The lips are one of the body systems that is formed long before the birth of a child. The primordia of milk appear at 7-13 weeks of pregnancy, and permanent ones at 20 weeks, and continue to develop after the birth of the baby. The first teeth erupt at 3-7 months, but earlier and later teething occurs. It happens that children are born with teeth, and in some babies they appear only after 1.5 years. This is not always an indicator of deviation from the norm. By the age of 3, a child already has 20 milk teeth, and from 6 to 13 years they are replaced by permanent teeth.
Peculiarities
The function of the first teeth is to grind the first solid food in the child’s diet, and serve as a “guide” for the eruption of molars. The correct formation of a permanent bite depends on their growth and development.
Types
Baby teeth form a temporary bite. They come in several types: incisors, canines and premolars. Each of them performs its own function. The incisors grasp and cut food. The fangs help tear food into smaller pieces. Molars grind crushed pieces of food.
Advice Usually baby teeth fall out on their own, but sometimes they are removed:
- if they erupt too early and interfere with breastfeeding
- if caries appears
- for jaw injuries
- for deep inflammations
It is necessary to monitor the eruption of the molar after the removal of the milk, since new tooth may grow crooked.
Problems with the growth of baby teeth in a child. Deviations in terms
M Primary teeth appear simultaneously and symmetrically. There is a certain order in which a baby's teeth erupt. If some of them grow ahead of time, while others are delayed, then the bite may subsequently be disrupted.Deviations in the timing of the appearance of baby teeth may be due to:
- heredity
- lack of nutrients, calcium, vitamin D, which causes rickets to develop and teeth not to grow
- endocrine disorders
- infections suffered by the baby
- weak immunity
- violations intrauterine development
Toxicosis or illness of the mother, and also not proper nutrition, taking strong medications or bad habits during pregnancy, they subsequently become the reason why children’s teeth do not grow.
Adentia is a disease in which the rudiments of teeth, all or some of them, are not formed in the gums, which is why children do not grow teeth, or grow, but not all.
To diagnose this pathology, the dentist prescribes a panoramic x-ray of the child’s jaw.
Advice The child’s diet should include a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals so that the baby’s first teeth appear on time and grow well. They need proper care, since the enamel of baby teeth is thinner than that of molars.
IN At the age of 5-7 years, a child’s baby teeth begin to fall out, and molars appear in their place. In general, new ones quickly replace the fallen ones, but it happens that this period drags on for several months.Main reasons Why children don’t grow new ones instead of those that fall out is:
- rickets suffered by a baby
- mechanical damage to the jaw, causing the rudiments to become stuck in the periosteum and they do not grow
- advanced caries, in which the molar tooth germ is damaged
- treatment and removal of baby teeth
- infectious diseases
One of the factors that causes delays or cessation of tooth growth in children is lifestyle changes. modern man and the general environmental situation. Posterior molars, the so-called “wisdom teeth,” have already become an atavism; many people simply do not have them. Eating carbohydrate-rich, sweet or overly ground foods is not only harmful to the enamel, but also becomes an explanation for why permanent teeth in children increasingly do not grow in time.

The child’s molars do not want to grow. Revealing the secret
H molars are most often called molars - back, chewing teeth, which had no analogues in the dairy range, and which appear first in the child after a long “lull” in growth. This usually occurs in children aged 6 years, but can occur earlier or later.The developmental characteristics of each baby are the answer to the question of why molars do not grow in due time.
Many parents call molars all the teeth that appear in the baby instead of the fallen milk ones, and form a permanent bite.
By the age of 13, children are fully formed permanent tooth new row, except for the last molars, which may appear much later.
Each change of teeth takes from a month to 2 years, this is why new ones may not seem to grow. If replacement does not occur before 8 years, then it is necessary full examination child to find out why the molars do not grow.
Child's front teeth, delayed eruption
P The front teeth, which include the incisors and canines, are the first to appear in the baby. However, it happens that the order of eruption is violated. If teeth do not grow for a long time, then an orthodontist will help you find out why.The change of teeth in children occurs according to the same pattern in which baby teeth grew, symmetrically and mirror-image: 4 central incisors, 4 lateral, 4 premolars and a little later four more. The last ones are replaced by fangs, after which the teeth no longer fall out.
Planting too deep baby tooth in the baby it causes a delay in its loss, creating an obstacle for the molars, which is why they long time don't grow.
