Forget about hormonal ointments, a hypoallergenic diet, mountains of pills and special skin care. Treat atopic dermatitis in 2019 with ALT and enjoy disease remission!
Atopic dermatitis(obsolete neurodermatitis) - chronic allergic inflammation of the skin. The disease is manifested by characteristic rashes in the form of persistent or passing redness, increased dryness, thickening of the skin with elements of weeping and peeling.
As a rule, skin lesions are widespread, but skin lesions on the face, arms and hands irritate the patient the most. Rashes of a local type, for example, on the head or legs, usually persist during a period of relative remission.
At severe forms course of dermatitis, in addition to superficial changes in the skin, persistent damage occurs subcutaneous tissue. The skin takes on the appearance of a shell that binds the entire body. The painful itching of the skin does not stop even in sleep.
Not only adults, but also children are susceptible to the disease. In children, atopic dermatitis usually begins in early age and only in 2-5% of cases occurs later.
In childhood, in case of severe disease, the so-called “atopic march” may develop, when allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma join the disease.
Atopic dermatitis is a non-conscription diagnosis (according to Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 25, 2003 No. 123), therefore, for young people of military age, it is a kind of lifesaver from military service.
In adults, atopic dermatitis usually has a chronic form with periods of exacerbations provoked by diet disorders, stress and adverse effects on the body. As soon as you drink alcohol, eat a chocolate bar or stand behind the wheel in a traffic jam, the manifestations of allergic dermatitis remind you of themselves - a rash, itching and skin lesions appear.
If the diet is systematically violated, severe skin lesions and weeping can occur, which, combined with itching, turns the life of an allergy sufferer into a real nightmare - ability to work and social activity are undermined, depression occurs, etc. And when complications arise in the allergy sufferer in the form of fungal skin lesions, a vicious circle arises.
It is not possible for atopic dermatitis to go away on its own or as a result of symptomatic treatment. It is important to understand that external treatment of the skin and the use of antihistamines are only an effect on the symptoms of the disease!
Therefore, if you are still wasting your time and money on:
- Hormonal ointments (Elocom, Advantan, etc.);
- Non-hormonal creams (Elidel, etc.);
- Various " folk remedies"and treatment at home;
- Expensive tablets in bulk (Suprastin, Ketotifen, Telfast, Kestin, Loratadine, Zyrtec, Erius, etc.);
- Shampoos, oils and medicated lotions.
Then you should tell yourself: “Stop!”
The only way to cure the cause of atopic dermatitis in 2019 is autolymphocytotherapy! Alt simply has no alternative.
Help yourself and your loved ones cure atopic dermatitis, tell your friends and acquaintances about this method, they will be grateful to you!
Problems of a patient with atopic dermatitis

It is possible to get rid of atopic dermatitis and restore healthy skin with the help of ALT!
“Autolymphocytotherapy” (abbreviated as ALT) has been widely used in the treatment of patients with various forms of allergic diseases for more than 20 years; the method was first patented in 1992.
Autolymphocytotherapy is the only method of treating the cause of atopic dermatitis!
For children, treatment with the Autolymphocytotherapy method is carried out after 5 years.
The method of "Autolymphocytotherapy", in addition to the treatment of "atopic dermatitis", is widely used for: urticaria, Quincke's edema, bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, hay fever, food allergies, allergies to household allergens, to pets, allergies to cold and ultraviolet rays (photodermatitis) .
Treatment with ALT is possible even in severe cases when the patient has, for example, atopic dermatitis and asthma at the same time.
THE ALT METHOD ELIMINATES INCREASED SENSITIVITY OF THE BODY TO SEVERAL ALLERGENS AT ONCE, DIFFERENTLY DIFFERENT FROM ASIT.
The essence of the ALT method is to use your own immune cells- lymphocytes to restore normal immune function and reduce the body's sensitivity to various allergens.
Autolymphocytotherapy is carried out on an outpatient basis, in an allergology office as prescribed and under the supervision of an allergist-immunologist. Lymphocytes are isolated from a small amount of the patient's venous blood under sterile laboratory conditions.
The isolated lymphocytes are injected subcutaneously into the lateral surface of the shoulder. Before each procedure, the patient is examined in order to individually prescribe the dose of the administered autovaccine. Apart from its own lymphocytes and physiological solution, the autovaccine does not contain any drugs. Treatment regimens and the number and frequency of immune cells administered depend on the severity of the disease. Autolymphocytes are administered in gradually increasing doses with an interval between injections of 2 to 6 days. Course of treatment: 6-8 procedures.

