In dentistry, inflammation of the oral mucosa is commonly called stomatitis. This disease can develop at any age, causing equally much inconvenience to both children and adults. The disease has several varieties with different symptoms, but they all have one thing in common - with stomatitis, the mucous membrane becomes painful and swollen, which makes it difficult to eat and worsens general well-being. What treatment is carried out if the oral mucosa is inflamed, you will learn from the article.
Types of disease
Depending on why inflammation of the oral mucosa developed, the following groups of stomatitis are distinguished:
- infectious;
- allergic;
- traumatic.
Traumatic
If the oral mucosa long time damaged in the same place, for example, incorrectly installed prosthesis or a protruding edge of the filling, inflammation develops in this place - the mucous membrane swells and turns red. An infection can get into the wound, as a result of which the symptoms will intensify and erosions will form on the surface of the mucous membrane.
Chronic injuries to the mucous membrane can lead to the development of inflammation on it.
The cause of traumatic stomatitis can be:
- eating too hard foods (crackers, candies with sharp edges);
- thermal burn mucous membrane (those who like too hot food and drinks are susceptible);
- exposure to chemicals ( chemical burn);
- smoking (under the influence of tar and tobacco smoke mucous membrane dries out);
- wearing (protruding elements of the brace system can rub the oral mucosa);
- habit of chewing toys in children.
Infectious
If an infection (this could be a virus, bacteria or yeast) gets into microscopic cracks or wounds in the mucous membrane, one of the following types of disease develops:
- bacterial;
- (the most common is herpetic);
- fungal (candidal) stomatitis.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane oral cavity can develop under the influence of bacteria such as streptococcus and staphylococcus, less commonly - gonococci and diplococci. Signs bacterial stomatitis is redness of the mucous membrane, the formation of numerous ulcers on it, and a dense coating on the tongue.
IN childhood stomatitis can develop due to infection entering the mouth with dirty hands and toys.
Among the viruses, the most common causes of oral inflammation are herpes virus, measles, rubella, influenza, and diphtheria. The disease is characterized by inflammation of the mucous membrane, the appearance of aphthae on it, which eventually develop into ulcers. The patient complains of aches, weakness, drowsiness, and his body temperature may rise.
Fungal stomatitis is caused by Candida fungi. They are part of normal microflora oral cavity healthy person, but in insufficient quantities for the development of the disease. Under unfavorable conditions, including decreased immunity and treatment with antibiotics, their number increases and inflammation of the oral mucosa occurs. Characteristic for fungal stomatitis Features include the appearance of a cheesy coating in the mouth white, itching and burning. When you try to remove plaque, you can see redness and ulcers underneath it.

If signs of inflammation appear, contact your dentist!
Allergic
The reason why the mucous membrane in the mouth becomes inflamed may be an allergy. The development of inflammation can be triggered by taking medications, wearing prostheses, materials used for dental treatment. In addition, allergens can affect the body outside the oral cavity, for example, allergies can develop to animal fur, plant pollen, and mold spores. Wherein allergic manifestations on the oral mucosa may not be the only unpleasant symptom. Stomatitis may appear in combination with skin reactions or rhinitis.
One of the most common cases is the development of allergic stomatitis in owners of acrylic plastic. The monomer they contain has a toxic effect on the body and provokes various unpleasant symptoms in the oral cavity, such as burning, itching, redness, and swelling. The monomer is necessary for the material to harden, but its increased content in the prosthesis is dangerous for the body.
Other causes of mucosal inflammation
In addition to the above factors, inflammation of the mucous membrane can lead to:
- chronic infection in the mouth, such as teeth affected by caries;
- low level of oral hygiene or complete absence(as a result, stone forms on the teeth);
- alcohol consumption;
- chronic diseases of the digestive tract;
- severe overwork, stress;
- weakened immunity, vitamin deficiency;
- anemia;
- HIV infection;
- taking medications that affect saliva production;
- unbalanced diet, strict diets;
- the use of toothpastes with surfactants and parabens;
- ecological situation;
- poisoning by toxins, chemicals.
What to do if you have inflammation of the oral mucosa?
Treatment of stomatitis should be comprehensive. The dentist should prescribe it based on the type of disease. Treatment can be carried out at home.
