Liver functions: production of substances for digesting food, production and purification of blood, ridding the body of waste, storage of fats and carbohydrates. Due to this load, the liver is susceptible to a number of acute and chronic diseases. Leptospirosis and infectious hepatitis are acute and quite rare in dogs. More often dogs suffer from chronic liver diseases. Old dogs are primarily at risk.
IN last years there has been an increase in the number of diagnosed liver diseases in dogs, which is directly related to feeding disorders, the widespread occurrence of autoimmune diseases, sometimes the cause of liver disease in dogs is iatrogenic lesions (caused by a veterinarian).
Symptoms of liver disease in dogs can be divided into several syndromes, among which are usually distinguished:
Cholestatic syndrome implies a violation of the secretion and release of bile, which manifests itself skin itching, jaundice, a tendency to eczematous skin lesions, discoloration of feces. Cholestatic syndrome is a consequence of the destruction of liver cells and leads to fever (increased temperature), enlargement and tenderness of the liver, and an increase in liver enzymes is observed in blood tests.
Mesenchymal inflammatory syndrome characterized by damage to the stroma and mesenchyme of the liver, which is manifested by an increase in the level of immunoglobulins.
Hemorrhagic syndrome manifests itself in various bleedings and hemorrhages, anemia.
Portal hypertension syndrome manifested by an increase in the size of the abdomen, expansion of the veins on the skin of the abdomen.
Dyspeptic syndrome manifested by lethargy, depression, vomiting, defecation disorders and weight loss.
Hepatolienal syndrome manifested by enlargement of the liver and spleen.
Hepatodepressive syndrome manifests itself as a violation of the protein-synthesizing, antitoxic and excretory functions of the liver, the symptoms of which are variable and numerous.
Shunt syndrome liver leads to the entry of life-threatening substances into the dog’s general bloodstream, which leads to damage to the central nervous system.
Each disease has its own special symptoms, but there are also general signs that there is something wrong with your pet's liver. This:
- weight loss due to food refusal,
- vomit,
- excessive thirst,
- drowsiness,
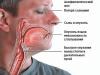
- yellowness is noticeable on the mucous membranes, they turn yellow especially strongly whites of eyes,
- The dog may have diarrhea and the stool looks too pale,
- the animal becomes apathetic
- intensively yellow urine
The most dangerous is that by the time symptoms become noticeable, about 80% of the liver may have already failed. Therefore, even if some of the symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms of hepatitis are made up of signs of the main infectious disease: depressed state of the dog, increased body temperature, enlarged and painful liver upon palpation. The body does not absorb fat well, digestion is upset, and the spleen also enlarges. In puppies often Conjunctivitis, keratitis, rickets appear, and paralysis and cramps of the limbs are common. With cirrhosis of the liver, hemorrhages appear on the conjunctiva, as well as the mucous membrane of the nose and mouth. The liver is enlarged and can be felt behind the last rib. A pear-shaped abdomen is often observed due to accumulation of abdominal cavity transudate.
Treatment. Chronic diseases liver disease in dogs is almost impossible to cure. Therefore, the doctor first of all tries to weaken the effects of the symptoms and stop the further development of the disease. Diet which you must adhere to throughout your life. Thanks to it, you can dramatically reduce the impact of harmful toxins that remain from the breakdown of proteins. 
IN dietary food for dogs includes easily digestible carbohydrates such as rice. Eggs are also needed. The daily diet is divided into 4-6 small portions. For dogs that eat dry food, a special diet food is good. The dog must be protected from overexertion and stress.
Before talking about liver disease in dogs, animal owners should have an idea of its role and the function that the liver performs in the dog's body.
Due to its diverse and complex functions In the body, the liver is simultaneously an organ of digestion, blood circulation and metabolism.
It is located in the anterior part of the abdominal cavity, lies directly behind the diaphragm, mostly in the area of the right hypochondrium.
The liver plays a very important role in the animal's body important role in metabolism, participating in the exchange of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, microelements and water.
The liver neutralizes toxic substances that enter it from the intestines. Liver supports normal level sugar levels in the blood, glycogen is deposited and broken down in the liver. In lactating dogs, many milk precursors are synthesized in the liver.
