Hypoglycemia, or, as this condition of the body is commonly called, low sugar in the blood is quite dangerous, especially for patients with diabetes. It can be determined by physiological manifestations, deterioration in general well-being, as well as by examining the blood for glucose levels, the result of which will show values below generally accepted norms.
Signs accompanying this state, are usually poorly tolerated by the human body, and can lead to a rapid and significant increase in negative symptoms. In some cases, hypoglycemia indicates insufficient quality of correction of diabetes mellitus or a parallel occurrence pathological processes of a different nature.
More about blood glucose
Initially, it is worth saying that a blood test for sugar is a generally accepted expression, but within the framework of modern medicine it is not entirely correct. The very phrase “blood sugar” dates back to the Middle Ages. Doctors and healers of that time believed that the amount of sugar was directly related to the appearance of excessive thirst, pustular infections and frequent urination.
Today it is no secret to doctors that there is no so-called sugar (sucrose) in the blood, because in the course of studies it was confirmed that simple sugars by chemical reactions are converted into glucose. And it, in turn, performs one of the leading functions in metabolism. And now, when we talk about the normal blood sugar level, we mean the content of glucose, a universal substance that supplies energy to all human tissues and organs.
With its participation, heat exchange occurs, the brain and the entire nervous system are nourished, and toxic substances are removed from the body. When supplied with food, glucose is consumed by tissues, and is also deposited and accumulated in muscles and liver in the form of glycogen, which, if necessary, can again be converted into simple sugars and returned to the blood.
Thus, the circulation of glucose in the body maintains its normal functioning, and therefore wellness person. Glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6) is the most important substance in terms of metabolism, and any disturbance in its concentration can cause the development of severe complications.
In addition to glucose, during the breakdown of sucrose in the gastrointestinal tract ( gastrointestinal tract) fructose is also formed, which is also a simple saccharide, like the first one. In diabetes mellitus, there is a deficiency of hormones that promote the absorption of glucose, as a result of which it is retained in the blood instead of being converted into glycogen.
Increased glucose in the blood, as well as in the urine, are direct laboratory signs of the disease and pose a danger to human life and health. Insulin, which is prescribed to such patients, helps transform free glucose into glycogen.
At the same time, it often happens that an incorrectly selected dosage of insulin or a meal taken at the wrong time leads to a lack of glucose and the development of hypoglycemia, which is the same dangerous condition like hyperglycemia. IN certain situations Serious health consequences can develop even with short-term glycemia, especially if the level drops very quickly.
Reasons for the decline
A drop in blood glucose levels can be either physiological, that is, observed in healthy people, or pathological, caused by the occurrence of certain diseases. The main causes of low sugar levels that are not related to disease are the following:
- low calorie content daily diet as a result of malnutrition, which can happen with a strict diet, for example, in order to quickly lose extra pounds;
- drug and alcohol intoxication, poisoning of the body with arsenic salts, chloroform, dehydration;
- long intervals between meals, lasting more than 8 hours, eating disorders (bulimia, anorexia), thirst;
- intravenous drip infusion of saline without adding glucose to it;
- excessive physical exertion, for example, fatigue during labor activity or professional sports;
- increased consumption of carbohydrates, that is, an excess of sweets, confectionery, carbonated drinks with a high sugar content, as well as foods with a high glycemic index.
Reference! Dessert and fortified wines, beer are called first fast growth glucose in the blood, and then a sharp and rapid drop in the level.
In such situations, there is a lack of energy, which the body eliminates through internal “reserves” - by reverse conversion of glycogen stored in skeletal muscles and liver. And also a decrease in blood sugar can occur due to the development various diseases, such as:
- diabetes Types 1 and 2 – glucose levels often drop as a result of an overdose of insulin or other medications that help lower it;
- diseases of the kidneys, adrenal glands or liver;
- renal and heart failure, stroke;
- obesity, pancreatitis, sarcoidosis, hormonal disorders,
- Insulinoma is a tumor of the pancreas, the cells of which are capable of producing insulin, thereby creating an excess of it in the body.
Most often, a decrease in blood sugar is observed with an incorrectly administered dose of insulin, which means that hypoglycemia is most dangerous for people suffering from diabetes mellitus and forced to take this hormone.
The second place is given to physical exhaustion that occurs against the background of starvation or malnutrition. Other options are quite rare, are not always accompanied by additional symptoms, and without a doctor it will be impossible to find out why the sugar dropped.