Common in the treatment of any type of stomatitis is the prescription of a diet. The patient is advised to avoid spicy, sour, hot, salty, sweet food, avoid consuming too hot or cold foods and drinks. This will prevent irritation of the mucous membrane and promote its restoration.
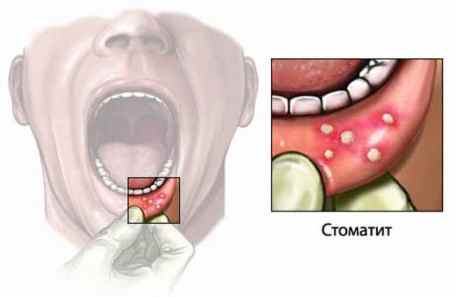
If painful aphthae have formed on the mucous membrane, they can be lubricated with anesthetics.
To increase the body's immunity, they are prescribed vitamin complexes. In addition, to strengthen local immunity, immunostimulants, for example, IRS-19, can be prescribed.
For the treatment of viral stomatitis are prescribed antiviral drugs in the form of tablets orally, as well as rinsing with antiseptic solutions and applying gels to the affected mucosa. The doctor may prescribe Valavir, Valtrex, Famvir, Acyclovir tablets. Viferon gel and Miramistin solution can be prescribed locally to treat the mucous membrane.
In case of traumatic and allergic stomatitis treatment of inflammation of the oral mucosa will begin with eliminating the provoking factor. Only symptomatic therapy, for example, anti-inflammatory ointment for the mucous membrane or taking antihistamines(Claritin, Suprastin), will not lead to full recovery, but will only give temporary relief. If the cause of stomatitis is not eliminated, inflammation will develop again.
When aphthae, ulcers and erosions form on the mucous membrane, they can be used to heal wounds. dental gels, Metrogil Denta. A wound-healing and disinfecting effect will be achieved by treating damaged areas with the drug. plant based. Will help speed up mucosal regeneration sea buckthorn oil and rosehip oil.
In some cases, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat bacterial stomatitis. Among the drugs for oral administration, the most frequently prescribed include Amoxiclav, Cefazolin, Flemoxin.
When inflammation of the oral mucosa develops, diagnosing the disease from a photo and self-medicating can be dangerous. If treatment tactics are chosen incorrectly, the disease can progress. Stomatitis is dangerous not only because of its unpleasant symptoms, but also a transition to chronic form. Don't self-medicate!
Inflammation of the oral mucosa can be different. This disease includes:
- Gingivitis
- Stomatitis
- Herpes stomatitis
- Traumatic inflammation and many other diseases.
Although all diseases are diverse, the symptoms are still almost the same - pain in the mouth, for example on the gums, cheeks, lips or throat. With all inflammatory processes, suppuration is observed, if left untreated, this or that disease will occur. Treatment, in principle, is also almost the same - rinsing with tinctures, teas, rubbing with antiseptic solutions, using ointments, less often treated with antibiotics. Let us consider in this article inflammation of the oral mucosa in more detail, how it occurs and what the symptoms are.
What is inflammation of the oral mucosa called?
In medicine, any inflammation of the mucous membrane is called Stomatitis, and even if all the diseases are different and the names are completely different, all the same, the inflammation is classified as a group of dental diseases.
The mucous membrane of the oral cavity becomes inflamed more often due to the fact that some serious changes are taking place in the human body that need urgent attention. If, of course, for example, a burn occurs in the oral mucosa and inflammation occurs for this reason, then you can not consult a doctor, but cure traumatic stomatitis with folk remedies. But if suddenly inflammation occurs for an unknown reason, then you need to consult a doctor.
What can a doctor do?
Since diseases of the oral mucosa are different, the doctor will, of course, first prescribe necessary tests. In general, by looking at the mucous membrane, he will be able to approximately determine for what exact reason the disease occurred. He will be guided by zones, since in a person’s mouth there are zones responsible for the internal organs. If inflammation occurs in any of the zones, the doctor immediately makes the first diagnosis and, based on it, prescribes tests and, if necessary, an x-ray of the internal organs.

If one of these diseases suddenly appears and is located in a certain area, it means there are problems with internal organs and if they are not eliminated, then the disease itself will be difficult to cure.