In the process of fat metabolism, phosphatides are synthesized in the liver, which subsequently enter the blood. The body's proteins are synthesized from amino acids carried through the bloodstream to the liver. The liver is a blood depot; up to 10% of a dog’s total blood is in the liver.
During the process of transamination in the liver, the amount of amino acids contained in excess in the body decreases and the missing ones increase. The liver in animals is a reserve “depot” of proteins. Blood plasma proteins (albumin, globulins, fibrinogen, prothrombin) are formed in the liver, from where they enter the blood. Protein renewal occurs in the liver. The liver stores vitamins “A” and “D”, microelements – iron, copper, manganese, zinc. The liver breaks down hormones such as thyroxine, insulin, ACTH, vasopressin, and sex hormones.
A specific function of the liver is bile formation.
The liver, unlike other organs, has an incredible ability to regenerate and has high reserves. Up to 75% of all hepatocytes (liver cells) work in the liver at the same time, so the liver always has reserves. Even in the case of severe liver damage by some kind of poison, if the dog still has at least a small number of healthy cells, the doctor has a chance for a successful outcome of this or that disease. Most liver diseases are accompanied by subclinical disorders that either resolve spontaneously or appear in the dog after a certain period of time.
Main symptoms of liver disease in dogs.
Liver disease in dogs is characterized by a number of signs that should alert its owner. An owner can suspect liver disease in their dog based on the following symptoms:
- Periodic digestive disorders - loss of appetite, vomiting (), constipation, diarrhea (). All this leads to severe emaciation of the sick dog.
- , is caused by bile acids, which the liver is unable to process as a result of illness, as a result of which they accumulate in the dog’s tissues, causing icteric staining of the mucous membranes and subcutaneous tissue in yellow color.
- Pale gray feces. The cause of such feces is stercobilin, which is formed from salts bile acids. In the case when, for some reason, bile is not produced in a sick dog, or does not enter the digestive tract, the color of the feces will be “faded.”
- Yellow urine. In a sick dog, it is a consequence of problems with the liver processing bile acids, as a result of which a large amount of bilirubin is excreted from the dog’s body through the kidneys.
- – an increase in abdominal volume due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. In severe cases, the stomach of such a sick dog becomes saggy and almost drags along the ground.
- Hepatodepressive syndrome. The dog becomes depressed, uncommunicative, does not want to play, and goes for a walk with great reluctance.
- Hepatic encephalopathy. With it, the dog can fall into a coma, become aggressive, or, on the contrary, overly affectionate. Individual dogs turn into “vegetables,” while becoming indifferent to the world around them.
- An increase in the size of the liver, which manifests itself in a sick dog as a protrusion through the abdominal wall.
- Skin itching. As a result of skin lesions, the dog often itches.
- Hemorrhagic syndrome associated with problems with blood clotting because... a number of proteins involved in the blood clotting process are synthesized by the liver.
- Abdominal pain. When palpating the abdominal area, the dog tenses, whines, and tries to escape from the hands.
- Polydipsia and polyuria.
Major liver diseases in dogs.
Hepatitis(Hepatitis) – common name inflammatory diseases liver tissue. Hepatitis often occurs simultaneously with diseases of the stomach, intestines, pancreas and other organs. With hepatitis, the process almost always involves gallbladder and bile ducts. Hepatitis is accompanied deep violations protein, carbohydrate-fat and pigment metabolism, liver cells disintegrate.
In its course, hepatitis can be acute or chronic.
Clinical signs. During a clinical examination of a sick dog, a veterinarian finds jaundice (yellow discoloration of the visible mucous membranes, conjunctiva and skin). The dog becomes depressed and lethargic. The dog may have no appetite at all. Body temperature rises to 42 degrees. Owners of a sick dog note that it has diarrhea, vomiting with bile and blood. The liver is painful and enlarged on palpation. Urine has a dark tint and is opalescent due to bilirubin.
Diagnosis A veterinarian diagnoses hepatitis based on clinical signs illness, carrying out laboratory research blood and urine for bilirubin. On ultrasound, there is an increase in the borders of the liver, its swelling, expansion bile ducts, the vascular pattern is unclear.
