The organization of medical care to the population depends on the socio-economic, social and political changes occurring in the country. The main accessible and free type of medical care for the population in our country is primary health care (PHC), which since 2005 has been identified as a priority area for improving healthcare.
Primary health care includes treatment of the most common diseases, injuries, poisonings and other emergency conditions; carrying out sanitary-hygienic and anti-epidemic measures, medical prevention of the most important socially significant diseases; sanitary and hygienic education; family protection measures and other activities related to the provision of health care to citizens at their place of residence.
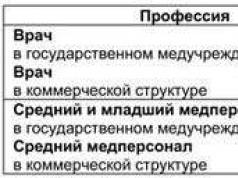
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 627 dated October 7, 2005 “On a unified nomenclature of state and municipal healthcare institutions” approved the following outpatient clinics:
- Outpatient clinic.
- Polyclinics, including city, consultative and diagnostic, physiotherapeutic, psychotherapeutic, central district, etc.
In the healthcare system, the outpatient service occupies a leading position. About 80% of patients receive care in an outpatient setting. The activities of polyclinics are based on the territorial-precinct principle of serving the population, when the polyclinic provides assistance to the population living in a designated territory.
Structure and organization of the clinic
Depending on capacity, there are five categories of clinics:
Approximate organizational structure of a city clinic:
Clinic management.
- Administrative and economic part.
Information and analytical department:
- Registry;
- Organizational and methodological department (office) with a statistics department (office).
Prevention department(cabinet):
- First aid room
- Examination room;
- Fluorography room;
- Health education office and hygiene education population;
- Health school office.
Treatment and prevention unit:
- Therapeutic department;
- Department of General Medical (Family) Practice;
- Surgical department (office);
- Dental department (office);
- Maternity consultation (if not included in the maternity hospital);
- Branch rehabilitation treatment;
- Treatment room.
Consulting and diagnostic department:
- Advisory department (offices of medical specialists);
- Department (office) functional diagnostics;
- Department of Radiation Diagnostics;
- Laboratory.
Emergency Department.
Ambulatory Surgery Center.
Day hospital.
Hospital at home.
Medical and paramedic health centers.
Equipping medical institutions with diagnostic equipment is carried out depending on the number of visits (up to 250, 250-500, more than 500) in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 753 dated December 1, 2005 “On equipping outpatient clinics and inpatient clinics of municipal institutions with diagnostic equipment formations."
Clinic opening hours: a six-day work week with specialist doctors and all departments working on Saturdays on a staggered schedule.
The staffing schedule depends on the number of population served (category of the clinic). The positions of clinic doctors are determined based on:
| Job title | Number of positions per 10 thousand adult population attached to the clinic |
| Local therapist | 5,9 |
| General practitioner (adult population) | 6,67 |
| General Practitioner (Mixed Population) | 8,4 |
| Ophthalmologist | 0,6 |
| Neurologist | 0,5 |
| Otolaryngologist | 0,5 |
| Surgeon | 0,4 |
| Cardiologist | 0,3 |
| Rheumatologist | 0,2 |
| Urologist | 0,2 |
| Infectious disease physician | 0,2 |
| Allergist-immunologist | 0,015 |
The activities of any medical institution are largely determined by the level of its management, while great importance has a clear distribution of functional responsibilities of all officials, working in the clinic, from a nurse to a chief physician. The practical activities of personnel are regulated by orders, regulations and instructions of the Ministry of Health and health authorities. The functional responsibilities of employees can be adjusted locally, taking into account the specifics of the medical institution.
Depending on the capacity of the clinic chief physician has several substituents. The first deputy - the second person in the clinic is the deputy chief physician for medical work (chief medical officer), who is appointed as the chief physician from among the most qualified doctors with organizational skills. In the absence of the chief physician, the chief medical officer performs his duties. The chief medical officer is responsible for all medical activities clinics. He organizes and controls the correctness and timeliness of examination and treatment of patients in the clinic and at home; monitors the implementation of modern, most promising methods of prevention, diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of patients, new organizational forms and methods of operation of the clinic.
The chief medical officer ensures continuity in the management of patients between the clinic and emergency medical care, clinics and hospitals, analyzes discrepancies in clinical and polyclinic diagnoses; organizes planned hospitalization sick.
All preventive work of the clinic is carried out under the leadership of the chief of medical services: periodic and targeted medical examinations, timely preventive vaccinations and medical examination of the population, sanitary and educational work.
The Deputy Chief Physician for the Examination of Temporary Disability (ED), who heads the Medical Commission (MC), is responsible for the quality examination of work capacity and interaction with insurance companies.
If there are 6–8 positions of general practitioners in the clinic, a therapeutic department is created, which is headed by the head of the department. He is entrusted with the responsibility of monitoring the activities of the department’s doctors in all sections of work, organizational and methodological work, drawing up plans, reports with analysis of key indicators, and introducing new technologies into the diagnostic and treatment process.
The first acquaintance of visitors with the clinic begins at the reception desk. This is one of the main structural divisions clinics. The duties of the registry include:
- organizing preliminary and emergency registration of patients for appointments with a doctor, both when the patient contacts them directly and by telephone;
- ensuring clear regulation of the flow of patients in order to create an even workload for doctors by issuing appointment vouchers;
- carrying out timely selection and delivery medical documentation to doctors' offices, proper maintenance and storage of clinic files.
Organization of the work of the local therapeutic service
Medical services for the population in the clinic are organized on a local basis in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 584 dated 08/04/2006 “On the procedure for organizing medical services for the population on a local basis” and is carried out taking into account the criteria of territorial (including transport) accessibility of all types of medical (pre-hospital, medical and emergency medical = emergency) care. The following medical areas with the recommended population size can be organized in medical institutions:
- therapeutic – 1,700 adults (18 years and older);
- general practitioner (GP) – 1,500 adults;
- family doctor – 1200 adults and children;
- complex therapeutic area - 2000 or more adults and children.
A comprehensive therapeutic area is formed from the population of the medical area of an outpatient clinic (APU) with an insufficient number of attached population (understaffed area) or the population served by an outpatient physician and the population served by paramedic and obstetric stations.
The distribution of the population among areas is carried out by the heads of the APU, depending on the specific conditions for the provision of primary health care to the population in order to maximize its accessibility and respect for other rights of citizens.
In order to ensure the right of citizens to choose a doctor and a medical institution, the heads of the APU assign citizens living outside the service area of the APU to local general practitioners (GPs) for medical observation and treatment, without exceeding the population size for one position of a local doctor by more than 15% normative.
Treatment and preventive care for the population of the site is provided by a permanent local physician and nurse. The local principle allows the attending physician to better know his area, carry out dynamic observation taking into account working and living conditions, identify frequently and long-term ill people, timely carry out therapeutic and preventive measures, and prevent the occurrence of infectious diseases. All this ultimately determines the effectiveness of the clinic.
The appointment and dismissal of a local general practitioner is carried out by the chief physician of the clinic. In his work, he reports directly to the head of the therapeutic department, and in his absence, to the deputy chief physician for medical work.
Responsibilities of a local physician
The activities of a local general practitioner are regulated by Order of the Ministry of Health No. 765 dated December 7, 2005 “On the organization of the activities of a local general practitioner.”
Local therapist:
- forms a medical (therapeutic) site from the population attached to it;
- provides sanitary and hygienic education, advises on the formation of a healthy lifestyle;
- carries out preventive measures to prevent and reduce morbidity, identify early and latent forms of diseases, socially significant diseases and risk factors, organizes and runs health schools;
- studies the needs of the population served for health-improving activities and develops a program for their implementation;
- carries out medical examination of the population, including those entitled to receive a set of social benefits;
- organizes and conducts diagnostics and treatment of various diseases and conditions, including rehabilitation treatment of patients in outpatient setting, day hospital and home hospital;
- provides emergency medical care to patients acute conditions(acute diseases, injuries, poisoning and other emergency conditions) in a clinic, day hospital and hospital at home;
- promptly refers patients for consultations with specialists, including for inpatient and rehabilitation treatment for medical reasons;
- organizes and carries out anti-epidemic measures and immunoprophylaxis;
- conducts an examination of temporary disability (TEI) and draws up documents for referring patients for a medical and social examination (MSE);
- issues a conclusion on the need to refer patients for medical reasons to Spa treatment and, if necessary, draws up a sanatorium-resort card after the examination;
- interacts with medical organizations, medical insurance companies, and other organizations;
- organizes, together with the social protection authorities, medical and social assistance to certain categories of citizens in need of care: lonely, elderly, disabled, chronically ill;
- manages the activities of the middle medical personnel providing primary health care;
- maintains medical documentation, analyzes the health status of the assigned population and the activities of the medical department.
The local doctor is the main organizer of medical care for the population of the district, but he cannot and should not do what doctors of narrow specialties are supposed to do. It is not the local doctor who is obliged to work for doctors of other specialties, but on the contrary, all other specialists, including doctors in functional diagnostics, x-ray, and dental rooms, must provide him with the information necessary for social and hygienic analysis and planning of general treatment and health measures. The local general practitioner must coordinate all work carried out.
The main sections of the work of a local physician-therapist
Therapeutic work
The work of the local therapist is carried out according to the work schedule approved by the administration of the clinic. A rationally designed work schedule allows you to increase the availability of local services to the population of the site. The working day consists of working at the reception for 3-4 hours, answering calls (3 hours) and other types of work (sanitary education work, writing reports, etc.).
Reception of patients is an important part of the work of a local doctor. At the first examination of the patient, the doctor must make a preliminary diagnosis, prescribe examination and treatment.
A large place in the activities of a local general practitioner is occupied by medical care for home calls. On average, a local doctor’s time spent providing care at home should be 30–40 minutes per patient. It is more difficult to examine patients at home than in a clinic or hospital. Moreover, most calls are made to patients of older age groups. Having examined the patient at home on call, the local doctor must subsequently schedule him to appear for an appointment or, if necessary, actively visit him. Repeated (active) visits, when properly organized, account for up to 70–75% of the total number of calls (a doctor must handle at least 6 calls per day).
The most important part of the work of a local doctor is the preparation and referral of the patient to planned hospitalization. The patient should be examined as completely as possible. Data from the examination, treatment provided and the purpose of hospitalization are entered in form No. 057u-04. The referral from the medical record must include diagnoses of all existing diseases, as well as conditions that require clarification. The diagnosis is written in accordance with the accepted classification, indicating the form of the disease, severity, phase, functional disorders and complications. The main one is indicated first, then the competing and concomitant diseases. In case of emergency hospitalization, fill out a free-form referral on the health care facility form.
Working with accounting and reporting documentation
In his work, the local doctor must use only forms approved by orders of the Ministry of Health: No. 1030 of 10/04/80 “On approval of forms of primary medical documentation of healthcare institutions”, No. 255 of 11/22/04 “On the procedure for providing primary health care citizens eligible to receive the kit social services", etc. The orders contain forms of primary documentation, rules for filling them out and storage periods in a medical institution. Therapists should use the following forms in their work:
| № | Form name | Form number | Shelf life |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 1 | Outpatient medical record | 025у-04 | 25 years |
| 2 | Dispensary observation checklist | 030у-04 | 5 years |
| 3 | Card subject to periodic inspection | 046-у | 3 years |
| 4 | Card of preventive fluorographic examinations | 052-у | 1 year |
| 5 | Vaccination card | 063-u | 5 years |
| 6 | Vaccination log book | 061-у | 3 years |
| 7 | Doctor's appointment voucher | 025-4-у | Year |
| 8 | Doctor's home call book | 031-у | 3 years |
