this proposal.
(11) All of Russia speaks Russian, but what kind of idiot are you? (12) Well, tell me someone in our family who doesn’t know Russian? (13) Eh, your poor grandfather, who, having lived in Russia for seven years, spoke Russian better than the postmaster Ivan himself!
(14) - What vi gavarite! – imitating my grandfather, I wondered in broken Russian.
(15) - Yes, yes, please don’t stare! (16) The deceased spoke with Ivan for two hours, Ivan listened to him with his mouth open for two hours, and then turned to the people and said that he had never heard such Russian speech in his life. (17) That's how it was!
1. Complex sentence with two subordinate clauses.
2.Complex sentence with conjunction and demon allied communications.
3.Complex sentence with a conjunctive subordination and coordinating connection.
4. Complex sentence with a union subordinating and non-union connection.
Indicate a sentence that does not have a attributive clause:
1. The innocence with which the little pockmarked soldier admitted to fleeing was especially terrible.
2. The man whose song I was in such a hurry to hear turned out to be a bandy-legged guy of about sixteen.
3. The huge house in which Gray was born was gloomy inside and majestic outside.
4. From Zhenya’s alarmed face, the woman guessed that Olga, who entered the garden, was dissatisfied.
(1) In 1922, when he was 14 years old, Lev Landau* successfully passed the exams at Baku University and was enrolled in the Faculty of Physics and Mathematics in two departments at once - mathematics and science. (2) He was very interested in chemistry, but he soon left the natural department, realizing that he liked physics and mathematics more. (3) Freshman Landau was the youngest at the university. (4)In the beginning this depressed him extremely. (5) Walking through the corridors, he raised his shoulders and bowed his head: it seemed to him that he looked much older this way.
Write out the subordinating phrase with the connection management from the sentence:1) High above, where the dark shaggy treetops met, rare stars twinkled.
2) It turns out that there is such an interesting award, which is awarded by the children radio listeners themselves.
Write out from the sentence a subordinating phrase with an adjacency connection:
1) Doctors forbade the famous painter to paint due to the harmful effects of paints.
2) A young lean woman slowly walks towards the house with a rocker on her shoulder. And it seems that along with the burden she carries her difficult thoughts.
2. What types of phrases based on the main word do you know? Give 2 examples for each type of phrase.
3. What is management? How are dependent words expressed in management? Give 3-4 examples with communication control.
4. Determine the type of subordinating connection: mother’s hands, getting up late, boiling broth, drizzling rain, far from the shore, my friend, talk about something, eat deliciously.
5. Parse the phrases: Night sea, issue a certificate, in winter snow, still interesting.
6.Additional task: replace phrases with the connection management with an agreement synonymous with the connection: autumn leaves, dad’s bag, silk dress, Kolya’s song.
A subordinate relationship is a relationship between the parts of a complex sentence or phrase in which one part is the control one, and the second is subordinate to it. Based on this, we will analyze the types of subordinating connections in phrases and sentences. For clarity, each of the above cases will be considered with an example.
Types of subordinating connections in phrases
There are only three of them. These are coordination, control and adjacency.
Coordination
Gender, number and case of the main word in this type of connection are consistent with the dependent word.
Examples: beautiful flower, another world, ninth day.
As you can see, this type of connection is typical for phrases where the noun is the main word, and the adjective, participle or ordinal number is the dependent word. Also, a possessive pronoun can act as a dependent word, for example, in the phrase “our souls.” The type of subordinating connection here will be agreement.
Control
The main word in management makes the secondary one dependent with the help of case. The combinations of parts of speech here can be quite varied: verb and noun, participle or gerund and noun, noun and noun, numeral and noun.
Examples: sitting on a bench, those who know the truth, entering the room, a clay bowl, ten sailors.
In GIA and Unified State Examination tasks, students are often faced with the task of changing the type of phrase from control to coordination or vice versa. Without understanding the material, a graduate may make a mistake. The task is actually quite simple. To do this, it is enough to know the types of subordinating connections and be able to use them.
The classic version of the task is a connection of two nouns. For example, “corn porridge.” The subordinating word must be changed into an adjective. Then it turns out to be “corn porridge”; accordingly, no other types of subordinating connections, except agreement, are suitable here. This means that everything has been done correctly.
If it is necessary to change the connection from agreement to control, then we change the adjective to a noun and put it in a certain case in relation to the main word. So, from a “strawberry cocktail” you get a “strawberry cocktail”.
Adjacency

