Quite often in women who are prescribed ultrasound Bladder, the question arises: how to prepare for this study correctly. Let's try to answer it, taking into account the specifics of the procedure.
Why is this type of examination prescribed?Before talking about how an ultrasound of the bladder is performed in women, let’s consider the main indications for its performance. To begin with, it is worth noting that this type of examination, along with examination of other pelvic organs, is not the last place in the process of diagnosing gynecological disorders.
More often ultrasonography is prescribed when symptoms appear indicating the presence of genitourinary diseases in a woman’s body. In particular, when:
- pain just above the pubis (suprapubic area);
- increased urge to urinate;
- suspicion of
- emergence
- development of difficulty urinating, etc.
Ultrasound is also performed to determine the functioning of the kidneys, to identify diseases such as chronic cystitis and pyelonephritis.
How should one prepare for an ultrasound of the bladder in women?
This type of procedure should be performed on a full bladder. This allows you to determine the shape and structure of the organ itself, assess its condition, wall thickness and other parameters.
Approximately 2 hours before the start of the study, the woman needs to drink 1-1.5 liters of liquid. You can use ordinary water, tea, juice, compote. A full bladder allows better visualization of the anatomical structures located behind it.
Also, along with the method of preparing for research described above, there is also the so-called physiological one. It consists of abstaining from urination for 5-6 hours. This is usually possible when conducting research in the morning. If the ultrasound is scheduled for daytime, then the first method is used.
Very rarely, ultrasound of the bladder can be performed transrectally, i.e. the sensor is inserted into the rectum. In this case, on the eve of the study, the woman is given a cleansing enema.
How is the research conducted?Having figured out when an ultrasound of the bladder in women is prescribed and what it shows, as well as what is needed to carry it out, let’s consider the sequence of the procedure.
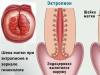
During this study, as a rule, they use the so-called transabdominal access, i.e. the sensor is placed on the front abdominal wall. In cases where there is severe obesity or a tumor is present, for example, an ultrasound is performed through the rectum. Access can also be made transvaginally.
The patient is located on the couch and lies on her back. The specialist applies a special contact gel to the suprapubic area, and then places a sensor on it. The duration of the procedure, as a rule, is no more than 15-20 minutes.
 During the inspection, an assessment is made external parameters organ, its size, shape, wall thickness. The final conclusion is given after completion of the procedure.
During the inspection, an assessment is made external parameters organ, its size, shape, wall thickness. The final conclusion is given after completion of the procedure.
Thus, as can be seen from the article, ultrasound of the bladder is a fairly simple study, but requires a certain kind of preparation on the part of the patient. If the above instructions are not followed, some structures may not be visible on the ultrasound machine screen, which will require the procedure to be performed again after some time. The woman is advised to drink even more fluid so that the bladder is completely filled and the ultrasound sensor can scan the organs located directly behind it.
Ultrasound is modern method diagnosis of a huge number of diseases various organs. It is considered to be absolutely safe, so this procedure indicated for people of any age, including newborns, and gender.
Very often, ultrasound is performed to assess the condition of the urinary system. But in order for the study to provide the most accurate information, some kind of preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder is required.
Indications and features of the procedure
Patients may be referred for an ultrasound examination of the bladder if they have:
- changes in urine color;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- pain when urinating;
- pain in the suprapubic region;
- sediment in the urine visible to the naked eye;
- blood in urine, etc.
In addition to diagnosing various diseases, this procedure is carried out to assess the effectiveness of treatment by the presence or absence of positive dynamics. Most often this is necessary when undergoing a course of chemotherapy or after surgical interventions.
Features of preparation
The procedure is performed on a full bladder, so the main preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder is to fill it. This can be achieved by drinking approximately 1 liter of still water an hour before the procedure. In cases where the study is scheduled for the morning, you can go to the clinic immediately after waking up, without visiting the toilet. If it is impossible to refrain from urinating in the morning, it is recommended to set the alarm clock 2-3 hours earlier than the scheduled wake-up time, visit the restroom and go back to sleep. Moreover, after the final rise, the intensity of the urge will not be too great, which will allow you to reach medical institution with a full bladder, ready for examination.
Important: water can be replaced with tea, compote or other non-carbonated drink, but not with milk or fermented milk products. If a patient is diagnosed with kidney pathologies, he may be advised to take diuretic medications.
In addition to filling the bladder, patients need to take care of the condition of the intestines before the study, since its overcrowding with gases can interfere with the procedure. Therefore, within a couple of days before the appointed date, it is recommended to take activated carbon or its analogue, as well as follow a diet that helps reduce gas formation. That is, on these days you should not consume:
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- legumes;
- carbonated drinks;
- baked goods;
- dairy and dairy products;
- alcohol.
Attention! The correct one allows you to conduct a full examination of not only the bladder, but also prostate gland in men, as well as the ovaries and uterus in women.
If, even before the study is carried out, it is known that it will be carried out through the rectum, then, among other things, a cleansing enema or a glycerin suppository must be done a few hours before the procedure.
How is the procedure performed?
How an ultrasound of the bladder is done depends on its condition, degree of fullness, presence accompanying pathologies and some other factors. In general, the examination is usually performed using the transabdominal (through the abdomen) method. With this approach, the patient is placed on the couch on his back. He is asked to remove clothing from his lower abdomen, to which the doctor applies special gel. After this, the doctor applies the sensor to the site where the gel is applied and, with slight pressure, runs it along the surface of the abdomen in different directions, examining the bladder and nearby organs.

Transabdominal ultrasound
Important: in certain cases, to clarify the situation, the specialist may ask the patient to visit the toilet and return to the ultrasound room to assess the condition of the bladder after emptying it. This is usually required to diagnose prostate pathologies.
As a rule, the procedure lasts no more than 20 minutes, after which the patient immediately receives a form with the examination results and is sent to his attending physician. But in some cases it may be necessary to conduct an examination through:
- Rectum. This type The study is indicated if an ultrasound of the prostate and bladder is necessary, but it can also be used if the patient has fluid in the abdominal cavity, obesity or other factors that make examination through the abdominal wall difficult. In addition, the indication for transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) is the need to examine girls who have not lost their hymen, for whom transabdominal examination is difficult.
- Vagina. Ultrasound of the bladder in women is performed using the transvaginal method in the presence of obesity, adhesions, tumor formation, etc.
