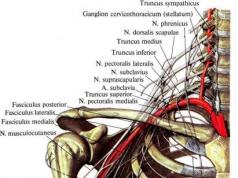
Dentists receive qualification categories in the same way as doctors of other specialties.
There are second, first and highest categories. In this article you will learn about the new procedure for obtaining qualification categories, according to Order No. 274 “On the procedure for obtaining qualification categories for employees with higher medical education, higher and secondary pharmaceutical education government agencies health care."
- the federal law dated November 21, 2011 No. 323-FZ “On the basics of protecting the health of citizens in Russian Federation,
- orders of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated July 23, 2010 No. 541n “On approval of a unified qualification reference book for positions of managers, specialists and employees,
- chapter " Qualification characteristics positions of workers in the field of healthcare”, dated 07.07.2009 No. 415n “On approval of qualification requirements for specialists with higher and postgraduate medical and pharmaceutical education in the field of healthcare”
- and dated July 25, 2011 No. 808n “On the procedure for obtaining qualification categories for medical and pharmaceutical workers.”
- Order No. 274
Requirements for dentists when awarding the category:
Second category At least 3 years of work experience in the certified specialty Good practical and theoretical preparation Work skills: modern methods of prevention, diagnosis and treatment of patients First category at least seven years Required practical experience and good theoretical and practical training in the field of his specialty, well acquainted with related disciplines modern methods of prevention, diagnosis and treatment of patients, active participation in scientific and practical activities medical institution Highest category work experience in the specialty for at least ten years high theoretical and practical professional training mastery in perfection modern methods prevention, diagnosis and treatment of patients in the field of their specialty, who are well acquainted with related disciplines, have good indicators of professional activity, take an active part in the scientific and practical activities of the medical institution and advanced training of specialists with higher medical education. What documents must a dentist provide to obtain a category?
- an application from a specialist addressed to the chairman of the certification commission, which indicates the qualification category for which he is applying, the presence or absence of a previously assigned qualification category, the date of its assignment, the specialist’s personal signature and date (Appendix No. 2);
- a completed printed qualification sheet certified by the HR department (Appendix No. 3);
- a report on the professional activities of a specialist, agreed upon with the head of the organization and certified by its seal, and including an analysis of professional activities over the past three years with a personal signature (Appendix No. 4).
Requirements for a specialist report (working for the category of doctor):
You can familiarize yourself with the documentation in more detail by downloading the documentation for .
What should be contained in the work for the category of dentist (in the certification report)
- The first chapter contains information about the healthcare institution where the dentist works, dental department, equipment of the dentist’s office and workplace,
- The second chapter is a report on the work over the past three years. It analyzes the dynamics of quality therapeutic work. The introduction of modern technologies, the doctor’s mastery of new treatment methods. Also here are the main indicators of the specialist’s work in the form of tables and graphs, namely qualitative and quantitative indicators (percentage and absolute number of sanitized, number of fillings, UET in direct connection with the number of working days of the year). Do not forget to indicate the number of sanitation per rate, the number of sanitation, the number of fillings per day and the ratio of uncomplicated to complicated caries, % of one-session treatment of complicated caries. Each table and graph should end with a brief conclusion (1-2 sentences). Write what treatment methods you use in your work. Indicators of preventive work and medical examination.
- The third section includes an analysis of new methods of treatment and prevention.
Dentists' reports on the category are available on the Internet for free access; you can read them on our website. I made a selection of reports and did some initial editing and formatting in Microsoft Office Word. However, all of them leave much to be desired and do not fully meet the requirements. They can only be used as a basis, an example.
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
MUZ dental clinic No. 2
REPORT ON THE WORK OF A DENTIST
FOR 2008 – 2010
MATVEEVA VALENTINA IOSIFOVNA
Kaliningrad – 2011
Report plan
1. General information……………………………………………. 3
2. Equipment of the office and organization of work in
dental office…………………………….. 4
3. The work of a dentist in a therapeutic clinic
reception ………………………………………………………5-19
4. Sanitary educational work … …………………19-20
5. Sanitary and epidemiological operating regime
office…………………………………………………………………… ….. 21-22
6. Conclusions ……………………………………………………… 23-28
1. General information
I have been working at dental clinic No. 2 since August 1991. Clinic No. 2 provides treatment and preventive dental care to the adult population.
The clinic is located in a two-story adapted building at the address: st. Proletarskaya 114. The clinic has a compressor room for supplying compressed air to dental units, a centralized washing and sterilization room, a physiotherapy and x-ray room, and a reception area. The clinic operates in two shifts from 7.45 to 20.15, Saturday from 9.00 to 15.00. There are 2 medical departments and one denture department. The treatment departments have 6 therapeutic rooms, 1 surgical room, 1 periodontal room, acute pain. Treatment rooms are equipped with modern drills. All turbine units are supplied with compressed air centrally.
2. Equipment of the office and organization of work in the dental office
The office in which I receive dental patients meets sanitary and hygienic standards. Equipped with a Marus dental unit. There is cold and hot water, the necessary instruments, a set of modern domestic and imported anesthetics and filling materials.
The workload at the reception consists of initial tickets and repeat patients.
I work on the principle of maximizing the number of sanitation procedures on the first visit.
The main tasks at the reception are:
1. Rendering qualified assistance to the population.
2. Carrying out sanitary educational work, training in oral hygiene.
3.Prevention of dental diseases.
3. The work of a dentist at a therapeutic appointment.
In recent years, the work of a dentist has undergone significant changes due to the use of:
1. Turbine units, which makes it possible to use modern filling materials and makes the preparation of hard tooth tissues painless and quick.
2. More effective pain relief (alfacaine, ultracaine, orthocoin, ubestezin).
3. Modern filling materials (light and chemical curing composites).
4. Endodontic filling material: pastes for filling tooth canals with antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, restorative properties, gutta-percha pins and endodontic instruments.
I see patients with the following diseases:
1. Carious damage to tooth tissue.
2. Complicated forms of caries.
3. Traumatic damage to teeth.
4. Non-carious lesions of dental tissues.
5. Combined destruction of tooth tissue.
The office has a set of domestic and imported filling materials. Among the domestic ones, I most often use the following materials: uniface, phosphate cement, silydont, silicin, stomafil for fillings.