| 9 | Certificate for obtaining a voucher (order No. 256) | 070-у | 3 years |
| 10 | Sanatorium-resort card (order No. 256) | 072-у | 3 years |
| 11 | Medical certificate (medical professional opinion) | 086-у | 3 years |
| 12 | Statistical card for registering final (refined) diagnoses | 025-2-у | Year |
| 13 | Summary record of diseases registered in this institution | 071-у | Year |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 14 | Record of medical visits | 039-u | Year |
| 16 | Referral to ITU (Project No. 77 dated January 31, 2007) | 088/у-06 | 3 years |
| 17 | Referral for hospitalization, rehabilitation treatment, examination, consultation | 057у-04 | |
| 18 | Emergency notice infectious disease, food poisoning, acute occupational poisoning, unusual reaction to vaccination | 058-y | Year |
| 19 | Certificate of temporary disability for students attending vocational schools | 095-у | Year |
| 20 | Journal for recording VK conclusions | 035-у | |
| 21 | Book of registration of certificates of incapacity for work | 036-у | 3 years |
| 22 | Journal of sanitary education work | 038-у | Year |
| 23 | Medical death certificate | 106 | Year |
| 24 | Recipes (order No. 110 dated February 12, 2007) | 107-1/у, | |
| 25 | Referral for hematological analysis | 201 | Month |
| 26 | Referral for analysis | 200 | Month |
| 27 | Referral for biochemical blood test | 202 | Month |
| 28 | Outpatient voucher | 025-12/у | |
| 29 | Passport of the medical district of citizens entitled to receive a set of social services | 030-P/u |
For better control of the entire situation at the site and targeted work planning, the local doctor fills out medical passport (therapeutic) area(form 030-P/u), approved by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 765 dated December 7, 2005 (Appendix No. 2).
The following sections must be highlighted in the passport:
- Characteristics of the medical therapeutic area:
- Population;
- site plan indicating the number of floors of buildings, number of apartments, location of schools, preschool institutions;
- a list of enterprises and institutions indicating the number of employees (lists are updated annually and certified by the administration of the enterprises).
- Characteristics of the attached population:
- age and sex composition of the population;
- working age population (men, women);
- population over 60 years of age (men, women);
- working population (men, women);
- non-working population (men, women);
- pensioners (men, women);
- number of persons with occupational hazards (men, women);
- the number of people belonging to risk groups and abusing alcohol, smoking, drugs (men, women);
- a list of people suffering from socially significant diseases (tuberculosis, diabetes, neoplasms, cardiovascular diseases and damage to the musculoskeletal system).
- Health status and treatment results of the attached population:
- age composition of the population, including able-bodied and disabled men and women;
- dispensary group (age and gender characteristics, movement “D” group, needed medical and recreational activities and received them (outpatient, inpatient treatment, VTMP, treatment in a day hospital, sanatorium treatment);
- number of activities carried out: vaccinations, tests, studies, procedures, consultations;
- the number of persons who received emergency medical care during travel (persons), including those sent to the hospital;
- becoming disabled (total, in the reporting year);
- number of deaths (total, including at home).
The local general practitioner is obliged to correctly draw up medical documentation. An important document is medical card outpatient(form No. 025/u), which is maintained in accordance with the Standard of Medical History of Inpatient and Outpatient Patients, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health of the Trans-Baikal Territory No. 155 dated 02/03/2009. The results of the examination, data on the prescribed treatment and examination are entered into the medical record. The diagnosis must correspond to complaints, objective examination data, and anamnesis. The formulation of the diagnosis is carried out in accordance with the accepted classification, indicating the clinical variant, severity of the course, phase, functional disorders and complications. It is necessary to distinguish the main, competing and concomitant diseases in the diagnosis.
The medical documentation contains information about the patient’s awareness and consent to examination and treatment, confirmed by his signature.
Diseases are coded by a doctor in accordance with ICD 10. Based on the doctor’s note, the nurse fills out a statistical form for each identified disease. If the disease is detected for the first time, the diagnosis is made with a “+” sign. If there is a chronic disease for which the patient was previously observed, the statistical coupon is filled out once a year with a “-” sign.
Statistical coupons(form 025-2/у) are used to record all cases of disease; based on their presence, accounting form No. 071/u is drawn up "Summary list of diseases", based on the results of which morbidity and overall morbidity rates are calculated at each site, department and clinic. The form is prepared quarterly.
Total registered for the first time
identified diseases on site
Incidence = ——————————————- × 1000
Total registered
diseases on site
Total incidence = ————————————— × 1000
Number of people in the area
Doctor's appointment voucher(form 025-4/у) is used for uniform distribution patients and drawing up medical visit records(form No. 039-u), which reflects the time spent on reception and calls, the number of patients received, and other types of work. The form can be completed by a physician or centrally. On a monthly basis, based on data from form No. 039, load indicators at receptions, at home, preventive examinations, locality and activity (percentage of active calls) are calculated.
Number of visits to the local doctor
residents of their area
Locality = ——————————————————- × 100
Total visits to the local doctor
Number of visits Total number of visits to doctors at the clinic
for one = ———————————————————
inhabitants per year Average annual population,
living in the service area
clinics
Number of active visits by residents to their site
Activity = ———————————————————- × 100
Total number of home visits
Hospital-replacing technologies in the work of a local general practitioner
Hospital care is expensive, and according to studies, from 20 to 50% of patients receiving treatment in a hospital are unreasonably sent to hospital and could receive more effective and less expensive care in an outpatient setting. To do this, it is necessary to use hospital-replacing technologies: day hospitals(DS) hospitals and clinics, hospitals at home(SD).
The regulatory document on the organization of DS is the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 438 dated December 09, 1999 “On the organization of activities of day hospitals in medical institutions.”
The local general practitioner uses hospital-replacing technologies in his work, in particular SD, which is created for the treatment of patients with acute and chronic diseases that do not require round-the-clock medical supervision. SD is created for the treatment of patients with follicular tonsillitis (for at least three days), acute mild pneumonia, acute bronchitis, and exacerbation of chronic diseases (hypertension, peptic ulcer, etc.).
A patient with diabetes must undergo an examination (general blood test, urine test, ECG, consultation with the necessary medical specialists), the local general practitioner is obliged to examine the patient in the first days of the illness - daily, then - as needed. Treatment must be comprehensive: procedures are performed at home by a nurse ( different kinds injections, cupping, mustard plasters), massage, exercise therapy, etc. Information about the organization of diabetes is entered into the medical record.
The work of the Board of Directors can be carried out centrally or decentralized. In the first case, the clinic allocates a doctor to service diabetes throughout the entire territory, and he is provided with transport. The normal load is visiting patients at 16 - 18 SD per day. In a decentralized form, each local therapist independently visits patients with diabetes in his or her area every day.
Work ability examination
A local general practitioner is an attending physician who provides medical care to a patient during the period of his observation and treatment in a health care facility. When examining a patient, he solves not only diagnostic and treatment problems, but also determines the possibility of continuing labor activity. He is responsible for the examination of temporary disability and registration of patients for medical and social examination.
Anti-epidemic section of the work of the local service
The local doctor is responsible for carrying out basic anti-epidemic measures. The local therapist must be well versed not only in the issues of diagnosing infectious diseases, but also in matters of epidemiology, since the ability to collect an epidemiological history allows the doctor to recognize the disease on its own. early stages and carry out the necessary measures in a timely manner.
If an infectious disease is suspected, the local general practitioner must notify the management of the clinic, the infectious disease specialist and the authorities. Federal service on supervision in the field of consumer rights protection and human well-being. The patient must be urgently hospitalized, and within 24 hours an emergency notification about an infectious patient (form No. 058/u) must be filled out and submitted. If the patient is not hospitalized, everything necessary is done to prevent the spread of infection (maximum isolation, monitoring of contacts, disinfection). When a patient is hospitalized, the local therapist monitors contacts in the outbreak for the entire incubation period of the disease with the preparation of the necessary documentation.
Preventative work
The local general practitioner pays great attention to preventive work aimed at preventing the occurrence of diseases and increasing the duration and quality of life. For this purpose, preventive examinations of the population are carried out to identify diseases in the early stages (target: tuberculosis, cancer, goiter, etc.) and mandatory preliminary and periodic examinations of workers (excluding exposure to harmful occupational factors).
Preliminary medical examinations upon entry to work are carried out in order to determine the suitability of the health status of the person being examined for the work assigned to him.
The purpose of periodic examinations is to dynamically monitor the health status of workers under conditions of exposure to occupational hazards. Prevention and timely detection of signs of general and occupational diseases that prevent continued work in these conditions, as well as the prevention of accidents. Timely implementation of preventive and rehabilitation measures.
The regulatory documents for this section of work are Order No. 90 of the Ministry of Health dated March 14, 1996 “On the procedure for conducting preliminary and periodic medical examinations of workers and medical regulations for admission to the profession,” Order No. 83 dated August 16, 2004 “On approval of lists of harmful and (or) hazardous production factors and work, during which preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) are carried out, and the procedure for conducting these examinations (examinations).”
The following lists were approved by orders:
- harmful, hazardous substances and production factors, work, the performance of which requires preliminary and periodic medical examinations of workers;
- medical contraindications;
- medical specialists participating in examinations;
- necessary laboratory and functional studies;
- general medical contraindications;
- occupational diseases.
The frequency of periodic inspections is determined by the territorial bodies of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare together with the employer based on the specific sanitary, hygienic and epidemiological situation, but should not be less than once every two years, and for persons under 21 years of age not less than once a year. Workers employed in hazardous industries 5 years or more, medical examinations are carried out by occupational pathology centers.
Medical examinations are carried out by medical institutions licensed for the specified type of activity.
The employer submits a name list of persons subject to inspection, previously agreed upon with the territorial bodies of the Federal Service for Supervision, indicating workshops, hazardous work and factors in medical institution 2 months before the start of the examination.
The chief physician of the healthcare facility approves the composition of the medical commission, the chairman of which must be an occupational pathologist or a doctor of another specialty with training in occupational pathology; members of the commission must also have special training. The commission determines the types and volumes of necessary research, taking into account the specifics of production factors and medical contraindications to work in this specialty.
To undergo the examination, the employee presents a referral issued by the employer, a passport, an outpatient card, and the results of previous examinations.
The main person conducting the examinations is the local doctor. The examination data is entered into the medical record (form No. 025-u). Each doctor taking part in the examination gives his opinion on professional suitability and, if indicated, prescribes therapeutic and recreational measures.
The employee is informed of the results of the medical examination. If signs of an occupational disease are detected in an employee during a medical examination or upon treatment, he is sent by the attending physician, the head of the health care facility or an occupational pathologist in the prescribed manner to the occupational pathology center to clarify the diagnosis.
The final report based on the results of the periodic examination is drawn up by the responsible doctor together with representatives of the Federal Surveillance Service and is submitted to the employer within 30 days.
One of the sections preventive work is vaccine prevention, which is carried out by the district service in accordance with the National Calendar of Preventive Vaccinations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health No. 673 dated October 30, 2007. A card file is created for the entire population of the district, in which data on vaccinations is entered.
Health education and patient education work.
The sanitary and educational work of the local doctor is determined by the needs of improving the health of society. In it, the doctor, with the help of public health activists, must pay attention to the fight against weakness, overeating, smoking, excessive and unnecessary drug therapy, stress, etc.
The responsibilities of a local therapist include teaching patients with socially significant diseases and their relatives in specialized schools.