Palate hurts
More often, pain in the palate occurs due to injury. People drink hot tea or coffee and don’t even notice how I injure the mucous membrane. Yes, in this part of the mouth, the skin is very thin and delicate; it can be damaged even by hard food. After the injury, a day or two passes, and pain begins, as bacteria got into the wound, and a slight ulceration resulted. Treatment of the oral cavity in this place, in general, is not difficult. It is necessary to rinse with medicinal tea and lubricate with an oil solution of vitamin A.
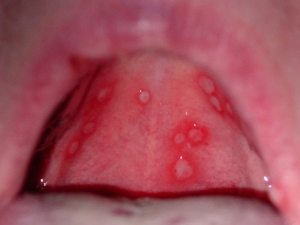 Damage to the oral mucosa can also occur simply due to too much strong love to tangerines or oranges. Minor ulcerations may also occur if there are too many seeds. In general, it is harmful to eat seeds the way many people are used to. They cannot be chewed with your teeth; they must be cleaned with your hands, only in this case there will be no problems with either inflammation of the mouth or the appendix.
Damage to the oral mucosa can also occur simply due to too much strong love to tangerines or oranges. Minor ulcerations may also occur if there are too many seeds. In general, it is harmful to eat seeds the way many people are used to. They cannot be chewed with your teeth; they must be cleaned with your hands, only in this case there will be no problems with either inflammation of the mouth or the appendix.
If the defeat occurs for these very reasons, then you need to reduce the consumption of sour foods and sour fruits. Stop eating the seeds and start rinsing your mouth with antiseptic solutions, and you can also use retinol ointment, apply it only to the affected areas in a thin layer.
What can you say about people who smoke?
 They do not care about their health, and even if they try to do so, it is all in vain, since nicotine clogs the body and kills all useful substances. Such people have stomatitis different types are common and sometimes difficult to treat if a person refuses to quit smoking. If smoking man If there is irritation in the oral cavity, you should immediately stop smoking and begin treatment. Again, rinse and lubricate the damaged areas medicinal ointments.
They do not care about their health, and even if they try to do so, it is all in vain, since nicotine clogs the body and kills all useful substances. Such people have stomatitis different types are common and sometimes difficult to treat if a person refuses to quit smoking. If smoking man If there is irritation in the oral cavity, you should immediately stop smoking and begin treatment. Again, rinse and lubricate the damaged areas medicinal ointments.
People who do not want to quit smoking suffer from the disease for more than one week, and in some cases, the disease progresses, despite good treatment. Nicotine corrodes the thin, delicate skin, you need to take pity on your body, because they won’t give you another one if this one wears out.
Treatment of mucous membranes in diabetics
In people suffering diabetes mellitus, the mucous membrane of the mouth is almost always inflamed. There is not enough saliva, it is dried out, cracked and therefore the treatment is quite complicated. A person with such a complex disease must constantly monitor the oral cavity and lubricate it with various medicinal ointments. Dentists recommend using. It softens the mucous membrane, moisturizes it and kills all pathogenic microbes.
The oral mucosa peels off
When the mucous membrane in the oral cavity peels off, this means that stomatitis has begun. It manifests itself, as already mentioned in different forms Oh. Sometimes the mucous membrane can peel off due to nerves.

How to treat this disease? Dentists advise consulting a doctor if the mucous membrane suddenly begins to peel off. This symptom indicates that there are problems with the stomach and the disease needs to be treated at the root. The doctor will prescribe treatment after examination.
- Well, if a chemical burn occurs, then you can simply lubricate the affected areas with retinol oil, that is, an oil solution of vitamin A. This composition quickly regenerates the skin
- If immunity is reduced, then you need to take immunomodulatory drugs, vitamins and sedatives. antiseptics, also lubricate with an oil composition.
In general, when treating diseases of the oral cavity, immunomodulating agents should be used, since the body is already weakened by the disease and needs to be helped to recover.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane due to injury
Tongue piercings are fashionable these days. Young people endure excruciating pain for several days while their tongue heals. But you need to know one nuance. Before you go to have this operation, you need to carry out a complete sanitation of your mouth, this is just before the visit to the cosmetologist. But a week before the operation, you need to prepare the body for stress and do this with the help of vitamins and minerals. We need to strengthen our immunity.
Since the piercing or traumatic object will penetrate deeply into the tongue and, moreover, pierce it through and through, at this very moment the body will experience, so to speak, “ breakdown" After this, rejection of the object may begin, glossitis will begin, and even an abscess. Exactly preparatory procedures will not allow the body to become too nervous. Or better yet, avoid piercing altogether.