At deep caries For therapeutic pads I use drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect and promote the formation of replacement dentin: calmecin, calradent, life, daikal.
In my work I give preference to composite filling materials. Glass ionomer cements stabilize the process due to the fact that they for a long time fluoride ions are released. I use cements such as stomafil, ketak-molar, and vetremer. These cements are used as cushioning, therapeutic and restoration cements. Their advantages: ease of use, increased adhesion, biocompatibility with dental tissues, high fluoride release, low solubility, strength.
I use chemical and light curing for composite materials.
From chemical available: alphadent, unifil, compokur, charisma, etc.
From light-curing : Herculite, Filtek, Valux, Filtek-suprime, Point, Admira.
They have the following positive properties: color stability, good marginal adhesion, strength, good polishability.
Requirements for composite materials:
1. Good adaptation.
2. Water resistance.
3. Color stability.
4. Simple technique applications.
5. Satisfactory mechanical strength.
6. Adequacy of working time.
7. Required curing depth.
8. R-contrast.
9. Good polishability.
10. Biological tolerance.
Standard scheme for using composite materials:
1. Preparation of the carious cavity.
2. Color selection.
3. Applying a gasket.
4. Etching.
5. Neutralization of acid.
6. Drying.
7. Application of adhesive.
8. Restoration of the anatomical shape of the tooth.
9. Tinting the filling.
10. Strict adherence to instructions.
Classification of composites
![]()
![]() Curing method Purpose
Curing method Purpose

 Chemical Light Class A
Chemical Light Class A
· Powder + curable for cavities of classes I and II.
Liquid one paste Class B
Paste paste for cavities III and
The most common disease in dental practice is dental caries.
The most common classification is clinical and anatomical, which takes into account the depth of distribution of the carious process:
· dental caries in the stain stage;
· fissure caries;
· average caries;
· deep caries.
Anatomical classification of cavities according to Black, taking into account the surface of the lesion localization:
1 class- localization of carious cavities in the area of natural fissures of molars and premolars, in the blind fossae of incisors and molars.
2nd grade- on the lateral surfaces of molars and premolars.
3rd grade- on the lateral surfaces of incisors and canines without violating the integrity of the cutting edge.
4th grade- on the lateral surfaces of incisors and canines with a violation of the integrity of the angle and cutting edge of the crown.
5th grade- in the cervical region.
Basic principles and sequence local treatment caries:
1. Anesthesia. The choice of pain relief method is determined by clinical and individual characteristics sick. Both domestic and imported anesthetics are available in the workplace.
IN present period We can firmly say that the problem of pain-free dental treatment has been solved. The painkillers used, based on articaine, relieve painful sensations both in the treatment of caries of any location and cavity depth, and all forms of pulpitis. Efficiency approaches 100%. On upper jaw Infiltration anesthesia is mainly used in the area of the root apex. In the lower jaw, the greatest effect is achieved by anesthesia near the condylar process of the lower jaw. Methodology: at maximum open mouth insert the needle 2 cm higher chewing surface lower molars - upward medially in the direction ear canal. The duration of anesthesia is 2-4 hours.
2. Opening of the carious cavity: removal of overhanging edges of the enamel, which allows you to expand the entrance hole into the carious cavity.
3. Expansion of the carious cavity . The enamel edges are leveled and the affected fissures are excised.
4. Necroectomy . Removing all affected tissue from the cavity and using a caries detector to identify damaged dentin and leave no traces on healthy areas.
5. Formation of a carious cavity. Creating conditions for reliable fixation of the filling.
The task of operational technology- the formation of a cavity, the bottom of which is perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth (the direction of inclination must be determined), and the walls are parallel to this axis and perpendicular to the bottom. If the inclination to the vestibular side - for the upper chewing teeth and to the oral side - for the lower ones is more than 10-15°, and the wall thickness is insignificant, then the rule for the formation of the bottom changes: it should have an inclination in the opposite direction. This requirement is due to the fact that occlusal forces directed at the filling at an angle and even vertically have a displacement effect and can contribute to chipping of the tooth wall. This requires creation towards the bottom additional cavity to distribute the forces of chewing pressure on thicker and, therefore, more mechanically strong areas of tissue. In these situations, an additional cavity can be created on the opposite (vestibular, oral) wall along the transverse intertubercular groove with a transition to the side of the main cavity. It is necessary to determine the optimal shape of the additional cavity, in which the greatest effect of redistribution of all components of chewing pressure can be achieved with minimal prompt removal enamel and dentin and the least pronounced pulp reaction.
The pattern of action of chewing pressure forces on tooth tissue and filling material.
a - the tooth is located vertically; b - the tooth is inclined.
R, Q, P - direction of forces.
Often the pathological process goes beyond the carious cavity and the pulp and periodontium are involved in the process.
In recent years, the emotional perception of visiting the dentist's office has changed for the better thanks to the use of modern painkillers based on articaine. The low toxicity of the drug, rapid penetration into tissues, rapid elimination from the body, high anesthetic effect allows the treatment of dental patients in a wider range: pregnant women, elderly people, children. Ultracaine does not contain a preservative, which causes allergic reactions. The concentration of antioxidant metabisulfate, a substance that prevents the oxidation of adrenaline, is minimal and amounts to 0.5 mg per 1 ml of solution. Ultracaine is 6 times more effective than novocaine and 2-3 times more effective than lidocaine, the onset of anesthesia is rapid - 0.3-3 minutes. allows you to maintain a favorable psycho-emotional background, the ability to replace conduction anesthesia with infiltration anesthesia when working on the lower jaw. The properties of ultracaine listed above allow it to be used in a wide range of dental diseases, in particular in the treatment of pulpitis.
Classification of pulpitis:
· limited;
· diffuse.
2. Chronic
· fibrous;
· gangrenous;
· hypertrophic.
3. Exacerbation of chronic pulpitis
Treatment of pulpitis:
I. Without pulp removal.
1. Preservation of the entire pulp.
2. Vital amputation.
II. With pulp removal.
1. Vital extirpation method.
2. Method of devital extirpation.
3. Method of devital amutation.
The canal is filled, not reaching the apex by 2 mm (information from the Semashko MMSI), taking into account the condition of the periapical tissues. Filling materials
1. Plastic:
Non-hardening;
Hardening.