Rarely, there are cases when children do not fall out their milk teeth due to the lack of permanent rudiments, then they remain milk teeth forever.
If a child’s baby tooth falls out too early or is removed, there may be a delay in eruption, which is why the indigenous ones do not grow for a long time. This often happens with the front teeth due to their easier injury. Surgery may be needed.
Conclusion
N One should not take lightly the peculiarities of tooth growth in a child, since not only the shape of the teeth themselves depends on the correctness of this process. The bite affects the shape of the jaw and face in general, speech, the quality of chewing food and even digestion.There are fewer baby teeth than molars: only 20 compared to 32. The fact is that in the first years of life, young children do not need as many of them as adults, because early age they feed mainly on soft food.
Further, as the child grows, his skeleton also grows, along with his jaws. At the same time, the teeth remain the same size and can no longer fully perform their functions. They are gradually being replaced by new molars - larger, stronger and adapted to chewing solid food.
The approach of these changes is noticeable even visually: over time, the interdental spaces become larger and larger, because the jaw is actively growing, but the teeth that have served their purpose are not.
Before they fall out, the roots of baby teeth dissolve; by the age of five they begin to become loose.
Age and timing of tooth loss
On average, teeth change begins at 6–7 years of age.
As for the order, it is the same for almost all children: first the central incisors change, then the lateral incisors (7–8 years), followed by the first molars (9–11 years), lower canines (9–12 years), and also the upper canines (10–12 years) and second molars (11–13 years). Thus, the entire process can take on average 5–6 years.

The structure of the skull in children
Answers to frequently asked questions
What time do baby teeth start falling out?
For most children, at 6–7 years old. However, in some children the process can start at 5 years old. Such slight deviations are allowed unless the fall out too early is the result of some kind of injury. But if teeth change has not begun by the age of eight, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
Which baby teeth fall out?
All twenty baby teeth must be replaced.
Why don't my child's baby teeth change?
There may be several reasons:
- past infections;
- disorders due to rickets, phenylketonuria and other diseases affecting metabolism;
- dyspepsia – disturbance of the stomach;
- absence of a molar tooth germ;
- heredity.

Why does a baby tooth become loose but not fall out?
The most common reason– excess calcium in the body.
What to do if the tooth is growing, but the baby tooth has not yet fallen out?
Contact your dentist and have the tooth removed. If this is not done in a timely manner, the molar will grow crookedly.
What to do if a baby tooth falls out, but the molar does not grow?
If the molar does not appear within a year after the loss of milk, the reason most likely lies in edentulous– a pathology in which the rudiments of molars are absent.
In other cases, the delay is usually caused by individual characteristics. The problem is that baby teeth set the vector for molars, indicating their place in the dentition. And if milk fell out too early, the molar may erupt crookedly. To prevent such a situation, it is recommended to consult a dentist in time.
How long does it take for teeth to grow after baby teeth fall out?
The central incisors replace each other very quickly - in a maximum of two months. But premolars and canines can take a long time to erupt – from four to six months. The entire transition process must be completed by age 14. The only exception is wisdom teeth - they erupt at the age of 18-25.
What to do when a tooth falls out
The socket in which the tooth was located may bleed. This is not scary and normally goes away quickly. Parents can make a small swab from a sterile napkin or bandage and let the baby bite on it for a few minutes. If bleeding does not go away after five minutes and only gets worse, you should consult a doctor.
In order not to irritate the socket for two hours after the tooth falls out, it is better not to give the child food or drinks. It is also recommended to exclude spicy, salty and bitter foods from your diet.
If you are concerned about the process of changing teeth in your child, contact one of the clinics that accept qualified pediatric dentists. Perhaps if you have problems, they will recommend you
Many parents ask what to do if a child’s baby tooth falls out and a new one does not grow. There comes a time when the life of baby teeth ends. Starting from 4 months, they served the baby, but now he has grown up, in the future he will need stronger permanent ones.
Why, after the loss of a baby tooth, the child did not grow a permanent one?
Since baby teeth grow in a certain order, their replacement occurs gradually. Moreover, the order in which new ones appear is slightly different from the order in which they erupted. After a baby tooth falls out, very little time passes, after which a small piece of a permanent one should grow in its place, which very quickly completely takes its place.
But sometimes a situation arises when baby teeth fall out and new ones do not grow. One week passes, two, three. The molar does not grow in its designated place. Parents begin to worry that the child’s front teeth are not growing.