IN in this case the main word is connected with the dependent word solely in meaning. Such a connection is between a verb and an adverb, a verb and a gerund, a verb and a verb, a verb and an adjective or an adverb of comparative degree.
Examples: “smile happily”, “speaks while sobbing”, “I can swim”, “be smarter”, “it has become worse”.
It is quite simple to determine this connection: the dependent word does not and cannot have case and gender. This can be an infinitive, a gerund, comparative degrees of an adjective and an adverb.
We looked at all types of subordinating connections in a phrase. Now let's move on to a complex sentence.
Subordinating connection in a sentence
Types of subordinating connections in a complex sentence can be distinguished when there are several subordinate clauses. They connect to the main clause in different ways. For this reason, it can be noted that the subordination relationship, the types of which we will analyze, can be expressed in different ways depending on the nature of the subordination.

Consistent submission
With this type of connection, subordinate clauses come into subordination to each other sequentially. This sentence pattern resembles a nesting doll.
Example. I asked a friend for a guitar who was helping me put on a show where we played Sherlock Holmes and Dr. Watson.
The basis of the main sentence here is “I asked.” The subordinate clause that enters into a subordinating relationship with it has the stem “which helped to arrange.” From this sentence comes another subordinate clause, subordinate to it - “we played Sherlock Holmes and Dr. Watson.”
Parallel subordination

This is a type of complex sentence in which several subordinate clauses are subordinate to one main clause, but at the same time to different words.
Example. In that park where lilacs bloom magnificently in spring, I was walking with a friend whose image seemed cute to you.
The main sentence sounds like this: “I was walking in that park with a friend.” It has a built-in subordinate clause “where lilacs bloom magnificently in spring.” It obeys the phrase “in that park.” From him we ask the question “in what?” Another subordinate clause - “whose image seemed cute to you” - is built from the word “familiar”. We ask him the question “which one?”
Thus, we see that the clauses are connected subordinating connection with one main sentence, but with different parts of it.
Homogeneous Subordination
Subordinate clauses with homogeneous subordination are associated with one main clause. They refer to the same word and answer the same question.
Example. They guessed that their action would have consequences, that it was better to abandon the idea and let everything be as it was.

The main sentence is “they guessed.” From him we ask the question “about what?” Both subordinate clauses answer this question. In addition, both the first and second subordinate clauses are connected to the main sentence using the predicate “guessed.” From this we conclude that the sentence is with homogeneous subordination.
All the examples given refer to sentences where there is a subordinating connection, the types of which we have discussed. This information will be necessary for everyone who is going to take exams in the Russian language, especially the State Examination and the Unified State Exam, where there are a number of tasks to test such knowledge. It is important to remember that without understanding how phrases and sentences are constructed, it is impossible to fully master literate speech. Any person who wants to learn how to write without errors needs to know this.
Complex sentences With different types communications- This complex sentences , which consist of at least from three simple proposals , interconnected by coordinating, subordinating and non-union connections.
To understand the meaning of such complex structures It is important to understand how the simple sentences included in them are grouped together.
Often complex sentences with different types of connections are divided into two or several parts (blocks), connected using coordinating conjunctions or without unions; and each part in structure represents either complex sentence, or simple.
For example:
1) [Sad I]: [there is no friend with me], (with whom I would drink the long separation), (whom I could shake hands from the heart and wish many happy years)(A. Pushkin).
This is a complex sentence with different types of connections: non-union and subordinating, consists of two parts (blocks) connected non-union; the second part reveals the reason for what is said in the first; Part I is a simple sentence in structure; Part II is a complex sentence with two attributive clauses, with homogeneous subordination.
2) [Lane was all in the gardens], and [grew at the fences linden trees, now casting, under the moon, a wide shadow], (so fences And gates on one side they were completely buried in darkness)(A. Chekhov).
This is a complex sentence with different types of connections: coordinating and subordinating, consists of two parts connected by a coordinating conjunction and, the relations between the parts are enumerative; Part I is a simple sentence in structure; Part II - a complex sentence with a subordinate clause; the subordinate clause depends on the main thing and is joined to it by the conjunction so.
A complex sentence can contain sentences with different types of conjunction and non-conjunction connections.
These include:
1) composition and submission.
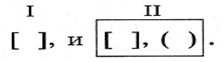
For example: The sun set and night followed day without interval, as usually happens in the south.(Lermontov).
(And is a coordinating conjunction, as is a subordinating conjunction.)
The outline of this proposal:
2) composition and non-union communication.
For example: The sun had long since set, but the forest had not yet died down: the turtle doves were murmuring nearby, the cuckoo was crowing in the distance.(Bunin).
(But - coordinating conjunction.)
The outline of this proposal:

3) subordination and non-union connection.
For example: When he woke up, the sun was already rising; the mound obscured him(Chekhov).
(When - subordinating conjunction.)
The outline of this proposal:

4) composition, subordination and non-union connection.
For example: The garden was spacious and there were only oak trees; they began to bloom only recently, so that now through the young foliage the entire garden with its stage, tables and swings was visible.
(And is a coordinating conjunction, so is a subordinating conjunction.)
The outline of this proposal:
In complex sentences with coordinating and subordinating conjunctions, coordinating and subordinating conjunctions may appear side by side.
For example: The weather was beautiful all day, but as we approached Odessa, it began to rain heavily.
(But - a coordinating conjunction, when - a subordinating conjunction.)
The outline of this proposal:

Punctuation marks in sentences with different types of communication
In order to correctly place punctuation marks in complex sentences with different types of connections, it is necessary to select simple sentences, determine the type of connection between them and select the appropriate punctuation mark.
As a rule, a comma is placed between simple sentences in complex sentences with different types of connections.
For example: [In the morning, in the sun, the trees were covered with luxurious frost] , and [this went on for two hours] , [then the frost disappeared] , [the sun has closed] , and [the day passed quietly, thoughtfully , with a drop in the middle of the day and anomalous lunar twilight in the evening].
Sometimes two, three or more simple offers most closely related to each other in meaning and can be separated from other parts of a complex sentence semicolon . Most often, a semicolon occurs in place of a non-union connection.
For example: (When he woke up), [the sun had already risen] ; [the mound obscured it].(The sentence is complex, with different types of connections: with non-union and union connections.)
At the site of the non-union connection between simple sentences within a complex possible Also comma , dash And colon , which are placed according to the rules for placing punctuation marks in a non-union complex sentence.
For example: [The sun has long since set] , But[the forest has not yet died down] : [doves gurgled nearby] , [the cuckoo crowed in the distance]. (The sentence is complex, with different types of connections: with non-union and union connections.)
[Leo Tolstoy saw a broken burdock] – and [lightning flashes] : [the idea of an amazing story about Hadji Murad appeared](Paust.). (The sentence is complex, with different types of connections: coordinating and non-conjunctive.)
In complex syntactic constructions that break up into large logical-syntactic blocks, which themselves are complex sentences or in which one of the blocks turns out to be a complex sentence, punctuation marks are placed at the junction of the blocks, indicating the relationship of the blocks, while maintaining the internal signs placed on their own syntactic basis.
For example: [The bushes, trees, even stumps are so familiar to me here] (that wild felling has become like a garden to me) : [I caressed every bush, every pine tree, every Christmas tree], and [they all became mine], and [it’s the same as if I planted them], [this is my own garden](Priv.) – there is a colon at the junction of blocks; [Yesterday a woodcock stuck his nose into this foliage] (to get a worm from under it) ; [at this time we approached], and [he was forced to take off without throwing off the layer of old aspen foliage from his beak](Priv.) – there is a semicolon at the junction of blocks.
Particular difficulties arise placement of punctuation marks at the junction of the composing And subordinating conjunctions (or coordinating conjunction and a conjunction word). Their punctuation is subject to the laws of the design of sentences with coordinating, subordinating and non-conjunctive connections. However, there are also special attention require sentences in which several conjunctions appear nearby.
In such cases, a comma is placed between conjunctions if the second part of the double conjunction does not follow. then, yes, but(in this case the subordinate clause may be omitted). In other cases, a comma is not placed between two conjunctions.
For example: Winter was coming and , When the first frosts hit, living in the forest became difficult. - Winter was approaching, and when the first frosts hit, it became difficult to live in the forest.