2. Primary hard.
Plastic hardening materials called endosealers or sealers.
They are divided into several groups:
1. Zinc phosphate cements.
2. Preparations based on zinc oxide and eugenol.
3. Materials based on epoxy resins.
4. Polymer materials containing calcium hydroxide.
5. Glass ionomer cements.
6. Preparations based on resorcinol-formalin resin.
7. Materials based on calcium phosphate.
Canal filling can be done using modern pastes and gutta-percha pins. In my practice, I most often use endomethasone, zinc-eugenol paste and paste based on resorcinol-formalin resin. I would especially like to note the work with endomethasone.
Endomethasone is a filling paste containing hormonal drugs, thymol, paraformaldehyde on a liquid basis of eugenol, anise drops. When filling canals with this paste, good therapeutic effect. The antibacterial properties of formaldehyde allow it to be used in treatment chronic periodontitis With bone destruction at the tops of the roots. Hormonal drugs reduce pain and inflammation, have a plastic effect on the periodontium.
I fill root canals using the lateral condensation method, which consists of the following.
1. Selection of the main gutta-percha point (Master-point).
A standard gutta-percha pin of the same size as the last endodontic instrument used to process the apical part of the canal (Masterfile) is taken and fitted into the canal. The pin does not reach the physiological apex by 1 mm.
2. Selection of spreader.
The spreader is selected to be the same size as the Master file, or one size larger, so as not to go beyond the apical opening. The working length of the spreader should be 1-2 mm. shorter than the working length of the canal.
3. Introduction of endosealant into the channel.
I use AN+, endomethasone, as an endosealant. The material is introduced into the canal to the level of the apical foramen and is evenly distributed along the canal walls.
4. Insertion of the main pin into the canal.
The pin is covered with filling material and slowly inserted into the canal to its working length.
5. Lateral condensation of gutta-percha.
A previously selected spreader is inserted into the root canal, and the gutta-percha is pressed against the canal wall.
6. Removing the spreader and inserting an additional pin.
7. Lateral condensation of gutta-percha, removal of the spreader and insertion of a second additional pin.
The operation is repeated until complete obturation of the canal is achieved, i.e. until the spreader stops penetrating into the canal.
8. Removing excess gutta-percha and paste.
9. X-ray quality control of filling.
10.Applying a bandage.
Classification of periodontitis:
· serous;
· purulent.
II. Chronic periodontitis
· fibrous;
· granulating;
granulomatous.
III. Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis.
I treat acute periodontitis and exacerbation of chronic periodontitis of single-rooted teeth under anesthesia in one visit using one of the listed pastes and gutta-percha pins, and send them to the surgical office for an incision in the area of the projection of the root apex.
I treat destructive forms of periodontitis in several stages. For temporary canal filling I use calcium-containing preparations: “Kollapan”, “Kalasept”, which can successfully cope with periapical infection and destruction bone tissue. Repeated R-images after 6 months show either a decrease in the destruction of bone tissue or restoration of the structure of the bone beams, which subsequently form bone, which depends on the state of the immune system of the patient. If the conservative method does not lead to the desired effect, then the patient is sent to the surgical office to remove the cyst or cystogranuloma.
I check the long-term results after 3-6 months together with the surgeon. After the operation, the teeth become immobile, and after 3-6 months, bone tissue is visible at the site of the cyst on the R-image.
When treating teeth with impassable root canals, I use copper-calcium hydroxide depophoresis. In addition, this method is used when the contents of the canal are severely infected, or the instrument breaks off in the lumen of the canal (without going beyond the apex).
While working with the patient, I explain to him the chosen method of treatment and possible complications, the need for root removal and timely prosthetics. Explaining the influence bad habits on the condition of the oral cavity.
Constantly improving the equipment of the office and clinic with equipment and dental materials allows you to receive patients at a modern level.
Working with modern filling materials
Filling is the final stage of treatment of caries and its complications, which aims to replace lost tooth tissue with a filling.
The success of treatment largely depends on the ability to choose the right required material and use it rationally.
IN Lately Light-curing composite materials have become widespread; in a number of indicators they perfectly imitate tooth tissue. Properties such as color, transparency, abrasion resistance and polishability have significantly expanded the possibilities of restoring teeth without prosthetics. The process of restoring damaged teeth directly in the oral cavity in one visit is called restoration.
Filling - clean medical procedure, while restoration combines elements of therapeutic and artistic work.
Stages of restoration (filling):
1. Patient preparation.
2. Tooth preparation.
3. Restoration (filling).
The patient should be taught how to properly brush his teeth, remove dental plaque, and, if necessary, send him to a periodontal office. All surgical interventions carry out before treatment. Improving the health of gum tissue is also important because the maximum effect is achieved with a combination of smooth, healthy teeth and pale pink gums.
The main requirement when restoring teeth with light-curing materials is precise and methodical adherence to the instructions. Only when all technological steps are completed will the necessary adhesion of the composite to the dental tissues be achieved and a good cosmetic result will be obtained. Despite some differences in the use of composites from different companies, there are general principles at work.
Preparing a tooth for restoration includes the following manipulations:
1. Removal of altered tissues.
2. Formation of the edges of the enamel.
3. Removing plaque from the tooth surface.
4. Opening of prisms.
5. Insulation from moisture and drying.
6. Applying a gasket.
7. Formation of the basis of restoration.
8. Etching tooth enamel.
9. Primer application.
10.Applying adhesive.
It is necessary to dwell on some stages of tooth preparation, namely the opening of enamel prisms. This somewhat conventional expression implies the removal of the thinnest surface structureless layer of enamel that covers the bundles of prisms. It is believed that removing the structureless layer and subsequent etching of the enamel with acid will create favorable conditions for fixing the composite. This is especially important to do in cases where the composite is applied to a significant surface of the enamel (in case of hypoplasia, erosion, chipping of part of the crown).
Etching tooth enamel produced in accordance with the instructions supplied with the material. It should be remembered that excessive etching should not be allowed, since the changing structure of the enamel does not provide optimal adhesion conditions. Careful removal of the acid or gel is very important. The time required for washing the etching area should be at least 20 seconds. After this, thorough air drying is carried out.