In general, piercings will cause a lot of trouble to their owner, and in particular they will cause frequent injuries oral cavity. As you can see, there are many different factors that can lead to inflammation of the oral mucosa.
To prevent stomatitis in any form from tormenting you need to do simple preventive procedures, namely:
- Brush your teeth twice a day. Not only use a brush, but also dental floss, as well as mouthwash; of course, the procedure is complicated and long, but all bacteria leave the mouth completely
- Rinsing your mouth after every meal
- Food should be healthy, there is no need to eat fast food leading to gastrointestinal diseases
- No smoking
- Drink alcoholic drinks in small doses
- Take vitamins and immunomodulators
The mucous membrane is the protective covering of organs. It covers the digestive, respiratory, genitourinary system, as well as surfaces ear canals and century. The name comes from the word mucus, which means the arrangement of many secretory cells. In this article we will look at treatment of inflammation of the oral mucosa. How to remove inflammatory process, directly depends on the location of the lesion.
Symptoms of inflammation of the oral mucosa of various forms
Signs of inflammation depend on the form of the disease. There are two main ones. The first form is aphthous, which occurs due to the action of infectious or allergic agents on the oral mucosa.
Aphthous inflammation of the oral mucosa
For aphthous stomatitis aphthae appear on the mucous membrane of the lips, tongue, cheeks and palate (rather painful round-shaped formations with a bright red rim and a whitish-gray coating). A sick patient develops general malaise, body temperature rises, refusal of food, and enlarged lymph nodes. In some severe cases, the aphthae merge and small ulcers appear.
Fungal inflammation of the oral mucosa
For fungal inflammation The oral mucosa is dry and takes on a red tint. White dotted formations appear, which soon merge with each other. After this, an easily removable white film is formed, after which a bright red surface remains, either without damage or with ulcers.
Inflammation of the oral mucosa: treatment of the disease
After examining and identifying the root cause of inflammation, the doctor will prescribe drug treatment if necessary.
Rules of therapy for inflammation
complete medical examination;
quitting smoking and alcohol;
ban on antibiotics and cauterizing agents;
rinsing at home with a solution of: Furacilin, peroxide, pink solution of potassium permanganate;
use of herbal medicine – collection of chamomile, sage.
How to relieve inflammation of the mucous membrane caused by injury?
Treatment of inflammation caused by mechanical injuries to the mucous membrane comes down to eliminating the damaging factor - this can be removing a tooth fragment, grinding a filling and other methods. The oral cavity is irrigated with antiseptic solutions, after which any antiseptic solutions for rinsing your mouth. In some cases, treatment may include anti-inflammatory therapy and keratoplasty to promote the healing process.
Treatment of inflammation of the mucous membranes with home methods
Today, inflammatory processes of the oral mucosa in dentistry are in second place after caries. Inflammation of the mucous membrane is characterized different symptoms, and the reasons for its occurrence are the most banal. Many have had to deal with these problems in everyday life, and often we try to independently treat inflammation of the oral mucosa traditional methods.
To make ulcers heal faster due to inflammation of the oral mucosa, rinse your mouth hot water several times a day.
Mix freshly prepared cabbage juice with water 1:1. If you have inflammation, you should rinse your mouth with this solution a couple of times a day.
To treat inflammation, you can rinse your mouth with a solution of hydrogen peroxide (1 teaspoon per half liter of water) to reduce soreness of the mucous membrane.
To relieve inflammation of the oral mucosa, cover the gums on both sides with thin slices of garlic when the oral mucosa is inflamed. Keep it for half an hour. Despite severe pain you need to repeat this procedure three times.
To relieve inflammation, you can also apply raw potatoes to inflamed gums to reduce pain.
Prepare a solution of freshly squeezed carrot juice and water 1:1. If the mucous membranes are inflamed, you should rinse your mouth three times a day. Beta-carotene contained in carrots will help fight infection.
To treat inflammation, prepare a tincture of St. John's wort with vodka or 40% alcohol in a ratio of 1:5. Dilute 30-40 drops of tincture in half a liter of water to rinse the gums for inflammation of the oral mucosa several times a day.
How to cope with inflammation of the mucous membranes in the mouth using baths?
