be translated. The types of business speech in this case are determined by the sphere of use. Trade agreements and contracts are conducted in the style of commercial correspondence. In the legal field, the language of codes, statutes, state and parliamentary decisions is used. The language of militarized business papers stands out separately.
Thus, the official business style of the English language is intended to serve as a tool with the help of which the parties understand the essence of the matter, which leads to the signing of various agreements.
Used to compose documents, letters and business papers in institutions, courts and in any type of oral business communication, this is an official business style of speech.
general characteristics
This is a long-established, stable and rather closed style. Of course, it too underwent some changes over time, but they were insignificant. Genres that have developed historically, specific syntactic turns, morphology and vocabulary give it a rather conservative character.
To characterize the official business style, the language must be given dryness, compactness of speech, conciseness and the removal of emotionally charged words. Linguistic means already exist in a complete set for every case: these are the so-called language stamps or cliches.
List of some documents that require official business style:
- international treaties;
- government acts;
- legal laws;
- various regulations;
- military regulations and charters of enterprises;
- instructions of all kinds;
- official correspondence;
- various business papers.

General characteristics of linguistic style
Genres can be diverse, content can be different, but the official business style also has common essential features. First and foremost: the statement must be accurate. If possible different interpretations, this is no longer an official business style. There are examples even in fairy tales: execution cannot be pardoned. The only thing missing is a comma, but the consequences of this error can go very far.
To avoid such situations, there is a second main feature, which contains the formal business style of documents, is the locale standard. It is he who helps to choose lexical, morphological, syntactic language means when drawing up business documents.
The order of words in a sentence is particularly strict and conservatistic; here much goes against the direct word order inherent in the structure of the Russian language. The subject precedes the predicate (for example, the goods are sold), and definitions become stronger than the word being defined (for example, credit relations), the control word comes before the controlled word (for example, allocate a loan).
Each member of a sentence usually has a place unique to it, which is determined by the structure of the sentence and its type, its own role among other words, interaction and relationships with them. A character traits official business style - long chains of genitive cases, for example: the address of the Head of the regional administration.

Vocabulary of style
The dictionary system includes, in addition to commonly used bookish neutral words, certain clichés - clericalisms, that is, linguistic cliches. This is part of the formal business style. For example: based on a decision, incoming documents, outgoing documents, upon expiration of a deadline, control over execution, and so on.
Here we cannot do without professional vocabulary, which includes neologisms: shadow business, arrears, black cash, alibi, and so on. The official business style also includes the inclusion of some archaisms in the lexical system, for example: this document, I certify with it.
However, the use of polysemantic words and words that have a figurative meaning is strictly prohibited. There are very few synonyms and they are included in the official business style extremely rarely. For example, solvency and creditworthiness, supply and delivery, as well as collateral, depreciation and amortization, subsidy and appropriation.
This reflects social experience, not individual experience, so the vocabulary is generalized. The conceptual series prefers generic concepts that fit well into the official business style. Examples: arrive instead of arrive, arrive, fly in, and so on; vehicle instead of a car, plane, train, bus or dog sled; locality instead of a village, a city, the capital of Siberia, a village of chemists, and so on.
So, the following elements of lexical constructions belong to the official business style.
- A high percentage of terminology in the texts: legal - law, owner and property, registration, transfer and acceptance of objects, privatization, deed, lease, and so on; economic - costs, subsidies, budget, purchase and sale, income, expenses, and so on; economic and legal - sequestration, implementation period, property rights, loan repayment, and so on.
- The nominal nature of the construction of speech due to the large number of verbal nouns, most often denoting a material action: shipment of goods, deferment of payment, and so on.
- High frequency of prepositional combinations and denominate prepositions: to the address, by force, in relation to the matter, by measure, and so on.
- Transition of participles into adjectives and pronouns to enhance clerical meanings: this agreement (or rules), current prices, appropriate measures and so on.
- Regulated lexical compatibility: the transaction is only concluded, and the price is set, the right is granted, and the payment is made.

Morphology of style
Morphological features of the official business style include, first of all, the frequency (repeated) use of certain parts of speech, as well as their types, which help in the language’s desire for accuracy and ambiguity of statements. For example, these:
- nouns that name people based on action (tenant, taxpayer, witness);
- nouns that call people by position or rank, including women strictly in the masculine form (salesman Sidorova, librarian Petrova, sergeant Ivanova, inspector Krasutskaya, and so on);
- particle non- in verbal nouns (non-compliance, non-recognition);
- use of derivative prepositions in wide range(due to, in connection with, to the extent of, by virtue of, on the basis of, in relation to, and so on);
- constructions in the infinitive (to provide assistance, to conduct an inspection);
- present tense of verbs in a different meaning (a fine will be charged for non-payment);
- complex words with two or more stems (employer, tenant, repair and maintenance, material and technical, below-mentioned, above-mentioned, and so on).
Style syntax
The characteristics of the official business style consist of the following syntactic features:
- Simple sentences are used with many rows homogeneous members. For example: An administrative penalty may include fines for violations of labor protection and safety regulations in construction, industry, agriculture and transport in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
- There are passive structures of this type: payments are made strictly at the specified time.
- Nouns prefer the genitive case and are strung with beads: the results of the activities of customs control units.
- Complex sentences are filled with conditional clauses: in cases of subscribers’ disagreement with the processing of their personal data in terms of the methods and purposes of processing or in full, subscribers sign a corresponding statement when concluding a contract.