In such cases, a condom is placed on a special sensor, a small amount of conductive gel is applied and it is inserted shallowly into the natural openings.

Transrectal ultrasound
Sometimes patients are prescribed an ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound. It is carried out if it is necessary to evaluate the parameters of urine flow through the ureters and the state of blood flow in the organs being studied. This is required if there is a suspicion of vesicoureteral reflux, in which urine, for one reason or another, is thrown back from the bladder into the ureters. Doppler ultrasound is also indispensable in diagnosing tumor formations.
Another variation of this diagnostic method is intravesical or transurethral ultrasound. To carry it out, a special, thinnest sensor is used, which is inserted into the patient’s body through the urethra. It is prescribed if necessary:
- determine the degree of damage to the walls urethra and the neck of the bladder;
- differentiate or find the relationship between diseases of the bladder and urethra;
- assess the degree of damage to neighboring organs.
Decoding the results
During the study, the specialist evaluates bladder parameters such as:
- structure;
- form;
- clarity of contours;
- Wall thickness;
- volume;
- filling speed;
- amount of residual urine (if necessary).
Normally, the bladder is a symmetrical, completely echo-negative organ, that is, it looks like a black spot without inclusions on the device screen. In different projections it can be round or ovoid. Its edges are clear and smooth, and the thickness of the walls is 0.3–0.5 cm. If the amount of residual urine is assessed, then normally its volume should not exceed 50 ml.
At the end of the examination, the ultrasound doctor gives the patient a completed form with the diagnostic results, which indicates the conclusion of this specialist, but the interpretation of the bladder ultrasound is performed by the attending doctor. He also makes the final diagnosis, since for this it is necessary not only to compare the obtained indicators with normal ones, but also to take into account the entire complex of symptoms that are present in the patient.
Thus, using ultrasound you can diagnose:
- tumors of the bladder and nearby organs;
- presence of stones or sand;
- wall diverticula;
- spicy and chronic inflammation mucous membrane;
- presence foreign bodies;
- anomalies of development and structure;
- backflow of urine into the ureters;
- blockage of the urethra with a stone, etc.

The procedure is completely safe even for pregnant women and newborns
Quite often, patients are prescribed an ultrasound of the bladder with cystitis to assess the extent of organ damage. In the case of the development of acute cystitis, sediment is found in the cavity of the bladder, that is, small echogenic particles, the number of which may vary. Thus, ultrasound reflects accumulations of various cells, for example, leukocytes, erythrocytes, epithelium, as well as salt crystals. In this case, the location of such sediment will change depending on the position of the patient’s body. But in acute cystitis, the walls of the bladder usually retain normal thickness and clear contour. Thickening of its walls and the appearance of irregularities is a sign of an advanced chronic process.
Ultrasound of the bladder is an important part of diagnosis, which is regularly used in modern medicine. It is with the help of this study that it is possible to determine whether there are any disturbances in the functioning of the bladder, whether there are changes in its structure and size. Based on the data obtained, the doctor can make a final diagnosis.
Ultrasound of the bladder: main indications for performing
Such a study can be prescribed for completely different reasons:
- It is prescribed to patients who have consulted a doctor with various types of urination disorders, for example, increased urge to urinate, blood levels in the urine, etc.
- In addition, ultrasound of the bladder is an integral part of the diagnosis for those patients who consult a doctor with complaints of symptoms of kidney and urethral diseases.
- The study is prescribed for men with possible diseases or prostate gland.
- Women may also be sent for ultrasound diagnostics if ovarian disease is suspected.
In addition, ultrasound is mandatory in cases where the patient’s test results indicate the possibility of developing any disease genitourinary system.
Ultrasound of the bladder: preparation
The results largely depend on proper preparation. In order to achieve maximum visibility, the bladder needs to be filled - its volume should be at least 250 - 350 milliliters. This state can be achieved in two ways:
- Two hours before the test, the patient is recommended to drink 1.5 - 2 liters of liquid without emptying the bladder.
- There is also a physiological way to fill the bladder - the patient must refrain from urinating for 4 to 6 hours before the diagnosis.
If the bladder is not filled enough, the doctor will not be able to clearly analyze the size and structure of the organ. In such cases, the patient is usually asked to wait, or drink some more fluid.
How is an ultrasound of the bladder performed?
The ultrasound diagnostic procedure is quite simple and takes no more than 10 - 15 minutes. The patient receives the results of the study immediately after the examination. In most cases, ultrasound of the bladder is performed using the transabdominal method. First, a contact gel is applied to the patient’s abdomen, after which the organ is scanned with a special device through the anterior abdominal wall.
In some cases, transrectal diagnosis is performed. In this case, a special probe is inserted into the person, which scans the organ through the walls of the rectum.
It is worth noting that the ultrasound diagnostic procedure is completely safe for human health. Moreover, it is painless. The patient can only complain of discomfort associated with a full bladder.
Ultrasound of the bladder: what can be found out?
First, the doctor must examine the organ, determine its size and shape, and also examine the structure and thickness of the wall. It is also very important to find out the exact location of the bladder relative to other organs.
In addition, during the study it is possible to determine the presence of any tumors or neoplasms. Ultrasound also makes it possible to see and measure the size kidney stones. The ureters are examined in the same way and checked for dilations.
With help, it becomes possible to notice any other changes in the structure and functions of the genitourinary system.
The ultrasound results must be delivered to the attending physician - they will allow him to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe the optimal treatment regimen.
The human body is a reasonable and fairly balanced mechanism.

Among all known to science infectious diseases, infectious mononucleosis has a special place...

About the disease that official medicine calls “angina pectoris”, the world has known for quite a long time.

Mumps (scientific name: parotitis) is called an infectious disease...

Hepatic colic is a typical manifestation of cholelithiasis.

Brain edema is a consequence of excessive stress on the body.

There are no people in the world who have never had ARVI (acute respiratory viral diseases)...

Healthy body A person can absorb so many salts obtained from water and food...
Bursitis knee joint is a widespread disease among athletes...
How to do an ultrasound of the bladder in women
How and why is an ultrasound of the bladder performed?
 Ultrasound is a modern method for diagnosing a huge number of diseases of various organs. It is believed to be absolutely safe, so this procedure is recommended for people of any age, including newborns, and gender.
Ultrasound is a modern method for diagnosing a huge number of diseases of various organs. It is believed to be absolutely safe, so this procedure is recommended for people of any age, including newborns, and gender.