Baths made from herbal decoction. To prepare the decoction you will need the following herbs in equal parts:
Herb thyme and medicinal sage
Inflorescences of chamomile and red clover
Herb St. John's wort, silverweed and woodlice
Common raspberry leaves – half part
To stop inflammation, take a collection of the above herbs in the amount of 1 tablespoon, after crushing and mixing thoroughly, and pour boiling water (250 ml). Leave for at least 2 hours, wrapped in a terry towel. The strained infusion is used for treatment in the form of baths, that is, without using rinsing or sharp movements, you just need to take the decoction into your mouth and hold it for a minute or two on the inflammation side.
Treatment of inflammation of stomatitis with purulent complications
This collection is very good for treatment residual effects after removal of advanced purulent teeth:
Medicinal sage herb and red clover inflorescences - one and a half parts each
Herb woodlice, St. John's wort, peppermint and thyme - in equal parts
Chamomile flowers – half part
Take 2 tablespoons of a collection of crushed and thoroughly mixed herbs, pour in 1.5 cups of boiling water and leave for one and a half to two hours, having previously wrapped it up. It is used for inflammation of the mucous membrane, also in the form of baths. It is worth noting that sage is the most effective folk remedy from this composition to relieve inflammation, and mint is an excellent pain reliever.
Treatment of inflammation of the mucous membranes in the mouth and bleeding gums
Treatment of inflammation with manifestations of bleeding gums and looseness of soft tissues consists not only of using baths of decoctions, but you should also drink decoctions that help strengthen the gums and eliminate looseness of the mucous membrane.
To prepare a collection for the treatment of inflammation, take in equal parts:
Leaves of currant, lingonberry, silver birch and plantain
Herb St. John's wort, tricolor violet and meadowsweet
Knotweed grass, wild strawberry leaves and horse sorrel - half a part each
Red clover flowers, common hop cones and chicory leaves - half each
Woodlice grass - one and a half parts
Rose hips - one part
A decoction for the diagnosis of inflammation is prepared based on:
- if the number of components included in the collection is no more than 5, then take 1 tablespoon of the folk collection and pour boiling water (250 ml) - this is enough to treat inflammation of the mucous membrane for 24 hours
- if the collection consists of more than 5 herbs, then brew 2-3 tablespoons herbal collection for 2-3 glasses of water.
- And this solution will be enough for 2-3 days of treatment.
- The decoction is stored well in the refrigerator, but no more than 4 days.
This folk remedy should be drunk half a glass 3 times a day warm, and also used as a bath for the gums.
Why does inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth occur?
Stomatitis occurs due to infection (viruses, bacteria) on the oral mucosa. Inflammation of the mucous membrane can be one of the symptoms of diseases gastrointestinal tract, blood, allergic diseases, infectious diseases. The causes of the inflammatory process are non-compliance with oral hygiene, microtrauma of the mucous membrane, abuse of certain medications, violations immune system. Inflammation may be one of the manifestations of damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Causes of inflammation include:
diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver;
disruption of the endocrine glands;
problems with the cardiovascular system;
mechanical injuries mucous membrane;
infectious agents;
damage to any internal organ.
Inflammation of the mouth and gums arises as a consequence of an action of local origin or as one of the manifestations of any systemic disease. Factors of local origin include, in particular: neglect of hygiene, consequences of tooth decay, excessive deposits of tartar, defects in dental restoration, excessive alcohol consumption and smoking. Among the factors general the most common are: gastrointestinal diseases, malnutrition, diabetes, hormonal disorders, pregnancy, drug intoxication, as well as some occupational diseases. If the disease concerns only the gums, then this is accompanied by redness, weakening, painful formation of warts, and there is also a tendency to bleeding.
Exist various shapes inflammation of the oral cavity. In most cases, this is due to microbes entering the body with food, as well as a general weakening of the body, for example, after fever and some other diseases. Failure to maintain hygiene of the mother's nipples and unclean bottles lead to the ingress of microbes, which causes inflammatory processes. In addition, the causes of the disease can be irritability sharp teeth or brushing too vigorously. Some chemical substances, in particular incorrectly prescribed mercury, can also initiate the disease. In some cases, microbes can multiply, for example, in unclean milk. Inflammation of the oral cavity is a disease mainly of children, and only in ulcerative form it is also typical for adults.