Medical examination of the population
The preventive section of the work of a local general practitioner includes medical examination, which is an active method of continuous medical supervision monitoring the health status of the population in order to early detection diseases; timely registration; dynamic observation and complex treatment of patients; preventing the development and spread of diseases; maintaining ability to work.
The main purpose of medical examination healthy is to preserve and strengthen their health, ensure proper physical and mental development, Creation normal conditions work and life, preventing the development of diseases, maintaining working capacity.
The purpose of medical examination of patients– prevention of exacerbations and deterioration clinical course diseases, reducing morbidity with temporary disability and preventing disability.
Clinical examination includes:
- annual medical examination with a specified volume of laboratory and instrumental studies;
- additional examination of those in need using all diagnostic methods;
- identification of persons with risk factors contributing to the occurrence and progression of diseases;
- detection of diseases at early stages;
- development and implementation of a set of necessary medical and social measures and dynamic monitoring of the health status of the population.
Clinical examination is carried out in three stages:
Stage 1 – registration: selection of contingents for dispensary observation;
Stage 2 – carrying out the actual dispensary observation and treatment;
Stage 3 – assessment of the effectiveness and quality of medical examination (after three years of observation and treatment).
The formation of dispensary observation groups is carried out in an active (using medical examinations) and passive (by referral, after hospital treatment) way.
The priority groups for registration at the dispensary include disabled people and participants of the Second World War and other military operations, workers of leading industries, transport, agriculture, students of higher and secondary specialized educational institutions, workers of hazardous industries, women of reproductive age and others.
Based on the results of the registration stage, the following should be formed: clinical observation groups(health):
Group 1 – healthy (formed mainly from students, workers in harmful and dangerous industries, women of childbearing age, etc.).
Group 2 – practically healthy people who have suffered acute illnesses in the past or have a chronic disease in stable remission (there has been no exacerbation of the disease for five or more years).
Group 3 – patients with diseases in the stage of compensation, subcompensation, decompensation.
Healthy and practically healthy people should be observed in the prevention department; in the presence of diseases, they should be observed by specialist doctors in the profile of the disease.
Order of the Ministry of Health No. 770 approved instructions for medical examination of healthy people and persons with risk factors in outpatient clinics (Appendix No. 9). The scheme of dynamic observation of patients has been compiled for doctors of all specialties; it includes, in accordance with the nosological form, the frequency of observation, the required volume of laboratory and instrumental studies, examination by specialists, basic medical and health measures, and criteria for the effectiveness of clinical examination.
Preparation of documentation during medical examination
For each dispensary patient, an outpatient medical record (form No. 025-u) and a dispensary observation control card (form No. 030-u) are filled out.
Medical cards must be marked with letters or colors; each card must be marked with the letter “D” and the dispensary observation (health) group must be indicated. When registering, an introductory epicrisis is written (data substantiating the diagnosis, information about the previously conducted examination and treatment, its effectiveness, a plan of treatment and recreational measures is drawn up, repeated appearances are scheduled in accordance with Appendix No. 9 of Order of the Ministry of Health No. 770). After a year of observation, a staged epicrisis is drawn up, in which the attending physician reflects a detailed diagnosis, the dynamics of the condition, the implementation of the examination plan and treatment and recreational measures; on New Year a plan of treatment and recreational activities is drawn up. To facilitate the doctor’s work, unified typographical epicrisis forms are currently used.
For each dispensary patient, a dispensary observation control card is filled out, which is also marked as a medical record, and is used for operational control of work with the dispensary group of patients. The card contains information about the registration of the patient, the timing of planned and actual appearances for dispensary examinations, which makes it possible to call the patient to the doctor on time. Form No. 030/u contains data on planned medical and health-improving activities, and at the end of the observation year a note is made about their implementation.
One patient may have several control cards for the number of etiologically unrelated diseases; they are marked “duplicate”. Control cards facilitate monitoring of patient visits and are stored in a box with 13 compartments (12 months and a cell for control cards of those who did not appear).
Quality indicators
- number of dispensaries in the area, distribution by health groups, number of dispensaries per 1000 population;
- percentage of coverage by dispensary observation of patients by nosological forms from the number of registered patients in a given area (in the clinic):
Total dispensary patients with ulcerative disease
= —————————————————— × 100
Registered patients with ulcerative disease (form 071/у)
100% of the time, patients who have suffered acute pneumonia, follicular tonsillitis, acute glomerulonephritis, acute myocardial infarction, patients with rheumatic fever, systemic diseases connective tissue, chronic atrophic gastritis, diabetes mellitus, COPD, bronchial asthma, etc.;
- timeliness of registration at the dispensary (the number of patients registered within a month from the date of diagnosis or discharge to work, of the total number of newly identified patients);
- completeness of the survey (number of people surveyed out of the number of people in need of survey);
- completeness of implementation of treatment and recreational measures in % (anti-relapse treatment, diet, sanatorium treatment, employment, planned hospitalization)
number of patients who received anti-relapse treatment
= ———————————————————————— × 100
number of patients requiring anti-relapse treatment
Performance indicators
(calculated in the group of patients observed for three or more years)
- dynamics of the condition over the year of observation: improvement, no dynamics,
- deterioration;
- % of patients transferred to the second observation group due to recovery or persistent improvement of condition (there have been no exacerbations for at least five years);
- temporary disability in cases and days (% change compared to the previous year);
- primary disability (per 100,000 workers);
- mortality from the underlying disease.
Additional medical examination
Since 2006, the country has been conducting additional clinical examination (DS) of citizens working in state and municipal institutions in the fields of education, healthcare, social protection, culture, physical culture and sports and research institutions. The procedure and scope of carrying out DD is regulated by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 188 dated March 22, 2006. In 2006, DD was carried out for the above-mentioned contingents aged 35-55 years; since 2007, all workers are subject to DD. DD is carried out by medical specialists using established laboratory and functional tests in the following scope:
Examination by medical specialists:
- therapist (precinct general practitioner, GP),
- endocrinologist,
- surgeon,
- neurologist,
- ophthalmologist,
- urologist (for men),
- obstetrician-gynecologist.
Laboratory and functional studies:
- Clinical blood and urine tests,
- Cholesterol, blood sugar,
- Fluorography once a year,
- Mammography (women 40-55 years old - once every 2 years) or ultrasound of the breast.
The local physician, taking into account the conclusions of medical specialists and the results of the examination, determines the health status of citizens who have undergone DD, and in order to plan further activities distributes into the following groups:
Group I - practically healthy citizens who do not need D-observation, with whom a conversation is held about a healthy lifestyle.
Group II – citizens at risk of developing diseases who need preventive measures. An individual prevention program is drawn up for them, carried out at a health care facility at their place of residence.
Group III – citizens who need additional examination to clarify (establish) the diagnosis (newly diagnosed chronic disease) or treatment on an outpatient basis (acute respiratory disease, influenza and other diseases, after treatment of which recovery occurs) “*”.
Group IV - citizens who need additional examination and treatment in inpatient conditions, who are on D-registration for a chronic disease “*”.
Group V – citizens with newly diagnosed diseases or those being observed for a chronic disease and who have indications for providing high-tech (expensive) medical care “*”.
“*” - additional examination in outpatient and inpatient settings is not included in the scope of DD.
The institution that carried out the DD not at the citizen’s place of residence transfers the “DD Registration Card” with the results of the examination to the health care facility at the citizen’s place of residence.
Based on information about the results of the DD, the local physician (GP), who carries out dynamic monitoring of the citizen’s health status, determines the required scope of additional examination, refers him for further treatment and carries out D-monitoring for the chronic disease.
Medical examination of women of childbearing age with extragenital pathology, is carried out in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated February 10, 2003 No. 50 “On improving obstetric and gynecological care in outpatient clinics” (Appendix 2, section 3 “Pregnancy and extragenital pathology”). The order contains a dynamic observation scheme indicating the duration of hospitalization.
Dispensary observation of patients with occupational diseases regulated by Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 555 dated September 29, 1989 “On improving the system of medical examinations of workers and individual drivers Vehicle" The general practitioner carries out observation in accordance with the approximate scheme given in Appendix No. 7 “Regulations on the procedure for medical examination of patients with occupational diseases.”
Disabled people and WWII participants observed in accordance with Federal Law dated January 12, 1995 No. 5-FZ “On Veterans”.
Medical examination of persons exposed to radiation as a result of the disaster Chernobyl nuclear power plant , is carried out on the basis of the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 293 dated October 3, 1997 “On improving the medical examination of persons exposed to radiation as a result of the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant.” This order regulates the frequency and scope of clinical examination of this category of persons.
Work of a local physician-therapist as part of the ATPC
Due to the current unfavorable demographic situation in the country the local physician must Special attention devote to work to preserve the health of women of childbearing age, which is carried out as part of local obstetric-therapeutic-pediatric complexes (ATPC). The local ATPC includes 4-5 therapeutic, 2-3 pediatric and 1 obstetric department, united on a territorial basis. In all medical institutions, doctors work according to an agreed schedule at the same time. The local therapist (general practitioner) must know what somatic pathology adversely affects reproductive function women, their state of health during pregnancy, intrauterine development fetus and the condition of the child in the postnatal period. He is obliged to transmit information about the state of women’s health to the antenatal clinic and organize the health improvement of women of fertile age.
All women of fertile age with extragenital pathology should be under dispensary observation; the tactics for their management are determined by Order of the Ministry of Health No. 50 of February 10, 2003 “On improving obstetric and gynecological care in outpatient clinics” (Appendix 2, section 3 “Pregnancy and extragenital pathology").
On the basis of clinics for adults, there is an advisory and expert commission (AEC) for women of childbearing age, the purpose of which is to control the quality of medical examination of women and the implementation of the plan of treatment and recreational activities. All women who come under the supervision of clinic doctors (transferred for observation upon reaching 18 years of age from pediatric health care facilities, who have changed their place of residence, etc.) must, after further examination, be submitted to the CEC to clarify their health group and the plan of treatment and recreational measures.
Examination of healthy pregnant women during adult clinic carried out upon registration and at 30 weeks of pregnancy (when applying for maternity leave), the results of the examination are transferred to the antenatal clinic. The local service also provides postpartum patronage with a set of necessary medical and rehabilitation measures.
The local service, together with employees of family planning centers, should carry out work on timely, high-quality contraception, especially for women with extragenital pathology. If medical contraindications to pregnancy are identified, the issue is resolved together with doctors antenatal clinics(on CEC for pregnant women) in accordance with the List of medical indications for artificial termination of pregnancy, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health No. 736 dated December 3, 2007, and social indications (RF Government Decree No. 485 dated August 11, 2003 “On the list of social indications for artificial termination pregnancy").
Registration of patients for sanatorium-resort treatment
An important issue in the activities of a local doctor is the selection and referral of patients for sanatorium-resort treatment. The regulatory document for this section of work is Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 256 dated November 22, 2004 “On the procedure for medical selection and referral of patients for sanatorium-resort treatment” with amendments approved by Order of the Ministry of Health No. 3 dated January 9, 2007. Medical selection and the referral of patients in need of sanatorium-resort treatment is carried out by the attending physician and the head of the department (if there is a benefit, the attending physician and the chairman of the VC).