Very often, ultrasound is performed to assess the condition of the urinary system. But in order for the study to provide the most accurate information, some kind of preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder is required.
IMPORTANT! Natural remedy Nutricomplex restores proper metabolism in 1 month. Read the article>>...
Indications and features of the procedure
Patients may be referred for an ultrasound examination of the bladder if they have:
- changes in urine color;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- pain when urinating;
- pain in the suprapubic region;
- sediment in the urine visible to the naked eye;
- blood in urine, etc.
In addition to diagnosing various diseases, this procedure is carried out to assess the effectiveness of treatment by the presence or absence of positive dynamics. Most often this is necessary when undergoing a course of chemotherapy or after surgery.
Features of preparation
The procedure is performed on a full bladder, so the main preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder is to fill it. This can be achieved by drinking approximately 1 liter of still water an hour before the procedure. In cases where the study is scheduled for the morning, you can go to the clinic immediately after waking up, without visiting the toilet. If it is impossible to refrain from urinating in the morning, it is recommended to set the alarm clock 2-3 hours earlier than the scheduled wake-up time, visit the restroom and go back to sleep. Moreover, after the final rise, the intensity of the urge will not be too great, which will allow you to get to the medical facility with a full bladder, ready for examination.
ADVICE! Get rid of dark circles around your eyes in 2 weeks. Read the article>>...
Important: water can be replaced with tea, compote or other non-carbonated drink, but not with milk or fermented milk products. If a patient is diagnosed with kidney pathologies, he may be advised to take diuretic medications.
In addition to filling the bladder, patients need to take care of the condition of the intestines before the study, since its overcrowding with gases can interfere with the procedure. Therefore, within a couple of days before the appointed date, it is recommended to take activated carbon or its analogue, as well as follow a diet that helps reduce gas formation. That is, on these days you should not consume:
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- legumes;
- carbonated drinks;
- baked goods;
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- alcohol.
If, even before the study is carried out, it is known that it will be carried out through the rectum, then, among other things, a cleansing enema or a glycerin suppository must be done a few hours before the procedure.
Our readers recommend! For the prevention and treatment of diseases gastrointestinal tract our readers recommend Monastic tea. This unique remedy which includes 9 medicinal herbs beneficial for digestion, which not only complement, but also enhance each other’s actions. Monastery tea will not only eliminate all symptoms of gastrointestinal and digestive diseases, but will also permanently eliminate the cause of its occurrence. Readers' opinions... »
How is the procedure performed?
How an ultrasound of the bladder is done depends on its condition, degree of fullness, the presence of concomitant pathologies and some other factors. In general, the examination is usually performed using the transabdominal (through the abdomen) method. With this approach, the patient is placed on the couch on his back. He is asked to remove clothing from his lower abdomen, to which the doctor applies a special gel. After this, the doctor applies the sensor to the site where the gel is applied and, with slight pressure, runs it along the surface of the abdomen in different directions, examining the bladder and nearby organs.
Important: in certain cases, to clarify the situation, the specialist may ask the patient to visit the toilet and return to the ultrasound room to assess the condition of the bladder after emptying it. This is usually required to diagnose prostate pathologies.
IMPORTANT! How to remove bags and wrinkles around the eyes at 50 years old? Read the article> >...
As a rule, the procedure lasts no more than 20 minutes, after which the patient immediately receives a form with the examination results and is sent to his attending physician. But in some cases it may be necessary to conduct an examination through:
- Rectum. This type of examination is indicated when an ultrasound of the prostate and bladder is necessary, but it can also be used if the patient has fluid in the abdominal cavity, obesity, or other factors that make examination through the abdominal wall difficult. In addition, the indication for transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) is the need to examine girls who have not lost their hymen, for whom transabdominal examination is difficult.
- Vagina. Ultrasound of the bladder in women is performed using the transvaginal method in the presence of obesity, adhesions, tumor formation, etc.
In such cases, a condom is placed on a special sensor, a small amount of conductive gel is applied and it is inserted shallowly into the natural openings.

Sometimes patients are prescribed an ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound. It is carried out if it is necessary to evaluate the parameters of urine flow through the ureters and the state of blood flow in the organs being studied. This is required if there is a suspicion of vesicoureteral reflux, in which urine, for one reason or another, is thrown back from the bladder into the ureters. Doppler ultrasound is also indispensable in diagnosing tumor formations.
Another variation of this diagnostic method is intravesical or transurethral ultrasound. To carry it out, a special, thinnest sensor is used, which is inserted into the patient’s body through the urethra. It is prescribed if necessary:
- determine the degree of damage to the walls of the urethra and the neck of the bladder;
- differentiate or find the relationship between diseases of the bladder and urethra;
- assess the degree of damage to neighboring organs.
Decoding the results
During the study, the specialist evaluates bladder parameters such as:
- structure;
- form;
- clarity of contours;
- Wall thickness;
- volume;
- filling speed;
- amount of residual urine (if necessary).
Normally, the bladder is a symmetrical, completely echo-negative organ, that is, it looks like a black spot without inclusions on the device screen. In different projections it can be round or ovoid. Its edges are clear and smooth, and the thickness of the walls is 0.3–0.5 cm. If the amount of residual urine is assessed, then normally its volume should not exceed 50 ml.
At the end of the examination, the ultrasound doctor gives the patient a completed form with the diagnostic results, which indicates the conclusion of this specialist, but the interpretation of the bladder ultrasound is performed by the attending doctor. He also makes the final diagnosis, since for this it is necessary not only to compare the obtained indicators with normal ones, but also to take into account the entire complex of symptoms that are present in the patient.
Thus, using ultrasound you can diagnose:
- tumors of the bladder and nearby organs;
- presence of stones or sand;
- wall diverticula;
- acute and chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane;
- presence of foreign bodies;
- anomalies of development and structure;
- backflow of urine into the ureters;
- blockage of the urethra with a stone, etc.
 The procedure is completely safe even for pregnant women and newborns
The procedure is completely safe even for pregnant women and newborns Quite often, patients are prescribed an ultrasound of the bladder with cystitis to assess the extent of organ damage. In the case of the development of acute cystitis, sediment is found in the cavity of the bladder, that is, small echogenic particles, the number of which may vary. Thus, ultrasound reflects accumulations of various cells, for example, leukocytes, erythrocytes, epithelium, as well as salt crystals. In this case, the location of such sediment will change depending on the position of the patient’s body. But in acute cystitis, the walls of the bladder usually retain normal thickness and clear contour. Thickening of its walls and the appearance of irregularities is a sign of an advanced chronic process.