Why didn't permanent teeth grow? First of all, it is worth noting that this state of affairs is not always a pathology. For example, molars take a little longer to replace baby teeth. In some cases, this process may take 1 or 2 months. Molars do not grow immediately after baby teeth fall out various reasons. In rare cases, milk teeth can also be found in adults, and doctors immediately detect this, since the milk teeth are very different in shape from the permanent ones.
Most often, the reason that a permanent tooth does not appear at all after the loss of a primary tooth is the absence of rudiments permanent teeth. In order to discover this pathology, just take a regular photo. Children, due to the fact that their jaw and dentition are just forming, are given braces, thus eliminating the deficiency.
Dental implantation is carried out in adulthood (approximately 18 years), when bone formation is already completed. If there are no rudiments of molars, then this cannot be corrected in any other way than prosthetics, since they are formed during intrauterine development and it is almost impossible to influence this process. The only teeth whose formation and formation occurs almost in adulthood are the eighth teeth. Usually their rudiments appear at the age of 14 years.
You should consult a doctor with the problem of missing permanent teeth if:
- More than 3 months have already passed since the baby tooth fell out, but the permanent one has not appeared;
- The gums in this area become red and swollen.
Sometimes the gums may turn black in this area, which means that the tooth cannot erupt and blood has accumulated in the gums. Usually this issue is very easily resolved; the surgeon opens the gum and allows the blood to drain out. Soon the tooth itself appears, which could not cut through the gum.
Parents should be especially concerned about the situation when baby teeth fall out one by one at the right time, but not a single permanent tooth appears in their place.
There are several reasons for such deviations; first of all, doctors talk about rickets suffered in childhood. Another reason that permanent teeth did not erupt on time is past infectious diseases that can affect the proper development of tooth germs. Serious injuries to the jaw may disrupt the order in which permanent teeth appear.
Sometimes incorrect treatment may cause the baby tooth to for a long time does not fall out, and a permanent one does not appear in its place. Since calcium is necessary for the formation of dental tissues, its lack in the body leads to problems with teething, so what foods end up on the child’s table is important.
In severe cases, milk caries can develop into permanent caries. As a result, it will not germinate for a long time or will appear with a defect. Such teeth very often grow incorrectly, disrupting the dentition, and the rest are forced to adapt to them.
Mechanical trauma to the jaw can lead to the fact that the position of the rudiment changes and it “drives” into the gum and periosteum. If the operation to eliminate this pathology occurs on time, then it grows at the right time and in the right place. The operation must be performed immediately after injury or as soon as possible.
Among other reasons not directly related to the child’s health, doctors name:
- environmental degradation;
- eating foods that are harmful to the health and development of the body;
- frequent stress.
Interestingly, eating certain types of food can also affect teething. If you organize a “greenhouse life” for your child’s jaws, that is, offer him food only in the form of pates and purees, then the teething process can slow down significantly. The reason for this is the low load on the jaws; permanent teeth seem to be unclaimed and do not erupt immediately. Therefore, the child should receive mandatory food both soft and hard.

The doctor’s actions after the patient addresses this problem are to establish the reason why the permanent incisors did not appear within the time limit set by him. For this purpose, an X-ray of the jaw is prescribed and directions for tests are given. If the child is dentally healthy, and the cause of the delay is infectious diseases, then the main treatment is to strengthen the immune system. After everything returns to normal, the body itself will cope with the problem. And milk teeth, although with a delay, will be replaced by permanent ones.
On average, recovery time takes 6 months. Parents need to reassure their child and be patient, as stress can become additional reason delayed dental growth. If the baby's baby teeth have fallen out, but the molars have not grown in, or there is no permanent canine for a long time, then the parents need to take the child to the doctor.
An x-ray immediately reveals tooth germs or their absence. After studying it, the doctor can give an approximate time for the appearance of permanent ones. In some cases, a timely examination can give a chance to quickly resolve the problem. Therefore, if the doctor says that an X-ray is necessary, it cannot be refused, no matter how serious the reasons may be, according to the parents.
Parents should also help their child. First of all, ensure proper nutrition in full accordance with his age and body needs. It’s not bad if they turn to a pediatrician for help and ask them to prescribe a good vitamin complex. In addition to vitamins, it should also contain minerals, then the effect of the course will be significant, and many problems associated with the growth and formation of organs and tissues may disappear.
zubi.pro
A baby tooth has fallen out, but a new one is not growing.