Normalization of the functions of the immune system and a decrease in the body's sensitivity to allergens occurs gradually. The expansion of the hypoallergenic diet is carried out within 1-2 months. The withdrawal of supportive symptomatic therapy is also carried out gradually under the supervision of an allergist. The patient is given the opportunity to have 3 free follow-up consultations within 6 months of observation after completing the course of treatment using the Autolymphocytotherapy method.
The effectiveness of treatment is determined by the individual characteristics of the immune system. This process to a certain extent depends on the patient’s compliance with the recommendations of the allergist during the period of treatment and rehabilitation. If IgE levels are high, a patient with atopic dermatitis will likely undergo two courses of treatment with ALT.
Video about the treatment of atopic dermatitis with ALT (About the most important thing, May 10, 2016)
The story about the treatment of atopic dermatitis begins at the 27:45 mark.
And one more story about the treatment of neurodermatitis (About the most important thing, 03/21/2017). Watch from the 30:00 mark
You can familiarize yourself with possible contraindications on our website.
Ask a question to a specialist
The effectiveness of autolymphocytotherapy in the treatment of atopic dermatitis
When assessing long-term treatment results, the effectiveness of the method is confirmed by the duration of remission:
- Remission for more than 5 years - in 88% of cases
- Remission for a period of 1 to 5 years - in 8% of patients
- Remission was observed for less than a year - in 4% of patients
Benefits of treating the disease with ALT
We treat the cause of the disease, not its symptoms
Minimum contraindications
No hospitalization or time away from work required
The course of treatment is only 3-4 weeks
1 procedure takes only 1-2 hours
Treatment is possible in the absence of persistent remissions
Autolymphocytotherapy can be combined with any symptomatic treatment
THE METHOD IS AUTHORIZED BY THE FEDERAL SERVICE FOR SUPERVISION IN THE FIELD OF HEALTHCARE
How much does it cost to treat atopic dermatitis?
When undergoing treatment for atopic dermatitis in Moscow, the cost of 1 procedure is 3700 rubles. The cost of a course of subcutaneous autolymphocytotherapy (6-8 procedures) is respectively 22,200-29,600 rubles.
After a course of ALT, 3 observations are carried out by an allergist for 6 months. free consultations. If a repeated course of treatment for patients diagnosed with atopic dermatitis is necessary, individual system discounts
Initial allergy testing and diagnosis are carried out in accordance with the standards of the Department of Health. Previous examinations and tests for IgE and allergens performed in other medical institutions are taken into account.
You can donate blood for IgE and allergens in all medical centers, where autolymphocytotherapy is performed.
Allergist-immunologist Nadezhda Yuryevna Logina will see you in Moscow on a weekday
- Fill out the application for admission
- Elimination of the allergen, hypoallergenic diet;
- antihistamines (relieve itching) (erius, tavegil, suprastin, ketotifen, claritin, fexadine, loratodine, telfast, etc.);
- detoxification agents (cleansing) (enterosgel, polyphepan, activated carbon, sodium thiosulfate, etc.)
- hyposensitizing agents (calcium gluconate, sodium thiosulfate);
- corticosteroids (anti-inflammatory effect) (elokom, lokoid, celestoderm, acriderm, sinaflan, diprosalik, belosalik, etc.);
- antiseptics (fucarcin, brilliant green, methylene blue, etc.)
- sedatives (calming) (glycine, persen, various sedative herbs, valerian, peony, etc.);
- enzymes (if pancreatic function is impaired) (Creon, Mezim, Pancreatin, etc.);
- antibacterial agents (in case of infection) (ointments, celestoderm cream with garamycin, Lorinden C, lincomycin ointment, sumamed table, zitrolide, doxycycline, erythromycin, zanocin, rovamycin, etc.);
- eubiotics (for intestinal dysbiosis) (Linex, Probifor, etc.);
- with the addition of both a fungal and a bacterial component (externally: triderm, acriderm GK, etc.);
- upon joining viral infection(acyclovir, valtrex, famvir, alpizarin, etc.).
- If Kaposi's eczema or other viral infections are suspected, antiviral agents are prescribed. For infection - antibiotics (to which the pathogen is sensitive). When wet in acute stage- wet-dry dressings or corticosteroid aerosols.
- Wear cotton clothes. The skin must breathe. Clothing made of wool or synthetics will increase irritation and itching.
- Frequent wet cleaning and ventilation of the room is necessary. Minimum carpets and upholstered furniture - minimum dust.
- It is better to use bedding with synthetic filling, without down or feathers.
- When washing, including your hands, use only warm water.
- After washing, do not rub the skin, but gently pat dry with a towel.
- Be sure to use moisturizers after showering. Skin care products should be neutral, without fragrances or dyes.
- Timely treatment of all chronic diseases, courses of vascular strengthening agents, sedatives(especially before significant events, such as exams, weddings, etc.), hardening, vitamins, exclude allergic foods, even during the period of resolution of rashes.
- development is associated with genetic predisposition;
- chronic nature of the course;
- tendency to relapse;
- clear seasonality of manifestation (the manifestation of severe symptoms of the disease after a latent period occurs in the winter);
- clinical manifestations depend on the age of the patient;
- morphological manifestations are exudative rashes with lichenification (sharp thickening of the skin in the area where the rash appears, increased severity of its pattern, changes in pigmentation);
- the development of dermatitis occurs in childhood (a synonym for the disease is diathesis), after which either complete clinical recovery can occur, or the disease remains for life (a synonym for atopic dermatitis in adults is neurodermatitis or diffuse neurodermatitis);
- a constant symptom characteristic of all stages of the development of the disease (children and adults) is paroxysmal itching.
- up to 20% – if both parents are healthy;
- 40–50% – if one of the parents has atopy (atopy is transmitted from the father in 40–50% of cases, from the mother in 60–70%);
- 60–80% – if both parents suffer from hyperreactivity.
- Contact with allergens. The most common substances that can have an allergenic effect include dust and mites contained in it, tobacco smoke, pollen, food products, medicinal substances (usually antibiotics of the penicillin group, antimicrobial agents, local anesthetics), physiological secretions of insects (cockroaches, ticks), hair and skin particles of pets, chemical products (washing powders, cosmetical tools etc.), molds.
- Sedentary lifestyle. This factor indirectly influences the triggering of the mechanism for the development of an allergic reaction. Physical inactivity leads to a decrease in the level of oxygen saturation of the body (hypoxia), which causes disruption of the functioning of internal organs and systems and increases the tendency of the immune system to sensitization.
- Moral and biological violations. Psycho-emotional overload, frequent nervous breakdowns, fear, anxiety and excitement also often act as causes of allergic dermatitis.
- Instability of thermal parameters. The development of the disease can be triggered by temperature changes, changes in climate zones, and exposure to strong winds.
- Aggressive impact of the technogenic environment. The deterioration of the environmental situation and the use of chemical products in everyday life create the preconditions for changes in the internal environment by disrupting the functioning of the endocrine glands and nervous system.
- Impaired functionality of the gastrointestinal tract. This factor can influence both the development of neurodermatitis and act as a catalyzing factor in the manifestation of the disease.
- prurigo (pruritus) – severe itching that can appear even with minimal rashes, the sensation intensifies with sweating;
- dry skin – occurs due to a lack of natural moisturizing factors, which leads to disruption of the formation of the lipid layer and dehydration of the epidermis;
- the appearance of a blistering rash - typical places of localization of rashes are the face, neck, armpits, popliteal and elbow bends, groin area, scalp, area under the earlobes;
- swelling of the affected surfaces;
- hyperemia, darkening and thickening of the skin in places where the rash is localized (occurs in later stages of the disease);
- anxiety-depressive state, caused both by a reaction to a deterioration in the quality of life, and by the development of functional disorders of the central nervous system that occurred as a result of pathological changes in the body;
- increased susceptibility to infectious agents;
- follicular hyperkeratosis - in adult patients, as a result of neurodermatitis, keratinization of the skin surface of the lateral surfaces of the shoulders, elbows, and forearms may occur (looks like “goose bumps”);
- the appearance of cracks on the heels, bald spots in the occipital region - manifestations are typical for older people;
- peeling of the skin of the feet, madarosis (excessive loss of eyelashes and eyebrows) is a consequence of dysfunction of the thyroid gland, which is caused both by the allergic process itself and by the hormonal therapy undertaken.
- gastroenterologist;
- otolaryngologist;
- allergist;
- therapist;
- psychotherapist;
- neurologist;
- endocrinologist
- elimination or reduction of the severity of external symptoms;
- treatment of background pathologies that aggravate the course of dermatosis (bronchial asthma, hay fever);
- preventing the disease from reaching a severe stage;
- restoration of the structural and functional structure of the affected skin.
- medicinal (using external and systemic agents);
- physiotherapeutic (physical or physico-chemical effects on the affected surface);
- psychotherapeutic (to prevent the development of neuroses or psychoses against the background of illness, electrosleep, hypnosis and, in agreement with a neuropsychiatrist, medications are used);
- resort therapy (sanatorium-resort treatment);
- therapeutic and prophylactic diet (to restore intestinal microflora), hypoallergenic diet therapy;
- herbal medicine (the use of traditional medicine recipes must be agreed with the attending physician).
- antimicrobial (usually local action);
- cytostatics (antitumor);
- anti-inflammatory drugs of nonspecific action;
- membrane stabilizers;
- antimediators;
- psychotropics and desensitizers (tranquilizers, antipsychotics, antidepressants, alpha-blockers, M-anticholinergics);
- antimycotics;
- immunocorrectors (immunostimulants, immunosuppressors), adaptogens;
- enterosorbents;
- drugs to normalize intestinal function (bacteriophages, prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotics, enzymes, hepatoprotectors);
- vitamins, multivitamin complexes;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- reducing agents (ointments, creams, patches for resorption of infiltrates);
- keratolytics (soften skin seals).
- 1st generation – Clemastine, Atarax;
- 2nd generation – Loratadine, Cetirizine;
- 3rd and 4th generation – Levocetirizine, Desloratadine.
- ointments – have pronounced nutritional properties, are prescribed in the presence of infiltration (ichthyol ointment);
- creams - ointment bases, which additionally have a cooling effect and have a gentle effect on the skin (Aisida cream, Atoderm);
- gels - high-molecular mixtures that keep low-molecular compounds (water, alcohols) from spreading (Solcoseryl);
- emulsions, solutions, aerosols - use is advisable during the acute stage of the disease, which is accompanied by exudation and weeping.
- membrane stabilizers;
- antihistamines;
- psycholeptics (sedatives).
- Levomekol (cost from 102 rubles) - has a multifactorial effect due to the combined composition, which includes an antibiotic (chloramphenicol) and an immunostimulant (methyluracil). Levomekol for dermatitis helps relieve inflammation by inhibiting protein synthesis in pathogen cells and accelerates the process of tissue regeneration by accelerating the exchange of nucleic acids. The ointment should be applied to sterile napkins that are applied to the wound surface. The dressings should be changed daily until the wound is completely clean.
- Erythromycin (cost from 80 rubles) - an ointment based on erythromycin (the first antibiotic of the macrolide class). The antibacterial effect consists of disrupting peptide bonds between amino acid molecules and disrupting the protein synthesis of pathogenic cells. Along with the bacteriostatic effect, a bactericidal effect may appear (with increasing dose). The medicine should be applied to the affected skin 2-3 times a day for 1.5-2 months.
- Dioxidin (cost from 414 rubles) is an antibacterial agent, a derivative of quinoxaline, that can have a bactericidal effect on those strains of microorganisms that are insensitive to other types of antibiotics. Treatment of wounds with dermatitis with ointment accelerates the process of marginal epithelization and reparative regeneration. The medicine should be applied in a thin layer once a day; the duration of therapy for adult patients is no more than 3 weeks.
- Phototherapy is dosed irradiation of affected areas of the skin with ultraviolet rays, thereby suppressing local cellular immunity.
- Phototherapy is the effect of bright light from artificial sources (lasers, diodes, fluorescent lamps) on the body of a patient who has previously consumed a photosensitizing substance (psoralen or ammifurin).
- Acupuncture – stimulation of biologically active points general action(at the acute stage of the disease) and local (during treatment of subacute and chronic forms), corresponding to the localization of the inflammatory process.
- Electrotherapy is the action of dynamic currents on the paravertebral ganglia (autonomous ganglia located along the spine) gives a sedative effect.
- Hyperbaric oxygenation is the saturation of tissues with pure oxygen under high pressure, which leads to an improvement in the rheological properties of blood and acceleration of the process of tissue regeneration.
- Electrosleep - electrical stimulation of parts of the brain helps to inhibit those structures whose excessive activity can provoke the development of neurodermatitis.
- Paraffin therapy is a heat treatment method that involves heating tissue in areas of lichenification using paraffin. The purpose of the procedure is to moisturize the affected skin and increase its elasticity.
- Electrophoresis - due to the intranasal administration of medicinal substances (Diphenhydramine, Novocaine) with the help of electric current, a direct effect is exerted on the vessels and vegetative sections nervous system through the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity.
- retinol (vitamin A) - drugs Tigazon, Neotigazon for diffuse neurodermatitis are used for a long time and in high dosages;
- B vitamins (thiamine, riboflavin, cyanocobalamin, pyridoxine, a nicotinic acid) – used in isolation or as part of vitamin-mineral complexes;
- ascorbic acid - during the acute phase, taking mega-doses of vitamin C is indicated;
- vitamin D3 – prescribed in combination with calcium salts;
- tocopherol – the effectiveness of therapy increases when combining vitamin E and retinol (Aevit);