Manifestations of moderate hypoglycemia
To always be on guard and be able to quickly respond to changes in the general well-being of your or loved one, you should know the main signs that accompany low blood sugar. In an adult, the following manifestations are most often present:
- general weakness, causeless fatigue;
- headaches, dizziness;
- trembling (tremor) in the limbs, their numbness;
- tachycardia (rapid heartbeat);
- rapid, uneven pulse, drowsiness;
- excessive nervousness, irritability;
- feeling severe hunger, sweating;
- poor coordination of movements, pale facial skin,
- Pupils are dilated, there is double vision, darkening.
All of the above symptoms low sugar in the blood can be observed both in a motionless sitting or lying person, and in a sleeping person. They are due to the fact that the brain consumes glucose in approximately the same quantities as the muscles, and if there is a lack of it, it also goes hungry.
Reference! Signs of nocturnal hypoglycemia develop due to decreased functional activity endocrine system at this time of day.
As a rule, a person has restless sleep, often accompanied by nightmares, he may behave noisily, and try to get up without waking up. As a result, the patient often falls out of bed, sweats profusely, wakes up with cramps in lower limbs, and suffers from a headache in the morning.
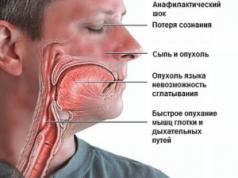
If at this stage of hypoglycemia a person is not given glucose (best in a quickly digestible form: sugar, sweets, honey, cake, etc.), then his condition will worsen. A further drop in glucose concentration can cause more severe and life-threatening symptoms for the patient:
- confusion;
- incoherent speech;
- convulsive attacks.

The most common signs of hypoglycemia
Symptoms of a sharp drop in sugar
A sharp decline glucose deficiency in most cases develops in patients with type 1 diabetes who require regular subcutaneous injections of insulin. In some situations, a rapid drop in sugar concentration is caused by an overdose of insulin due to incorrect use.
However, it can also decrease sharply in patients with type 2 diabetes who take medicines stimulating the synthesis of insulin by the pancreas. Most often these are sulfonylurea derivatives and drugs of the meglitinide group. When blood glucose drops sharply, a person develops characteristic symptoms, namely:
- tachycardia, tremors of extremities;
- pallor skin;
- loss of ability to navigate in space;
- slower reactions or, conversely, restless behavior and aggressiveness.
Reference! The appearance of hallucinations, delirium, confusion, and convulsions in the patient are signs of a developing hypoglycemic coma, which can lead to cerebral edema and death of the patient.
Low blood sugar in pregnant women
The symptoms of low blood glucose in women are not much different from the symptoms of this condition in men. When the described substance declines, representatives of the weaker half of humanity may experience:
- increased heart rate, combined with strong inexplicable fear and anxiety;
- dizziness, disturbance visual function, tremor and weakness in the limbs;
- increased sweating and severe hunger.
Low sugar levels are often observed in women carrying a child, especially in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. This is due to a significant change in hormonal levels, which increases the sensitivity of the body's cells to insulin. As a result, the body tissues of a pregnant woman utilize glucose faster.
And the fetus’s body also needs glucose. Unlike diabetes that develops in pregnant women, low blood glucose in women preparing to become mothers does not pose any particular danger, but only requires fractional meals. That is, they need to eat often, but in smaller portions.
When should you see a doctor?
The threshold for reducing glucose levels at which symptoms of hypoglycemia appear is individual for each patient. Some people may feel fine with a reading below 2.2 mmol/l, while for others a reading of 3 becomes critical and they are likely to develop coma.
Patients with type 1 diabetes should measure their blood sugar several times a day using a portable personal glucose meter. Those who do not use this device and are often unaware of the presence of diabetes (mostly adults who become ill in mature age type 2 diabetes) the following should alert you and be a reason for a visit to an endocrinologist:
- sudden increase in resting heart rate;
- feeling of fatigue and weakness in the lower extremities;
- increased sweating in the absence of physical activity;
- attacks of unreasonable fear, trembling in the hands;
- inability to concentrate;
- attacks of weakness or dizziness;
- visual impairment.
If one or several manifestations arise, the first action of a person should be to seek help. medical care and passing all necessary tests. The doctor will consult the patient in detail, tell you what to do in such situations, and possibly recommend adjusting your lifestyle.