You've probably already heard that there are people whose so-called “wisdom teeth” do not grow? But it turns out that the same phenomenon can also be observed in preschool and younger children. school age. Most often, the upper lateral incisors (“twos”) and the lower second premolars (“fives”) do not want to show. And parents usually do not pay attention to this problem, because it does not create any discomfort for the child.
Read also: What fillings should be given to a child?
Pattern of growth of baby teeth in a child
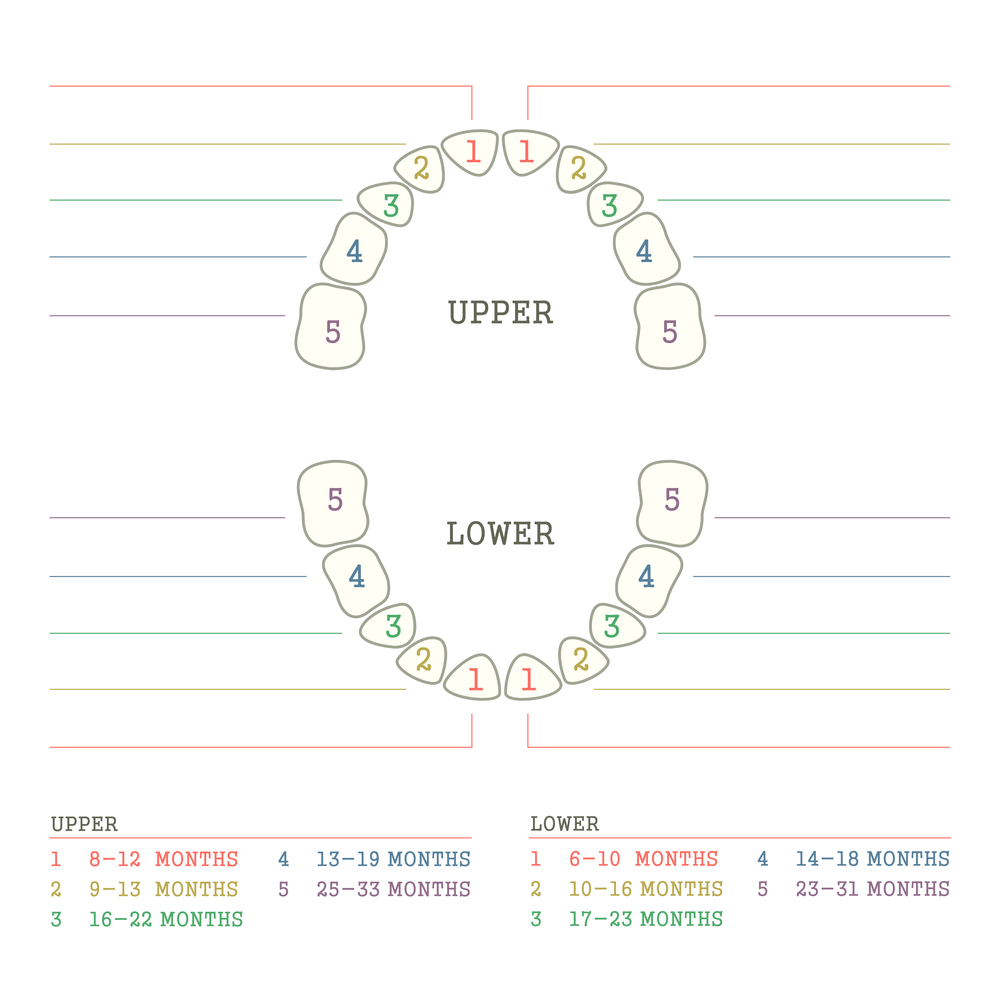 Experts say that the cause of this problem is the absence of a permanent tooth germ. And, unfortunately, this problem is not that big of a deal. a rare event. Why is this happening? There is still no clear answer to this question. Most likely, some kind of failure occurred during the formation of teeth. Some say it's due to genetics or evolution.
Experts say that the cause of this problem is the absence of a permanent tooth germ. And, unfortunately, this problem is not that big of a deal. a rare event. Why is this happening? There is still no clear answer to this question. Most likely, some kind of failure occurred during the formation of teeth. Some say it's due to genetics or evolution.