Etching of dentin is carried out simultaneously with etching of enamel. This achieves the removal of the smear layer and the formation of intercollagen spaces, which are filled with primer.
The primer is applied with a clean brush onto dentin, and after 30 sec. excess volatile components of the drug are removed from the gun with air; contact of the primer with the enamel does not affect the adhesion of the composite.
Application of adhesive is the final stage of preparing the tooth for filling. The adhesive is introduced into the cavity with a brush and then with a stream of air.
distributed evenly over the walls. If the adhesive is chemically cured (two-component), then it does not need to be illuminated, but if it is light-curing (one-component), then it is illuminated with a lamp. Usually this is 10 seconds.
Restoration (filling) of a tooth
This stage includes:
1. Insertion of the anchor.
2. Adding the composite.
3. Curing of the composite.
4. Formation of the restoration surface.
5. Final highlighting.
1. In case of significant tooth decay, I use anchor pins. The anchor pins have Various types, dimensions - length and diameter of the section vary from 1 to 10 units. An important stage of restoration is adjusting the anchor. The anchor must fit tightly into the channel to a certain depth. I think the most optimal is 2/3 of the root in the front group of teeth and up to ½ in the lateral teeth. The anchor pins are screwed in all the way with a special tool, opening the petals. I always cover the anchors with light-curing Opaque material to avoid it being visible through the layer of the main composite.
2. The composite is applied using trowels that do not have defects. For deep cavities, the composite is applied in layers (up to 3 ml). This is especially important with light-curing materials. The “outset” that forms on the surface of the composite, called the “oxygen-inhibited layer,” ensures the connection of the composite layers without adhesive. This layer must not be damaged - washed or contaminated. The curing of the material is associated with shrinkage, which occurs in the direction away from the light source.
3. The next step is grinding and polishing. First of all, it is necessary to remove excess materials using burs. It is important to create the main details of the surface shape: longitudinal stripes of incisors, cusps and fissures of molars. After correction of errors and re-finishing, the surface of the restoration is polished with plastic or rubber heads. Contact surfaces are polished using strips and floss. The final processing of the restoration is carried out using sponges and polishing pastes. At the end of the work, finishing lighting is carried out. The maximum effect is achieved with a perpendicular position of the light beam.
4. Sanitary education work
For any country, preventing a disease is cheaper than treating it, so health education should be a government program.
A dentist is obliged to conduct sanitary and educational work with the population. 70% of the condition of the oral cavity depends on the patient himself. First of all, how and with what he brushes his teeth. Domestic pastes use highly alkaline chalk with low whiteness and a high content of highly abrasive oxides of aluminum and iron. That's why our pastes don't foam well and have a grayish color. If used constantly, they can lead to thinning of the enamel. The chalk used by Western companies does not have these disadvantages. The pastes contain antimicrobial components, plant extracts, mineral resins, and fluorine.
Russian, Bulgarian, Indian pastes are 90% hygienic.
I recommend Colgate, Blend a Honey, Signal, and Pepsodent pastes to my patients. These pastes contain chlorhesedine, which helps fight bacterial plaque, cleansing agents, and fluoride. The effectiveness of fluoridated toothpastes in the fight against caries is 30%.
I conduct conversations with patients. List of conversations:
1. Oral hygiene.
2. How to choose the right toothbrush and toothpaste.
3. Prevention of dental diseases.
I conduct explanatory work about bad habits.
Over three reporting periods, I prepared and presented abstracts at medical conferences on the following topics:
1. HIV infection in the oral cavity.
2. Technique of root canal treatment.
3. Errors and complications during canal instrumentation.
5. Sanitary and epidemiological regime in the office
The dental office in which I work meets sanitary standards (24 sq. m.). Availability of cold and hot water. The office is equipped with a bactericidal lamp, which is turned on 3 times a day for 30 minutes. Centralized air sterilizers are available. A log of their work is kept. I use disposable masks, gloves, and goggles.
Daily wet cleaning three times using 5% lysitol or 5% alominal or Septodor-Forte.
General cleaning once a month.
The rules of personal hygiene and measures to prevent self-infection of AIDS and HIV "B" are observed. If blood gets on the intact skin of the hands, the blood should be removed with a dry swab, then wiped with a 70° alcohol solution or a 0.5% alcohol solution of chlorhexidine 2 times, wash your hands with soap and treat with alcohol.
If blood gets on damaged skin, it is necessary to squeeze the blood out of the wound, lubricate it with a 5% iodine solution, wash your hands with soap and treat with a 70% alcohol solution.
All manipulations with patients are carried out wearing rubber gloves, a mask, and goggles.
If saliva gets on the mucous membranes of the eyes, they must be rinsed with a stream of water or a 1% solution boric acid and add a few drops of silver nitrate. It is recommended to treat the nasal mucosa with a 1% solution of protargol, the mouth and throat additionally (after rinsing with water) with a 70% solution of alcohol or a 1% solution of boric acid.
After removing gloves, hands are treated with 70% alcohol and soap.
Handpieces for drills, plasters, ultrasonic instruments, needleless syringes are wiped with a sterile swab moistened with 70% alcohol (twice) after each patient. At the end of the shift in 6% hydrogen peroxide for 1 hour.
The viewing mirrors are collected in a storage cup with a 6% solution of hydrogen peroxide, then washed with water, a detergent-disinfectant solution for 15 minutes, rinsed, dried with a swab and immersed in a 0.5% alcohol solution of chlorhexidine or 70% alcohol for 30 minutes. After this, “clean mirrors” are transferred into a container.
Modern aseptic solutions, such as Septador-Forte, Lysitol (5%) do not require pre-treatment with a washing solution.
Burs - after use, immerse in a container with a Septador-Forte solution for 1 hour. Afterwards, rinse with a brush and swab for 3-5 minutes. After this, the burs are subjected to pre-sterilization treatment and exposure for 15 minutes. The burs are then washed with a brush. Irrigation for 10 minutes with distilled water, sterilization-air method at a temperature of 180° and 1 hour in a Petri dish. Used burs are placed in the “Disinfection of burs” container.