Treatment. Treatment of hepatitis in a dog should be comprehensive and primarily aimed at the main cause that caused hepatitis - infectious, invasive or other diseases. Simultaneously with the treatment of the underlying disease, veterinary specialists carry out therapeutic measures aimed at restoring damaged liver function. A sick dog is prescribed a diet that should not contain sugars or fatty foods. On the first day of treatment, the dog is put on a starvation diet, free access to water is not limited, water can be replaced with decoctions of herbs that have choleretic and restorative properties - chamomile flowers, marshmallow root, sage, bird cherry and blueberry fruits. From the second day, broths based on fish, veal, and chicken begin to be included in the diet of a sick dog. Then they are switched to feeding porridges cooked in water or meat broth. The number of feedings should be 4-6 times a day, and a single portion should not exceed 200 grams. After a week, they gradually begin to introduce chopped meat. You can start giving your dog boiled vegetables in the second week of the treatment course. Treatment of a sick dog should be comprehensive with the use of symptomatic, antihistamine, antiviral drugs, antibiotics wide range action (cephalosporin, penicelin series). To eliminate intoxication of the body and restore liver function, the dog is injected intravenously with a 5-10% glucose solution, sometimes up to 300 ml can be administered once, saline solution up to 2000 ml, Ringer's solution - up to 1000 ml, polyglucin, hemodez - up to 600 ml, disol, sanasol. Hemodez and polyglucin allow you to restore blood plasma in a sick dog and normalize protein and sugar levels. Intravenous infusions(drip or jet) are carried out daily, sometimes 2 times a day. Considering that toxic substances in a sick dog are formed in digestive system, the dog is given a gastric lavage with a weak solution of potassium permanganate or furatsilin. For release gastrointestinal tract, the dog is prescribed emetics and laxatives. good therapeutic effect provides a cleansing enema. From medicines The dog is prescribed B vitamins (B6, B12), gamavit, eleovit. In order to maintain metabolism and the work of liver cells, the dog is given Essentiale Forte (two capsules 3 times a day), Legalon (1tb. 3 times a day), LIV 52. To reduce pain syndrome and elimination stagnation antispasmodics are used in the liver. To remove acute condition for liver failure, aminazine and fosprenil are used. If there are signs of dehydration, a dropper with saline solution, Ringer's, Ringer-Locke, Trisol solutions. For elimination allergic reaction antihistamines. In order to normalize the intestinal microflora, cleansing enemas are given and preparations containing lactobacilli are used. For edema - diuretics. For hepatitis, to normalize liver function, it is prescribed choleretic drugs– allahol, colagon, decolin, festal, cholenzin, lyobil and others, soldered herbal teas, which have a diuretic and choleretic effect (decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbal decoction chamomile, St. John's wort, yarrow, coltsfoot, immortelle flowers, corn silk, peppermint, parsley).
Dog owners should choose the following types of industrially produced food as their main food products:
- Royal Canin Hepatic Canine dry food
- Royal Canin Hepatic Canine Cans.
Cirrhosis of the liver in dogs
Liver cirrhosis in dogs is accompanied by changes in the liver's structure due to growth in the liver connective tissue. With liver cirrhosis in a dog, necrosis of the liver parenchyma and its degeneration occurs, the replacement of parenchymal elements with connective tissue. With the growth of intralobular connective tissues in the liver, the liver enlarges and thickens, and with the growth of interlobular connective tissues, with their further contraction, the liver becomes smaller and thicker. In the first case, veterinary specialists have to deal with hypertrophic cirrhosis, in the second - with atrophic cirrhosis.
Etiology. The dog has had hepatitis in the past, prolonged exposure to toxic substances on the body, feeding the dog poor-quality and spoiled food, deficiency in the dog’s diet of minerals, protein and B vitamins, infectious diseases bacterial and viral origin, heart problems, disruption of the bile flow process.