Why can't the problem be ignored?
If parents do not pay attention to this problem in their child in time, this is fraught with displacement of the dentition and malocclusion, since adjacent teeth will begin to shift towards the empty space.
Read also: Caries in children: modern methods treatment of baby teeth
What to do if the tooth has no germ?
It is possible to detect that there is no germ at the site of the fallen tooth using an X-ray image taken by an orthodontist. Only after this the specialist selects a form of correcting the problem that is suitable for the small patient. Tactics most often depend on the child’s bite. For example, a doctor may recommend putting braces in place of missing teeth (at 11-12 years old), and then in adulthood, implantation of missing teeth (at 18-21 years old).
Read also: The whole truth about braces: what is important for parents to know
It is important to know! Unfortunately, the rudiments of permanent teeth are formed in the prenatal period. And if the child does not have them, then they will not appear later; there is no point in hoping that teeth will grow over time for this very reason. Exception in in this case constitute only “wisdom teeth”, which are formed before the age of 14 years.
tvoymalysh.com.ua
Growth of baby teeth
Most children begin to erupt their first baby teeth at 5-7 months. In rare cases, this process is delayed up to 8-9 months. The slow growth of teeth is primarily influenced by the nutrition of both the baby and his mother. With a lack of vitamins and nutrients in food and the body there is a significant slowdown in the appearance of the first incisors.
Experts note that slow teething can be caused by genetic characteristics and can be inherited. In any case, there is no need to panic ahead of time. A cause for concern is the complete absence of baby teeth at 10 months. The child should definitely be shown to a specialist.
Try to evaluate objectively general state baby. The fact is that many infectious diseases can negatively affect tooth growth. If a child is often sick, then most likely his teeth will grow more slowly than those of his peers. If the mother suffered from some illnesses during pregnancy, this also affects the health of the child after birth.
Problems when changing teeth
The process of replacing baby teeth with permanent ones can be very lengthy. The first permanent teeth appear in children, as a rule, closer to 6 years. They change gradually. Some teeth are in no hurry to appear for quite a long time.
There may be several reasons for this condition. Firstly, poor nutrition. Secondly, weakened immunity. Thirdly, heredity or the presence of deviations. If a child’s teeth do not grow within 6 months after the baby teeth fall out, then you should definitely consult a doctor.
The fact is that there are gum diseases in which the baby tooth falls out, but the molar does not appear in its place. Only a doctor can correct such a defect and prescribe a course of treatment. The diagnosis is made only on the basis of an x-ray image.
How to speed up teeth growth
You can help your teeth grow strong and healthy with calcium-rich food supplements and special vitamins. The child's nutrition should be complete and balanced. In addition, special attention should be paid general strengthening immunity.
If you see that the child’s gums are swollen, the baby feels discomfort, and the teeth are in no hurry to erupt, then help light massage. Gently massage the swollen area with a clean teaspoon or finger. Be sure to wash your hands well before the procedure.
To facilitate the process of cutting baby teeth, infants buy special teethers in the form of rings or toys. At the same time, the gums are massaged and softened, making it easier for teeth to grow.
www.kakprosto.ru
Some facts about teething in humans
Teething is a dynamic and complex physiological process that continues for several years. At this time, the maturation of tooth germs or follicles occurs and their migration inside the jaw until they finally erupt into the oral cavity and take their proper functional position in the dentition.
Eruption involves a gradual transition from one bite to another: temporary or milk bite replaced by a constant. This process is very closely related to the child’s bone development, especially correct height skull bones. In this case, there is a parallel formation of bone structures, soft tissues surrounding the tooth, and resorption of the roots of baby teeth to make room for permanent teeth. The rate of eruption depends on the timing of completion of the formation of dental follicles on both sides of the dental arch.
The first stages of dental development begin in the embryonic stage, this process ends with the eruption of third molars (wisdom teeth) at the age of 20 years. The direct mechanism of eruption has not yet been fully studied; scientists have put forward some guesses, but none of them have been proven in practice.
When do the first teeth usually appear?
A child's teeth are in a state of internal maturation at the time of birth. jaw bones. There is a complete set of baby teeth on various stages growth and hardening (mineralization). The front teeth form earlier than the others and begin to emerge into the oral cavity, cutting through the gums, already when the child reaches the age of six months. Under normal and proper development A child's teeth continue to erupt on time and in pairs - one on each side, and a full set of twenty milk teeth appears by the age of three.