All other instruments used in treatment are subject to a full cycle of treatment for prevention viral hepatitis and AIDS. Immediately after use, the instruments are rinsed in a disinfectant solution marked “Rinsing in a disinfectant solution” and immersed in a “Disinfection of instruments” container with lysitol or alominal for 1 hour. Then they are washed under running water for 3-5 minutes.
All instruments, including pulp extractors and canal fillers (newly received), are subject to disinfection with alcohol, rinsing with water, pre-sterilization treatment and sterilization.
There should be nothing unnecessary on the doctor's table. The table should be wiped with a 6% hydrogen peroxide solution or disinfectant solution.
Cotton swabs must be sterile (steam sterilization at 120 degrees for 20 minutes, changed after 6 hours).
conclusions
The reforms carried out in our country since the 90s have also affected the dental service – Market factors began to work, competition appeared, and patients were able to choose a clinic and a doctor.
At present, we can firmly say that the problem of pain-free dental treatment has been solved. Type of painkillers used
“Ultracain” relieves pain both in the treatment of caries of any location and cavity depth, and in all forms of pulpitis. Efficiency is approaching 100%.
In the competition for patients, attention should be paid to providing highly qualified dental care in the most short term, as a result of which the number of visits to the dentist is reduced to a minimum due to effective use modern technology and materials; such as carpule anesthesia, which allows you to completely remove the patient’s sensitivity to the doctor’s instrumental manipulations and dental restoration with composite materials, whose advantage is that the work is carried out in one visit and the patient does not experience discomfort associated with the presence of ground teeth. Once every six months, the patient visits the dentist to polish the surface.
When carrying out restoration work, high-class materials and equipment are used that allow the tooth cavity to be opened without vibration.
Among patients dental clinics and offices, there has recently been an increased interest in the aesthetic side of dental treatment, the desire to have fillings that are absolutely no different in color from natural teeth.
In this regard, training in methods of working with composite materials remains a serious challenge. Currently, creating the image of a highly qualified specialist is impossible without the introduction of new generations of light-curing composite materials into practical activities.
Participation in all-Russian dental forums, seminars for dentists, and medical conferences in the clinic allows us to become more familiar with achievements in dentistry, and also gives us the opportunity to master modern methods of treating dental diseases.
In three reporting years 2002 – 2004 at a therapeutic appointment.
| Work days | 165 | 134 | 187 |
Accepted patients |
1894 | 1425 | 1526 |
| Accepted primary patients | |||
| Teeth filled (total) | 1930 | 1465 | 1767 |
| Teeth filled due to caries | 1540 | 1167 | 1315 |
| Complicated forms of caries | 390 | 298 | 452 |
Treatment of complicated teeth in one visit |
283 | 223 | 290 |
| Total sanitized | 228 | 133 | 150 |
| Produced by UET | 8101,95 | 6900,25 | 10446,45 |
| UET for 1 visit. | 4,3 | 4,8 | 6,8 |
| UET for 1 sanitation | 35,5 | 51,8 | 69,6 |
QUALITATIVE INDICATORS
CONCLUSIONS
1. There was a decrease in the number of working days in 2003, as major renovations were carried out at the clinic. This was also affected by the increase in the number of vacation days in connection with the provision of 12 additional days for working with hazardous materials.
2. In 2003, there was a decrease in the number of patients admitted per day due to the reconstruction of the clinic and the re-equipment of offices with modern dental units. In their work they began
more use of modern light-polymer materials, which require more time for this work.
3. The number of fillings supplied per day has decreased due to preventive and restoration work using modern light-polymer materials, which require more time to work with.
4. Treatment for caries decreased by 14.6% as treatment of teeth with complicated forms of caries increased by 15.8% for previously treated teeth using amputation methods and re-treated root canals.
5. The rate of treatment of teeth with complicated forms of caries has increased due to the use of modern endodontic instruments and filling materials for root canals.
6. The use of modern anesthetics and endodontic instruments has allowed the wider use of the one-session method of treatment of complicated forms of caries compared to 2003 by 10.5% in 2004. We treat more than 64% of complicated forms of caries in 1 visit.
7. Patients are admitted mainly on a case-by-case basis. This may explain the decrease in the number of sanitized patients.
8. To increase the number of UET per day in 2004. the transition of work under order No. 277 and the treatment of complicated forms of caries in 1 visit affected.
9. Thanks to the use of modern filling materials, endodontic instruments, depophoresis, which require repeated visits to a dentist, the UET has increased by 1 sanitation. This was also affected by the work under order No. 277.
In 2004 The number of teeth treated with a conservative method for chronic granulomatous periodontitis has increased, thanks to the use of modern filling materials for root canals, which contain calcium-containing preparations.
If in 2002 11 teeth with DS were successfully treated using a conservative method: chronic granulomatous periodontitis, then already in 2004. 19 teeth. When treating these teeth, the depophoresis method was also used. The use of depophoresis and calcium-containing drugs can successfully cope with periapical infection and destruction of bone tissue. Repeated R-images after 6 months show a decrease in bone destruction. Of the 19 teeth, after 12 months, 14 showed restoration of the structure of the bone beams, and after 24 months full recovery bone structure in all treated teeth with DS: chronic granulomatous periodontitis.
Report
about the work done
during the period1999 -200 0 G.
dental nursedepartments
Due to the high prevalence of dental diseases, dental care in our country is one of the most widespread forms of medical care. More than 80% of all patients with dental pathology occur in outpatient services. An even larger proportion of dental patients (98.5%, i.e. the vast majority) are indicated for treatment in a clinic setting. This is explained by the high incidence of dental caries and its complications. Every year, conservative methods of treating both therapeutic and surgical diseases occupy more and more space. The number of goiters removed is reduced and the number of cured ones increases. If in the recent past the ratio of extracted teeth to cured teeth was 1:1, now it is 1:10. This has been achieved thanks to the therapeutic and practical success of dental science.
New diagnostic and treatment methods are introduced into dental practice every year, which make it possible to diagnose, treat patients and carry out rehabilitation.
According to order No. 8 of March 26, 2001. Federal State Institution "Central clinical Hospital Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation" reorganization in the form of a merger into the State Institution "State medical Center Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation" and is a medical and preventive institution, being a structural subdivision of the center.