Clinical picture. Symptoms of liver disease in dogs appear gradually, due to chronic changes they long time not expressed. Dog owners have been noticing changes in their appetite for a long time. Then the dog becomes immobile and depressed, and symptoms of a catarrhal condition of the stomach and intestines appear. When examining the mucous membrane of the nose, mouth, conjunctiva, and skin, the veterinarian records hemorrhages. The dog's abdomen begins to enlarge, abdominal dropsy develops, the enlarged liver can be easily felt behind the last rib, and is painful on palpation. With atrophic and hypertrophic cirrhosis, the dog’s sclera turns yellow, and the urine also turns yellow.
Diagnosis liver cirrhosis is diagnosed based on the collected medical history, clinical picture illness, results of laboratory blood tests - complete blood count (including the study of the number of platelets, red blood cells and leukocytes), biochemical analysis blood (bilirubin, urea, glucose, electrolytes, creatinine, albumin, cholesterol, globulin, alkaline phosphatase, alanine aminotransferase, gammaglutamyl transpeptidase, aspartate aminotransferase), urine analysis, stool examination, additional - radiography of the abdominal cavity and ultrasound diagnostic results. A histological examination of liver tissue (biopsy) is performed.
Forecast. The prognosis depends on how much functional liver tissue is left that is capable of regeneration and whether the processes that led to liver cirrhosis can be stopped. Based on this, the prognosis for cirrhosis is often uncertain.
Treatment. When treating cirrhosis in a dog, it is first necessary to eliminate the causes that contributed to the appearance of cirrhosis in the dog. In secondary cirrhosis, treatment should be aimed at treating the underlying disease. For cirrhosis in dogs, treatment is aimed mainly at eliminating portal blood stasis and toxicosis. It is necessary to review the feeding diet, transfer the sick dog to dietary and complete food with plenty of proteins and vitamins. Symptomatic treatment should be aimed at prolonging the dog's life. Diuretics, choleretic drugs, as well as hepatoprotectors are used as symptomatic remedies for dogs. If ascites is present, a sterile needle is inserted into the dog's abdomen and the fluid is released. If the dog has anorexia and dehydration, glucose solution and saline solutions are administered intravenously.
When it comes to the most important organs in the body of animals and humans, as well as the function they perform, the heart and brain immediately come to mind. The liver is much less often remembered. But in vain. This giant gland is a source of constant scientific discoveries and unexplored mysteries. It is extremely important, and therefore liver diseases in dogs are extremely dangerous, as they directly threaten the life of your pet.
This organ is truly unique. The fact is that the regenerative ability of the liver is simply amazing: when 70-80% of it is affected by the disease, it is almost always restored. Alas, this is not always good: often the animal feels great and does not show any signs of illness, being, in fact, on the verge of death. Simply put, there are considerable problems with diagnostics in the case of the liver. Because external manifestations pathologies arise too late and acquire a huge role regular examinations pet at the veterinarian.
Unfortunately, in some cases it is necessary to resort to a biopsy to identify a particular disease. This procedure is painful, but necessary. Don't worry: as we said, the liver's healing abilities are fantastic, so your dog's health is not at risk.
General symptoms
To detect liver disease in dogs as early as possible, you need to be very careful. Record the smallest signs and, if you suspect anything wrong with your dog’s health, urgently take him to the clinic. Perhaps you will save her life. Here is the general clinical picture, which one way or another manifests itself in any trouble with the liver:
- Unstable but recurrent digestive disorders: loss of appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation.
- Progressive depression or lethargy. The dog does not want to play and is also reluctant to go for walks.
- In the most severe cases, it occurs (edema of the abdominal cavity). The dog's belly is saggy and almost drags along the ground.
- Pale gray feces. The fact is that the color of feces is given by stercobilin, obtained from bile salts. If for some reason there is no bile (it is not produced, or does not enter the digestive tract), then the excrement will be “faded.”
- "Orange urine." Again, if there are problems with the processing of bile acids in the liver, huge amounts of bilirubin begin to be excreted from the body by the kidneys. By the way, this process causes severe harm to the entire excretory system.
- . This phenomenon is also directly related to bile acids. If the liver cannot process them, these substances accumulate in the tissues of the body, turning them into a characteristic yellowish color.