How can you tell if teething is delayed?
If a child is 18 months old but still does not have a single tooth, this is a reason to contact pediatric dentist. The normal timing of the appearance of the first teeth in the oral cavity is from 4 to 15 months of age, subsequent teeth usually appear gradually and within a period after the first. Permanent teeth begin to emerge around 6-7 years of age. A slight discrepancy from the established deadlines should not cause severe anxiety, Unlike complete absence child's teeth.
Table. Approximate timing of teeth appearance.
What types of delayed eruption are there?
Most often, the delay in the appearance of teeth occurs in the mixed dentition and does not manifest itself clinically. A departure from the average time for the eruption of baby teeth by more than six months is considered a delay. Permanent teeth should erupt no later than one year from the average date.
There are two distinct subtypes of late teething.
- Associated late maturation dental follicle. In this case, coordination between the development of the tooth and its appearance in the oral cavity is observed, but both processes occur more slowly than usual.
- Late eruption. In such a situation, the tooth forms and matures fully, its root grows, but a physical obstacle prevents the tooth from reaching the surface. Thus, fully formed teeth become encased in bone, or impacted. They can be completely hidden by the gum or come out from under it partially - with one or two bumps.
However, before talking about delayed eruption, you need to make sure that the tooth germ is even present in the bone. To do this, it is necessary to take a panoramic photograph of the teeth, which will distinguish partial primary adentia (the dental follicle was not initially embedded in the jaw) from delayed tooth formation.
What causes delayed teething in children?
Delays in teething in children can be caused by a number of reasons. In some cases, the main role is played hereditary factor. If parents teethed later than other children, most likely, the same symptom will be observed in their children.
Another reason for delayed eruption is prematurity or low birth weight of the baby. This group of causes also includes illnesses of the mother during pregnancy, illnesses of the child in the first months of life, and injuries during childbirth. All these factors most strongly influence the time of eruption, as well as the quality of tooth formation. It is the factors listed above that serve as the main reasons for the formation of defective enamel and dentin, which are manifested by fragility of teeth, strange shape and unusual appearance(spots, grooves and discolorations on the enamel surface).
The group of external circumstances that directly affect the timing of teething includes malnutrition of the child, a lack of certain groups of vitamins and minerals in the diet, and hypothyroidism. Vitamin D-resistant rickets and its consequences should be highlighted in a separate category.
Eruption becomes untimely in diseases such as Down syndrome, panhypopituitarism and other similar developmental defects.
It is also necessary to remember that girls grow faster than boys, which means they will develop teeth earlier.
What determines the timing of teeth appearance?
The age of formation of primary and permanent teeth in children has relative variations that can be correlated with certain phenomena.
- Floor. All teeth, except the upper first chewing one, erupt earlier in girls than in boys.
- Height. The literature reports a special relationship between the child’s body length and the time of teething. On average, short children develop teeth a little later.
- Jaws. Teething on lower jaw occurs faster than at the top.
- Position of teeth. The last teeth in each group (third molars, second premolars) are more likely to experience delayed eruption.
- Bite. In temporary dentition, delayed eruption occurs much less frequently than in permanent dentition.
- Population. Various dates for the appearance of teeth in people living in different countries. For example, among Europeans, delayed eruption is a relatively common occurrence.
- Climate. In warm climates, children's teeth erupt faster than in cold climates.
- Socio-economic conditions. Children raised in poor conditions are more likely to suffer from delayed teething.
- Level of urbanization. In urban conditions, children's teeth develop faster than in rural areas.
- Phylogenetic evolution. The modern population of people more often has problems with the eruption of wisdom teeth and canines. upper jaw. Researchers attribute this phenomenon to the evolution of humans as a species and the lack of space on the jaw due to a decrease in its overall size.
- Birth order of the child. Children born later than their siblings are more likely to have delayed teething.
Is late teething dangerous?
As such, late teething is not a problem unless it serves as a signal of more serious problems in the child’s body. However, untimely teething can cause dental problems in the future. A study was conducted that found that people with hereditary delayed teething had a 35% greater chance of needing orthodontic treatment by the age of thirty. In addition, you need to remember that having the proper number of teeth helps children eat right and get the nutrients they need from food for growth.
In addition, correctly positioned baby teeth help permanent teeth erupt in their proper places in the mouth, which is a key point in the formation of a healthy bite.