But perhaps it would be more correct to treat not the effect, but the cause?
ozhivote.ru
Ultrasound of the bladder
Often, according to doctor's indications, an ultrasound of the bladder is performed in women and men, thanks to which many diseases are diagnosed. It is done at any age and condition (newborns or people old age, pregnant or after surgery). It is important to prepare properly before the procedure, then you can get an accurate result. And the correctness of diagnosis and treatment depends on this. A urinary ultrasound (UU) is performed to check the result of surgery on the genitourinary system. This is often how complications can be identified.
 Ultrasound examination of the bladder gives good foundation to analyze the state of health or the course of diseases in a given organ.
Ultrasound examination of the bladder gives good foundation to analyze the state of health or the course of diseases in a given organ. Indications for use
All indications are related to problems in the genitourinary system (GUS).
This study can be very informative. It is carried out in order to determine diseases of the kidneys and genitourinary system. Indications include:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- frequent urination;
- problems with urination;
- blood in urine;
- symptoms of urolithiasis.
In addition, it is carried out in men if there is a suspicion of prostate disease. This is how an adenoma or inflammation of this organ is detected. Ultrasound of the genitourinary system may show the presence of cystitis or chronic pyelonephritis. In women it is carried out because it detects diseases of the genital organs located in the pelvis. Sometimes an ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system may include examination of the uterus and appendages. Sharp pain in the lower abdomen, accompanied by strong increase temperatures are also an indication for research. It is worth doing this procedure for preventive reasons.
Return to contents
Preparing for the study
It is imperative to prepare for the procedure, especially since the algorithm is simple: stick to a diet and drink a lot. A bladder examination involves a full bladder. Preparing a patient for a study is sometimes carried out according to the following scenario: a person should not go to the toilet for 5-6 hours before the procedure. This method is suitable for people who have severe swelling. If you can’t bear it, you can let out a little urine, but then quickly fill the bladder again. When the bladder is empty, its contours are poorly visible, the same applies to the prostate and appendages. The doctor should explain how a prostate ultrasound is performed. It is necessary to prepare not only the patient, but also the equipment: gel is generously applied to sensitive areas of the device. This will give a clear image. During transvaginal examination, a special disposable condom is put on it.
Return to contents
How to fill your bladder? How much fluid for ultrasound?
Preparing for an ultrasound of the bladder during menstruation requires drinking a lot of fluids. Approximately 2 liters of still water (water, compote, tea - it doesn’t matter). The amount of fluid may depend on approximately how much water a person drinks. In children this dose is much less. Carbonated drinks are not allowed because they cause increased gas formation, which closes the internal organs. It is also undesirable to drink alcohol before an ultrasound scan of organs. It is important to take a responsible approach to the preparation process. Otherwise the result will be inaccurate.
Return to contents
How is the procedure done?
The ultrasound technique and algorithm depend on its type. It is important that the patient knows in advance what awaits him and how the study will proceed. The following types are distinguished:
Return to contentsTransabdominal
Transabdominal ultrasound of the bladder is suitable for everyone (children, men, women). Requires patient preparation. It consists of eliminating all foods that cause increased gas formation a few days before the procedure (baked goods, legumes, dairy and fermented milk products, coffee, mineral water). For prevention, these days you need to drink 2 tablets “ Activated carbon"(not recommended for children). This is necessary so that gases do not block the view. In the evening, it is advisable to give a cleansing enema. Immediately before the procedure, you need to fill your bladder. During the procedure, the patient lies on his back. It is worth noting that this type is less accurate, but more common.
 Transrectal ultrasound of the bladder is more suitable for people with low sexual activity. Return to contents
Transrectal ultrasound of the bladder is more suitable for people with low sexual activity. Return to contents Transrectal (TRUS)
TRUS is used to diagnose diseases in women who do not sex life, and men. During the procedure, the patient lies on his side with his back to the doctor (preferably on the left) with his legs pressed to himself. TRUS includes ultrasound of the prostate and bladder. TRUS of the prostate is performed. Going through this examination can be painful. It is necessary to prepare for the study in a special way. To do this, you must select one of the methods:
- drink a laxative;
- give a microenema;
- put a glycerin suppository.
TRUS shows a clearer picture than transabdominal ultrasound.
Return to contents
Transvaginal
Transvaginal ultrasound of the bladder is suitable only for women who are sexually active. The procedure is allowed during menstruation and pregnancy. It is important to inform the doctor about your piquant situation. This method is carried out when the bladder is empty. But preparation for the procedure is mandatory: diet and cleansing the body of gases. During menstruation, an ultrasound of the uterus may show abnormalities.
 Transurethral ultrasound of the bladder is performed through the urethra of the male penis. Return to contents
Transurethral ultrasound of the bladder is performed through the urethra of the male penis. Return to contents Transurethral
This method used very rarely. For this study we use local anesthesia, this is due to the fact that insertion of the device into the urethra can be painful. This method is used only in men. Before the procedure, you should not eat heavily, smoke, or drink alcohol. In addition, it is important to tell the doctor what drugs you are allergic to and whether you have chronic liver or kidney diseases. Transurethral examination of the bladder and urethra can detect bladder tumors.
Return to contents
Peculiarities of implementation in different groups of patients
Ultrasound in women
Everyone without exception undergoes research. Ultrasound of the genitourinary system in women is performed using both transabdominal and transvaginal methods. In the first case, sometimes an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is also performed at the same time. Ultrasound can detect many inflammatory diseases, as well as neoplasms, and determine whether they are benign or malignant. Before an ultrasound of the bladder, you need to make sure that the woman has no problems with the central circulation (especially during menstruation). An ultrasound of the kidneys clearly shows the neoplasm.
 Ultrasound of the bladder during pregnancy does not have any special restrictions or prohibitions, because does not provide negative influence for fruit.Return to contents
Ultrasound of the bladder during pregnancy does not have any special restrictions or prohibitions, because does not provide negative influence for fruit.Return to contents During pregnancy
There is an opinion that pelvic ultrasound is contraindicated. This is wrong. Ultrasound does not have a negative effect on the fetus, the same applies to the placenta. Thus, this procedure is completely safe for a woman in an interesting position. But telling your doctor about pregnancy is very important. In this case (depending on the age and size of the fetus) he will be able to select correct method research. This is important because in the later stages or if there is a threat of miscarriage, transvaginal ultrasound is prohibited. This may lead to undesirable consequences. Sometimes the test can detect the presence of a fetus.