- Rarely, problems with blood clotting occur. This is due to the fact that some proteins, which are the most important components of this defense mechanism, are also synthesized in the liver.
- Hepatic encephalopathy. Accompanied by severe behavioral anomalies. The dog can fall into a coma, become aggressive, and overly affectionate. It is possible to turn into a “vegetable”, indifferent to what is happening around.
- Abdominal pain. This is relatively easy to notice when caring for your dog. A sick animal immediately tenses up and whines; the dog tries to run away as soon as you start stroking its belly.
- Chronic weight loss. It's simple. The liver processes great amount toxins from the gastrointestinal tract. If this does not happen, the body poisons itself. The intoxication process is accompanied by intense weight loss.
Read also: Warts in dogs - causes and 6 methods of removal

These are the signs of liver disease in dogs that can be observed in the vast majority of cases. Now let's discuss some specific pathologies.
The most common diseases
Infectious hepatitis
As a rule, it is viral in nature. Most often, the pathogen is transmitted through nutrition (along with food). Treatment consists of supportive care, antibiotics are prescribed to prevent the development of secondary bacterial infections. For all hepatitis should be prescribed proper diet. The dog is given only low-fat, high-quality chicken, low-fat offal, boiled and finely pureed vegetables, and is prescribed vitamin supplements.
There are also many bacterial infections that affect the liver. In this case, they are assigned loading doses antibiotics and hepatoprotectors that level Negative consequences actions antibacterial drugs to the liver itself.
Other causes of hepatitis
Blastomycosis, histoplasmosis and coccidioidomycosis are mycoses. These are fungal infections, which, among other things, hit the liver especially hard. It is very difficult to treat, and diagnosis causes many problems. Tuberculosis also poses a great danger to the organ. As for the first, it cannot be treated in animals, since there is a high risk of infecting people. Leptospirosis is defeated with strong antibiotics, and polyvalent vaccines are used for prevention.
Read also: Treatment of distemper in dogs
Secondary liver diseases
This is the name for pathologies that, without directly affecting the liver in any way, still contribute to its damage. This, for example, is acute pancreatitis. The pancreas and its ducts are quite closely anatomically connected to the liver, and therefore, in the event of their inflammation, there is always a far from zero probability of developing hepatitis. As a rule, fairly powerful broad-spectrum antibiotics are used to treat pancreatitis, and therefore no additional measures are taken to treat the liver.

Likewise - inflammatory phenomena in thick and small intestine. Since the ducts of the gallbladder open into the lumen of these organs, pathogenic microflora can migrate into it. With all the ensuing consequences. The diagnosis is made on the basis of the general clinical picture, as well as by seeding the pathological material on nutrient media.
Very dangerous for the liver... congestive, acute and chronic, hypoxia. The fact is that this organ is the largest blood depot. If there is not enough oxygen in this very blood, this is fraught with massive death of hepatocytes (liver cells). Of course, in this case, you should focus on treating anemia or hypoxia itself. The liver subsequently regenerates, but the brain tissue can no longer be restored.
All abdominal injuries are extremely dangerous: they are fraught with liver ruptures, the formation of adhesions, and other unpleasant and fatal dangerous consequences. Therapy is urgent only surgical intervention. If a simple liver bruise is diagnosed (due to a fall or collision with a cyclist), then the organ regenerates on its own. During the treatment period, a diet may be recommended, general provisions which we have already discussed above.
Toxic liver degeneration
Many medicinal substances, mineral fertilizers, pesticides, salts heavy metals and other compounds, when ingested by animals and humans, have an extremely negative effect on the condition of their liver. In particular, all this is fraught with fatty degeneration of the organ, when normal hepatocytes, roughly speaking, are replaced by fat. This leads to a very strong drop in its functionality. The organ can no longer perform its physiological functions. As a rule, such a disease is incurable in its final stages.
The situation can be saved in cases where the dog has at least 10-12% normal liver tissue. Veterinarians relieve intoxication, prescribe hepatoprojectors and therapeutic diet, which involves the dog consuming only light, highly digestible food that does not contain a lot of fat.