What to do if teething is delayed?
Changes in the normal eruption path of some permanent teeth, insufficient space in the dentition, and premature tooth extraction cause movement of existing teeth. When such problems arise, it becomes necessary regular visits to the dentist to clearly monitor the process of bite formation at all stages. Quantity negative consequences will be reduced as much as possible if the correction is carried out in a timely manner.
Using an overview image, the dentist will determine the path of teeth eruption, their size and inclination, the number of follicles, the stages of their formation, and the amount of free space in the dentition. X-rays allow you to assess the risk of potential problems with a child’s bite and suggest what treatment will help improve the situation.
The specialist can offer several options: waiting for eruption, tooth traction, surgical correction, implantation. Often, simply removing baby teeth that have been stuck in the mouth for too long can help.
If your baby has good health and more or less correct development, sooner or later his first teeth will erupt. One way or another, if parents have reason to doubt the correct timing of teething in their child, the best solution would be to contact a pediatric dentist. A competent specialist will perform necessary research And x-rays, which will help to establish the cause and outline a plan for further treatment.
expertdent.net
When the first baby tooth falls out and a new one grows in
There are no clear deadlines for such an individual issue as changing baby teeth to permanent ones. Just as the eruption of the first teeth in some babies begins already at 4-5 months, and in others only after a year, so their loss occurs in at different ages. The protracted change of baby teeth to molars is a very, very relative concept. Some people begin to worry after just a week if the tip of the new tooth has not yet erupted. And some people are in no hurry to see a doctor even after six months.
If a child’s first baby tooth appears early, one can expect that it will also be replaced by a permanent one earlier than those of his peers – at about 4-5 years. Most often, it happens that baby teeth fall out - and in their place the tip of the molar is already visible. But if a tooth falls out and there is no new one yet, there is no reason to worry. Wait a few weeks.
Sometimes the permanent tooth does not grow in for another month or two after the temporary one falls out. This normal phenomenon. Children often begin to worry about this, they fear that the mouse or tooth Fairy I took the old tooth and forgot about the new one. And now they have to walk around with a gap in their mouth for the rest of their lives - but their peers are laughing!
Reassure the baby and explain that the tooth will definitely appear in the near future. It’s just important not to forget to take care of oral cavity and eat well. Give him a raw carrot, apple cracker, or hard cookie to chew on. Perhaps the tooth is really on its way and needs to be helped to break through the gums.
You should consult a doctor if:
- there is no new tooth even 2-3 months after the old one fell out;
- the gums become swollen and red, the child is in pain, but the tooth is still missing;
- One by one, the remaining teeth fall out, but new ones never grow.
First of all, parents whose children have suffered from rickets, severe infectious diseases, jaw injuries, or have undergone treatment and removal of baby teeth should be concerned.
Why a new tooth does not grow - reasons
You've made an appointment with your doctor, but you're still very worried. What awaits you, what diagnosis will be given? Delayed growth of molars can occur for the following reasons:
- Past infectious diseases. Any disease for child's body– this is a lot of stress and energy consumption. Those resources that should have gone to the structure and mineralization of molars were thrown into the fight against the disease. Experienced pediatricians usually warn about this and prescribe vitamin therapy in advance for preventive purposes.
- Lack of calcium in the body. Calcium deficiency may have nothing to do with pathologies and diseases. It is often congenital in children, especially if the baby is born ahead of schedule or the mother did not eat well during pregnancy. Then the child also experiences delayed hair growth, pale skin, soft, thin, brittle nails. This problem is usually solved by adjusting the diet. There are also folk recipes– for example, the well-known eggshell powder. But you definitely need to consult a doctor: it happens that a child consumes enough calcium, but at the same time with those foods that interfere with its absorption. A nutritionist will tell you how to feed your baby correctly so that the balance is improved.
- Caries and other diseases of primary teeth. With advanced caries, not only the short root of the baby tooth is affected, but also the rudiment of the future permanent one. If this happens, the tooth may grow with a delay, in the wrong direction. You need to be very vigilant, as in this case the risk of developing malocclusion is very high.
- Mechanical injuries. If a child falls and hits his jaw hard, the rudiments can be literally “driven” into the gums and periosteum. The problem can only be corrected through surgery. The sooner it is carried out, the greater the chance that the new tooth will grow straight and healthy.