- zinc preparations - internal administration of zinc-containing preparations (Zincteral) enhances the effect of external agents used to care for affected tissues;
- multivitamin complexes - indicated for use in chronic dermatoses (Centrum, Oligovit).
- oat decoction (taken orally for 1 month);
- potato compresses;
- ointments based on herbal ingredients;
- decoctions of medicinal herbs that have anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects;
- alcohol tinctures;
- herbal baths.
- chamomile (flowers);
- fireweed;
- decoction of hay dust (0.5 cups of hay dust per 1.5 cups of water);
- butter (1 tbsp);
- glycerol.
- peloidotherapy (mud baths or applications);
- thalassotherapy (treatment using all factors formed in the marine climate - water, algae, seafood, etc.);
- balneotherapy (use of medicinal properties mineral waters– shower, irrigation, drinking, intestinal lavage, etc.);
- heliotherapy (solar therapy, sunbathing);
- climatotherapy (staying in a dry, warm climate zone for more than 2 months ensures long-term remission, more than 3 years - complete recovery).
- spicy, fried, pickled, extracted (dry mixtures) foods;
- pickles;
- smoked meats;
- citrus;
- Tea coffee;
- chocolate;
- milk;
- chicken eggs;
- jam;
- chicken, goose, duck meat;
- seafood;
- fatty fish;
- red fruits and vegetables;
- inclusion in the diet of foods containing all the necessary vitamins and minerals;
- ensuring the supply of substances that accelerate regeneration processes (sunflower oil, olive oil, corn, flax);
- reducing the consumption of gluten (protein amino acids found in cereal products);
- maintaining normal functioning of the liver and intestines (exclude alcohol, fatty foods, consume more fiber);
- short-term fasting under medical supervision;
- Maintaining water balance (drink at least 2 liters of water daily);
- monitoring the body’s reactions to consumed foods (keeping a food diary).
- before starting to keep a diary, you must abstain from food for 1 day (you are allowed to drink clean water, unsweetened tea);
- introduce foods into the diet gradually (first dairy, then eggs, meat, fish, vegetables and citrus fruits);
- describe in detail the composition of the dishes consumed (ingredients, quantity, time of intake, method of preparation);
- record all body reactions, indicating the time of their occurrence and severity.
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- non-compliance with the diet (the child eats too often or too much);
- the body's reaction to some food;
- exposure to cosmetics or household chemicals with which the child came into contact;
- allergy to lactose.
- erythematous-squamous dermatitis. Occurs in children under 2 years of age, accompanied by excoriation, increased dry skin, itching and papular rash;
- eczematous dermatitis. This type of dermatitis is diagnosed mainly in children under 6 years of age. Eczematous atopic dermatitis is accompanied by severe itching, papular-vesicular rash and swelling of the skin;
- lichenoid dermatitis. A common form of pathology, which is most often encountered by school-age patients. In addition to standard symptoms, such as itching of the skin, swelling and hardening of the affected areas of the skin appears;
- pruriginous dermatitis. Manifests itself in the form of numerous papules and excoriation. A prurigo-like type of atopic dermatitis is diagnosed in adolescents and older children.
- initial. Accompanied by swelling of the affected areas of the skin;
- expressed. Additional symptoms appear, for example, skin rashes, peeling. The expressed stage of the pathology can be chronic or acute;
- remission. Gradual reduction in the severity of symptoms until their complete elimination. The duration of this period can range from 4-6 months to several years;
- recovery. If relapses have not been observed for more than 5 years, then he can be considered clinically healthy.
- inflammation of the skin, causing severe itching. The patient begins to uncontrollably scratch all the affected areas of the skin;
- redness of thinner areas of the skin (neck, knee and elbow joints);
- pustular formations on the skin and acne.
- coprogram (laboratory stool analysis for helminthiasis and dysbacteriosis);
- general urine analysis;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- identification of possible allergens using provocative (through the nasal mucosa) or skin scarification (through a small scratch on the skin) tests.
- antihistamines – have antipruritic properties. Such products as “Zodak”, “Cetrin” and “Finistil” are used;
- antibiotics - prescribed in cases where the disease is accompanied by bacterial infection(“Differin”, “Levomikol”, “Bactroban” and others);
- antimycotics and antivirals are required when diagnosing additional infections. If a viral infection occurs, the doctor may prescribe Gossypol or Alpizarin, and if a fungal infection develops, Nizoral, Pimafucin, Candide, etc. are used;
- immunomodulators - used for atopic dermatitis, if signs of immune deficiency have been added to the symptoms of the pathology. These are potent drugs, so only the attending physician should select them;
- drugs to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Glucocorticosteroids are steroid hormones designed to eliminate pronounced symptoms of dermatitis. They are used in rare cases due to the large number of contraindications and side effects.
- do not overfeed the child, because this will lead to disruption of metabolic functions, which is fraught not only with obesity, but also with the development of skin diseases;
- reduce the fat content as much as possible breast milk. To do this, a nursing mother must also follow a special diet, do not overeat fatty foods and drink enough fluids;
- When feeding a baby, you need to make a small hole in the nipple, thereby slowing down this process. This manipulation promotes normal digestion of food.
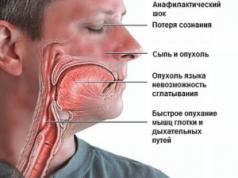
- psychological disorder;
- hives;
- bronchial asthma;
- allergic form of conjunctivitis and rhinitis;
- the development of lymphadenopathy - a pathology that is accompanied by enlargement of the lymph nodes.
- lichenification of the skin;
- development of a viral infection (as a rule, patients develop herpetic or papillomatous lesions);
- candidiasis, dermatophytosis and other fungal infections;
- infectious inflammation accompanied by pyoderma.
- ventilate the children's room, maintain a cool climate;
- regularly walk with your child in the fresh air, preferably not on city streets, but in nature;
- maintain a drinking regime, especially in the summer;
- Monitor your baby’s diet – it should contain a sufficient amount of nutrients;
- Don't overdo it with hygiene. Too frequent bathing procedures can harm the baby’s skin by disrupting its protective lipid barrier;
- buy clothes exclusively from natural materials, which is comfortable and does not restrict movement. experts recommend giving preference to cotton products;
- Use only “baby” laundry detergent.
- underdevelopment of sweat glands;
- fragility of the stratum corneum of the children's epidermis;
- high lipid content in the skin of newborns.
- food;
- professional;
- household
- infant (from 1 month to 2 years);
- children's (from 2 years to 13);
- teenage
- early onset of the disease in an infant;
- itching of the skin, often occurring at night;
- chronic continuous course with frequent serious exacerbations;
- exudative nature of the rash in newborns and lichenoid in older children;
- presence of close relatives suffering from allergic diseases;
- dry skin;
- positive skin tests during allergy testing;
- white dermographism;
- presence of conjunctivitis;
- pigmentation of the periorbital region;
- central protrusion of the cornea - keratoconus;
- eczematous lesions of the nipples;
- strengthening of the skin pattern on the palms.
- folliculitis;
- boils;
- impetigo;
- anular stomatitis;
- candidiasis of the oral mucosa;
- skin candidiasis;
- Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis;
- molluscum contagiosum;
- genital warts.
- breakfast. Dairy-free porridge: rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, butter, tea, bread;
- lunch. Fruit puree from pears or apples;
- dinner. Vegetable soup with meatballs. Mashed potatoes. Tea. Bread;
- afternoon tea Berry jelly with cookies;
- dinner. Vegetable and cereal dish. Tea. Bread;
- second dinner. Formula or .
- Polyoxidonium has a direct effect on monocytes, increases resistance cell membranes, is able to reduce the toxic effect of allergens. It is used intramuscularly once a day with an interval of 2 days. A course of up to 15 injections.
- Lycopid. Strengthens the activity of phagocytes. Available in 1 mg tablets. May cause an increase in body temperature.
- Zinc preparations. They stimulate the restoration of damaged cells, enhance the action of enzymes, and are used for infectious complications. Zincteral is used at a dose of 100 mg three times a day for up to three months.
- in case of severe exacerbation, treatment begins with the use of strong hormonal drugs— Celestoderma, Cutiveita;
- to relieve symptoms of dermatitis on the torso and arms in children, the drugs Lokoid, Elokom, Advantan are used;
- It is not recommended to use Sinaflan, Fluorocort, Flucinar in pediatric practice due to serious side effects.
- sanatorium named after Semashko, Kislovodsk;
- sanatoriums “Rus”, “DiLuch” in Anapa with a dry maritime climate;
- Sol-Iletsk;
- sanatorium "Klyuchi" Perm region.
- limit your child’s contact with all types of allergens as much as possible;
- give preference to cotton clothes for your baby;
- avoid emotional stress;
- Trim your child’s nails short;
- the temperature in the living room should be as comfortable as possible;
- try to keep the humidity in the child’s room at 40%.
- use alcohol-based cosmetics;
- wash too often;
- use hard washcloths;
- take part in sports competitions.
Atopic dermatitis– one of the most common and severe allergic diseases, and the most common allergic skin lesion. Statistics indicate that the prevalence of atopic dermatitis exceeds 12% (that is, out of 100 people, 12 suffer from atopic dermatitis). Despite the huge strides made in this area over last years, the treatment of atopic dermatitis is a rather complex problem and requires collaboration between the doctor, the patient and his family members.
Atopic dermatitis– chronic, genetically determined, allergic inflammation of the skin, characterized by a typical clinical picture ( typical symptoms). The leading clinical symptom of atopic dermatitis, found in all age groups ah - itchy skin.
Atopic dermatitis in the vast majority first appears in children aged 6 to 12 months. Less often from 1 to 5 years. The first disease corresponding to the symptoms of atopic dermatitis was described in 1844.
Currently, atopic dermatitis can be hidden under the names eczema and neurodermatitis. It is sometimes mistakenly called allergic dermatitis or diathesis.
Causes of atopic dermatitis.
Atopic dermatitis is a disease that develops through the mechanism of immediate hypersensitivity (IgE-dependent immune response). This is one of the most common mechanisms for the development of allergies. Its main feature is the rapid reaction of the immune system to an incoming allergen (minutes, or less often hours, pass from the moment the allergen arrives until the symptoms appear).
Family history plays an important role in the development of atopic dermatitis, that is, among close relatives you can almost always find a person with an allergic disease. Most often, allergic mood is transmitted through the maternal line. Recent studies indicate that this is a polygenic disease, that is, about 20 genes located on several chromosomes are responsible for the development of allergic inflammation.
But in order for an allergic predisposition to develop into an allergic disease, in particular atopic dermatitis, it is necessary to be exposed to a number of external factors. The main trigger points: toxicosis of pregnant women, especially those developing in later stages, smoking and alcohol consumption by the mother during pregnancy, infectious diseases in the mother during pregnancy. A major role in the development of allergic diseases in children is played by the pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular intestinal dysbiosis, insufficient duration or complete absence of breastfeeding, early introduction of complementary foods, introduction of age-inappropriate foods into the diet, earlier and inadequate prescription of antibiotics, etc. .
A number of studies conducted in Europe and the USA have shown that atopic dermatitis is more common in families with more high level life. There are several theories as to what this may be connected with, but no consensus has yet been reached.
Among the allergens that cause the development of atopic dermatitis, the most important are food ones (allergy to various foods). Household ticks (various types of ticks) have less clinical significance house dust, house dust, library dust, pillow feathers) and epidermal (animal hair and dander, bird feathers, fish food, etc.) allergens. Allergy to pollen as a cause of atopic dermatitis is extremely rare.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis with photographs
Currently, the following diagnostic criteria for atopic dermatitis have been identified::
1) early onset of the disease (before two years of age),
2) the presence of allergic diseases in close relatives,
3) widespread dry skin,
4) localization of skin rashes in the area of the flexor surfaces of the arms and legs,
5) availability skin itching.
If four of the five criteria are found, the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis can be considered practically proven.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis vary depending on the age of the patient. Thus, there are three variants of the clinical course of atopic dermatitis: the infant form, the childhood form, and the adolescent-adult form.
Infantile form of atopic dermatitis (diathesis). Symptoms of atopic dermatitis in newborns and infants.
The infantile form of atopic dermatitis occurs before the age of 2 years. Inflammatory elements like red spots appear on the child’s skin, localized mainly on the face in the forehead and cheeks. Such skin rashes are popularly called diathesis, although in fact diathesis is atopic dermatitis.
The disease is characterized acute course, weeping, swelling, crusting. Foci of inflammation may also appear in other areas: in the area of the legs, buttocks, and scalp of the child. Periods of severe exacerbation, accompanied by weeping, are replaced by a subacute stage, which is characterized by papular elements (a papule is a skin element that rises above the skin like a tubercle) against the background of hyperemic (reddened) skin.
The photo shows an infant form of atopic dermatitis
Children's form of atopic dermatitis, symptoms.
During the period of exacerbation of atopic dermatitis, skin elements (red spots, papules) are located mainly in the area of skin folds, on the flexor surfaces of the elbow and knee joints, as well as behind the ears. The skin becomes dry, peeling and lichenification appear (on dry skin there is a clearly defined, enhanced skin pattern). The child develops a so-called “atopic face”: dull skin color, increased pigmentation around the eyes, an additional skin fold of the lower eyelid. Outside of exacerbation, severe dryness of the skin. The skin may crack, especially on the backs of the hands and fingers.