Everything you need to know
WOLMAR
FOR DOGS

An enlarged dog's liver, or hepatomegaly, is a symptom of injury, cancer, and other diseases and conditions. If treatment is not started in time, it can lead to liver failure and even death. Any disease or damage to a dog’s liver is very dangerous and threatens its life, so care must be taken to ensure that the dog does not receive any abdominal injuries in its daily activities.The liver performs a number of functions in the body: cleanses the blood of toxins, removes waste and produces bile, which is involved in the digestion of food and also fights disease, provides the body with energy and performs functions necessary for a dog If you notice that your dog is suffering from liver disease, it should be taken to the vet to avoid more serious conditions.Diseases and recommendations for the Rottweiler
Signs of liver enlargement
The main signs of liver damage in dogs are jaundice, restlessness, diarrhea, vomiting and white feces. The dog rarely urinates, and this is also a symptom of an enlarged liver. Loss of appetite leads to fast weight loss animal, and this further aggravates its condition.
Causes
There can be several reasons for liver enlargement in dogs. One of them is the presence of heartworms. These worms affect not only the heart, but also the liver, which leads to its enlargement. The presence of toxic substances in an animal's environment can also cause liver disease. These include arsenic, insecticides, carbon tetrachloride and many others. The liver may also become enlarged after recent injury, as well as diseases such as diabetes, liver neoplasia, obesity, or encephalopathy. Sometimes it is a genetic factor. Most often, the liver becomes enlarged in Skyterriers, Dobermans and Bedlington Terriers.
Diagnostics
If the dog's liver is enlarged, a full diagnostics. It is important to clarify what diseases occurred throughout the animal’s life. Including immediately after birth. Perhaps among them there will be one in which there is an enlargement of the liver. All tests and examinations are carried out by a veterinarian in the clinic. The most important is a biochemical analysis, which allows you to find out the level of cholesterol in the dog’s blood, as well as the degree of activity of liver enzymes. Their high content may indicate improper liver function. A tissue culture study can also be carried out to diagnose the stages of development of certain diseases. To determine the intensity of the disease, an x-ray of the dog's abdomen and chest is taken. Using these diagnostic tools, your veterinarian makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatments.
Treatment
Sometimes when treating a dog, you continue to feed it its usual food. Sometimes you will have to give her what the vet prescribed. Make sure your pet drinks enough fluids. Keep it away from harmful chemical substances and gases. Provide him a good place for relax. Treatment often includes intravenous fluids and antibiotics. Infusions are usually given when dehydration occurs to replace lost substances. If a dog has hepatitis, it is prescribed corticosteroids. If others, more serious illnesses in advanced stages, corticosteroids are no longer required. If a tumor is present, surgery is sometimes recommended.If your dog is sick, don't think that he will get better on his own. We need to take her to the vet and get started.drugs for treatment. If you do this in time, it will be much easier to cure any disease.Note: This article is provided for informational purposes only. Not worth ittreat and care for your pets via the Internet. If your animal has any medical problems, contact your veterinarian as soon as possible.
Liver disease in dogs is very dangerous. They begin almost asymptomatically, the first signs are similar to simple malaise or fatigue. If your pet's behavior is different from usual, and his health causes you concern, consult a doctor. A dog can't pretend. If she feels bad, it means that something is wrong with her body. Only timely treatment of any disease can be successful.
There are many liver diseases, they may have similar symptoms, but different causes, further development and method of treatment.
The most common:
- infectious diseases (leptospirosis, viral hepatitis and others);
- toxic diseases that manifest themselves in liver failure (poisoning with poor-quality food, medications, toxic chemicals);
- helminthic infestations;
- tumors;
- cirrhosis of the liver.
Liver failure is divided into two types:
Some dogs have a pathology called true liver failure. For some reason, the blood does not pass through the liver for cleansing, and carries toxins throughout the body. At the same time, the liver is completely healthy.

Symptoms
Liver diseases in dogs early stage almost invisible. On possible problems liver function may indicate:
- lethargy, weakness, apathy;
- lack of appetite;
- weight loss;
- thirst.
If you notice such ailments in your pet, and they do not go away for several days, then you need to consult a doctor to clarify the cause and determine the diagnosis.