If there are indications (healthy people cannot recommend treatment at a resort) and there are no contraindications for sanatorium-resort treatment, the doctor issues the patient a certificate (070/u-04) about the need for treatment, which is valid for 6 months, which is noted in the outpatient’s medical record. Beneficiaries are issued a certificate for obtaining a voucher by the VC, and disabled people - if there is a recommendation in the individual rehabilitation program issued by the ITU authorities.
In complex and conflict cases, upon the recommendation of the attending physician and the head of the department, a conclusion on the indications for sanatorium-resort treatment is issued by the Institutional Clinical Hospital.
Patients with concomitant diseases or age-related health problems for whom sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated, in cases where a trip to remote resorts can adversely affect general condition health, should be sent to nearby sanatorium institutions.
When receiving a voucher (course), the patient is obliged to visit the attending physician no earlier than two months before the start of its validity period for the necessary additional examination. Attending physicians and heads of departments must be guided by the following mandatory list of diagnostic studies and consultations with specialists, the results of which must be reflected in the sanatorium-resort card (form 072/u-04):
- clinical blood and urine analysis;
- fluorography;
- for diseases of the digestive system - X-ray examination(if more than 6 months have passed since the last examination), ultrasound, endoscopy;
- in necessary cases, additional studies are carried out to clarify the diagnosis: biochemical, instrumental and others;
- when sending women to the resort, a conclusion from an obstetrician-gynecologist is required; for pregnant women, an additional exchange card is required;
- if there is a history of neuropsychiatric disorders, a psychiatrist’s opinion;
- with the main or concomitant diseases(urological, skin, blood, eyes and others) - the conclusion of relevant specialists.
Examination data and research results are entered into the outpatient card. The health resort card is certified by the head of the department. If a person entitled to a set of social services is registered for treatment, the sanatorium-resort card is certified by the attending physician, the head of the department or the chairman of the VC.
If contraindications to treatment are identified in the patient during the first five days of his stay at the resort, the VC of the resort (sanatorium) decides on the possibility of the patient’s continued stay there, transfer to a hospital or transportation to his place of residence. When a patient makes a claim against a healthcare facility, all material costs are reimbursed by the attending physician.
Work on providing medications to patients
A responsible section of the work of a local therapist is the work of prescribing drug therapy and prescribing medications, including in the system of additional drug supply (DLO).
Medicines are prescribed by the doctor who is directly caring for the patient (the attending physician). In cases of a typical course of the disease, the prescription of drugs is carried out based on the severity and nature of the disease, in accordance with the standards of medical care and the list of vital and essential drugs approved by the Government of the Russian Federation, as well as the list of drugs dispensed to persons entitled to receive state social assistance.
The main regulatory documents regulating drug provision are orders of the Ministry of Health and social development No. 785 dated 12/14/05 “On the procedure for dispensing medicines” and No. 110 dated 02/12/07 “On the procedure for prescribing and prescribing medicines and products medical purposes and specialized products therapeutic nutrition" Order No. 110 approved prescription forms and rules for filling them out.
Special prescription form for narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances is produced on pink paper with watermarks and has a serial number. It must be filled out legibly and clearly by the doctor; corrections are not allowed. Medicine is written out on Latin, the amount of the drug is indicated in words, recommendations for use are indicated in Russian and must be specific. The prescription indicates the number of the outpatient’s medical card (number of “attachment” to the pharmacy institution, the full last name, first name, patronymic of the patient and the doctor. The prescription is signed by the doctor and certified by his personal seal, the chief physician of the health care facility (his deputy or head of the department) and certified by a round seal Health care facility. The prescription must be stamped with the details of the health care facility. Only one drug is prescribed on the form (a narcotic or psychotropic drug included in List II of the List of narcotic drugs, psychotropic substances and their precursors subject to control in the Russian Federation. The validity period of the prescription is 5 days.
Rules for the storage and accounting of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances, estimated standards for the need for them, provisions for write-off and destruction are regulated by Order No. 330 of November 12, 1997 (as amended by Orders No. 2 of January 9, 2001 and No. 205 of May 16, 2005 G.).
On the prescription form (form No. 148-1/u-88) Schedule III psychotropic substances are prescribed; other drugs subject to subject-quantitative accounting, anabolic steroids. The prescription form has a series and number. Only one name of the drug can be written on the form; corrections are not allowed. The prescription contains the full last name, first name and patronymic of the patient, his age, address (or medical card number) and the full last name, first name and patronymic of the doctor. The prescription is signed by the doctor and certified with his personal seal and the seal of the health care facility “For prescriptions”. The prescription must be stamped with the details of the health care facility. The validity period of the prescription (10 days, 1 month) is indicated by striking through.
On recipe form No. 107/у all drugs are prescribed, with the exception of narcotic, psychotropic substances, drugs subject to subject-quantitative accounting, anabolic steroids. No more than three drugs are prescribed on one form. Requirements for filling out a prescription are the same as in previous cases. The prescription must be stamped with the details of the health care facility. The prescription is signed by the doctor and certified with his personal seal. The validity period of the prescription (10 days, 2 months, year) is indicated by striking through.
Recipe form No. 148-1/u-04 is intended for prescribing drugs and medical products included in the lists of drugs sold free of charge or at a discount. The prescription form is issued in triplicate, each with a single series and number. When filling out the form, indicate the full last name, first name, patronymic of the patient, date of birth, SNILS, medical insurance policy number, address or medical card number, disease code according to ICD X. It is allowed to fill out a prescription using a computer. The prescription is signed by the doctor, certified by his personal seal and the seal of the healthcare facility “For prescriptions”. When a drug is prescribed, by decision of the medical commission (MC), a special stamp is placed on the back of the form. According to the decision of the High Commission, drugs are prescribed in cases of simultaneous prescription of five or more drugs; prescription of narcotic drugs, psychotropic substances; Medicines subject to subject-quantitative accounting; anabolic steroids.
Prescription of “preferential” drugs is carried out in accordance with the annually updated List of drugs dispensed by prescription from a doctor (paramedic) when providing additional free medical care to certain categories of citizens entitled to receive state social assistance.” Currently, the current regulatory document is Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 665 dated September 18, 2006.
Population groups:
- Participants and disabled people of the Second World War, combat operations to defend the country.
- Parents and wives of military personnel who died defending the country or performing other military service duties.
- Citizens who worked during the siege in Leningrad, awarded the medal “For the Defense of Leningrad”, citizens awarded the badge “Resident of besieged Leningrad”.
- Former minor prisoners of concentration camps and ghettos created by the Nazis during World War II.
- Citizens from among former internationalist soldiers who took part in hostilities in Afghanistan and on the territory of other countries.
- Disabled people, disabled children.
- Citizens exposed to radiation as a result of the Chernobyl accident, the Techa River, Mayak Ave. and others
Disease categories(regional benefit): cerebral palsy, AIDS, HIV-infected, oncological diseases, acute intermittent porphyria, cystic fibrosis, hematological diseases, hematological malignancies, cytopenia, hereditary hemopathy, radiation sickness, tuberculosis, bronchial asthma, rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, SLE, ankylosing spondylitis, myocardial infarction (first 6 months), condition after valve replacement, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, myopathy, etc.
Analysis of the activities of a local doctor
Performance indicators:
- Appeal for medical care in the office and at home;
- Morbidity in the area: primary, general;
- Infectious morbidity;
- Incidence of illness with temporary disability, compliance with the terms of temporary disability;
- Fluorographic examination coverage;
- Efficiency of clinical examination (according to established criteria);
- Hospitalization rate of patients;
- Mortality at the site;
- Preventive work: vaccinations, targeted examinations, sanitary education, etc.;
- Incidence of tuberculosis and cancer pathology;
Each case is assessed by experts
- sudden death;
- deaths at home of people of working age;
- discrepancies in diagnosis during hospitalization;
- discrepancies in terms of temporary disability of MES;
- temporary disability for more than 120 days;
- justified complaints from patients;
- issuing preferential prescriptions through VK;
- primary access to disability;
- advanced forms of cancer, tuberculosis, diabetes.
Criteria for the effectiveness of the work of a local physician-therapist
The assessment of the effectiveness of the work of a local general practitioner is carried out according to the criteria approved by Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 282 of April 19, 2007 “On approval of criteria for assessing the effectiveness of the activities of a local general practitioner.”
When assessing work efficiency, the main accounting documents are:
- outpatient medical record (025/у-04),
- passport of the medical district (030/u-ter),
- record of medical visits to the APU, at home (039/u-02),
- control card of dispensary observation (030/у-04),
- outpatient card (025-12/у),
- card of a citizen entitled to receive a set of social services for recording the dispensing of medicines (030-L/u).
Criteria for assessing performance:
- stabilization or reduction in the level of hospitalization of the attached population;
- reducing the frequency of emergency calls to the assigned population;
- increasing the number of visits to the assigned population for preventive purposes;
- complete coverage of treatment and preventive care for persons under dispensary observation;
- complete coverage of preventive vaccinations of the attached population against diphtheria (at least 90% in each age group), against hepatitis B (at least 90% of women under 35 years of age), against rubella (at least 90% of women under 25 years of age), against influenza (fulfillment of the plan).
- stabilization or reduction of the mortality rate of the population at home due to cardiovascular diseases, tuberculosis, diabetes;
- reduction in the number of people who died at home from diseases of the circulatory system under the age of 60 and were not observed for last year life;
- stabilization of the incidence of social diseases: tuberculosis, hypertension, diabetes, cancer.
- complete coverage of dynamic medical monitoring of the health status of certain categories of citizens entitled to receive a set of social services, including drug provision, sanatorium-resort and rehabilitation treatment;
- the validity of prescribing medications and compliance with the rules for discharge to patients, including those entitled to receive a set of social services.
Specific indicators of the criteria for assessing the effectiveness of the work of a local general practitioner are determined by the head of a health care institution, taking into account the size, density, age and sex composition of the population, morbidity levels, geographic and other features.
The performance indicators of local doctors are used to form the performance indicators of the clinic as a whole:
Key performance indicators of the clinic
- Indicators allowing to assess the state of organization of medical care to the population:
- the average number of visits to the clinic per resident living in the service area of the clinic;
- locality of service to the population in the clinic and at home;
- proportion of active home visits;
- share of medical services provided in the compulsory health insurance (CHI) system (%).
- Indicators allowing to evaluate the organization and results of preventive medical examinations of the population:
- implementation of the plan for preventive examinations of the population;
- morbidity according to preventive examinations per 100 (1000) examined persons.
- Indicators of the quality and effectiveness of clinical examination:
- coverage of the population with medical examinations by clinical observation groups;
- indicator of the morbidity structure of persons under dispensary observation;
- completeness of dispensary observation coverage;
- indicator of compliance with the terms of dispensary examinations;
- indicator of the completeness of medical and recreational activities;
- clinical examination effectiveness indicators.
- Indicators that allow you to evaluate the quality of the clinic’s work and the level of staff training: The quality of work of a clinic as a whole can be characterized by the dynamics of the morbidity level of the population over several years, the percentage of coincidence of diagnoses between the clinic and the hospital, etc.
Organization of the work of a local SSMU physician-therapist, Department of Polyclinic Therapy
Approximate organizational structure city clinic; management of the clinic; Registry; Prevention Department; Treatment and prevention units; Auxiliary diagnostic units; An office for processing medical documentation using sound recording equipment; Accounting office and medical statistics; Administrative and economic part of SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy

Regulations on the organization of activities of a local general practitioner These Regulations regulate the activities of a local general practitioner; Specialists with a higher medical education in the specialty “General Medicine” or “Pediatrics” and a certificate of a specialist in the specialization “Therapy” are appointed to the position of local general practitioner; The local physician is guided by the legislation of the Russian Federation, regulatory legal acts of the federal executive body in the field of healthcare; A local physician carries out his activities to provide primary health care to the population in medical organizations; Remuneration for the work of a local therapist is carried out in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy

Responsibilities of a local general practitioner Formation of a medical district from the population attached to it; Implementation of sanitary and hygienic education, consulting on the formation of a healthy lifestyle; Implementation of preventive measures to prevent and reduce morbidity, identification of early and latent forms of diseases, socially significant diseases and risk factors; Studying the needs of the population it serves for health-improving activities and developing programs for these activities; Carrying out dispensary observation, including those entitled to receive a set of social services, in the prescribed manner; Providing emergency medical care to patients in case of acute diseases, injuries, poisoning and other emergency conditions; SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy

Referring patients for consultations with specialists, including for inpatient and rehabilitation treatment for medical reasons; Organization and implementation of anti-epidemic measures and immunoprophylaxis in the prescribed manner; Carrying out examinations of temporary disability in the prescribed manner and preparing a document for referral to a medical and social examination; Issuing opinions on the need to refer a patient for medical reasons to sanatorium treatment; Interaction with medical organizations of the state, municipal and private healthcare systems; Maintaining medical records in the prescribed manner, analyzing the health status of the attached population of SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy Responsibilities of a local therapist