Return to contents
Ultrasound in men
An ultrasound of the bladder is performed in men to show a full bladder. There is no need to do an ultrasound of the prostate and bladder separately; both organs are clearly visible in this study. In addition, you can look at the condition of the prostate gland. The most common type of this study is transabdominal. It is ideal for men. It is used to check for bladder tumors.
It is important that the doctor knows about everyone chronic diseases internal organs.
 Ultrasound of the bladder can also be performed on children if problems arise with the urinary system. Return to contents
Ultrasound of the bladder can also be performed on children if problems arise with the urinary system. Return to contents Ultrasound in children
Most often, ultrasound is performed on a full bladder in older children. With the advent of diapers, cystitis is becoming more common in infants. This may be due to wearing a filled diaper for a long time. Ultrasound examination can determine the presence of this disease. In addition, diseases of the genitourinary system in infants may be associated with abnormal development of the kidneys, bladder and ureters. The pathology in this situation is congenital. Girls are more likely to suffer from this disease. Preparation for an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder is impossible in this situation. You can suspect a problem if the baby cries when urinating. The size of the bladder in children is smaller than in adults. Ultrasound does not harm the baby.
Return to contents
Ultrasound with determination of residual urine
If residual urine is detected by ultrasound of the prostate gland, then sometimes this is considered normal if the amount of urine does not exceed 40 ml (approximately 10% of total number). If there is more urine, this indicates the presence of diseases of the bladder and prostate gland. This problem can be expressed by severe spasms or muscle strain bladder walls. Most often seen in children and older men. Preparing for the study involves having a bowel movement in a normal position if desired (you cannot wait long before doing this).
Return to contents
Decoding: what is the norm
The data that the study provides is very useful for making a diagnosis. According to the MP standard, it has the following indicators:
 The doctor calculates the norm or deviation after an ultrasound of the bladder using several indicators.
The doctor calculates the norm or deviation after an ultrasound of the bladder using several indicators. Normally, the bladder wall is smooth and uniform. It is important to examine the ureters and make sure there are no tumors there. The remainder of the urine is checked for an empty MP. If it is not visualized, it means that the patient was not prepared in good faith and the ultrasound must be done again. If the result repeats, this indicates the presence of the disease. The concept of norm may vary depending on individual indicators person. The volume and size may vary depending on the amount of liquid a person drinks daily. Ultrasound of the bladder can reveal inflammatory diseases.
Interpretation of the results is the prerogative of the attending physician.
 Inflammation of the bladder on ultrasound is shown by formations at the bottom of the organ. Return to contents
Inflammation of the bladder on ultrasound is shown by formations at the bottom of the organ. Return to contents Signs of inflammation
Inflammation is clearly shown by ultrasound of the bladder. In the presence of cystine in the bladder, a clot is formed consisting of epithelium, leukocytes, and erythrocytes. It settles at the bottom of the MP. In this case, the conclusion will write “sediment in the bladder.” If inflammation progresses, the walls begin to thicken and the contours become uneven. The sediment begins to look more like flakes. Ultrasound picks it all up. In this case, in the conclusion you can see the entry “flakes in the bladder.”
Return to contents
Other pathologies
Using this method, it is possible to see the formation of the bladder (both inside the bladder and on its walls). Foreign bodies and air are visible. Hypertension or prostate hypertrophy is determined, urolithiasis disease, urethral injuries and other diseases. To exclude the occurrence of complications, once every 2 years you need to undergo an examination and a urine test (for men over 40 - once a year). Then you can be sure that everything is in order with your health.
etopochki.ru
Ultrasound of the bladder in women and men - how to prepare for the procedure
This examination method, such as ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, is based on the special properties of the ultrasound wave, which consists in its ability to be reflected from organ tissues with the formation of their image on the viewing monitor of a special apparatus. The ultrasound diagnostic method does not cause any inconvenience and discomfort and is suitable for people of any age category, including pregnant women.
When is an ultrasound performed?
There are a lot of indications for this study, but there are no contraindications at all. But each patient on the day when he will have an ultrasound scan must follow certain rules, which we will talk about a little later.
This diagnostic method is used for cystitis and suspected cystitis, for changes in urine tests, for pyelonephritis, and so on.
Ultrasound helps identify:
- Tumor formations
- Diverticula
- Sand, stones
- Foreign bodies
- Developmental pathologies
- Vesicoureteral reflux
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane
And also, with the help of ultrasound diagnostics, you can quite accurately determine the size of the organ itself (wall thickness, volume) and other structures.
Ultrasound examination with Dopplerography makes it possible to assess the patency of the ureters, their location and the symmetry of the processes occurring in them, and assess the blood flow in tumor vessels in comparison with normal ones. Dopplerography is also used to study reflux.
 There are a lot of indications for ultrasound, but there are no contraindications at all.
There are a lot of indications for ultrasound, but there are no contraindications at all. Preparation
Many patients do not know how to prepare for a bladder ultrasound. There is nothing complicated here. Preparing for an ultrasound of the bladder is just about filling it. To prepare for the study, one to one and a half hours before the procedure, the patient drinks at least a liter of still water, compote or tea. Milk is not suitable for these purposes. You will need to refrain from urinating until the end of the study. With cystitis and some other diseases, this can be especially difficult, and the patient feels acute discomfort. In such cases, you can go to the toilet, but after that drink two or three glasses of water again.
 Preparing for a bladder ultrasound is just about filling it
Preparing for a bladder ultrasound is just about filling it If the ultrasound is not scheduled for a specific time, then you can not drink a large amount of liquid at one time, waiting until the bladder is full naturally. This usually happens within three to four hours.
Note! Correct visualization on the monitor of an ultrasound machine during an ultrasound scan of the kidneys and bladder can be hampered by the intestines when they are filled with gases and feces. If you are prone to constipation and flatulence, two days before the test the patient should exclude legumes, fresh fruits and vegetables, carbonated drinks, and alcohol from the diet.
 If you are prone to constipation and flatulence, two days before the test the patient should exclude legumes, fresh fruits and vegetables, carbonated drinks, and alcohol from the diet.