In the photo: Atopic dermatitis. Children's uniform. Patient 3 years old.
Adolescent-adult form of atopic dermatitis, symptoms.
Skin lesions in atopic dermatitis are widespread and permanent. Changes are noted on the skin of the face, neck, chest, back, neck. The skin is dry, widespread lichenification, traces of scratching. There may be cracks in the hands and feet. Exacerbations of atopic dermatitis, manifested by redness of the skin, are quite rare.

The photo shows atopic dermatitis in a 15-year-old teenager (dry skin, peeling).

In the photo: atopic dermatitis. Adult form.
If an infection occurs, fungal lesions, pustules, and greenish crusts may appear.

Depending on the severity, atopic dermatitis is classified into mild, moderate and severe.
Symptoms of chronic atopic dermatitis
People with atopic dermatitis are characterized by thickening of the skin and increased skin pattern, painful cracks in the skin, especially on the palms and soles, hyperpigmentation of the eyelids (more dark color skin on eyelids).
The symptom of “winter foot” is hyperemia and moderate infiltration of the soles, peeling, cracks.
Morgan's sign (Denier-Morgan, Denier-Morgan folds) - deep wrinkles on the lower eyelids in children.
The symptom of “polished nails” is the disappearance of longitudinal striations and the characteristic appearance of the nail, due to constant scratching of the skin.
The symptom of a “fur hat” is dystrophy of the hair in the occipital region.
Pseudo Hertog's symptom is a temporary loss of hair, first in the outer third, and then in other areas of the eyebrows in some patients.
What tests will you need to take if you suspect atopic dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is in the area of interest of two medical specialties: an allergist-immunologist and a dermatologist. Taking into account the high prevalence of this problem among children, according to modern medical standards, mild forms of atopic dermatitis can be treated by a pediatrician, but it is better to still try to get to a specialist.
The diagnosis of atopic dermatitis is made on the basis of characteristic clinical symptoms and data obtained after questioning the patient or his parents (if the patient himself does not yet speak properly).
A patient newly diagnosed with atopic dermatitis must undergo an in-depth examination, which will identify the factors that provoke an exacerbation of the disease and underlie its development.
If the rashes are persistent and localized strictly in certain areas, then consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist (or better yet both) is necessary, since concomitant pathology of the spine is possible.
If the child is hyperexcitable, a consultation with a neurologist is required.
It is mandatory to conduct an allergic examination aimed at identifying those substances that directly cause the development of allergic disease.
Taking into account that atopic dermatitis is a disease that occurs with skin lesions, the only acceptable method of diagnosis is a blood test for IgE-specific (specific immunoglobulins E produced in response to specific allergens). First of all, they donate blood for food allergens. In patients over three years of age, it is advisable to donate blood for household and epidermal allergens.
In case of infection, the discharge from the inflammation sites is cultured for microflora and fungi, as well as for sensitivity to antibiotics.
Sometimes a skin biopsy is performed (a small area of skin is taken for analysis) to clarify the nature of inflammatory process. But this method Research is carried out quite rarely and only for strict indications, for example, if skin lymphoma is suspected.
If exacerbations of atopic dermatitis coincide in time or begin immediately after a cold, then it is advisable to take a blood test for an immunogram. This will help identify possible problems with the immune system.
In general, when designing an examination program, the doctor must understand that atopic dermatitis is not only an allergic disease. Both nervous and endocrine system. There are almost always problems in other organs and systems of the body. And if these provoking and aggravating factors are not found, then it will be extremely difficult to transfer the child into a state of stable and long-term remission (recovery). It is in finding and eliminating the cause of atopic dermatitis that the main task of the attending physician is, and not in prescribing only creams and tablets to relieve the symptoms of the disease.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis
Treatment of atopic dermatitis should be prescribed by a specialist only after an accurate diagnosis has been established. You should not start treatment on your own if symptoms of atopic dermatitis occur. A number of very serious diseases can have similar symptoms, and inadequate treatment tactics can be a threat to the life of the patient, especially the patient - a child. Never increase the duration of the course of medications recommended for you on your own, even if they help well and cope with the symptoms of the disease, and there is no time to go to the doctor. Even the most harmless creams with banal vitamins have side effects which may occur if treatment tactics are not followed.
General principles of treatment of atopic dermatitis:
Therapeutic tactics during exacerbation of atopic dermatitis and without exacerbation differ significantly.
Treatment of exacerbation of atopic dermatitis
Treatment of exacerbation of atopic dermatitis consists of the complex use of the following groups of drugs:
1) Topical glucocorticosteroids. The most commonly used group of drugs for external use, used to relieve symptoms of exacerbation. The drugs have a number of side effects and contraindications, so they can only be used as prescribed by a doctor. It is preferable to use the latest generation drugs that do not contain fluorine in their structure. Their safety profile is much higher. Examples: Advantan, Afloderm, Elakom, etc. Topical glucocorticosteroids are available in the form of ointments, creams, emulsions, fatty ointments, and lotions. It is not recommended to use drugs in this group for more than 7-10 days in a row. The instructions for a number of drugs imply the possibility of prescribing them for up to 1 month, but this should still be avoided. Gradual withdrawal of topical glucocorticosteroids is recommended. For example, during the main part of the treatment course you apply ointment to the entire affected area. Then apply it using the stroke method every day, leaving a little more distance between the strokes.
Another option for gradual withdrawal is to apply the cream one day, and then give the skin a rest the other day, using non-hormonal remedies.
It should also be remembered that no glucocorticosteroids for external use should be applied to the skin of the eyelids in the immediate vicinity of the eyes, as this can lead to the development of glaucoma and cataracts.
2) Combined drugs. Drugs in this group contain a combination of glucocorticosteroids, antibiotics and antifungal drugs. Medicines of this pharmacological group are used if an infection is associated with allergic inflammation in atopic dermatitis. Examples: Triderm cream, pimafucort, etc.
3) Preparations with active zinc. These are products for external use (ointments, creams). Some experts regard it as an alternative to local glucocorticosteroids. The duration of treatment must be monitored by a doctor, preferably with experience in working with these drugs, as the development of chronic dermatoses of other, non-allergic, origin is possible.
4) Antihistamines. Preference should be given to drugs of the second and third generations. The average duration of treatment is ten days. Although there are treatment regimens that provide for long-term (at least three months) use of third-generation drugs. Examples: Zyrtec, Erius.
5) Pimecrolimus derivatives. This group includes the drug Elidel. A relatively new group of drugs used to relieve symptoms of exacerbation. Its effectiveness is not inferior to local glucocorticosteroids and, at the same time, according to studies conducted by the manufacturer, it is much safer. Disadvantages of the drug: high cost, little clinical experience in its use.
6) Sorbents. Carrying out detoxification therapy with the help of sorbents is a necessary component in the treatment of exacerbations of most allergic diseases. Examples of drugs: lactofiltrum, enterosgel, filtrum, etc. The drugs are prescribed two to three times a day at an average age dosage for 7-14 days.
7) Glucocorticosteroids. Oral medications are prescribed only for severe forms of atopic dermatitis. The dosage and duration of treatment are determined by the doctor. Examples of drugs: metypred, prednisolone.
8) Cytostatics. Can be used only for severe forms of atopic dermatitis that are resistant to all other treatment methods. The dosage and duration of treatment are determined by the doctor. Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis beyond exacerbation.
Atopic dermatitis– a chronic disease that requires long-term treatment even beyond the symptoms of exacerbation.
Currently, much attention is paid to the use of medicinal cosmetics during this period. Due to the presence of allergic inflammation, even sluggish without external clinical manifestations, the properties of the skin change. Its permeability and humidity are impaired. And the purpose of regular use of fortified cosmetics is to restore the damaged properties of the skin. Examples of drugs related to medicinal cosmetics: radevit, bipanten, pantoderm, locobase-ripea, etc.
In addition, treatment of concomitant diseases identified during the examination of the patient is carried out. The functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is corrected, the functioning of the nervous system is normalized, etc. The nature of the measures is selected individually, depending on the specific test results.
Thus, it is not enough to simply relieve the exacerbation of atopic dermatitis; it is necessary to identify and eliminate the factors that caused the development of the disease or provoke its exacerbations. Only in this case can you stop the progression of allergies, bring atopic dermatitis into remission, and then completely get rid of it.
Folk remedies for the treatment of atopic dermatitis
In folk medicine, there are a number of methods actively used by patients with atopic dermatitis. Thus, in mild forms of the disease, baths with decoctions of medicinal herbs, such as chamomile and string, have a good effect.
For children, baths with soothing herbs such as oregano, hops, valerian, and motherwort can be recommended. To prepare the bath, take 2 tablespoons of the herb, pour 1 glass of boiling water and leave for at least 10 minutes. The resulting broth is added to the baby’s bathtub.
But still, allergists are quite wary of traditional medicine, since patients with allergies very often experience individual allergic reactions to “traditional” recipes.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis during pregnancy.
Atopic dermatitis does not manifest for the first time during pregnancy. The disease always begins in early childhood.
There are some features for treating an existing disease in women during pregnancy. Moisturizing cosmetics are carefully selected to soften the skin without exacerbation. For a number of fortified creams, for example, the fairly popular Radevit cream, pregnancy is a contraindication.
The principles of treatment during exacerbation of atopic dermatitis during pregnancy are practically no different from those in the rest of the population. If there is a need for local hormonal therapy or the prescription of antihistamines, then it is preferable to use the latest generation of drugs that are safer (Advantan, Elakom, Lokoid).
The main focus should be on creating a hypoallergenic environment.
There is no negative effect of atopic dermatitis on the fetus. Although toxic effects on a child are still possible, but only when using medications prohibited for this period of a woman’s life.
Features of nutrition, diet and lifestyle with atopic dermatitis
Creating a special hypoallergenic, that is, devoid of allergens, environment and following a diet are the most important components of the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Without following these recommendations, the effectiveness of treating the disease is significantly reduced.
Let's start by creating a hypoallergenic environment. In essence, it is the observance of a special way of life. The goal is to eliminate factors that can irritate the skin and thereby provoke exacerbations of atopic dermatitis.
It is also preferable to avoid intense physical activity or factors that increase sweating and itching. For the same reason, it is not recommended to participate in sports, as this causes active sweating and is accompanied by close contact of the skin with clothing. Avoid if possible stressful situations(as far as possible of course). It is not recommended to wear rough clothes, especially those made of wool, synthetics, or animal fur. New clothes should be washed before wearing. When washing clothes and bedding, use a minimal amount of fabric softener, after which the laundry should be rinsed additionally. Do not use personal hygiene products containing alcohol.
You will have to install a hood in the kitchen. It would be a good idea to install an air purifier in your bedroom. During the hot season, use an air conditioner with an outlet filter.
Bed linen should be changed 1-2 times a week. Sources of dust and mold accumulation must be eliminated. The TV, computer, and household appliances must be removed from the patient’s bedroom. Light wet cleaning is carried out once a day, general cleaning is carried out at least once a week. Use vacuum cleaners with good filters (the best ones with HEPA filters). If there is a confirmed allergy to house dust mites, treat the apartment with acaricidal (mite-killing) drugs, for example, Allergoff, once every 3-6 months.
Smoking is not allowed in the house. This means family members. The patient should not smoke anywhere: neither in the house nor on the street.
Much attention is paid to water procedures. You cannot use regular soap; it is better to use shower oil or medicated shampoo (for example, Friederm series shampoos). After a shower, be sure to lubricate your skin with moisturizers.
The patient's nails should be cut as short as possible to avoid involuntary damage to the skin in case of exacerbation of the disease and the appearance of skin itching.
People with atopic dermatitis should not sunbathe. Extended exposure to the sun is a common mistake. Immediately after this there will be a slight improvement, which parents usually notice and strive for, but then a severe exacerbation of the disease almost always follows.
Do not comb or rub the skin; no products will be effective if you scratch the lesions.
Be sure to consult with your doctor regarding adherence to the principles of hypoallergenic living. The recommendations offered on our website may be supplemented depending on the allergens to which you (or your child) react.
Hypoallergenic diet for atopic dermatitis:
It is also necessary to adhere to a special diet. During an exacerbation, the diet should be observed especially strictly; outside of an exacerbation, it can be expanded a little so as not to cause some kind of neurosis-like state in the child due to the fact that he “cannot do everything.”
Products excluded for atopic dermatitis:
It is not recommended to consume citrus fruits, nuts, seafood, fish, chocolate, coffee, mustard, spices, mayonnaise, tomatoes, eggplants, red peppers, milk, eggs, mushrooms, sausages, carbonated drinks, strawberries, wild strawberries, watermelons, pineapples, honey . Alcohol is strictly prohibited.
Products allowed for atopic dermatitis:
You can eat boiled beef; cereal and vegetable soups; vegetarian soups; olive oil; sunflower oil; boiled potatoes; porridge from buckwheat, rice, oatmeal; lactic acid products; cucumbers; parsley; dill; baked apples; tea; sugar; bran or whole grain bread; apple or dried fruit compote (except raisins); organic yoghurts without additives; one-day cottage cheese; curdled milk.
Atopic dermatitis– a disease that begins in early childhood. Most often within a period of 6 to 12 months. Atopic dermatitis in children is popularly called " Diathesis", in medicine concepts diathesis no, there is a concept infant stage of atopic dermatitis.
The clinical picture (symptoms with photos) of infant and childhood forms of atopic dermatitis is described in detail in the section Symptoms of atopic dermatitis. The younger the child is, the more prone he is to exudation (wetting).