You can call me, but , If you don't call today, we'll leave tomorrow. – You can call me, but if you don’t call today, then we’ll leave tomorrow.
I think that , if you try, you will succeed. – I think that if you try, you will succeed.
Syntactic analysis of a complex sentence with different types of connection
Scheme for parsing a complex sentence with different types of connection
1. Determine the type of sentence according to the purpose of the statement (narrative, interrogative, incentive).
2. Indicate the type of sentence based on emotional coloring (exclamatory or non-exclamatory).
3. Determine (by grammatical basics) quantity simple sentences, find their boundaries.
4. Determine the semantic parts (blocks) and the type of connection between them (non-union or coordinating).
5. Give a description of each part (block) by structure (simple or complex sentence).
6. Create a proposal outline.
SAMPLE EXAMPLE OF A COMPLEX SENTENCE WITH DIFFERENT TYPES OF CONNECTION
[Suddenly a thick fog], [as if separated by a wall He me from the rest of the world], and, (so as not to get lost), [ I decided
Non-union and allied coordinating connections are one of the ways of constructing. Without them, speech is poor, because they provide more information and are capable of containing two or more sentences telling about different events.
Complex sentences and their types
Depending on the number of parts, complex structures are divided into two- and polynomial. In any of the options, the elements are connected either by a conjunction (which, in turn, is provided by the corresponding part of speech) or by a non-conjunction.
Depending on what types of relationships are present, complex formations create the following groups:
- Complex sentence with non-union and allied coordinating connection: The sky suddenly darkened, a distant rumble was heard, and a wall of rain covered the ground, driving down dust and washing away the city smog.
- Constructions that combine elements with a subordinate relationship, for example: The house we entered was depressing, but in this situation we had no choice.
- Complex sentences with subordinating and non-conjunctive types of connections: No matter how he hurried, his help was late: another car took the wounded.
- In polynomial constructions, subordinating, non-union and allied coordinating connections can be used simultaneously. The next time the phone rang, my mother answered it, but heard only the voice of a robot informing her that her loan was overdue.
It is important to be able to distinguish between complex sentences and constructions complicated, for example, by homogeneous predicates. As a rule, in the first case, the syntactic lexical unit contains several grammatical stems, while in the second there will be one subject and several predicates.
Non-union designs
In this type of lexical constructions, 2 simple sentences or more can be combined, which are connected by intonation and meaning. They can communicate with each other in the following ways:
- Sentences are linked by enumeration. The evening gradually faded, night fell on the earth, the moon began to rule the world.
- Constructions in which elements are divided into several parts, two of which are opposite fragments. The weather was as if to order: the sky cleared of clouds, the sun was shining brightly, a light breeze blew across the face, creating a slight coolness. In this non-union construction, the second fragment, consisting of 3 simple sentences connected by enumerative intonation, explains its first part.
- A binary combination of simple elements into a polynomial complex structure, in which the parts are combined into semantic groups: The moon rose above the ridge, we did not immediately notice it: the haze hid its radiance.

A non-conjunctive, like a conjunctive coordinating connection, in a complete connection separates individual sentences from each other with punctuation marks.
Commas in non-union polynomial constructions
In complex compounds, their parts are separated by commas, semicolons, dashes and colons. Commas and semicolons are used in enumerative relations:
- The parts are small in size and connected to each other in meaning. After the storm there was silence, followed by a light whisper of rain.
- When parts are too common and not connected by a single meaning, a semicolon is used. Chamomiles and poppies covered the entire clearing; Grasshoppers were chirping somewhere below.