If you are prone to constipation and flatulence, two days before the test the patient should exclude legumes, fresh fruits and vegetables, carbonated drinks, and alcohol from the diet. Through a bladder filled with fluid, you can view the uterus before and during the first trimester of pregnancy, the ovaries, and in men, identify cysts and other formations in the prostate gland.
Study
Let's figure out how an ultrasound of the bladder is done, what the “norm” is in this case, and how to decipher ultrasound data.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs is generally carried out in two ways, it all depends on what and from whom we are looking:
- Through the abdominal wall;
- Through the rectum, urethra or vagina in women.
With both methods, a video image of the organs being examined is received from a scanning sensor and transmitted to the monitor screen; the procedure lasts about twenty minutes.
 The video image of the organs being examined with both methods comes from a scanning sensor and is transmitted to the monitor screen
The video image of the organs being examined with both methods comes from a scanning sensor and is transmitted to the monitor screen If the doctor suspects a pathology of the bladder, the doctor asks the patient to empty the organ and takes control measurements of it with the remainder of the urine.
A sonologist may perform a transvaginal or rectal ultrasound examination if:
- extensive adhesive process,
- to confirm the identified pathology,
- for obesity and difficult visualization,
- with tumors and large amounts of effusion in the abdominal cavity.
The way an ultrasound of the bladder is performed in females differs from conducting the same study in men due to the anatomical and physiological differences in their bodies. In women, the examination is more often performed externally, in some cases resorting to transvaginal examination.
Note! In this case, the bladder should also be full.
Ultrasound of the genitourinary system in the male population is also often performed through the abdominal wall. However, in case of significant obesity, as well as with ascites and prostate tumors, the patient undergoes a transrectal ultrasound.
 Ultrasound of the genitourinary system in the male population is also often performed through the abdominal wall
Ultrasound of the genitourinary system in the male population is also often performed through the abdominal wall Naturally, before performing an ultrasound, the intestine must be free (microlax enemas, laxatives (sodium picosulfate, senade) or glycerin suppositories.
In some situations, intracavitary examination is recommended for both men and women, in which a thin sensor is inserted through the urethra into the bladder cavity.
How are ultrasound data interpreted?
Deciphering the ultrasound of the bladder, coupled with the anamnestic data obtained from the patient and the history of his illness, makes it possible to most accurately make a diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe adequate therapy to the patient.
 The normal bladder has an echo-negative structure
The normal bladder has an echo-negative structure - The normal bladder has an echo-negative structure; it is a round-shaped organ in the transverse projection and ovoid in the longitudinal projection. The contours of the bladder are normally smooth and clearly visualized. The cavity should be free from foreign inclusions, the wall thickness should be uniform throughout its entire length and be 0.3-0.5 cm. The maximum speed of urine outflow is normally approximately 14.5 cm/s. To evaluate it, as well as to give a more detailed description of the urethra and bladder neck, an intravesical examination is performed, which was already mentioned above. The normal level of residual urine in an adult is approximately 50 ml or less.
- If its quantity is increased, this may indicate a tumor or inflammatory process, and also possibly about compression urinary tract stone.
- The acute phase of cystitis gives an ultrasound picture of small areas of positive echogenicity. This is what sediment looks like on the monitor - accumulations epithelial cells, erythro- and leukocytes, as well as salt crystals. In a lying patient, it is localized along the posterior wall of the bladder, and when the person gets up, it moves to the front. On initial stage diseases, the contours of the walls remain clear, and the thickness remains normal.
 The acute phase of cystitis gives an ultrasound picture of small areas of positive echogenicity
The acute phase of cystitis gives an ultrasound picture of small areas of positive echogenicity As the process becomes chronic, the wall thickens, the contour ceases to be smooth, and the sediment looks like flocculent structures. When blood clots form, a picture of hyperechoic formations (sometimes hypo-echoic) is first observed, and then they liquefy and acquire uneven contours and, in places, an anechoic structure.
- Thickening over the entire surface of the bladder wall with characteristic trabecularity in patients childhood may indicate obstruction by the urethra's own valve.
- If thickening of the bladder wall is combined with ureterohydronephrosis, then we will talk about the so-called neurogenic bladder.
- Echogenic structures, visually fused to the wall of the organ, can be polyps, stones, signs of urethrocele and prostatic hypertrophy.
- Mobile echogenic formations can be stones, air bubbles, foreign bodies and blood clots.
- Enlarged organ, depending on history and data laboratory tests, may be a consequence of hypertrophy, edema, inflammation, injury and other pathological processes.
Ultrasound examination of the bladder is a highly informative method that allows you to identify quite wide range pathologies of this organ and those closest to it anatomical structures.
This method is safe, painless and requires minimal preparation from the patient.
Home » Diagnostics » Ultrasound of the bladder in women and men - how to prepare for the procedure
symptom-treatment.ru
Indications and norms of ultrasound of the bladder
Ultrasound of the bladder is recognized as an important diagnostic method in urology and related fields of medicine (gynecology, andrology, etc.). Typically, this procedure is performed in conjunction with an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvis. This is necessary for differential diagnosis bladder disorders from other diseases with similar symptoms.

Why is an ultrasound examination of the bladder necessary?
Ultrasound of the bladder is indispensable for diagnosing inflammatory kidney diseases and urinary system, with cystitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the organ), urinary incontinence. And also with enlarged prostate gland in men and other disorders. The scan shows the size of the organ, its shape, volume, wall thickness, and the volume of residual urine (with a double procedure).
As a result of an ultrasound scan, a doctor can identify the following pathologies:
- urinary tumors (benign and malignant);
- stones, sand and foreign bodies in the organ cavity;
- degree of inflammation of the mucous membrane (with cystitis);
- wall diverticula;
- congenital developmental anomalies;
- reflux of urine from the bladder back into the ureters;
- blockage of the urethra (stone or tumor).
Ultrasound with Doppler (Doppler) is also often used. This procedure allows you to evaluate not only the size of the organ, but also see how freely urine moves through the ureters. In addition, Doppler ultrasound makes it possible to trace the direction of urine flow, its shape and symmetry.
Indications for the study
Ultrasound of the bladder is usually done as part of comprehensive examination patient. The doctor may prescribe a referral for an ultrasound if there are characteristic symptoms, as well as when monitoring recovery after surgery or chemotherapy is necessary. Portable ultrasound machines are also used at home if daily monitoring is required to analyze the function of the urinary system.