The photo shows a child with atopic dermatitis
The nature of activities aimed at creating a hypoallergenic environment around a child does not differ from those for adults and is described in detail above.
Particular attention in children is paid to restoring damaged skin properties through the constant use of moisturizing cosmetics. It should be applied 3-4 times a day, sometimes more often.
It is very important to maintain breastfeeding for as long as possible (at least 6 months). But at the same time, the mother should not eat foods that can aggravate allergies (see the diet in the section Features of nutrition and lifestyle with atopic dermatitis).
It is important to properly bathe a child in the first year of life, especially a newborn. You can't use soap. It is better to use medicated shampoos. For example, Friederm shampoo with zinc during an exacerbation and Friderm Balance during an exacerbation. Before bathing, add one capful of shampoo to a bath of water. After bathing, do not rub your child with a towel - this will irritate the skin. It is better to lightly blot the skin with a towel or let it dry on its own.
An urgent problem is vaccination of a child with atopic dermatitis. The very fact of having a disease is not a reason to refuse vaccinations, but vaccination is possible only during the stage of stable remission of the disease (at least 2-3 months). It is mandatory to take antihistamines 7 days before vaccination on the day of vaccination and 3-5 days after vaccination. Multiple vaccines cannot be administered on the same day. If several vaccinations have already been missed, then vaccination should begin with less allergenic vaccines. Your attending physician (allergist-immunologist or pediatrician) will help you correctly draw up an individual vaccination calendar.
Complications of atopic dermatitis and prognosis for cure
The prognosis for life is favorable. However, skin lesions, especially in adolescence may contribute to the patient's social maladjustment.
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic allergic skin disease. In case of adequate treatment, elimination of risk factors, most patients experience stable remission and subsequently the diagnosis can be removed. But since the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis is a reflection of a general allergic mood (atopic constitution), a large proportion of these patients (more than 40%) may develop other allergic diseases in the future, most often associated with damage to the respiratory tract ( allergic rhinitis, atopic bronchial asthma). This progression of allergic mood and the change of allergic diseases from less severe to more serious in the medical literature is called the atopic march.
In case of severe disease and/or inadequate treatment, non-compliance with a special lifestyle, the disease continues into adolescence and adults.
The most common complications of atopic dermatitis are the addition of a bacterial infection (pyoderma) and skin atrophy (most often due to unreasonably long use of local glucocorticosteroid drugs). Constantly scratching the skin atopic dermatitis leads to a violation of its protective, barrier properties, which contributes to the addition of infection caused by microbial and fungal flora.
Pyoderma is characterized by the appearance of pustules on the skin, which gradually dry out and crusts form. The rash can be located on the body, arms, legs, and scalp. This may be accompanied by a disturbance in the person’s general condition, and the temperature may rise.
Another common complication when atopic dermatitis- viral infection. Bubbles with transparent contents form on the skin. The causative agent is the herpes simplex virus, the same one that causes “colds” on the lips. Usually the rashes are located in the area of inflammatory foci, but they can also involve healthy skin, and also affect the mucous membranes (oral cavity, throat, genitals and conjunctiva). A particularly common localization of the rash is the skin of the face (around the mouth, lips, wings of the nose, on the cheeks, ears, eyelids).
A common complication of atopic dermatitis is fungal (most often candidal) infection. In adults, the skin (especially skin folds), nails, scalp, feet, and hands are most often affected; and in children - the oral mucosa, the so-called thrush (a “curdled” coating appears, which may be accompanied by soreness and redness). Sometimes bacterial and fungal infection are combined together.
Prevention of atopic dermatitis
There are no measures aimed at preventing the development of atopic dermatitis. The only recommendation that really works is to continue breastfeeding for as long as possible (at least 6 months). Some authors recommend excluding cow's milk from the diet of children under 1 year of age if there is a patient with an allergic disease in the family.
In case of an already manifested (started) disease, preventive measures are reduced to eliminating the causally significant allergen (allergen causing allergies) from the environment, following the general principles of diet, creating a hypoallergenic lifestyle and carrying out adequate treatment.
Answers to frequently asked questions on the topic of atopic dermatitis:
Why should a child with atopic dermatitis follow a diet?
The diet should exclude foods directly to which allergies develop, and foods containing large amounts of histamine. Histamine is one of the the most important participants allergic disease. Absorbed in the intestines, it enhances the existing allergic process. Eating foods rich in histamine for patients with allergic diseases can be compared to throwing wood on a fire.
Can atopic dermatitis be completely cured?
Modern medical methods make it possible in most cases to put the disease into remission in a child. In this case, during adolescence, the disease may completely go away. In the old medical literature this was called "outgrowing the disease."
But for this to happen, long-term joint work between the doctor and the patient is necessary.
I have atopic dermatitis, what is the likelihood of passing it on to my child?
The probability of transmitting an “allergic mood” from the father is about 15-20%, from the mother about 40%, if both parents are sick - 70%. But for this attitude to result in disease, a combination of a number of external factors is necessary. Therefore, the real probability is less. Talk to your doctor about preventive measures.
Allergist-immunologist, Ph.D. Mayorov R.V.
As evidenced medical statistics Over the past decade, the prevalence of skin pathologies has increased significantly. One of the most common reasons for visiting a dermatologist is atopic dermatitis, the symptoms of which manifest themselves to one degree or another in 80% of children under school age. As patients grow older, signs of the disease disappear in 60% of cases; in the remaining patients, dermatitis becomes chronic. The clinical course of the disease in adults is distinguished by its specificity, which requires a special approach to treatment.
What is atopic dermatitis
The occurrence of an allergic reaction in a person is preceded by sensitization (acquisition of increased sensitivity) of the body by a certain allergen. The reasons that provoke the process of sensitization are varied - from non-compliance with hygiene standards to genetic predisposition. If disturbances in the mechanism of the immune response are congenital features, the term “atopy” is used in relation to them.
The hereditary form of allergy has several manifestations, one of which is dermatitis - an inflammatory skin lesion with eczematous signs. The specific features of atopic dermatitis (or atopic eczema syndrome) include the following facts:
Atopic eczema syndrome is of two types in terms of prevalence and severity: moderate (focal rashes) and severe (extensive skin lesions). If left untreated, the skin disease can lead to serious complications - damage to the skin by pyogenic bacteria (pyoderma), viruses or fungi. Inherited hyperreactivity of the skin (increased sensitivity) acts as a predisposing endogenous factor to the development of pathology, but potentiation of the appearance allergic manifestations due to a number of exogenous reasons.
Development factors
Pathophysical changes in the skin that occur during periods of exacerbation of atypical dermatitis are caused by natural allergic reactions of the body of immediate type. Consecutive changes in the internal biological environment (formation, release of skin-sensitizing antibodies and tissue reaction to the processes that have occurred) have their own genetically determined characteristics.
The main factor determining the implementation of hereditary atopy in the form of atopic eczema is the tendency to hyperreactivity of the skin, the risk of inheritance of which is:
The presence of a predisposition to the disease alone does not lead to the appearance of clinical signs of allergic dermatosis - this requires the presence of other exogenous causes. Manifestations of diffuse neurodermatitis can occur under the influence of the following factors:
Features of the course in adults
Under the influence of allergens or other potentiating factors for the development of atopic eczema, a chain of inflammatory reactions is triggered in the body, resulting in the formation of a cellular infiltrate at the site of inflammation. The affected cells begin to secrete mediators (biologically active substances, transmitters of nerve impulses), hormone-like substances (cycotins) and immunoglobulin E, ensuring self-maintenance of inflammation. The processes occurring inside the body are reflected in specific symptoms.
Due to the presence of differences in the functioning of organs and systems in children and adults, the clinical manifestations of atopic dermatitis in different age groups of patients differ. Characteristic symptoms diseases in persons over 13 years of age (the stage of development of the disease is defined as “adult” if the patient’s age is more than 13 years), are:
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in adults
After diagnostics confirming the diagnosis of “atopic dermatitis” and identification of allergens that provoke the disease, a dermatologist prescribes a treatment regimen. To determine optimal therapeutic methods, specialists in the following specialized areas may be involved:
Before starting treatment, there is a need to conduct a complete examination of the body in order to detect accompanying pathologies and assessment of the functionality of all organs and systems. Based on all the measures taken, treatment tactics are determined, the basis of which is control of the symptoms of atopic eczema. It is very difficult to achieve complete recovery in an adult patient with diffuse neurodermatitis, so the main goals of therapy are:
The methods used to achieve treatment goals are prescribed to adult patients on an individual basis, taking into account the characteristics of the body and the clinical picture of the disease. Complex therapy may include the following methods:
Acute period
The goal of treatment of neurodermatitis during the acute phase is to quickly relieve key symptoms and normalize the patient’s condition. The basis of therapeutic measures during exacerbation of the disease is medications group of topical corticosteroids (Prednisolone, Triamsinolone, Sinalar). At atopic eczema for moderate severity, corticosteroids of mild and moderate activity are used; for severe disease and large areas of damage, high activity is used. Drugs of this pharmacological class are prescribed in short courses.
At the acute stage of neurodermatitis, it is advisable to prescribe intravenous antihistamines (sodium thiosulfate solution or calcium gluconate). If there is exudation, it is recommended to use antiseptic lotions (Fukortsin, methylene blue solution, etc.). If the course of the disease is complicated by a secondary infection, systemic antibacterial agents (Erythromycin, Leukomycin) are prescribed. To potentiate the effectiveness of the treatment, the therapeutic course can be supplemented with immunomodulators (Levamisole, Thymus extract).
Remission period
During the latent phase of atopic dermatitis therapeutic measures aimed at preventing exacerbations. Due to the allergic nature of neurodermatitis, the main preventive measure is compliance with a treatment and prophylactic regimen, which is aimed at limiting the patient’s contact with potential allergens. At the stage of remission, drug therapy also plays a role important role in ensuring the maximum duration of the asymptomatic period of the disease.
The drugs used to maintain a stable condition of the patient belong to the third generation of antihistamines, which can be taken continuously for six months. If there is a connection between the exacerbation of the disease and emotional stress, taking psychotropic medications in small or moderate doses is indicated. To prevent the appearance of symptoms of neurodermatitis, it is recommended to carry out therapy with sorbents, after which a course of drugs that normalize the intestinal flora (pre-, pro-, synbiotics, bacteriophages, enzymes) is prescribed.
For weakened adult patients whose disease occurs in a moderate to severe form, the use of anabolic steroids (Nerobol, Retabolil), which correct the effect of corticosteroids on the body, is indicated. At all stages and forms of dermatosis, the use of vitamin and mineral complexes is recommended. Depending on the patient’s condition, a course of mono- or multivitamin therapy is carried out. Vitamin supplements are often prescribed for a short period of time in dosages that significantly exceed normal physiological needs.
Drug treatment
Treatment protocols for atopic eczema in adult patients include a large number of medications, but antihistamines and tranquilizers are of greatest practical importance. Medicines of other groups are prescribed taking into account the prevalence of the inflammatory process, the presence of complications and concomitant pathologies. The range of drugs used during the treatment of neurodermatitis may include the following pharmacological groups:
Glucocorticosteroids
Drugs belonging to the group of glucocorticosteroids (GCS) are artificially synthesized analogues of natural steroid hormones produced by the adrenal cortex. GCS have a multifactorial effect on the body, being simultaneously desensitizing, anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, antitoxic, antiproliferative and immunosuppressive agents.
For the treatment of atopic eczema in adults, internal and external forms of GCS are used. To non-external hormonal agents for intramuscular injection refers to Betamethasone, injections of which are prescribed in a course with a frequency of use of 1 time every 2 weeks. The most frequently prescribed tablet medications in this group are Prednisolone, Metypred, Triamcinolone. For external use, the treatment regimen may include Laticort (hydrocortisone-based cream), Advantan ointment (methylprednisolone) and Afloderm cream (alclomethasone)
The use of GCS for the treatment of allergic dermatoses is due to their mechanism of action, which is to mediate the body's adaptive capabilities to external stress factors. Indications for the prescription of glucocorticosteroids are unbearable itching during the exacerbation phase of the disease (external forms) and lack of effect from the treatment (systemic corticosteroids). During remission, GCS can be used in the form of ointments to achieve an occlusive effect (blocking the release of pathogenic exudate).