It includes a hospital and a clinic where patients receive emergency and routine medical care.
The dental service is represented by a network of clinics with dental offices; in addition, dental offices have salaries and ports.
The dental department provides assistance to the assigned contingent of departmental organizations that have entered into contracts for medical care with Clinical Hospital No. 1, and patients are admitted for cash payment. The dental department of clinic No. 1 is represented by two services:
1. Dental department, which consists of four therapeutic rooms, a surgical room, and a periodontology room.
2. Department of orthopedic dentistry, consisting of two rooms for an orthopedic doctor and a dental laboratory.
For these two departments there is a registry with a file cabinet for dental patients.
Here, pre-registration is made by telephone and the information necessary for patients is given; assistance is provided to patients at home, as well as to those who are being treated in a hospital.
A nurse provides preparation for departure and assistance to the doctor.
The dental department has undergone a complete technical re-equipment and renovation of offices. The offices are equipped with Eurostar dental units (made in Italy), medical furniture for dental offices, and also have all the necessary equipment and tools for work.
To improve the quality of diagnostics, modern electronic equipment is used, for example, a tip with an apex locator “Marita” (Japan) and a device for determining pulp viability “Didi test” (USA). An X-ray room is equipped with a Trophy Elitys radiovisiograph (France) with computer wiring to all work rooms.
Each office has:
1. Glasperlin sterilization (Italy) for immediate sterilization of the necessary instruments.
2. “Piezo-Master” devices (Switzerland) for removing dental plaque with different attachments, as well as for treating root canals.
3. Ultraviolet boxes “TAU-steril” (Italy) for storing sterile instruments.
4. Halogen lamps (USA, Germany) for placing fillings made of light-curing materials.
5. Germicidal lamps have been installed.
6. Monitors installed for viewing R-images
7. Medical dental furniture “Lotus” (Italy), which includes a workplace for a nurse and a doctor.
8. Built-in air conditioners.
Nurses are the closest assistants to the dentist and make a huge contribution to the prevention and treatment of dental diseases. At each nursing station, hermetically sealed plastic containers are installed for pre-sterilized cleaning and disinfection of instruments and separate containers for burs.
Pre-sterilization cleaning and disinfection are carried out simultaneously using a 5% Alaminole solution; exposure time is 1 hour.
Alaminol is a blue, odorless liquid. It is effective against bacteria, fungi of the genus Candida dermatitis, viruses (including pathogens HIV, ARVI, HB, herpes, rotaviruses).
Possesses cleaning properties. The “Alaminol” product is intended for disinfection of indoor surfaces, furnishings, devices, and equipment. For this purpose, a 1% solution of alaminol is used, exposure time is 60 minutes. Ultrasonic devices “Serga” and “Transonic” are also used for mechanical and pre-sterilization cleaning of instruments.
Cleaning is carried out in a working solution according to the following scheme:
1. Preparation “Biolot” - 3.0 g.
2.Chlorhexidine bigluconate – 2.5 mg (standard solution)
3.Ethyl alcohol – 2.5 mg
4.Distilled water up to 1000 mg.
The instructions were compiled by the Central Research Institute of Dentistry.
Thermal time indicators are used to control the quality of sterilization. Diapers, gauze wipes, waterrolls are sterilized in autoclaves. All material is pre-packed in craft bags.
In the dental department, sterilization of instruments is carried out in a separate, specially designated room.
After soaking and processing, surgical instruments are packaged in special bags and sterilized in a dry-heat oven. The advantage of these bags is that they remain sterile for two weeks.
For prevention nosocomial infections Of great importance is strict adherence to the sanitary and epidemiological regime in the department, as well as compliance with asepsis and antiseptics.
Monitoring the implementation of these rules is carried out by the senior nurse.
In order to prevent infection, medical personnel use disposable gloves, masks, and protective goggles. If necessary, protective helmets and aprons. For rinsing the mouth, aromatized, deodorizing tablets are used. Disposable bibs, glasses, and syringes are used for the patient.
Job responsibilities of a dental assistant include:
1. Preparing the workplace for a doctor’s appointment.
2. Preparation of the necessary instruments and medications for anesthesia, applications, and preparation of filling material.
3. Call the patient.
4. Seat and ensure a comfortable position for the patient in the chair, both for him and for the doctor.
5. Invite the dentist to the patient as soon as he is ready.
6. Adjust the dental light.
7. Presenting the instruments to the doctor.
8. Provide prevention infectious infection patient and staff.
9. Work with a saliva ejector and a vacuum cleaner.
10. Carry out hygiene measures independently, determine indices and, together with a doctor, evaluate the effectiveness of the preventive measures taken.
11. Together with the administrator, schedule the patient for a follow-up visit.
So, the efficiency of a dentist working with a nurse is 50% higher than that of a dentist working without a nurse.
For local anesthesia carpule aspiration syringes and sterile disposable needles are used.
Anesthetics such as “Ultracaine, ubestezin” are used. Syringes are disinfected during operation by wiping them twice with an alcohol-based sterile gauze swab before and after the procedure.
At the end of the shift they are sterilized in a dry-heat oven at a temperature of 180 0 - 60 minutes.
Immediately after use, dental mirrors are soaked in a 5% Alaminol solution for 60 minutes, then rinsed under running water, dried with a sterile cloth and stored in a sterile U.F. tray. boxing
Immediately before admission, the patient is sterilized for 60 seconds in an eyepearlin sterilizer.
Used disposable syringes, gloves, saliva ejectors are disinfected in a 3% chloramine solution, then collected in bags and disposed of centrally.
The needles, also pre-disinfected, are collected in a special container and disposed of.
Cotton and gauze swabs are disinfected in a 3% solution of chloramines for 120 minutes, after which they are disposed of.
Disinfection is carried out in closed containers in special rooms.
The premises are cleaned twice a day using a 1% chloramine solution with 0.5 SMS, followed by ventilation and UV irradiation for 30 minutes.
General cleaning of therapy rooms is carried out once a month using a 3% chloramine solution.
Walls, furniture and equipment are treated with a 1% Alaminol solution; exposure time is 60 minutes - single ventilation.
After spring cleaning The room is illuminated with UV light for 2 hours.
General cleaning of the surgical room is carried out using the same products once a week.