The rights of a local physician-therapist To establish a diagnosis based on clinical observations, data from clinical and laboratory diagnostic methods; Carry out diagnostics, treatment and rehabilitation of therapeutic patients in the volumes stipulated by the organizational and administrative documents of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation; Take part in meetings, seminars, scientific and practical conferences and congresses; Be a member of professional and other public organizations; Make proposals on issues of protecting and promoting public health to higher health authorities; Participate in scientific research and use archival materials for it; Visit enterprises, institutions and organizations in order to study the working conditions of workers from among the population served, SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy

Indicators of the work of the local therapist Demographic and social characteristics of the district; Performance indicators of the local general practitioner; General and primary morbidity by main classes of diseases per year (per 1000 population); Number of patients with acute heart attack myocardium, stroke, with pneumonia, primary cancer patients and patients with diabetes, infectious. Average length of stay on sick leave for acute and chronic diseases; Number of emergency, planned and repeat hospitalizations per 1 thousand population; Number of patients treated in day hospital and hospital at home; Indicators of general and primary disability, their causes; Mortality in the area, their causes; Medical and recreational activities among WWII participants; The number of vaccinated ADSM at the site of SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy

Registration forms 1.Passport of the medical site f.030/u-ter. 2. Outpatient medical record f.025/u Control card of dispensary observation f.030/u Prescription form f.148-1/u-04, 107/u. 5. Journal of registration of prescription forms form 148-1/u Card of preventive fluorographic examinations f.052/u. 7. Card of preventive vaccinations f.063/u. 8. Journal of preventive vaccinations f.064/u. 9. Coupon for an appointment with a doctor f.025-4/u Book of recording of doctor's home calls f.031/u. 11.Certificate for obtaining a trip to sanatorium-resort establishment f.070/u. 12. Sanatorium and resort card for adults and teenagers f.072/u. 13. Medical certificate (for those traveling abroad) f.082/u. 14.Medical certificate (medical professional opinion) 086/у. 15. Notebook for recording work at home for a district police officer nurse f.116/at SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy

16.Statistical coupon for registration of final diagnoses of the patient. 17. Diary of a doctor at the clinic f.039/u. 18. Referral for hospitalization, examination, consultation f.057/u Referral to MSEC f.88/u. 20. Extract from the medical record of an outpatient, f.027/u. 21. Emergency notification of an infectious disease, food poisoning, acute occupational poisoning, unusual reaction to vaccination f.058/u. 22.Certificate of temporary disability of students attending vocational schools f.095/u. 23. Book of registration of certificates of incapacity for work f.036/u. 24. Journal of sanitary educational work f.038-0/u. 25.Medical death certificate f.106/u. 26. Referral for tests to F.F. 01/у, 202/у, 204/у, 207/у. 27. Results of analysis by F.F. 209/у-246/у. 28. Card of registration of additional medical examination of a working citizen f.131/u-DD SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy Registration forms

Regulations on day care in polyclinics Day care in a polyclinic is organized for the hospitalization of patients with acute exacerbation of chronic and chronic diseases; The capacity of hospitals is determined individually in each specific case by territorial health authorities; Funding for a hospital is provided for in the budget of the institution within which it is organized; The operating hours of the hospital are determined by the head of the institution; The selection of patients for treatment in a hospital is carried out by local therapists; A doctor working in a day hospital keeps diary entries in the outpatient card; Working patients undergoing treatment in a day hospital are issued sick leave on a general basis, SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy 10

Indications for referral to a day hospital Acute focal pneumonia of mild severity; Chronical bronchitis in the acute stage without severe respiratory failure; Bronchial asthma of moderate severity without severe respiratory failure; Hypertension stage 1-2; Angina pectoris of FC 2 and 3 without pronounced deterioration on the ECG; Chronic heart failure 1 and 2 – Art. A; Atherosclerotic and post-infarction cardiosclerosis without acute rhythm disturbances; Vegetative-vascular dystonia; Myocardial dystrophy; Biliary dyskinesia; Chronic prostatitis, prolonged course; Chronic colitis SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy 11

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy 12 Current issues of additional drug provision

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy13 Increasing the availability of modern effective medicines when providing outpatient medical care to certain categories of citizens entitled to receive state social assistance Reducing the population's need for unreasonably expensive inpatient medical care as a source of free medicines Effective use of bed capacity and time spent in hospital Freeing up healthcare resources for modernization, improving the quality of medical care, introducing new diagnostic and treatment methods. Goal of the program

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy 14 Patient health care facility Pension Fund AOFOMSDZO Supplier winner Pharmacy warehouse PHARMACY

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy15 Procedure for information exchange Order of DZO / AOFOMS g / 91-0 On approval of the procedure for exchanging information on additional drug provision for certain categories of citizens and provisions on the format of files for exchanging information on additional drug provision for certain categories of citizens

SSMU, department of Polyclinic Therapy16 Monitoring of the program (federal and regional beneficiaries) Register of beneficiaries Register of medical workers who have the right to prescribe preferential medications. Register of health care facilities and dispensing points for subsidized drugs Monitoring of services. preferential prescriptions Monitoring of prescriptions issued in health care facilities Financial monitoring

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy17 Organizational measures The list of health care facilities and medical specialties in the register has been shortened The list of pharmacies has been revised The financial limits of medical institutions and health care institutions have been determined The procedure for generating an application has been approved Citizens suffering from the most financially costly nosologies (diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis, oncohematological diseases, etc.) .) formation of registers calculation of the volume of financing formation of an application for medicines

SSMU, department of Polyclinic Therapy 18 Formation of an application for medicines from health care facilities MO SDC State Joint Stock Company "Pharmacy" Doctor Software product Program R+ Formation of an application Monitoring the discharge of health care facilities Pharmacy

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy19 Patient Health Institution Pension Fund AOFOMSDZO Supplier Winner Pharmacy Warehouse PHARMACY Monitoring of the program problem Management decision Program monitoring

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy 20 Additional medical examination of the working population Priority: Development preventive direction medical care

SSMU, department of Polyclinic Therapy21 Main goals of medical examination Early detection and effective treatment of diseases that are the main cause of mortality and disability of the working population of the country (diabetes mellitus, cancer, tuberculosis, cardiovascular diseases, diseases of the musculoskeletal system) Preservation of the labor potential of citizens, extension of the period active labor activity Creation of a health passport for the working population

SSMU, department of Polyclinic Therapy22 Programs for additional medical examination of the working population Additional medical examination of workers in the public sector (education, healthcare, social protection, culture, physical culture and sports and those working in research institutes) In-depth medical examinations of workers engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous production factors

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy 23 Population working in budgetary sphere in the Arkhangelsk region is a person Working citizens of budgetary institutions Institutions in the field of education Institutions in the field of healthcare Institutions in the field of social services Institutions in the field of organization and recreation, entertainment, culture and sports Institutions in the field of scientific research and development

SSMU, department of Polyclinic Therapy 24 Regulatory documents Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2006 860 Orders of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated January 17, 2007 47 and August 9, 2007 537 Order of the head of the administration of the Arkhangelsk region dated May 2, 2007 353r Order of the regional health department and AOFOMS dated February 27, 2007 29-0/29 (list of health care facilities) Order of the regional health department and AOFOMS dated April 19, 2007 53-0/55-0 (monthly estimated number)

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy 25 Conditions for additional medical examination Municipal health care institutions providing primary health care are involved Availability of a license for medical activities, including work and services in the specialties of “surgery”, “ophthalmology”, “endocrinology”, “neurology”, “urology”, “ obstetrics and gynecology”, “therapy”, “radiology”, “clinical laboratory diagnostics” Availability of a separate current account for transferring funds for payment and a financing agreement with the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund for expenses for carrying out DD of citizens Funds received by health care facilities for carrying out DD of working citizens are sent for payment labor of medical workers involved in medical examinations and the purchase of consumables.

SSMU, department of Polyclinic Therapy 26 Standard of medical examination Examination Fluorography 1 time in 2 years Mammography (1 time in 2 years) or ultrasound of the mammary glands for women over 40 years old Electrocardiography General blood test General urine test Blood cholesterol Blood sugar Examination of specialists Local therapist or general practitioner practices Gynecologist or urologist (for men) Neurologist Surgeon Oculist Endocrinologist Cost standard per employee in 2008 rub.

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy 27 Additional medical examination of the population 2007 The age limit for working citizens was abolished. The cost standard for one worker was established in the amount of 540 rubles. Increasing the volume of medical examinations The duration of research has been reduced to 3 months. Registration and reporting forms have been approved. The estimated number of citizens subject to DD in 2008 in the Arkhangelsk region is planned to carry out medical examination of people, the estimated amount of funding will be 18 thousand rubles.

SSMU, department of Polyclinic Therapy 28 Organization and conduct of DD in 2007 A list of health care facilities has been determined (21) Lists of budgetary institutions and name lists of employees have been prepared. AOFOMS agreements have been concluded with health care facilities. A monthly schedule for carrying out DD has been drawn up. The principles of medical examination have been determined (territorial or territorial-shop) Licensing of health care facilities to comply with the DD standard Control and monitoring of DD is organized Submission of register accounts to the AOFOMS

SSMU, department of Polyclinic Therapy 29 Participate in the conduct of DD 21 health care facilities of municipalities: Arkhangelsk (6 health care institutions) Severodvinsk (3 health care institutions) Novodvinsk Kotlas Koryazhma Mirny Velsky district Vilegodsky district Krasnoborsky district Lensky district Mezensky Nyandoma district Onega district Kholmogory district 10 out of 21 health care facilities can meet the entire DD standard

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy 30 Problems during additional medical examination: Lack of specialists (endocrinologists, urologists) in the regions Lack of licenses to provide individual species medical care Lack of a software product for recording DD Increased workload on clinics Insufficient motivation of employers and employees Impact of long-term leave of absence for certain categories of citizens (teachers, doctors, etc.)