The main indications for ultrasound diagnostics are:
- change in color or noticeable blood in the urine;
- sediment or flakes;
- pulling or sharp pain when urinating;
- unnatural frequent urge to urination (even if there is no pain);
- urine volume is too small;
- discomfort or pain in the bladder area (above the pubis).
A control ultrasound of the bladder is always prescribed after tumor removal, regardless of whether it was organ resection or endoscopic surgery. Removal of stones from the urinary tract, surgery on the ureters and urethra, transurethral resection of the prostate also require a final ultrasound scan.
The doctor may also send the patient for such an ultrasound if there is a suspicion of inflammation of the prostate (in men) or the uterine appendages (in women). This procedure is mandatory when diagnosing inflammation and congenital anomalies ureters, kidney diseases.
Types of ultrasound
How is an ultrasound of the bladder performed? For cystitis, the doctor usually recommends one of two methods: transabdominal or transvaginal. But modern medicine knows and applies 4 options for ultrasound diagnostics of this organ.
- Transabdominal (through the external abdominal wall).
External ultrasound of the bladder is used most often; the main condition is a full bladder. This method does not bring any discomfort to the patient, but with urinary incontinence and obesity such ultrasound is impossible.
Helps to make a more accurate diagnosis of patients in comparison with the previous method. The procedure is performed with an empty bladder.
The method is suitable for men and girls who are not sexually active. This procedure is also considered more informative than external ultrasound. In men, this makes it possible to assess the relationship between prostate damage and diseases of the urinary system.
This type of ultrasound is used least often - inserting a sensor into the urethra can lead to damage and requires mandatory anesthesia. However, this procedure is indispensable for inflammation of the urethra. Transurethral scanning shows the extent of damage to the canal walls and allows you to assess the condition of neighboring organs.
Ultrasound of the bladder may include an assessment of the volume of the organ with determination of residual urine and examination of its wall.
Measuring the volume of the organ itself and residual urine takes place in 2 stages. First scanned full bubble, then the patient is sent to the toilet and a second ultrasound is performed. Fluid volume is measured before and after urination. This procedure is necessary when identifying the causes of urinary outflow problems. For cystitis and other disorders of the urinary system, scanning of the bladder wall is also performed - transverse and longitudinal.
Preparing for a bladder ultrasound
Proper preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder is a guarantee that the results will be accurate and the diagnosis will be error-free. Each type of ultrasound requires special preparation, so you need to ask your doctor in advance which diagnostic method is right for you.
For a transabdominal procedure for cystitis and other disorders, you need to go with your intestines prepared. To do this, in 3-4 days you will have to exclude from the diet all dishes that provoke flatulence and bloating. These are cabbage, peas and beans, fresh apples, milk and baked goods. You can take Espumisan. It is advisable to do a cleansing enema or just go to the toilet the day before the procedure.
External ultrasound is the only one that requires a full bladder. This condition can be ensured in two ways: either do not go to the toilet in the morning before the procedure (4-5 hours), or drink 1.5 liters of liquid an hour and a half before the ultrasound. It can be water without gas, Herb tea, fruit drink or compote.
For transrectal ultrasound, it is necessary to thoroughly cleanse the intestines the day before. Microenemas, mild laxatives or anal suppositories are suitable. Transvaginal ultrasound is performed with an empty bowel and an empty bladder. And if transurethral ultrasound is prescribed, it is enough to give up a hearty breakfast and cigarettes a few hours before the procedure. The last two varieties also require careful hygiene procedures before analysis.
Norms of ultrasound results
Interpretation of the results of an ultrasound scan of the bladder includes several parameters, on the basis of which the attending physician makes a final diagnosis. These indicators include:
- bladder shape and volume;
- residual urine (volume);
- organ structure;
- wall thickness;
- filling and emptying.
The shape of the organ differs between men and women, with the latter having a significant influence on appearance bladder are influenced by the position of the uterus and pregnancy, the number of births. Normally, a full organ is shaped like a pear, while an empty organ is shaped like a saucer. In women it is wider on the sides and compressed at the top.
The volume also varies depending on the gender of the patient. For women – 250-550 ml, for men – 350-750. Residual urine should not exceed 50 ml (in healthy person it shouldn't exist at all). Normal wall thickness is in the range of 2-4 mm, and the average emptying rate is 50 ml/h.
Ultrasound of the bladder is one of the most informative methods for diagnosing disorders of the urinary system. And the variety of methods of this research allows us to take into account individual characteristics patient and make the most accurate diagnosis.
Treatment of any disease begins with its diagnosis. In diagnosing various diseases, all kinds of methods are used, because in some cases just an examination and interview with a doctor will be enough, and in others you will only need best practices. Pathologies of the genitourinary system are not uncommon today and, although most women suffer from them, men can also get sick.
Diseases associated with the bladder in men often cause many problems for patients, especially if the patient, for some reason, for a long time didn't see a doctor.
As instrumental diagnostics In men, ultrasound of the prostate and bladder is often used, which will allow you to quickly and effectively diagnose pathology.
About ultrasound
Ultrasound diagnostic methods currently occupy one of the most important places in medicine. The range of diseases that ultrasound covers is difficult to list. But the reasons why this method is so popular will be covered further.
Ultrasound is one of the relatively new diagnostic methods, which quickly became widespread not only throughout the world, but also in many branches of medicine. Urologists are one of those doctors for whom ultrasound is one of the key methods.
This popularity is due to several factors:
- Safety. Ultrasound diagnostics of the bladder in men is absolutely safe for the human body and will not cause any harm;
- Accuracy. One of the most important criteria for all diagnostic methods, because no matter how safe the method is, if it is ineffective, it will simply not be used. In the case of ultrasound, it wide application speaks for itself in the matter of accuracy;
- Painless and non-invasive. When an ultrasound is performed, there is no need to puncture the skin, and the diagnosis itself is absolutely painless;
- Availability. Many people suffer from diseases of the genitourinary system, including pathologies of the bladder, and the study needs to be performed in both men and women. Ultrasound is a cheap and accessible method, because it is widespread everywhere.
Not without its shortcomings. In some cases, ultrasound of the bladder and prostate is not enough and you will need to resort to more complex and expensive types of research. Also, after an ultrasound, it may often be necessary to additional diagnostics, as for example with bladder tumors.
What does an ultrasound of the bladder show in men? Indications for the study
 What does an ultrasound of the bladder and prostate show:
What does an ultrasound of the bladder and prostate show:
- During the examination, the doctor can assess the condition of the bladder walls and measure the necessary structures. The thickness of the walls, the presence of inflammation and pathological elements on them are assessed. As for inflammation, ultrasound can distinguish a chronic process from an acute one.