As a result of the operation of bactericidal lamps, the air in the room is ionized, nitrogen oxides and ozone are formed.
All work in this direction is carried out on the basis of the methodological letter “On the organization of sanitary-hygienic and disinfection-sterilization regimes in dental institutions” - developed by the State Committee for Sanitary Inspection of R.F.
All rooms are equipped with eye-perlin sterilizers, which provide immediate sterilization.
It is a container (up to one liter) filled with ceramic balls, which are heated to t-240 0.
The working surface of the tool is placed in this environment:
Mirror – 60 seconds
Burs and endontic instruments – 20 seconds
Tweezers, probes, scalpels – 15 seconds
Main advantage this method sterilization is:
1. Short time for sterilization of instruments
2. Small dimensions and constant readiness of the device for work
3. Possibility of sterilization in the presence of the patient
Dental handpieces are disinfected by wiping the outer surfaces and the bur channel twice (before and after use) with a sterile gauze swab moistened with 70% ethyl alcohol.
After use, small endodontic instruments and burs are placed to remove organic particles in a solution consisting of equal parts of 10% ammonia and 3% hydrogen peroxide solution.
Then it is subjected to disinfection and pre-cleaning.
In a 5% Alaminol solution for 30 minutes.
Instruments with plastic holders are sterilized in an eye-perlin sterilizer for 20 seconds.
Quality control before sterilization cleaning is carried out by a senior nurse at least once a week using an azopyram test.
The quality of cleaning from SMS and from medicinal devices is checked using a phenolphthalein test.
Each office is equipped with a first aid kit for the prevention of HIV infections.
1. If contaminated or suspicious material comes into contact with the skin, treat it with a 70% solution ethyl alcohol, wash with soap and water and re-disinfect with a 70% ethyl alcohol solution.
2. If infected material gets on the mucous membranes, immediately treat them with a 0.05% solution of KMnO, rinse the mouth and throat with a 70% solution of ethyl alcohol. Don't rub.
3. In case of injections or cuts, immediately squeeze the blood out of the wound and treat the wound with a 5% iodine solution.
The staffing schedule of the dental department provides
Head of department – 1 position
Doctor-dentist – 9.25 rates
Surgeon-dentist – 1 rate
Periodontist – 1 rate
Senior med. sister – 1 bet
Honey. sisters – 10 bets
Nurse – 4.75 rates
All bets are off.
Reporting data for 2001
Total patients admitted – 30,226
Primary patients – 13,940
Teeth filled – 28253
Regarding caries – 21,260
Regarding complicated caries – 6,900
Teeth treated in one visit for a complicated problem
caries – 2,816
A course of treatment for periodontal disease was completed – 1,106
A course of treatment was carried out for diseases of the oral mucosa - 405
Teeth removed – 2240
Preventative work:
Inspection in accordance with planned sanitation - 7,522
Of those examined, 1852 were in need of rehabilitation
Sanitized from among those identified during planned sanitization - 1822
Standard units of labor intensity produced – 75,350
The Department of Orthopedic Dentistry has on its staff:
Orthopedic dentist – 4 rates; not busy – 2
Orthodontist – 1; not busy – 1
Dental technicians – 8; not busy – 4
Foundry worker – 1; ---------
Nurse – 6; not busy – 3
Nurse – 2; not occupied – 1.5
Medical registrar – 1; --------
Reception in the orthopedic department is carried out in two shifts, by two orthopedic doctors.
The dental laboratory is equipped with the latest electronic equipment from leading Western companies.
For the manufacture of dentures, materials of 3-4 generations are used.
The following types of services are provided to the population:
1. Manufacturing of metal-ceramic crowns.
2. Solid dentures.
3. Removable dentures.
4. Clasp dentures with locking fastening.
5. Manufacturing of plastic crowns.
Dental nurses have the knowledge and skills necessary to work with doctors in all offices of the department. If necessary, they can replace each other at the workplace (surgery, periodontology). During work, they perform the role of a doctor’s assistant, maintain all the necessary documentation, and, in addition, conduct therapeutic and preventive conversations with patients. They explain how to properly care for your mouth, what pastes to use, rinses, etc. Five nurses have qualification category I, almost all have a specialist certificate.
There is an atmosphere of friendly support and mutual assistance among the employees.
Certification work of a dentist
therapist of the highest category
Clinic …………… (name)
…………………(FULL NAME)
for 2004-2006
Moscow, 2007
I. Brief CV 3
II. Brief description of the work of the dental office 4
III. Analysis of work for 3 years (2004-2006) 14
IV. Introduction into practice of elements of scientific organization of labor, new forms of therapy, testing of new medical equipment 23
V. Work with medical personnel of department 34
VI. Sanitary education work 35
VII. List of published works (2004-2006) 36
I. Brief CV
I, …. (full name), born on …… (date) in ………. (place of birth), in the family……….. (origin).
…. (information about studies)
…. (job information)
…. (information about advanced training, courses and cycles)
…. (information about academic degrees)
…. (information about professional achievements)
…. (information about publications and printed works).
II. Brief description of the work of the dental office
There are certain standards and requirements for the organization of a dental office, determined, on the one hand, by the equipment used, and on the other, by the volume of work and the use of potentially hazardous materials, which, if used incorrectly, can have an adverse effect on the health of medical personnel: we are talking about amalgam , which contains mercury.
According to the current situation, a dental office per doctor must occupy an area of at least 14 m2. If several chairs are installed in the office, then its area is calculated based on the additional standard - 7 m2 for each chair. If the additional chair has a universal dental unit, its area increases to 10 m2.
The height of the cabinet should be at least 3 m, and the depth with one-sided natural lighting should not exceed 6 m.
In connection with the use of amalgam for filling teeth Special attention paid to the finishing of the floors, walls and ceiling of the office. The walls of the dental office should be smooth, without cracks. Corners and junctions of walls, floors and ceilings should be rounded, without cornices or decorations. Walls and ceilings are plastered or rubbed with the addition of 5% sulfur powder to the solution to bind sorbed mercury vapor into a durable compound (mercury sulfide) that is not subject to desorption, and then painted with silicate or oil paints. The floor of the office is first covered with thick cardboard, and rolled linoleum is laid on top, which should extend onto the walls to a height of 10 cm. The junction of the linoleum sheets, as well as the places where the pipes exit, must be puttied and covered with nitro paint. These measures are necessary to ensure effective sanitation and cleaning without the possibility of mercury accumulation.