Symptoms of oral inflammation
Common symptoms of oral inflammation include a feeling of heat in the mouth, redness, dryness, and excessive sensitivity. At the same time, children become capricious and irritable, and difficult to care for. They often reject the breast of a nursing mother. May also be observed heat, symptoms of indigestion (vomiting). Quite often the disease occurs during a fever.
Treatment of oral inflammation with folk remedies
Treatment of oral inflammation begins, first of all, with eliminating the causes of irritation, if they are the cause of the disease. In some cases, oral treatment helps treat the underlying disease. In both cases, a diet excluding spicy foods is recommended, as well as complete ban alcohol and tobacco.
In herbal medicine for treatment inflammatory diseases oral cavity use the following remedy: pour about a half-centimeter layer of liquid linden honey onto the bottom of a small saucepan. They take a very old and very rusty nail. Having heated it red hot, put it in honey. A thick black substance like tar forms around the nail. This black substance should be lubricated on the gums, mainly at night, before going to bed. The gum abscess usually breaks out soon, the swelling quickly subsides, and the patient’s health improves. Rust in in this case plays very important role. When heating a nail, do not blow on it or touch it to prevent rust.
To strengthen your gums and cleanse your teeth from plaque, it is useful to chew honey in a honeycomb.
For diseases of the oral mucosa and inflammation of the gums, you can use an infusion of chamomile with honey. Pour 3 tablespoons of dry crushed chamomile flowers into 0.5 liters of boiling water, let it brew for 15 minutes in a water bath, cool under the lid. Then strain, dilute 2 tablespoons of bee honey in the infusion and use for rinsing.
Pour 40 g of crushed propolis with 70% alcohol (100 g), leave for 7-10 days, shaking occasionally, then filter through gauze. By adding water to the alcohol, bring the solution to 4% concentration and use it to lubricate the gums. The course of treatment is from 3 to 10 applications.
At home, oral diseases are treated with St. John's wort oil. To prepare it, take 1 part of St. John's wort flowers and 2 parts of its leaves. Then the herb is placed in a transparent bottle and filled with four parts of olive oil. The oil is then left in the sun for two weeks, followed by a straining procedure. After this, the oil, which has taken on a blood-red color, needs to be heated to 50C, cooled slightly, moistened with a swab and wiped the areas affected by inflammation five to six times during the day.
Stomatitis - inflammation of the oral mucosa - pathological process, developing on the inner surfaces of the oral cavity in the presence of certain etiological factors. The disease occurs at any age, but children are more susceptible to it due to the peculiarities of the development of the jaw apparatus and the craving for testing foreign objects. Inflammation of the oral cavity is treated by a dentist or, if the patient is a child, a pediatrician.
Stomatitis is considered only a superficial pathological process. Purulent-necrotic pathology that affects the deep layers of the tissues of the oral cavity, gums and jaw bones does not apply to stomatitis. In this case we are talking about gingivitis, subperiosteal abscess, soft tissue phlegmon. Stomatitis can be an independent disease or be secondary in nature, being one of the symptoms of internal diseases such as:
- weakened immunity;
- herpetic infection;
- fungal infection;
- presence of a source of infection from which pathogenic microflora carried throughout the body by blood
Primary inflammations in the mouth usually respond to local treatment. Secondary stomatitis requires complex therapy, mainly aimed at eliminating the underlying disease.
Causes of stomatitis
The basis of primary inflammation of the oral mucosa is the entry of an infectious agent into the “gate” of infection. The role of the pathogen can be played by:
- fungi;
- viruses;
- bacteria.
Non-infectious causes of stomatitis exist. We are talking about damage from chemical or physical factors(acid burn, thermal burn). However, in this case, the traumatic agent only creates an entrance gate, violating the integrity of the mucous membranes. As a rule, already in the first minutes after injury, it is possible to identify some types of pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria in the lesion.
Damage to the internal surfaces of the mouth is often mechanical. The reasons for this phenomenon lie in the presence of sharp tooth fragments, children’s attempts to bite foreign hard objects, and incorrectly selected dentures. Bacteria enter microtraumas obtained in this way. Inflammation of the oral mucosa develops. With secondary stomatitis, the presence of an entrance gate of infection is not necessary. The microflora is brought in by blood from the main infectious focus.