The sphere of official business style in genre diversity
Here, first, you need to highlight two areas of subject matter: official-documentary and everyday-business styles.
1. Official documentary style is divided into two categories: legislative documents related to work government agencies, - The Constitution, charters, laws are one language (J), and diplomatic acts related to international relations, - memoranda, communiqués, statements, conventions - this is a different language (K).
2. Everyday business style is also subdivided: correspondence between organizations and institutions is the j language, and private business papers are the k language. All official correspondence belongs to the genres of everyday business style - commercial correspondence, business letters, as well as business papers - autobiography, certificate, act, certificate, application, protocol, receipt, power of attorney and so on. Standardization, characteristic of these genres, facilitates the preparation of papers, saves language resources and prevents information redundancy.
Standardization of business papers
Specially selected words in an official business style ensure communicative precision, giving documents legal force. Any piece of text must have a single interpretation and meaning. For such high accuracy, the same words, terms, names are repeated many times.
The form of the verbal noun complements the features of the official business style with an analytical expression of actions and processes: instead of the word “supplement” the phrase “make additions” is used, instead of “decide” - “make decisions” and so on. How much harsher it sounds to be “responsible” instead of just “responsible.”
Generalization and abstraction to the highest degree and at the same time the specific meaning of the entire lexical structure are the main features of the official business style. This inconceivable combination, used simultaneously, gives the document the possibility of a single interpretation and, in the totality of information, legal force. The texts themselves are full of terms and procedural vocabulary, and, for example, appendices to contracts contain nomenclature vocabulary. Questionnaires and registers, applications and specifications help terminology to be deciphered.
In addition to emotionally charged text, the use of any swear words, reduced vocabulary, jargon, colloquial expressions. Even professional jargon has no place in the language business correspondence. And most of all, because it does not meet the requirements of accuracy, since it is assigned strictly to the sphere of oral communication.

Oral business speech
Emotionlessness and dry logic of texts, the standard arrangement of material on paper differs significantly from oral speech, which is usually emotionally charged and asymmetrical according to the principles of textual organization. If oral speech is emphatically logical, the communication environment is clearly official.
Features of the official business style are that oral business conversation, despite the professional topic, should proceed in the sphere of positive emotions - sympathy, trust, respect, goodwill.
This style can be considered in its varieties: clerical and business style is simpler, but the language of public administration, diplomatic or legal requires special attention. The areas of communication in these cases are completely different, so the style of communication must also be different. Statements, protocols, orders, decrees - everything that is thought out, written down, read, is not as dangerous as oral negotiations, business meetings, public speaking, and so on. The word, like a sparrow, cannot be caught if it flies out.
The main features of the formal business style of speech are brevity, accuracy and influence. To achieve these goals, you will need an appropriate selection of words, correctly composed structures, correct syntax, and standardization in your mind of entire blocks of prepared speech. Just as in written business text, there is no place for emotionally charged vocabulary in oral speech. It is better to choose a neutral one, to be closer to the standards of clerical language means in order to accurately state what is planned.
Requisites
The most striking characteristic of the official business style is not even the text itself, but all the essential elements of its design - the details. Each type of document has its own information set, provided for by GOST. Each element is strictly assigned to a specific place on the form. The date, name, registration number, information about the compiler and all other details are always located the same way - some at the top of the sheet, others at the bottom.
The number of details depends on the content and type of document. The sample form shows the maximum details and the order in which they are located on the document. These are the State Emblem of the Russian Federation, emblems of an organization or enterprise, images of government awards, code of an organization, enterprise or institution (All-Russian classifier of enterprises and organizations - OKPO), document form code (All-Russian classifier of management documentation - OKUD) and so on.

Stencilization
Machine processing, computerized office work - new era in the process of standardization. Economic and socio-political life is becoming more complex, technological progress is gaining momentum, therefore the features of the official business style are to justify economically the choice of one language option from all possible and to consolidate it in practice.
Using a stable formula, an accepted abbreviation, and a uniform arrangement of all material, drawing up a document is much faster and easier. This is how all standard and template letters, tables, questionnaires, etc. are compiled, which allows information to be encoded, ensuring the informative capacity of the text, with the ability to expand its full structure. Such modules are implemented into the text of contracts (lease, work, purchase and sale, etc.)
From fifty to seventy percent of word usage in a document is procedural vocabulary and terminology. The subject of the document determines the unambiguity of the context. For example: The Parties undertake to comply with the above rules. The word “parties”, used outside the document, is very ambiguous, but here we can read a purely legal aspect - the persons who enter into the agreement.