Norms and deviations
In order not to miss a sharp and significant drop in glucose, but, on the contrary, to track hypoglycemia in time, you need to go to the laboratory on an empty stomach and take a finger prick blood test. This can be done at home using a glucometer, which every person with diabetes should have.
Blood sugar is in the range of 3–6 mmol/l, namely:
- newborn infants 2.7–4.5 mmol/l;
- older children – 3–5.5 mmol/l;
- adults – 3.5–6 mmol/l.
It should not be forgotten that for adults, a value of 5.5–6 mmol/l is considered an alarm bell, which in medicine is called the state of prediabetes. A shift in the coefficient to the lower limit of normal may indicate exhaustion of the body or persistent hypoglycemia.
A condition in which blood glucose is sharply reduced, and at the same time it is accompanied by neurological symptoms: convulsive syndrome, loss of consciousness, is very dangerous, and therefore requires immediate hospital treatment. During therapy and correction of blood sugar levels, it will be necessary to carry out additional research, which will help to understand the cause of these deviations.
And the doctor will also talk with the patient about measures to improve the health of the body, which include diet, refusal bad habits, combating obesity and getting enough rest. As a rule, changing lifestyle, regimen and diet to initial stages diseases help reduce the likelihood of developing serious health problems.

Portable device (glucometer) for measuring blood glucose levels
How to help with severe hypoglycemia?
The condition of acute sudden hypoglycemia must be stopped within 5–10 minutes, otherwise there is a risk of fainting and other life-threatening complications. To make up for the lack of glucose in the blood, you should eat or drink something sweet or containing carbohydrates.
The most effective products that help relieve an attack in 5–10 minutes are:
- fruit juice (half a glass is enough);
- sugar (1–2 teaspoons);
- honey (2 teaspoons);
- jam (1–2 tbsp);
- caramel (1–2 pcs.);
- lemonade or other sweet drink (1 glass).
After eating, the attack will be stopped, but you should not ignore the symptoms preceding it, even if it is still minor and does not cause much discomfort. It should be remembered that at any moment (if the dosage of blood sugar-lowering drugs is incorrect or a meal is skipped), the attack may recur, and it is not known what intensity it will be.
For patients. Any sign of hypoglycemia should be a reason to visit a doctor and undergo a thorough examination. If no pathologies are found, then it is necessary to use the doctor’s recommendations to reduce the likelihood of recurrence of alarming symptoms. If a disease is detected, get advice and therapeutic prescriptions that will stabilize the state of the endocrine system.
High or low blood glucose levels can lead to the development of various diseases.
Lack of sugar in the body, the symptoms of which are detected, must be subject to mandatory treatment.
In some cases, it may be enough to follow a special diet; sometimes it is impossible to do without taking medications.
The main reasons for low blood glucose
Today, hypoglycemia is a disease that most often manifests itself in chronic form and difficult to treat.
Insufficiency of glucose in the blood can be caused by the following factors:
- in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, hypoglycemic drugs are used in increased dosages, which lead to a decrease in blood sugar below standard values
- dehydration of the body
- excessive physical exercise or hard physical labor
- alcohol abuse
- general chronic fatigue body or exhaustion
- poor nutrition, as a result of which the body receives too few vitamins and other nutrients; glucose deficiency can often occur when following modern strict diets or during fasting
- administering too much saline through an IV
- various chronic diseases. These include pathologies of the kidney, liver, heart failure
- development hormonal imbalance in the body, which manifests itself in the form of an insufficient amount of certain hormones, which is accompanied by inhibition of the synthesis of glucacone, adrenaline, cortisol and somatropin.
- during menstruation in women
- as a result of intoxication with alcohol or a substance containing arsenicꓼ
- for intestinal diseases that are associated with impaired absorption of nutrients
Lack of glucose can occur in the body in the presence of diseases of the pancreas, various inflammatory processes or neoplasms in it, also a lack of glucose occurs due to a lack of oxygen.
Symptoms and main signs of hypoglycemia
Sugar level
The development of glycemia and lack of glucose levels in the blood can begin with the manifestation various signs and symptoms.
The main sign that you should pay attention to is constant fatigue of the body and lack of energy for normal functioning. Even completely healthy people experience low blood sugar levels after waking up. This is absolutely considered normal occurrence, and manifests itself in the form of drowsiness, increased irritability and lethargy. If a person does not have enough glucose throughout the day, such signs accompany him constantly.