SSMU, department of Polyclinic Therapy 31 Conducting DD depending on the field of activity March-August 2007 Subject to DD Reviewed DD coverage level (%) Education (M 80) ,3 Health care (K 85.1 - 85.14) ,3 Provision of social services (M 85.3) , 8 Activities for organizing recreation, entertainment, culture and sports (O 92) .6 Scientific research institutions (K 73) 700 Total 4

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy32 Results of additional medical examination for March-August: distribution by health status groups (%)

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy33 Results of additional clinical examination for March-August Diseases were identified for the first time, of which 14 (0.12%) were at a late stage (0.6 diseases per one past DD)

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy 34 First identified: 59 cases of diabetes mellitus 89 cases of coronary artery disease and 458 hypertension 8 malignant neoplasms(all in the early stages) and 293 benign Based on the results of additional. medical examination: 1998 employees (9.8%) were taken under clinical observation 31 people were sent to hospitalization 1438 people (7.1%) need sanatorium treatment 6 people need VTMP

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy 35 Diseases first identified in late stages- 12: illness endocrine system– 4, incl. diabetes mellitus – 1 (Kholmogory district) diseases of the circulatory system – 2 diseases of the digestive system – 1 disease genitourinary system– 5 Diseases detected within 6 months. after passing DD - 64: diseases of the musculoskeletal system - 13 diseases of the circulatory system - 12 diseases of the endocrine system - 11 diseases of the genitourinary system - 10 diseases of the digestive system - 7 diseases of the blood - 5

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy 36 Tasks when conducting additional medical examinations for health care facilities Strict adherence to the schedule for conducting DD Concluding contracts for missing specialists with other municipalities. and government medical institutions Organization of on-site forms of work, changes in the work schedule of APU Licensing of health care facilities to meet the DD standard Staffing of vacant medical positions, disaggregation of medical areas Monitoring and control of DD Timely submission of register accounts to the AOFOMS Control of the distribution of financial resources Implementation of plans for health-improving activities of citizens

SSMU, department of Polyclinic Therapy 37 Financing of in-depth medical examinations in 2007 (regulatory documents) Federal. Law of December 19, 2006 234-FZ “On the budget of the Social Fund. fear. RF for 2007 "Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 30, 2006 859 "On financial procedures. in 2007, conducting in-depth medical examinations of workers" Order of the Ministry of Health and Social. Development of the Russian Federation dated January 11, 2007 23 “On approval of the Rules for financing in 2007 for conducting in-depth medical. inspections of workers engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous production factors" (registered with the Ministry of Justice on February 20) Order of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation dated February 27, 2007 62 "On the organization of the work of the Social Insurance Fund. insurance of the Russian Federation for financing in 2007 the conduct of in-depth medical examinations of workers engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous production factors" Order of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation dated February 27, 2007 63 "On approval of the register containing information on the results of in-depth medical inspections of workers engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous production factors"

SSMU, Department of Polyclinic Therapy 38 Increase in the number of visits for preventive purposes In the Arkhangelsk region - 3.5%, including to local therapists - 24.3% In the North-Western federal district– 5.2% In the Russian Federation – 4.9%