Non-union constructions are most often used to convey a large amount of information that is not always connected in meaning.
Dividing marks in non-union formations
These signs are used for the following types of relationships between elements of a syntactic structure:
- Dash - when the second part is sharply opposed to the first, for example: We knew about his fears - no one knew about his readiness to die.(In such a construction with a non-union, as well as a union, coordinating connection between parts, I would like to put the conjunction “but”).
- When the first part talks about a condition or time, then a dash is also placed between it and the second fragment. The rooster crowed - it's time to get up. In such sentences, the meaning of the conjunctions “if” or “when” is appropriate.
- The same sign is placed if the second part contains a conclusion about what was discussed in the first. There was no strength to object - he silently agreed. In such conjunction constructions, “therefore” is usually inserted.
- When the second part of the sentence is compared and determined by what is narrated in the first. He makes a speech - he breathes hope into people. In these constructions you can add “as if” or “as if”.
- In sentences with an explanatory connection and justification of the reason, a colon is used. I’ll tell you to the point: you can’t let your friends down.

Sentences with a non-union, as well as a union, coordinating connection between parts are separated by signs depending on their semantic relationship.
Complex constructions
In sentences of this type, a coordinating connection is used, carried out using coordinating conjunctions. In this case, between their parts there may be:
- Connective relationships interconnected by unions and, yes or, particles also, also and neither...nor. No birds chirp, no mosquito squeaks, no cicadas chirp.
- In separating relationships, conjunctions are used that and, or, particles either... or, not that... not that and others. Either the wind brings an incomprehensible sound, or it itself is approaching us.
- Sentences with both non-union and allied coordinating connections with comparative relations indicate the identity of events, but in the second case with the use of conjunctions namely And that is. Everyone was happy to see him, that is, that’s what he read on their faces.
- Explanatory relationships tend to use conjunctions yes, but, ah, particles but, and therefore and others. A blizzard was raging outside the window, but it was warm near the fireplace in the living room.

Often it is conjunctions and particles that explain what connects simple sentences into a single complex structure.
Complex sentences with mixed types of communication
Constructions where there is both a non-union and a union coordinating connection at the same time are found quite often. They can contain separate blocks, each of which contains several simple sentences. Within blocks, some elements are connected to others in meaning and are separated by punctuation marks with or without conjunctions. In a complex sentence with a non-conjunctive and a conjunctive coordinating connection, the line between them is separators, although individual blocks may not be connected in meaning.
Complex sentences with different types of connections- This complex sentences , which consist of at least from three simple sentences , interconnected by coordinating, subordinating and non-union connections.
To understand the meaning of such complex constructions, it is important to understand how the simple sentences included in them are grouped together.
Often complex sentences with different types of connections are divided into two or several parts (blocks), connected using coordinating conjunctions or without unions; and each part in structure is either a complex sentence or a simple one.
For example:
1) [Sad I]: [there is no friend with me], (with whom I would drink the long separation), (whom I could shake hands from the heart and wish many happy years)(A. Pushkin).
This is a complex sentence with different types of connections: non-union and subordinating, consists of two parts (blocks) connected non-union; the second part reveals the reason for what is said in the first; Part I is a simple sentence in structure; Part II is a complex sentence with two attributive clauses, with homogeneous subordination.
2) [Lane was all in the gardens], and [grew at the fences linden trees, now casting, under the moon, a wide shadow], (so fences And gates on one side they were completely buried in darkness)(A. Chekhov).
This is a complex sentence with different types of connections: coordinating and subordinating, consists of two parts connected by a coordinating conjunction and, the relations between the parts are enumerative; Part I is a simple sentence in structure; Part II - a complex sentence with a subordinate clause; the subordinate clause depends on the main thing and is joined to it by the conjunction so.
A complex sentence can contain sentences with different types of conjunction and non-conjunction connections.
These include:
1) composition and submission.
For example: The sun set and night followed day without interval, as usually happens in the south.(Lermontov).
(And is a coordinating conjunction, as is a subordinating conjunction.)
The outline of this proposal:

2) composition and non-union communication.
For example: The sun had long since set, but the forest had not yet died down: the turtle doves were murmuring nearby, the cuckoo was crowing in the distance.(Bunin).
(But - coordinating conjunction.)
The outline of this proposal:

3) subordination and non-union connection.
For example: When he woke up, the sun was already rising; the mound obscured him(Chekhov).
(When - subordinating conjunction.)
The outline of this proposal:

4) composition, subordination and non-union connection.
For example: The garden was spacious and there were only oak trees; they began to bloom only recently, so that now through the young foliage the entire garden with its stage, tables and swings was visible.
(And is a coordinating conjunction, so is a subordinating conjunction.)
The outline of this proposal:
In complex sentences with coordinating and subordinating conjunctions, coordinating and subordinating conjunctions may appear side by side.
For example: The weather was beautiful all day, but as we approached Odessa, it began to rain heavily.
(But - a coordinating conjunction, when - a subordinating conjunction.)
The outline of this proposal:

Punctuation marks in sentences with different types of communication
In order to correctly place punctuation marks in complex sentences with different types of connections, it is necessary to select simple sentences, determine the type of connection between them and select the appropriate punctuation mark.
As a rule, a comma is placed between simple sentences in complex sentences with different types of connections.
For example: [In the morning, in the sun, the trees were covered with luxurious frost] , and [this went on for two hours] , [then the frost disappeared] , [the sun has closed] , and [the day passed quietly, thoughtfully , with a drop in the middle of the day and anomalous lunar twilight in the evening].
Sometimes two, three or more simple offers most closely related to each other in meaning and can be separated from other parts of a complex sentence semicolon . Most often, a semicolon occurs in place of a non-union connection.
For example: (When he woke up), [the sun had already risen] ; [the mound obscured it].(The sentence is complex, with different types of connections: with non-union and union connections.)
At the site of the non-union connection between simple sentences within a complex possible Also comma , dash And colon , which are placed according to the rules for placing punctuation marks in a non-union complex sentence.
For example: [The sun has long since set] , But[the forest has not yet died down] : [doves gurgled nearby] , [the cuckoo crowed in the distance]. (The sentence is complex, with different types of connections: with non-union and union connections.)
[Leo Tolstoy saw a broken burdock] – and [lightning flashes] : [the idea of an amazing story about Hadji Murad appeared](Paust.). (The sentence is complex, with different types of connections: coordinating and non-conjunctive.)
In complex syntactic constructions that break up into large logical-syntactic blocks, which themselves are complex sentences or in which one of the blocks turns out to be a complex sentence, punctuation marks are placed at the junction of the blocks, indicating the relationship of the blocks, while maintaining the internal signs placed on their own syntactic basis.
For example: [The bushes, trees, even stumps are so familiar to me here] (that wild felling has become like a garden to me) : [I caressed every bush, every pine tree, every Christmas tree], and [they all became mine], and [it’s the same as if I planted them], [this is my own garden](Priv.) – there is a colon at the junction of blocks; [Yesterday a woodcock stuck his nose into this foliage] (to get a worm from under it) ; [at this time we approached], and [he was forced to take off without throwing off the layer of old aspen foliage from his beak](Priv.) – there is a semicolon at the junction of blocks.
Particular difficulties arise placement of punctuation marks at the junction of the composing And subordinating conjunctions (or coordinating conjunction and allied word). Their punctuation is subject to the laws of the design of sentences with coordinating, subordinating and non-conjunctive connections. However, at the same time, sentences in which several conjunctions appear nearby stand out and require special attention.
In such cases, a comma is placed between conjunctions if the second part of the double conjunction does not follow. then, yes, but(in this case the subordinate clause may be omitted). In other cases, a comma is not placed between two conjunctions.
For example: Winter was coming and , When the first frosts hit, living in the forest became difficult. - Winter was approaching, and when the first frosts hit, it became difficult to live in the forest.
You can call me, but , If you don't call today, we'll leave tomorrow. – You can call me, but if you don’t call today, then we’ll leave tomorrow.
I think that , if you try, you will succeed. – I think that if you try, you will succeed.
Syntactic analysis of a complex sentence with different types of connection
Scheme for parsing a complex sentence with different types of connection
1. Determine the type of sentence according to the purpose of the statement (narrative, interrogative, incentive).
2. Indicate the type of sentence based on emotional coloring (exclamatory or non-exclamatory).
3. Determine (based on grammatical basics) the number of simple sentences and find their boundaries.
4. Determine the semantic parts (blocks) and the type of connection between them (non-union or coordinating).
5. Give a description of each part (block) by structure (simple or complex sentence).
6. Create a proposal outline.
SAMPLE EXAMPLE OF A COMPLEX SENTENCE WITH DIFFERENT TYPES OF CONNECTION
[Suddenly a thick fog], [as if separated by a wall He me from the rest of the world], and, (so as not to get lost), [ I decided