It is better to rule out liver disease than to start it. Liver failure leads to the death of the animal.
With extensive liver damage, the dog’s condition becomes noticeably worse. Can appear:
- nausea, vomiting;
- diarrhea, which may alternate with constipation;
- feces light color, closer to gray;
- flatulence;
- bright yellow urine, sometimes orange or brownish in color;
- abdominal pain;
- an enlarged liver can be felt in the right hypochondrium;
- dry, flaky skin with a yellowish tint;
- dry mucous membranes;
- temperature increase;
- disturbance in behavior (the dog can become aggressive, or vice versa – affectionate and docile, performs actions that are not characteristic of it in a healthy state);
- ascites - dropsy of the abdominal cavity. Outwardly, this manifests itself in the fact that the stomach swells and hangs lower than usual. If you lift a dog by its front paws, its body is shaped like a pear.
At severe form diseases, the dog may lose sight and sense of smell. Her movements become uncertain, coordination is impaired. Mental disturbances may occur.

Diagnostics
Install accurate diagnosis and the cause of the disease can only be determined after full examination. It includes:
- blood chemistry;
- urine and stool analysis;
- ultrasonography;
- biopsy.
A blood test shows whether there is inflammatory process, anemia, blood clotting level. In addition, the amount of various enzymes produced by the liver is determined. If they are higher or lower than normal, this indicates which liver function is impaired.
The totality of all studies: ultrasound, blood tests, urine, feces and clinical manifestations allow you to establish an accurate diagnosis, the degree of liver dysfunction and the condition of the dog’s entire body. Only then can the veterinarian prescribe treatment.
Unfortunately, in some cases, the disease is in an advanced state, the liver is so damaged that it is impossible to restore its functions. At the same time, the dog experiences pain and suffering. Due to the fact that it is impossible to improve this condition of the animal, the right way will put her to sleep.

Treatment
The treatment complex depends on the established diagnosis and cause of the disease. It may include:
- antibiotics – if the disease is viral;
- antitoxic drugs - for various poisonings or when the disease has progressed;
- for weight loss - plasma replacement drugs; replenishing proteins; lack of microelements;
- painkillers;
- antipyretics;
- hepatoprotectors;
- choleretic.
Therapeutic measures are carried out under the supervision of a doctor. It may be necessary during treatment additional research blood composition to determine the effectiveness of the prescribed drug.
Self-medication of liver diseases is prohibited. This will only worsen the dog’s condition, and the moment when there is still a chance to cure the animal will be missed.
If the disease is caused by poisoning, then at an early stage it is necessary to lavage the stomach with a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate. You may need to do an enema to cleanse your colon.
In case of true liver failure, it is important to urgently perform intracavitary surgery. This will direct blood flow through the liver and stop intoxication of the body.
For any liver disease, you must adhere to a strict diet.

Diet food
With liver disease, a dog almost always refuses to eat. At first, various droppers are prescribed to restore the body. When the appetite appears, you should not feed your pet regular food. Meals should be dietary and fractional.
Drinking must be constant. Instead of water, you can pour infusions of herbs: chamomile, St. John's wort, sage. The infusion should not be strong and rich, otherwise the dog will not want to drink it.
- the first day, as soon as your appetite appears, use low-fat and weak broth. Preferably veal or fish;
- second day – rice porridge, buckwheat, rolled oats. It is recommended to add some minced meat;
- the third and subsequent days - porridge and minced meat are mixed in equal proportions;
- fourth day - you can add low-fat cottage cheese or kefir to the porridge;
- fifth day - at one of the feedings, a little grated boiled vegetables are mixed into the main food: potatoes, carrots, zucchini.
Be sure to divide the daily portion into 5-6 parts and give at regular intervals. This will help avoid negative extra stress on the digestive system.
In the future, the following is contraindicated for dogs:
- fat meat;
- bones;
- expired products;
- cheap low quality food.
If your pet has eaten before ready-made food, then the doctor may recommend a special premium diet food.
The liver does not recover completely after illness. The dog will have to be examined once or twice a year, and the diet must be followed for life. The doctor may prescribe hepatoprotectors continuously or in courses.