Precinct is the territorial principle of medical care for the population. Working hours of local doctors. Dispensary method of work of a local doctor and the main indicators of performance assessment.
Therapeutic areas are formed based on 1,700 residents aged 18 years and older. (pediatric - based on 800 children and adolescents under the age of 18; obstetric and gynecological - per 6,000 adults or (if the population is over 55% women) based on 3,300 women per site.)
Regulations on the organization of activities of a local physician-therapist
· Specialists with a higher medical education in the specialty “General Medicine” or “Pediatrics” and a certificate of a specialist in the specialization “Therapy” are appointed to the position of local general practitioner;
· The local physician is guided by the legislation of the Russian Federation, regulatory legal acts of the federal executive body in the field of healthcare;
· A local physician carries out his activities to provide primary health care to the population in medical organizations;
· Remuneration for the work of a local therapist is carried out in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Responsibilities of a local physician:
· Formation of a medical area from the population attached to it;
· Implementation of sanitary and hygienic education, consulting on the formation of a healthy lifestyle;
· Implementation of preventive measures to prevent and reduce morbidity, identification of early and latent forms of diseases, socially significant diseases and risk factors;
· Studying the needs of the population it serves for health-improving activities and the programs being developed for carrying out these activities;
· Carrying out dispensary observation, including those entitled to receive a set of social services, in the prescribed manner;
· Providing emergency medical care to patients in case of acute diseases, injuries, poisoning and other emergency conditions;
· Referring patients for consultations with specialists, including for inpatient and rehabilitation treatment for medical reasons;
· Organization and implementation of anti-epidemic measures and immunoprophylaxis in the prescribed manner;
· Carrying out examinations of temporary disability in the prescribed manner and drawing up a document for referral to a medical and social examination;
· Issuing opinions on the need to refer a patient for medical reasons to sanatorium-resort treatment;
· Interaction with medical organizations of the state, municipal and private healthcare systems;
· Maintaining medical records in the prescribed manner, analyzing the health status of the assigned population.
· Local general practitioners, as a rule, have the greatest number of visits on Mondays and Fridays, so their work schedules on these days of the week may allow 4-4.5 hours to see patients. total duration work shift up to 5.5-6.5 hours.
On days of the week with more low level attendance (Tuesday, Thursday), other types of activities should be planned: medical examinations, preventive, sanitary and educational work, etc. The number of visits to patients at home by local doctors should also be established based on specific conditions, depending on the size of the population and the length of the area. By establishing a differentiated number of work hours and the number of home visits for local doctors, it is necessary that the overall monthly balance of working time be within the established standards. Required condition When drawing up any schedule, there should be a maximum opportunity to provide routine medical care to workers during their non-working hours.
As a result of differentiation During the appointment, the therapist has the opportunity to pay more attention to the primary patient. This organization of reception helps improve the quality of medical care for the population.
Based on the specific work schedule of each doctor, you can calculate annual load - function of a medical position. For a local therapist, this workload is usually calculated from 3 hours of work in a clinic and 3 hours of work at a site serving patients at home, taking into account the number of working hours per day and the number of working days per year. A local doctor can provide assistance to about 6 thousand patients during the year. 30 minutes daily are allocated for sanitary education and preventive work.
Dispensary method is an active method of dynamic monitoring of the health status of the population (healthy and sick) with the aim of early detection of diseases, registration and comprehensive treatment of patients, carrying out measures to improve working and living conditions, preventing the occurrence and spread of diseases, and strengthening working capacity.
The goals of the dispensary method of service are:
1. prevention of diseases (primary or social-hygienic prevention)
2. maintaining the ability of patients to work, preventing complications, exacerbations, crises (secondary or medical prevention)
To achieve this goal, the dispensary method involves carrying out the whole system events:
1. formation of contingents (healthy and sick) for dispensary registration, dynamic observation and carrying out planned medical, health-improving and preventive measures among them
2. assessment of the health status of each person and provision of systematic dynamic medical supervision
Stages of medical examination:
1st stage. Registration, examination of the population and selection of contingents for registration at the dispensary.
A) census of the population by area by conducting an average census medical worker
B) survey of the population to assess health status, identify risk factors, and early detection of patients.
Identification of patients is carried out during preventive examinations of the population, when patients seek medical care in health care facilities and at home, during active calls to the doctor, as well as during special examinations regarding contacts with an infectious patient.
2nd stage. Dynamic monitoring of the health status of those being examined and carrying out preventive and therapeutic measures.
Dynamic observation of the person being examined is carried out differentiated according to health groups:
A) monitoring of healthy people (group 1) - carried out in the form of periodic medical examinations. Mandatory populations undergo annual examinations according to the plan within the established time limits. In relation to other contingents, the doctor must make the most of any patient’s appearance at the medical facility. In relation to this group of the population, health-improving and preventive measures are carried out aimed at preventing diseases, promoting health, improving working and living conditions, as well as promoting a healthy lifestyle.
B) monitoring of persons classified in group 2 (practically healthy) is aimed at eliminating or reducing risk factors for the development of diseases, correcting hygienic behavior, increasing the compensatory capabilities and resistance of the body. Monitoring patients who have suffered acute diseases is aimed at preventing the development of complications and chronicity of the process. The frequency and duration of observation depend on the nosological form, the nature of the process, possible consequences(after acute tonsillitis, the duration of medical examination is 1 month). Patients with acute diseases that have a high risk of chronicity and development are subject to dispensary observation by a general practitioner. severe complications: acute pneumonia, acute tonsillitis, infectious hepatitis, acute glomerulonephritis and others.
C) observation of persons classified in group 3 (chronic patients) is carried out on the basis of a plan of treatment and health measures, which provides for the number of clinical visits to the doctor; consultations with specialist doctors; diagnostic studies; drug and anti-relapse treatment; physiotherapeutic procedures; physical therapy; dietary food, Spa treatment; sanitization of foci of infection; planned hospitalization; rehabilitation measures; rational employment, etc.
3rd stage. Annual analysis of the state of dispensary work in health care facilities, assessing its effectiveness and developing measures to improve it.
Carrying out clinical examination of the population is regulated by the following documents:
1. Order of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus No. 10 dated January 10, 1994 “On mandatory medical examinations of workers employed in hazardous and hazardous conditions labor" (Appendix 1).
2. Order of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus No. 159 dated October 20, 1995 “On the development of integrated prevention programs and improvement of the clinical examination method” (Appendix 2).
3. Order of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus No. 159 dated June 27, 1997 “On the implementation of the program for the integrated prevention of non-communicable diseases (CINDI) in the Republic of Belarus.”
Statistical analysis of dispensary work is carried out based on the calculation of three groups of indicators:
Indicators characterizing the organization and volume of clinical examination;
Indicators of the quality of clinical examination (activity of medical supervision);
Indicators of clinical examination effectiveness.
A) indicators of the volume of clinical examination
1. Coverage of patients with this nosological form by dispensary observation:
2. Structure of patients registered at the dispensary:
B) indicators of the quality of clinical examination
1. Timely coverage of newly identified patients with dispensary observation:
The work of a local therapist carried out according to a schedule approved by the head of the department or the head of the institution. Drawing up a work schedule for local therapists is an important organizational event. A rationally designed work schedule makes it possible to increase the availability of a local physician-therapist for the population of his area, in particular, to ensure a high degree of compliance with locality in serving the population. The work schedule should include fixed hours for outpatient visits, home care, preventive and other work.
When drawing up a schedule it is necessary to take into account the monthly balance of working time, strive to establish a uniform load at outpatient appointments, and reduce the loss of working time while waiting for an appointment. The working day is functionally divided into outpatient appointments at the clinic (outpatient clinic) and providing care to patients at home. The work time of a local therapist should not be automatically distributed equally between appointments at the clinic and work at the site, much less evenly throughout the week. It should be determined depending on the size and composition of the population of the site, its distance from the clinic, the level of attendance and the number of calls by day, season, etc.
When drawing up a schedule, you should also take into account the nature of the visits: they were made for therapeutic or preventive purposes. On average, a doctor should work on an outpatient basis from 2.5 to 3.5 hours, and on providing care at home - from 3 to 4 hours, but to ensure differentiated planning of doctors’ working hours by type of activity and duration of patients’ appointments by day of the week, the head The department determines the types of activities that should be included in work schedules and the days of the week with higher levels of attendance. After this, work schedules are drawn up for the month, in which differentiated lengths of time for receiving patients are planned by day of the week.
I CONFIRM:
[Job title]
_______________________________
_______________________________
[Name of company]
_______________________________
_______________________/[FULL NAME.]/
"_____" _______________ 20___
JOB DESCRIPTION
Local therapist
1. General Provisions
1.1. This job description defines and regulates the powers, functional and job responsibilities, rights and responsibilities of the local physician [Name of the organization in the genitive case] (hereinafter referred to as the Medical Organization).
1.2. A local therapist is appointed to a position and dismissed from a position in the manner established by the current labor legislation by order of the head Medical organization.
1.3. A local general practitioner belongs to the category of specialists and is subordinate to [names of subordinate positions in the dative case].
1.4. The district physician reports directly to [name of the position of the immediate supervisor in the dative case] of the Medical Organization.
1.5. A person who has a higher professional education in one of the specialties “General Medicine”, “Pediatrics” and postgraduate professional education (internship and (or) residency) in the specialty “Therapy” or professional retraining if there is a postgraduate degree is appointed to the position of local physician-therapist. vocational education in the specialty "General medical practice(family medicine)”, a specialist certificate in the specialty “Therapy” without any work experience requirements.
1.6. The local therapist is responsible for:
- effective performance of the work assigned to him;
- compliance with the requirements of performance, labor and technological discipline;
- the safety of documents (information) in his custody (that have become known to him) containing (constituting) the commercial secret of the Medical Organization.
1.7. A local physician should know:
- Constitution of the Russian Federation;
- laws and other regulations legal acts Russian Federation in the field of healthcare;
- Fundamentals of legislation on protecting the health of citizens;
- general issues of organizing therapeutic care in the Russian Federation;
- the work of medical institutions, the organization of ambulance and emergency care for adults and children;
- organization of the clinic’s work, continuity in its work with other institutions;
- organization of day hospital and hospital at home;
- basic questions of normal and pathological anatomy, normal and pathological physiology, relationship functional systems organisms and their levels of regulation;
- the basics of water-electrolyte metabolism, acid-base balance, possible types of their disorders and principles of treatment;
- hematopoiesis and hemostasis system, physiology and pathophysiology of the blood coagulation system, homeostasis indicators in normal and pathological conditions;
- basics of immunology and body reactivity;
- clinical symptoms and pathogenesis of major therapeutic diseases in adults and children, their prevention, diagnosis and treatment, clinical symptoms of borderline conditions in a therapeutic clinic;
- basics of pharmacotherapy in the clinic of internal diseases, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the main groups of drugs, complications caused by the use of drugs, methods of their correction;
- basics non-drug therapy, physiotherapy, physical therapy and medical supervision, indications and contraindications for spa treatment;
- the basics of rational nutrition for healthy individuals, the principles of diet therapy for therapeutic patients;
- anti-epidemic measures in the event of a outbreak of infection;
- medical and social examination in internal diseases;
- dispensary observation of healthy and sick people, problems of prevention;
- forms and methods of sanitary educational work;
- demographic and social characteristics of the site;
- principles of organization medical service civil defense;
- issues of connection between the disease and the profession.
1.8. A local therapist in his activities is guided by:
- local acts and organizational and administrative documents of the Medical Organization;
- internal labor regulations;
- rules of labor protection and safety, ensuring industrial sanitation and fire protection;
- instructions, orders, decisions and instructions from the immediate supervisor;
- this job description.
1.9. During the period of temporary absence of the local general practitioner, his duties are assigned to [name of the deputy position].
2. Job responsibilities
A local physician is required to perform the following labor functions:
2.1. Identifies and monitors risk factors for the development of chronic non-communicable diseases.
2.2. Implements primary prevention in high-risk groups.
2.3. Performs a list of works and services for diagnosing the disease, assessing the patient’s condition and clinical situation in accordance with the standard of medical care.
2.4. Performs a list of works and services for the treatment of a disease, condition, clinical situation in accordance with the standard of medical care.
2.5. Provides symptomatic care to cancer patients of clinical group IV in collaboration with an oncologist.
2.6. Carries out examination of temporary disability of patients, presentation to a medical commission, referral of patients with signs of permanent disability for examination for medical and social examination.
2.7. Issues conclusions on the need to refer the patient for medical reasons to sanatorium-resort treatment, draws up a sanatorium-resort card.
2.8. Carries out organizational, methodological and practical work on medical examination of the population.
2.9. Organizes vaccination of the population in accordance with national calendar preventive vaccinations and for epidemic indications.
2.10. Prepares and sends emergency notifications to Rospotrebnadzor institutions when an infectious or occupational disease is detected.
2.11. Organizes and conducts events on sanitary and hygienic education (health schools, schools for patients with socially significant non-communicable diseases and persons at high risk of their occurrence).
2.12. Monitors and analyzes the main medical and statistical indicators of morbidity, disability and mortality in the service area in the prescribed manner.
2.13. Maintains accounting and reporting documentation of the established form.
In case of official necessity, the local therapist may be involved in the performance of his duties. job responsibilities overtime, in the manner prescribed by the provisions of federal labor legislation.
3. Rights
A local physician has the right to:
3.1. Give instructions and tasks to his subordinate employees and services on a range of issues included in his functional responsibilities.
3.2. Monitor the implementation of production tasks, timely completion of individual orders and tasks by the services subordinate to him.
3.3. Request and receive necessary materials and documents related to the activities of the district physician, subordinate services and departments.
3.4. Interact with other enterprises, organizations and institutions on production and other issues related to the competence of the local general practitioner.
3.5. Sign and endorse documents within your competence.
3.6. Submit proposals on the appointment, transfer and dismissal of employees of subordinate departments for consideration by the head of the Medical Organization; proposals to encourage them or to impose penalties on them.
3.7. Exercise other rights established Labor Code RF and other legislative acts of the RF.
4. Responsibility and performance evaluation
4.1. The local general practitioner bears administrative, disciplinary and material (and in some cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, criminal) responsibility for:
4.1.1. Failure to carry out or improperly carry out official instructions from the immediate supervisor.
4.1.2. Failure to perform or improper performance of one's job functions and assigned tasks.
4.1.3. Illegal use of granted official powers, as well as their use for personal purposes.
4.1.4. Inaccurate information about the status of the work assigned to him.
4.1.5. Failure to take measures to suppress identified violations of safety regulations, fire safety and other rules that pose a threat to the activities of the enterprise and its employees.
4.1.6. Failure to ensure compliance with labor discipline.
4.2. The assessment of the work of a local therapist is carried out:
4.2.1. By the immediate supervisor - regularly, in the course of the employee’s daily performance of his labor functions.
4.2.2. Certification Commission enterprises - periodically, but at least once every two years, based on documented results of work for the evaluation period.
4.3. The main criterion for assessing the work of a local physician is the quality, completeness and timeliness of his performance of the tasks provided for in these instructions.
5. Working conditions
5.1. The work schedule of a local physician is determined in accordance with the internal labor regulations established in the Medical Organization.
6. Signature right
6.1. To ensure his activities, the local general practitioner is given the right to sign organizational and administrative documents on issues within his competence by this job description.
I have read the instructions ___________/___________/ “____” _______ 20__