Predisposing factors

Normally, the entry of a small amount of bacterial flora into a wound does not lead to inflammation. Triggered defense mechanisms that destroy the pathogen. In order for the process to continue for any significant time, the intensity of defensive reactions should be reduced. This occurs in the following pathological conditions:
Inflammation of the oral cavity can also be of autoimmune origin. In this case, the patient’s body begins to produce antibodies against its own tissues, destroying them.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Symptoms of inflammation of the inner mucous membrane of the oral cavity are divided into general and local signs. To the number local symptoms include:
- the appearance in the mouth of small ulcers covered with a white coating and bordered by areas of hyperemia;
- swelling of the oral mucosa;
- bleeding gums;
- soreness of the mucous membranes when touched;
- bad breath;
- burning sensation;
- increased salivation.
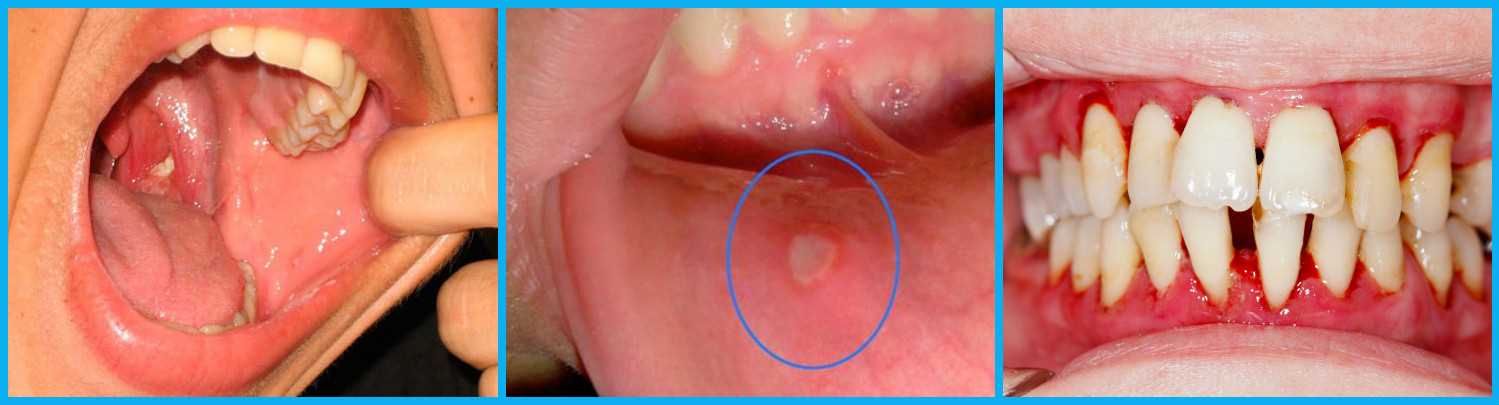
As a rule, when trying to separate the white plaque, the patient experiences sharp pain. The exposed surface of the ulcer bleeds by capillary type. Foci of the disease are most often located on the cheeks, the inner surface of the lips, and the soft palate. Viral stomatitis appears in the form of small blisters with serous contents that cover the mucous membrane. Swelling and pain are noted.
General symptoms develop with severe stomatitis and high prevalence of inflammation. The symptoms that arise are similar in adults and children and are mainly due to intoxication. General symptoms of stomatitis include:
- an increase in the patient’s body temperature sometimes up to 39°C;
- pain in muscles, joints;
- weakness, fatigue, tearfulness;
- headache;
- decrease or complete loss of performance;
- aches throughout the body;
- flying pains in bones.
Intoxication during stomatitis is caused not only by the release of bacterial waste products into the blood, but also by the disintegration of necrotic tissue. At the same time, people who have chronic diseases kidneys, accompanied by a decrease in their excretory capacity, the general intoxication syndrome is most pronounced.
Against the background of intoxication and painful sensations During swallowing, the patient may refuse to eat. In such cases, an adult should be given liquid foods. In the case of infants, it may be necessary to switch to parenteral (intravenous) nutrition or nasogastric tube to introduce food directly into the stomach.
Treatment
For inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, treatment can be general and local.
Local treatment
Necrotic inflammation of the oral cavity requires careful treatment of foci of pathology. Ulcers are washed with a solution baking soda. Sterile infusion solutions of sodium bicarbonate, sold in 200 ml glass bottles, can also be used for treatment. Contact with ulcers should be done with a sterile or clinically clean gauze pad. It is worth noting that cotton wool is not used to treat ulcerations. Microscopic lint may remain in the wound, which will complicate the process.