The walls and floor in the dental office must be painted in light colors with a reflectance coefficient of at least 40. It is advisable to use a neutral light gray color that does not interfere with the correct color discrimination of the mucous membranes, skin, blood, teeth and filling materials. Doors and windows in the office are painted white with enamels or oil paint. Door and window fittings should be smooth and easy to clean -
The dental office should have natural light. It is advisable to orient the windows of the office to the northern directions in order to avoid significant differences brightness in workplaces due to direct exposure sun rays with other types of orientation, as well as overheating of premises in the summer. In offices that have incorrect orientations, in the summer it is recommended to resort to shading of windows using curtains, blinds, awnings and other devices.
The light coefficient (the ratio of the glazed surface of windows to the floor area) should be 1:4 - 1:5. The office must have general artificial lighting provided by fluorescent or incandescent lamps. For general fluorescent lighting, it is recommended to use lamps with an emission spectrum that does not distort color rendering, for example, fluorescent lamps with corrected color rendering or fluorescent lamps of cool natural color. The illumination level of the office when using fluorescent lamps should be 500 lux.
General lighting lamps are placed so that they do not fall into the field of view of the working doctor.
Dental offices, in addition to general lighting, must also have local lighting in the form of a reflector on dental units. The illumination created by the local source should not exceed the level of general illumination by more than 10 times, so as not to cause light readaptation that is tiring for the doctor’s vision when moving his gaze from differently illuminated surfaces.
A prerequisite for working with amalgam is the presence of a fume hood in the office in which it is prepared. In such a cabinet, autonomous mechanical draft must ensure an air movement speed of at least 0.7 m/s and air must be removed from all zones of the cabinet. A plumbing sink with a mercury trap should be installed in the cabinet. Inside the cabinet there is a cabinet for storing a daily supply of amalgam and utensils for preparing amalgam, as well as demercurization agents. The amalgam mixer, which eliminates manual operations when preparing silver amalgam, should be kept in a fume hood at all times.
The dental office must be provided with supply and exhaust ventilation with an air exchange rate of 3 times per hour for exhaust and 2 times per hour for inflow, and also have vents and transoms.
The doctor's office must have a quartz lamp (table or portable), which is used to quartz the air in the office. This procedure is usually performed during a break between shifts or after the end of the working day.
The dental office must have workplaces for a doctor, a nurse and an orderly. Workplace The doctor's room includes a dental unit, a chair, a table for medicines and materials, and a screw chair. The nurse's workplace should include a table for sorting instruments, a dry-air cabinet, a syringe sterilizer, a sterile table and a screw chair. For a nurse to work, there must be a table for sorting used instruments and a sink for washing instruments. In addition, the office should have a cabinet for storing materials and tools, a cabinet for poisonous and a cabinet for potent medicinal substances and a desk.
Currently, there is a tendency towards more complex dental equipment. A modern dental unit is a complex set of pneumatic, electrical, hydraulic and electronic components. The installation includes an automatic control chair, a reflector lamp, a compressor and a device for carrying out the necessary manipulations in the oral cavity: preparation of hard tissues, removal of dental plaque, removal of saliva and dust. The preparation of tooth tissue is carried out with instruments that rotate with at different speeds. The modular block of the dental unit has 2-3 hoses for the micromotor and turbine tips. The kit may contain an ultrasonic unit for removing dental plaque, and there should be a gun for supplying water and air. Micromotors allow you to rotate the bur from 2000 to 12,000-15,000 rpm, and turbine tips rotate the bur at a speed of 300,000-450,000 rpm. Some dental units are equipped with light curing lamps. Modern dental...
**************************************************************
St. Petersburg, 2004
- Introduction
- About the author
- Characteristics of the place of work
- Certification material for the last 3 years
- caries
- complicated caries
- preparation for prosthetics
- non-carious lesions of teeth
- aesthetic dental restoration
- Training
- Conclusion
I. Introduction
About the author
I, Full Name, born 19.., graduated in 19.. from the 1st Leningrad Medical Institute named after. Academician I.P. Pavlov, Faculty of Dentistry, specializing in dentistry.
From 19.. to the present time I have been working as a dentist in the 1st therapeutic department in dental clinic No. ... of the administrative district of St. Petersburg.
Characteristics of the place of work
In the treatment room there are 6 doctor’s chairs with stationary dental units “Hiradent 654” and “Hiradent 691”. The office is equipped necessary tools and equipment for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases (DSK-2, EOM-3 devices, etc.)
Instruments are sterilized centrally in the sterilization room. The Terminator device is used to process the tips. Burs and instruments are processed and sterilized by a nurse. For endodontic instruments there is a glassperlene sterilizer. Small tools are stored in the Ultraviol shelf.
There is a UV-KB-Ya-FP bactericidal chamber for storing sterile medical instruments. To work with light-curing composites, I use lamps - dental polymerizer ESTUS-Profi, Cromalux, etc.
II. Certification material for the last 3 years
My main tasks are the treatment and prevention of dental diseases among the adult population of the region. I usually accept patients on compulsory medical insurance. The work shift lasts from 5.5 to 6.5 hours. During a shift, I provide assistance to an average of 11-12 patients, of which 4-5 are primary. During a working day, I fill on average 13 teeth, 2-3 of them with complicated forms of caries. There are 1-2 sanitizations per day. From time to time I work in the duty room of the clinic, where I provide emergency dental care to the population.
During the reporting period of work (2001-2003), I examined a total of 7638 patients, of which 2702 were primary, 849 patients were sanitized, which is an average of 33.1% of the number of primary patients. During the reporting period, 8704 teeth were cured, of which 6861 were caries, 1843 were complicated forms. 27280 UET were produced.
I begin working with the patient by collecting anamnesis, then I conduct an external examination and examination of the oral cavity, during which I determine the hygiene index, identify bite pathologies, assess the condition of the oral mucosa, and always palpate the submandibular lymph nodes. Based on the data received, I make a diagnosis and draw up a treatment plan.
| Page 1 |