In addition, symptoms of hypoglycemia can manifest themselves in the form of the following signals given by the body:
- chills followed by fever
- hand shaking
- weakness throughout the body
- increased level of sweating
- severe headaches accompanied by dizziness
- painful sensations in the muscles, numbness of the limbs, a feeling of constant heaviness in the legs
- constant feeling of hunger, inability to get enough
- nausea, sometimes with vomiting
- darkening of the eyes, the appearance of a white veil or spots.
As a result of the neglect of the hypoglycemia process, a person’s condition may worsen. In this case, the following characteristic signs may appear:
- severe leg cramps
- speech coherence is lost
- Coordination of movements is impaired, which manifests itself as an unsteady gait.
- attention is scattered, it is impossible to concentrate.
In the presence of similar symptoms You must consult a doctor, take a blood test to determine your glucose level and follow all doctor's recommendations.
How to normalize low glucose levels?
 If there is low blood sugar, the attending physician should, first of all, prescribe a special dietary food. Diet therapy should be based on individual characteristics each patient, taking into account availability concomitant diseases, the degree of development of hypoglycemia and the general well-being of the patient.
If there is low blood sugar, the attending physician should, first of all, prescribe a special dietary food. Diet therapy should be based on individual characteristics each patient, taking into account availability concomitant diseases, the degree of development of hypoglycemia and the general well-being of the patient.
There are certain points that are taken into account when drawing up the daily menu.
It is necessary to increase the amount of complex carbohydrates consumed. As a rule, such products should prevail in the daily diet. This is, first of all, fresh vegetables, durum pasta and whole grain bread. This one is very useful.
Prohibited foods should include regular pasta, sweet confectionery and bakery products, semolina, alcoholic drinks, fatty foods, rich broths, fatty meats, spicy and smoked foods.
Honey and fruit juices should be consumed in minimal quantities. The number of meals should be at least five, and food should be consumed in small portions.
It is mandatory to consume legumes, corn and jacket potatoes, as they help slow down the drop in blood sugar levels, which is extracted human body from complex carbohydrates.
Unsweetened fruits should always be present in the diet. At the same time, both fresh and dried fruits are perfect.
Protein is best consumed in the form of low-fat cheese and chicken meat, fish or seafood.
Ideally, you should give up coffee or at least reduce its amount to a minimum. The fact is that caffeine contributes to the development of hypoglycemia and can provoke an even greater drop in glucose. In this case, it may develop.
The menu should be designed in such a way that there are soups or non-rich meat broths at least several times a week. Thus, metabolic processes in the body improve.
It is better to boil or steam all dishes.
This will not only help normalize sugar levels, but will have a beneficial effect on the patient’s overall health.
Drug treatment and traditional medicine
Various treatments are used to treat hypoglycemia. medications, which in combination with diet therapy bring a long-term normalizing effect.
You can eliminate symptoms and bring your sugar levels back to normal using the following groups: medical supplies:
- Introduced required level glucose intravenously or oral medications are used, which immediately increase glucose levels as they bypass the digestive tract and are immediately absorbed into the blood; as a rule, the monosaccharide dextrose is used.
- The use of light and heavy carbohydrates in prescribed quantities is combined.
- In some more severe cases, a glucagon injection may be required, as is one of the stronger medications.
- Critical situations that require an immediate rise in blood sugar require the use of fractional injections of medications from the group of corticosteroids. Most often, these medications include hydrocortisone or epinephrine.
- In consultation with your doctor, you can use various sugar-increasing drugs that are offered by ethnoscience. The most effective today are the following methods of normalizing low glucose levels.
- You can buy Leuzea tincture at the pharmacy and take it fifteen to twenty drops diluted with water. You will need a little water, one tablespoon will be enough for the indicated dosage.
- Grind rose hips (about one tablespoon) and pour two cups of boiling water. Leave to infuse for twenty to thirty minutes, then strain. Take the resulting infusion half a glass twice a day. The course of treatment should be two weeks.
In order to quickly bring your glucose levels back to normal at home, you can use the following emergency methods:
- eat a small piece of a regular chocolate bar
- drink a cup of tea with honey
- A few pieces of dried fruits also help increase sugar. It can be dried apricots, raisins or prunes
- Bananas or fruit juices will also help increase your glucose levels.
Such methods are designed only for temporary enhancement and should not be used regularly as the main “treatment”. If problems arise with a constant decrease in glucose, it is necessary to use radical therapy prescribed by the attending physician. The video in this article will tell you what to do if you have a lack of sugar.