- Pathologies such as diverticula, that is, protrusions of the bladder, are also detected. They can and do become inflamed much more often than the normal bladder wall. Although sometimes a person can live his whole life and not even know about this diverticulum.
- The contents of the bladder, its nature, quantity, adhesion to the bladder wall are also assessed. Rocks and sand are found. Stones can cause blockage of the urethra and severe pain.
- There are also more curious cases when foreign bodies are found in a man’s bladder and ultrasound is used to detect them. Often, during an ultrasound of the bladder, the prostate is also examined.
Sometimes a conventional ultrasound is not enough and is used. This method allows us to evaluate the flow of fluids in our body. In this way, backflow of urine may be detected or, if there is a tumor, a change in blood flow will be detected. Doppler ultrasound will help assess the severity of the blockage, determine at what level it occurred, and also help surgeons in surgical intervention.
Ultrasound of the bladder and prostate in men is done both routinely and in the presence of symptoms and signs. The indications are:
- Of the complaints, the first signs may be difficulty, and sometimes even the absence of urination. The cause may be inflammation of the prostate gland, blockage of the urethra with a stone (aka calculus), tumors of both the walls of the bladder and the prostate. The process can also be intermittent and with the presence of air. As for the first, this may well happen both with tumors and stones, and with diverticulosis.
- Another common problem is soreness. Its causes are similar to those for difficulty urinating, but cystitis can also be added here. It is an inflammation of the bladder.
- One more a clear sign, signaling the need for diagnosis, and then further treatment- change in urine color. It may be cloudy, with some inclusions or blood. The presence of blood can indicate a wide range of diseases.
- Increased urination is one of the most common symptoms. It is often combined with difficulties during the urination process and pain. Therefore it is difficult to name this symptom very specific and if such symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
- In addition to color, a sick man may notice “flakes” or any other inclusions in his urine that are visible to him with the naked eye. But their nature can only be established after a thorough examination.
Types of ultrasound for examining the bladder in men
 Ultrasound examination of the bladder and prostate in men is performed mainly through the anterior abdominal wall. However, there are cases when it is necessary to use a transrectal examination.
Ultrasound examination of the bladder and prostate in men is performed mainly through the anterior abdominal wall. However, there are cases when it is necessary to use a transrectal examination.
- performed through the abdominal wall. Does not require external damage skin and any other penetration of foreign bodies into the body, as well as the introduction of contrast agents.
- Transrectal ultrasound is performed less frequently. There are several indications for it. This is obesity, ascites, that is, the presence of a large amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity, and with suspected or existing tumors of the prostate gland and bladder.
Preparation for ultrasound of the prostate and bladder
Preparing for an ultrasound examination of the prostate and bladder for a man includes a number of simple steps:
- An ultrasound is performed on a full bladder. This will allow us to examine all the pathologies that ultrasound can detect, since ultrasound waves travel best in a liquid medium.
- It is advisable for a man to adhere to a diet about a day before an ultrasound of the bladder. This is especially true for patients with increased gas formation for any reason. The diet excludes fresh baked goods from the diet, a lot fresh vegetables and fruits, dairy products. If this does not help, then before the ultrasound you will need to take several carminative tablets.
- As for filling the bladder, everything is simple - you need to drink from 0.5 to 1 liter of liquid an hour before the test. It is desirable that this be plain water. Under no circumstances should you fill your bladder with a carbonated drink. Then, you will need to wait until the ultrasound examination of the bladder is completed. In addition to the bladder, you can also see the prostate gland.
- Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate and bladder differs in preparation, but will also require a full bladder. Before such a study, you will need to cleanse the rectum. You can use laxatives, special suppositories or microenemas. The methodology is also different, about which we'll talk Further.
How is an ultrasound examination of the bladder performed in men?
Now the patient will be interested in the question: “How is an ultrasound of the bladder done?”
- Transabdominal ultrasound is performed extremely simply: the patient comes to the ultrasound room and the doctor asks him to lie on the couch and expose his stomach. Then a special gel is applied to the area of study, which is necessary to improve its glide over the skin and improve the quality of the study, because the air that accumulates between the transducer (sensor) and the skin is a rather strong distorting element. Because of this, the accuracy and reliability of the data obtained may be greatly reduced. After completing the study, the patient can go to the toilet and remove the remaining gel using a towel or napkins.
- Transrectal ultrasound of the bladder and prostate is performed with a different sensor, which is adapted for research through the rectum. The advantages of such a study are that the sensor is located in close proximity to the bladder and all that separates them is the wall of the rectum.
Thus, if there is a prostate tumor, it can be seen much better than with a transabdominal ultrasound.
Contraindications

- There are practically no contraindications to transabdominal ultrasound of the bladder for men, and those that exist are treatable, after which diagnosis can be made. These include extensive and severe inflammatory skin lesions, burns and other injuries. The main reason for the impossibility of performing ultrasound, in this case, is its lack of information, since it is impossible to ensure optimal contact between the sensor and the skin, especially since it can cause severe discomfort and pain to the patient.
- Transrectal ultrasound examination of the prostate and bladder also does not have strict contraindications, but here they are much more dangerous. It cannot be carried out after surgical interventions on the rectum if the patient has chronic anal fissures or hemorrhoids in the acute stage. If there is still urgency in conducting transrectal ultrasound, it can be performed through the skin of the perineum, but the quality of such a study will be lower.
results
The results are assessed by the urologist who referred the patient for an ultrasound or to whom the patient was referred after the examination. The doctor does not just compare the ultrasound of the bladder with the norms, but performs a comprehensive assessment of all the data obtained, not only from the ultrasound.
The norms for ultrasound of the bladder in men and determination of residual urine are:
- Shape: when the bladder is full, it is pear-shaped, and after urination it becomes saucer-shaped;
- Structure: echo-negative (on ultrasound images of the bladder it appears as dark spots);
- Volume: from 350 - 750 ml.;
- Wall thickness: from 2 to 4 mm;
- Filling: normal filling rate is 50 ml/hour
- Volume of residual urine: no more than 50 ml.
Finally
Ultrasound today is one of the safest methods of examining the body and, at the same time, affordable. In the case of diagnosing bladder pathologies, safety is extremely important due to the close proximity to the organs reproductive system, which are quite susceptible to various types of radiation exposure.