After processing and departure white plaque ulcers are treated with antiseptic solutions. For this, miramistin, chlorhexidine, octenisept, and a weak solution of potassium permanganate can be used. Some recipes can be used traditional medicine(decoction of chamomile). Such treatment leads to the fact that the inflammatory process subsides, giving way to regeneration.
After antiseptic treatment, the ulcers are treated with agents that accelerate recovery. Solcoseryl and sea buckthorn oil can act as a regenerating drug. In case of severe pain, ointments with anesthetics (lidocaine, Kamistad) can be prescribed. The viral nature of stomatitis is an indication for prescribing to the patient antiviral agents(acyclovir).
Local treatment of stomatitis also includes sanitation of lesions chronic infection in the mouth. Sick teeth are filled, damaged teeth are removed or restored. If this is not done, the mucous membrane will become inflamed again and again.
General treatment
General therapy is used for severe stomatitis. Patients are prescribed the following groups of drugs:
- antibiotics (amoxiclav, metronidazole, ciprofloxacin);
- antiviral (acyclovir, Zovirax);
- vitamins (complivit, injectable monovitamins);
- agents that improve blood microcirculation (pentoxifylline, trental);
- immunostimulants (levamisole).
In addition to the above, general therapy should be aimed at correcting the underlying disease. Depending on the diagnosis, patients are prescribed immunomodulators, chemotherapeutic agents, antihistamines, etc. The question of how to treat the underlying pathology is decided individually.

For stomatitis, a certain diet is required. Products consumed should not cause irritation of the mucous membrane and aggravate the course of the disease.
- citrus;
- fried foods;
- spicy food;
- excessively salty foods;
- acidic components;
- crackers; cookies, waffles, chips;
- hot dishes;
- alcohol.
The patient's table should consist of:
- slimy soups;
- dairy and fermented milk dishes;
- chilled tea, decoctions of medicinal plants;
- cottage cheese, yogurt;
- porridge from soft cereals;
- vegetable juices.
Before consumption, it is recommended to grind the products until smooth using a blender. After eating you need to rinse your mouth with broth medicinal herbs or an antiseptic. The absence of such treatment leads to the retention of food particles between the teeth and the active proliferation of bacteria in the oral cavity. A gentle diet should be maintained until the ulcerations are completely healed.
As an alternative nutrition option for stomatitis (especially in childhood), specialized nutritional mixtures (nutrison, nutridrink) can be used.
Such formulations have a certain specialization, being intended for patients with diabetes mellitus, anorexia, etc. In order to feed a patient suffering from stomatitis, you should choose neutral formulations that are as close in content as possible to natural food.
Prevention of stomatitis
Prevention of primary stomatitis is quite simple and should be carried out by every person who cares about their health. Inflammation of the oral cavity usually develops due to poor personal hygiene. Therefore, the first and most important rule To prevent the disease in question is to regularly brush your teeth twice a day with a soft toothbrush. However, dentists do not recommend using a paste that contains sodium lauryl sulfate.
We should not forget that the causes of stomatitis are often a lack of vitamins. You should regularly, in spring and autumn, undergo a preventive course of vitamin therapy, eat seasonal fruits and vegetables that do not have an irritating effect. If you already have vitamin deficiency, you should consult a doctor to prescribe appropriate treatment.
It is necessary to monitor the health of the oral cavity, prevent the formation of microtraumas, and promptly treat diseased teeth, if any are present in the oral cavity. You should also pay attention to other somatic diseases that can cause stomatitis. In order to timely identify and treat foci of pathology, it is recommended to undergo a preventive examination once a year, and after 40–45 years, 2 times a year.
Forecast
The prognosis for primary stomatitis is favorable. Recovery occurs on average 2–3 weeks after the onset of the disease. If the mucous membrane is inflamed for a longer period, the patient must undergo comprehensive examination for the presence of diseases that provoke stomatitis. Prognosis for the secondary form of inflammation directly depends on the main diagnosis and prognosis for it.
http://www.youtube.com/embed?layout=gallery&listType=playlist&list=PLrSwuot9sM0an0Jj_HqkJLLJ9dBCuMlGf