If a person has low blood sugar or hypoglycemia, this is considered no less dangerous than hyperglycemia, when plasma glucose levels go off scale. It is important to determine the reasons why blood sugar has dropped, eliminate such factors from life and carry out adequate therapeutic and preventive actions. Self-medication is unacceptable; in advanced cases, the situation can be fatal.
Causes of pathology
Constantly fluctuates and not only in diabetics, this condition can be observed in men, women and children who do not have problems with the absorption of glucose. More often, a decrease in blood sugar occurs due to long breaks between meals. In this case, hypoglycemia comes in two types:
- On empty stomach. When a person last time ate food 12 hours ago.
- Reply. When your last meal was 4-6 hours ago.
A sharp decrease in blood sugar during hypoglycemia on an empty stomach develops for the following reasons:
- moderate or forced long-term abstinence from eating food;
- dehydration;
- the use of medications that are characterized by a decrease in glucose levels;
- chronic diseases of the stomach, intestines, pancreas and liver;
- excessively overweight;
- kidney and heart diseases;
- lack of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- for oncological pathologies.
 Pregnancy can cause low blood sugar.
Pregnancy can cause low blood sugar. A low blood sugar level in response to hypoglycemia indicates that the patient is developing early diabetes or other internal illnesses, due to which blood sugar is very low. Sometimes occurs due to previously produced surgical interventions on the digestive organs, the consequences of which are a decrease in blood sugar;
Other factors can also cause a drop in blood sugar in an adult:
- excessive physical activity;
- allergic reactions to foods and medications;
- pregnancy.
Causes of lack of glucose in the blood during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the main reasons affecting the lack of glucose are basically the same as in other people. The basic rule that applies to pregnant women is to watch your diet, eat proper food, do not abuse sweets. Low glucose levels have Negative influence for the fruit. He does not receive enough necessary for growth and development nutrients, hypoxia develops. Signs of low blood sugar in pregnant women are:
- increase in apatite;
- increased thirst;
- increased blood pressure;
- sleep disturbance;
- increased urge to urinate;
- weakness, drowsiness, apathy.
If the condition is stably disturbed, and when correcting nutrition and eliminating negative factors, plasma glucose does not normalize, it is not recommended to self-medicate, you must urgently call ambulance. After diagnosing and establishing the cause, the doctor will select a therapy that will take into account the woman’s situation and will not harm the unborn child.
Symptoms of pathology
Most often, symptoms of low sugar appear after waking up, when the person last ate in 6-8 hours. In this case, the blood sugar level can be increased by having breakfast and, after a few minutes, the situation will return to normal. If you want to see how naughty mom, son and daughter have a hot threesome fuck, then be sure to visit our site. Here the dear trinity arranges real incest FFM https://incestik.cc/jmj, which you will see at the link. Surrendering to the will of pleasure, partners tirelessly please each other with oral caresses, and then try different poses when they fuck sexually. But if a person experiences hypoglycemia in response, and a drop in blood sugar is noted after a meal, in this case the patient should not ignore the symptoms; an urgent test must be taken to diagnose diabetes mellitus. early stages. Symptoms of low plasma glucose are:

Signs of low blood sugar during sleep appear as follows:
- excessive sweating occurs;
- sleep becomes restless, superficial;
- after waking up, a person feels exhausted and lethargic.
Why is low blood sugar dangerous?
All these signs appear due to the fact that the glucose content in the body’s cells is less than the prescribed norm. A person is advised to measure the glucose level in the body, and if it is below 3 mmol/l, then the disease hypoglycemia develops. This disease is very dangerous, especially for diabetics, since with rapid deterioration it develops, which can be fatal in especially severe cases.
Analyzes and norms
To identify low blood sugar and properly treat the problem, it is important to first measure the blood glucose level, and if it is significantly reduced, it means that the person has hypoglycemia and is diagnosed accordingly. To determine how little sugar is in the plasma of a child or adult, diagnostic tests are performed.
 Blood sampling to determine glucose tolerance is done on an empty stomach.
Blood sampling to determine glucose tolerance is done on an empty stomach. Testing for glucose tolerance is carried out. First, blood is taken from a person on an empty stomach, then he needs to drink a glucose solution, which is distributed throughout the body’s cells within 2 hours. After this period, the sample is taken again; in a healthy person, the values will be in the range of 3.2-5.6 mmol/l. If blood sugar is reduced, this indicates a violation of the condition and the development of an internal picture of the disease. When sugar is high, a person develops a disease called diabetes.