Antihistamines
The drugs of first choice in the treatment of neurodermatitis are 2nd and 3rd generation antihistamines. To this pharmacological group include drugs that can block histamine neurotransmitter receptors and inhibit their potentiating effects. When treating allergic pathologies, H1 blockers are used, which are represented by 4 generations of drugs:
Antihistamines for atopic dermatitis in adults have a pronounced antiallergic effect, effectively eliminating the key symptoms of the disease (redness, itching, swelling). 2nd and 3rd generation antihistamines are more effective than 1st generation drugs, are less likely to cause side effects and have reduced cardiotoxicity. During treatment chronic form diseases, H1-blockers are prescribed in tablets; in the acute phase, the medicine can be administered intravenously.
Immunosuppressants of the macrolide class
Basic therapy prescribed to adult patients after relief of the acute process includes external agents, which include immunosuppressants. Drugs in this group, unlike steroids, are non-hormonal drugs. The most well-known representatives of the macrolide class of immunosuppressants are tacrolimus (Protopic) and pimecrolimus (Elidel), the targets of which are T-lymphocytes and mast cells of the skin.
According to the results of a comparative analysis of the clinical effectiveness of immunosuppressive drugs for topical use with GCS of low and moderate activity, it was found that the use of tacrolimus and pimecrolimus in the face and neck area is more effective and safe than GCS. Using macrolide class drugs 2 times a week for a year increases the remission period by 3 times.
Moisturizers
Dermatological practice involves the widespread use of local therapy, which can be etiological, symptomatic or pathogenetic in nature. In the treatment of dermatitis in adult patients, reducing agents play an important role, restoring the structure and functionality of the skin. Dry skin is not only a symptom of neurodermatitis, but also a factor that supports inflammatory processes. Constant itching that occurs due to excessive dryness causes nervous disorders that interfere with the treatment process.
Reducing the dryness of the epidermis and accelerating the healing process is an important stage of therapy during remission, the purpose of which is to prolong the asymptomatic period of the disease. To achieve this task, moisturizing creams, ointments, gels, emulsions, lotions based on lanolin or thermal water are used. The choice of dosage form depends on the severity and localization of the inflammatory process:
Tablets for atopic dermatitis in adults
The basis of systemic treatment of atopy in adults is drugs in tablet form. Due to the variety of factors influencing the development and course of the disease, the list of drugs for the treatment of neurodermatitis is extensive. All medications are prescribed exclusively by a doctor, based on the clinicopathological etiology of the disease. The main groups of medications in the form of tablets that can be used to treat atopic eczema are:
Membrane stabilizing drugs
In diseases of an allergic or inflammatory nature, cell membranes are primarily damaged. Favorable conditions for the functioning of receptors built into the membrane are provided by the lipid component, which is especially vulnerable to the action of pathogens. The effectiveness of therapy for diffuse neurodermatitis depends on the degree of protection cellular structure, and therefore the complex of therapeutic measures should include membrane-stabilizing drugs that restore cell integrity.
During the treatment of allergic dermatosis, patients may be prescribed the following membrane stabilizers:
|
Name |
Mechanism of action |
Method of administration |
|
|
Suprastin |
The main active ingredient (chloropyramine) has an antihistamine effect by blocking H1-histamine receptors and may have a weak hypnotic effect. |
The daily dose for adults is 3-4 tablets (75-100 mg), taken with meals. The duration of the treatment course is determined individually, on average it is 5–7 days. |
|
|
Clemastine |
H1-histamine blocker, in case of atopy, prevents the development of allergic symptoms, has a calming effect, relieves itching and swelling. |
Tablets should be taken in the morning and evening, 1 piece, the maximum daily dose is 6 tablets. |
|
|
Sodium cromoglycate |
Reduces the severity of allergic manifestations and the inflammatory process by stabilizing the mast cell membrane (the release of histamine and inflammatory mediators is slowed down). |
||
|
Ketotifen |
Suppresses the development of allergy symptoms by inhibiting the release of inflammatory and allergic mediators. |
The tablets are taken before meals twice a day. The recommended daily dosage is 2 mg. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 4 mg. |
Sedatives
Psycholeptics (sedatives, sedatives) are prescribed for atopic dermatitis, if a connection between exacerbation of the disease and stress factors has been identified. Drugs in this group are also indicated in the case of psycho-emotional disorders that arise against the background of neurodermatitis. The calming effect is achieved due to the regulating effect of the active components of psycholeptics on the nervous system. During the treatment of adult patients, the following sedative medications may be used:
|
Name |
Mechanism of action |
Method of administration |
|
|
Grandaxin (Tofisopam) |
The anxiolytic has a general calming effect, normalizes the emotional background, and reduces the level of anxiety. |
The medicine is prescribed to adults 3-6 tablets per day, the daily dose must be divided into 3 doses. |
|
|
Bellataminal |
Relieves itching in neurodermatitis, prevents the development of depression and anxiety. |
Take 1 tablet after meals. three times a day. The duration of the course is from 2 to 4 weeks. |
|
|
Psycholeptic of plant origin, has a pronounced antispasmodic and calming effect, eliminates symptoms of anxiety and irritability. |
Adults should take 2-3 tablets 2 or 3 times a day (maximum daily dose 12 tablets). The duration of the continuous course should not exceed 1.5–2 months. |
||
|
Diazepam |
The sedative effect is manifested in the relief of anxiety, nervous tension, and anti-panic effect. |
Depending on the severity of nervous tension, you should take from 1 to 3 tablets per day. The course continues until the emotional state improves. |
|
|
Amitriptyline |
An antidepressant with an analgesic effect, reduces restlessness, anxiety, agitation (nervous agitation). |
The tablets should be swallowed whole immediately after meals. The recommended daily dosage for neurodermatitis is 2 tablets. (after 2 weeks you can increase to 4 tablets). |
Drugs to normalize intestinal function
In order to speed up the healing process for atopic dermatitis, it is necessary to cure dysbiosis (violation of the ratio of beneficial and pathogenic bacteria inhabiting the intestines), which is often a provoking factor for exacerbation of the disease. The first stage of restoring normal intestinal microflora is detoxification, which is carried out using agents that can adsorb substances harmful to the body (Polysorb, Enterosgel).
The next stage after cleansing should be the restoration of the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which is achieved through the use of medications that improve intestinal microflora:
|
Name |
Mechanism of action |
Method of administration |
|
|
It has pronounced enveloping properties due to which it enhances the barrier functions of the mucous membrane, increases its resistance to irritants, adsorbs and removes toxic substances from the body. |
Dissolve the contents of 1 sachet in 0.5 cups of water. Take the suspension after meals 3 times a day. The duration of the course is determined individually. |
||
|
Preparations containing Lignin (Lactofiltrum, Polyphepan) |
Regulation of the balance of intestinal microflora, adsorption and elimination of exogenous, endogenous toxins and allergens, increasing nonspecific immunity. |
Take the sachet 1 hour before meals, after dissolving it in a small amount of water. The frequency of doses for adults is 2–4 times a day, the course duration is 2–4 weeks. |
|
|
Bifidumbacterin |
Normalization of the digestive tract, prevention of dysbacteriosis. |
1 bottle (5 doses) 2-3 times a day with meals or 20-40 minutes before. before eating, course – 10–14 days. |
|
|
Hilak forte |
Regulation of intestinal microflora composition, regeneration epithelial cells intestinal walls. |
The daily dose is 9.9 ml (180 drops). It is recommended to take 40–60 drops diluted with liquid (except milk) three times a day with meals. |
Hyposensitizing agents
There are two main ways of influencing the immunological phase of an allergic reaction - complete limitation of contact with the allergen and specific desensitization (reduction of the body's hypersensitivity). The first method is preferable, but due to a number of factors it is difficult to implement (it is not always possible to identify the allergen or completely eliminate contact with it).
The method of specific desensitization in practice gives satisfactory results and is used during an exacerbation of atopic eczema or in the absence of data on the cause of the allergic reaction. Specific hyposensitizing therapy is associated with a risk of exacerbation of the disease, so it is combined with nonspecific hyposensitizing antihistamines.
Hyposensitizers reduce the body's sensitivity to irritants by inhibiting the immunological mechanism of allergy development. The basis of drugs in this group are histamine antagonists (calcium preparations, sodium thiosulfate, corticosteroids, etc.), injections of which are often used during the acute phase of neurodermatitis to achieve a rapid antiallergic effect.
Calcium gluconate
The development of allergic reactions is often accompanied by hypocalcemia, as a result of which the permeability of the vascular walls increases, and the allergen quickly enters the bloodstream. Calcium in the form of gluconate is a source of calcium ions, which are involved in the transmission of nerve impulses and prevent the release of histamine. In case of exacerbation of atopic eczema, the medicinal solution is administered intravenously for 5–7 days, 1 ampoule (10 ml). Before administration, the contents of the ampoule should be warmed to body temperature.
Sodium thiosulfate
The sodium salt and thiosulfuric acid is used in the treatment of neurodermatitis in order to achieve a detoxification effect. The drug is available in the form of a solution for intravenous injections. After introduction into the body, the substance is distributed in the extracellular fluid and forms non-toxic compounds with cyanides, facilitating their elimination. The medicine is prescribed for severe itching to minimize allergic manifestations of dermatitis. The duration of the course is 5 days, during which adult patients are administered 1–2 ampoules (5–10 ml) of sodium thiosulfate.
Prednisolone
To achieve maximum anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effect during the acute phase of the disease, the systemic glucocorticosteroid Prednisolone is used. The mechanism of action of the drug is due to the ability active substance bind to specific receptors in the cellular cytoplasm and inhibit the synthesis of mediators of an immediate allergic reaction.
The immunosuppressive effect is ensured by potentiation of lymphopenia (decreased lymphocytes) and involution (decreased mass) of lymphoid tissue. In case of exacerbation of severe allergic dermatosis, intravenous or intramuscular injections of Prednisolone are prescribed at a dosage of 1–2 mg per 1 kg of the patient’s body weight. The course lasts no more than 5 days
External therapy
Local treatment of atopy is aimed at eliminating the cause and symptoms of dermatitis. To achieve these tasks, a large arsenal of external medications is used. The success of therapy depends on the correct choice of active ingredients and dosage form of medications. During the treatment of atopic eczema, adult patients can be prescribed the following medications, which can be purchased in city pharmacies:
|
Pharmacological group |
Drugs |
Mechanism of action |
Mode of application |
Price range, rub. |
|
Corticosteroids |
Hydrocortisone (Laticort, Lokoid) |
Relieves inflammation, inhibits allergic processes, eliminates swelling and itching. The ointment has a cumulative effect. |
Apply to wound surfaces 2–3 times a day for 6–20 days. For limited areas of inflammation, it is recommended to use occlusive dressings. |
|
|
Dermovate |
Cream and ointment based on clobetasol propionate. Eliminates inflammatory processes, reduces exudation, has antiallergic and antipruritic effects. |
Lubricate the affected area every morning and evening until the desired effect is achieved. The duration of the course should not exceed 4 weeks. |
||
|
Inhibits the release of allergic reaction mediators, has an antiexudative and antipruritic effect. |
To eliminate peeling in case of increased dryness of the skin, ointment should be used (applied once a day); with active exudation, a cream should be used (1 time/day). For lesions on the scalp, it is recommended to use lotion, which is rubbed into the skin until completely absorbed. |
|||
|
Afloderm |
Prevents the expansion of capillaries, thereby slowing down the development of edema. Has immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effects. |
Apply cream (suitable for sensitive areas) or ointment to inflamed areas 2-3 times a day until the symptoms of the disease disappear. |
||
|
Macrolides |
Inhibits the synthesis and release of protein phosphatase (inflammatory mediator), which stops the development of the inflammatory process and reduces the severity of histopathological changes (disturbances in the intercellular connections of the epidermis). |
The cream should be used at the first sign of exacerbation of dermatitis. Apply twice a day and rub into the skin until completely absorbed. Continuous use can be carried out for no more than 6 weeks. |
||
|
Antihistamines |
Fenistil gel |
Reduces the severity of skin itching, eliminates irritation, blocks H1-histamine receptors and reduces capillary permeability. |
The gel is applied externally 2–4 times a day. |
|
|
Emollients and moisturizers |
Ichthyol ointment |
The therapeutic effect is due to the presence of sulfur-containing compounds in the composition, which contribute to pain relief, softening and removal of infiltrates, potentiation of the process of tissue regeneration, local constriction of blood vessels, due to which the production of purulent secretion is reduced. |
The ointment is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin and distributed evenly (no need to rub in); the layer should be so thick that there are no gaps left. A sterile bandage is applied over the ointment, which should be changed after 8 hours. The course is 10–14 days. |
|
|
Accelerates the process of epithelization, has a moisturizing effect on all layers of the epidermis. |
Apply the cream to dry areas of the skin once a day, if necessary, you can increase the number of applications. |
|||
|
Trickzera |
Softens very dry skin, increases its elasticity, restores the lipid barrier. |
Apply to previously cleansed dry skin 2-3 times a day. |
||
|
Helps correct skin dryness and reduce hypersensitivity. |
The cream is applied twice a day, the skin should be pre-prepared (cleansed and moisturized). |
|||
|
Has a calming effect on irritated skin, restores the lipid layer. |
Apply the cream daily with gentle movements to the skin of the body and face. |
|||
|
Topicrem |
Moisturizing the upper layers of the epidermis, eliminating the feeling of “tightness” due to the formation of a moist film on the surface of the skin. |
Apply daily after hygiene procedures. |
||
|
Wound healing drugs |
Silver sulfathiazole (Argosulfan) |
It has a bactericidal effect, helps accelerate the healing process and epithelization of wounds. |
Apply a layer of 2–3 mm to the wound surface in the morning and evening. You can treat with cream in an open or closed way (applying the product under a bandage). |
|
|
Solcoseryl |
Wound healing effect, acceleration of regenerative processes, increased collagen synthesis. |
Apply to the wound surface pre-treated with an antiseptic 2-3 times a day (used only for weeping wounds without crusts). |
||
|
Actovegin |
Treatment of wounds at all stages of the disease (gel is used at the initial stage of wound formation, cream is indicated for wet wounds, ointment is optimally used for long-term therapy of dry wound surfaces). |
Apply to a wound cleaned of exudate, pus, etc. The product is applied 2-3 times a day in an open or closed way. |
||
|
Methyluracil ointment |
Accelerates the process of cell formation, activates humoral and cellular immunity, stimulates repair (correction of cell damage due to exposure to pathogens). |
Apply to damaged areas 2–4 times a day, duration of use should not exceed 2 weeks. |
Antibacterial ointments for secondary infection
When intensively scratching itchy skin, the integrity of its surface is disrupted, which facilitates the penetration of infectious agents from the environment into the inner layers of the epidermis. Pathogens cause irritation and itching, completing the “atopic skin cycle” (where symptoms of dermatitis become factors in its development). In order to break the vicious circle, it is necessary to stop the development of secondary infection. For this purpose, external antibacterial agents are prescribed, such as:

Physiotherapeutic procedures
The frequent use of various methods of physiotherapy in the practice of treating diffuse neurodermatitis in adults indicates their high effectiveness. When prescribing physical procedures, the indications and contraindications of specific types of exposure to physical factors are taken into account. The most common methods of physical treatment for dermatosis are:
Vitamins
Degradation of the skin often accompanies hypovitaminosis, therefore in the treatment of dermatological diseases great importance has vitamin support for the body. Therapy for neurodermatitis at the stage of remission is supplemented with vitamin and microelement complexes. The main vitamins that accelerate the healing process in atopy are:
Folk remedies
Traditional therapy for dermatitis can, in agreement with the doctor, be supplemented with non-traditional methods. Products made according to traditional medicine recipes can provide additional support to an organism weakened by disease and the action of highly active medicinal substances. To relieve the main symptoms of neurodermatitis, herbal remedies can be taken orally (decoctions, infusions) or used externally (ointments, lotions, compresses, lotions).
Before starting self-medication using traditional methods, it is necessary to agree with your doctor on the feasibility and safety of using certain medicinal herbs. Due to the effect they provide, the following methods of home therapy are very popular among patients with atopic eczema:
Raw potato compress
Traditional recipes for getting rid of allergic dermatosis based on potatoes are safe to use and easy to prepare. The tubers of this vegetable consist of 75% water, which determines its moisturizing and softening effect on the skin. To prepare the medicinal composition, you should peel fresh raw potatoes and chop them using non-metallic tools. The potato mass should be wrapped in gauze, squeezed out and applied to the affected surface overnight. Procedures are performed until the skin condition improves.
Antipruritic ointment made from chamomile and fireweed
You can get rid of severe itching, which is the main symptom that bothers patients, using an antipruritic ointment based on fireweed (fireweed) and chamomile. This herbal medicine can only be used on open areas of the body. To achieve a sustainable effect, it is necessary to carry out the procedure for a month, applying the ointment 3-4 times a day. If necessary, the course continues after a week's break. The components necessary for preparing the antipruritic composition should be prepared in advance. The recipe includes the following ingredients:
Chamomile and fireweed flowers should be crushed and mixed in equal proportions. 1 tbsp. l. Pour the mixture with 4 cups of water and bring to a boil. After boiling, the broth is covered with a lid and boiled for 5 minutes, then a decoction of hay dust and butter are added to it. The resulting mass should be cooked over low heat until it reaches a homogeneous consistency. The last step in preparing the ointment is adding glycerin in a ratio of 1 to 1. After cooling, the product is stored in the refrigerator.
Herbal decoction for oral administration
Along with traditional medicine for external use, decoctions for oral use have a good healing effect. The main components of the herbal drink are tree peony grass, motherwort, nettle, valerian root and mint. The decoction has a calming effect, helps strengthen the immune system and improves metabolic processes in organism. In order to prepare a healing drink, mix 50 g of ingredients, pour 1.5 liters of boiling water and leave for 1 hour.
The course of herbal medicine should last 20–30 days, during which the drink is prepared daily and drunk throughout the day. During the entire period of using the decoction, you should not take baths with hot or cold water (recommended temperature is 36–40 degrees). After water procedures, it is necessary to lubricate the wounds with emollient compounds.
Sanatorium-resort treatment of dermatitis in adults
Carrying out spa therapy within the framework of complex treatment allergic dermatitis in adult patients increases the overall effectiveness of therapy. This method is only indicated during remission. The direction of sanatorium-resort treatment is prescribed to the patient taking into account all indications and possible contraindications. The following procedures can be performed during spa therapy:

Diet therapy
An important stage in the course of treatment for atopy is the preparation of a hypoallergenic diet, the main task of which is to prevent allergens and histamine liberators (products that stimulate the release of histamine) from entering the patient’s body. If, using laboratory diagnostics, a specific product is identified that has caused sensitization of the body, a specific exclusion diet is prescribed (exclusion of products containing the identified substances).
In the absence of data on a specific allergen and during the acute phase of the disease, a nonspecific elimination diet is indicated. Foods that must be excluded from the diet in all cases of atopic eczema during relapse are:
In addition to avoiding foods with a high level of allergenicity, patients are advised to follow a number of food rules, the implementation of which will help achieve sustainable remission of atopy:
To determine the most likely food allergens, it is necessary to monitor and record reactions that occur in response to the consumption of a particular product. Guidelines for keeping records are as follows:
Video
Found an error in the text?
Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we will fix everything!
Atopic dermatitis in children is an inflammatory skin disease that occurs against the background of increased sensitivity of the body to contact and food allergens. The pathology manifests itself as itching, skin rashes, crust formation and other symptoms. Atopic dermatitis is predominantly encountered by young children, which makes the disease quite dangerous for their fragile bodies.
To diagnose atopic dermatitis in children, skin tests, specific IgE and other procedures are performed. If the diagnosis is confirmed, physiotherapy is prescribed, therapeutic nutrition and the use of medications (systemic and local). The child is also provided with psychological assistance to enhance the therapeutic effect.
Description of the pathology
Atopic dermatitis in children is a chronic disease allergic nature. In medicine, there are other names for this pathology - diffuse neurodermatitis, atopic dermatitis syndrome and atopic eczema. But all this is one and the same disease, the occurrence of which is determined by factors such as negative environmental influences and genetic predisposition.

Note! Symptoms of atopic dermatitis are often encountered by young patients, so the disease should be considered in pediatric practice. According to statistics, with chronic dermatological diseases in Lately predominantly encountered by representatives of the child population.
Causes
Genetics is far from the only factor that can trigger the development of dermatitis in children. There are other reasons:

If, while carrying a child, the mother often consumed harmful foods that contain potential allergens, then atopic dermatitis may occur in the newborn baby. Self-healing, as statistics show, occurs in approximately 50% of clinical cases. The second half of children are forced to suffer from signs of pathology for many years.
 Risk factors for the development of atopic dermatitis (AD) in children
Risk factors for the development of atopic dermatitis (AD) in children Classification
In medicine, there are several types of diseases that manifest themselves in different age categories:

Ignoring the disease can lead to unpleasant consequences Therefore, if suspicious symptoms appear in a child, you should contact your pediatrician as soon as possible.
Stages of occurrence
Doctors divide 4 main stages:

On a note! Correct definition The stage of atopic dermatitis is an important stage in the diagnostic examination, because this factor influences the choice of therapeutic course.
Characteristic symptoms
Regardless of the type of pathology or the age of the patient, dermatitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:

The most dangerous sign of atopic dermatitis in children is itching, because it forces the sick child to intensively scratch the affected area, which causes small wounds to appear. Through them, various bacteria penetrate the body, provoking the development of a secondary infection.
Will the symptoms of dermatitis go away with age?
In most cases, approximately 60-70%, the signs of atopic dermatitis in children disappear over time, but in the rest, the disease persists in the child and accompanies him throughout his life, periodically renewing. The severity of the pathology directly depends on the period of its occurrence, therefore, with early onset, dermatitis is especially severe.

Doctors say that if, in parallel with atopic dermatitis, children develop another allergic disease, for example, bronchial asthma or hay fever, then the symptoms will appear almost constantly, which will significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life.
Diagnostic features
At the first suspicious signs of atopic dermatitis in children, the child should be immediately taken to a doctor for examination. Diagnosis is carried out by an allergist and a pediatric dermatologist. During the examination, the general condition of the patient’s skin (dermatographism, degree of dryness and moisture), the localization of the rash, the intensity of the signs of pathology, as well as the area of the affected area of the skin are assessed.

To make an accurate diagnosis, a visual examination alone will not be enough, so the doctor prescribes additional procedures:

Note! During diagnosis, it is important to distinguish childhood atopic dermatitis from other diseases, e.g. pityriasis rosea, psoriasis, microbial eczema or seborrheic dermatitis. Only after differentiation will the doctor be able to prescribe an appropriate course of therapy.
Treatment methods
The main goal of therapy for atopic dermatitis in children is to desensitize the body, limit provoking factors, eliminate symptoms and prevent the development of serious complications or exacerbations of the pathology. Complex therapy should include medication (the use of local and systemic drugs), adherence to a special diet, as well as traditional medicine.

Pharmacy drugs
To relieve the symptoms of atopic dermatitis, the child may be prescribed the following groups of drugs:


To speed up the regenerative functions of the body and restore affected areas of the skin, the doctor may prescribe special ointments that stimulate regeneration. The most effective drug is Panthenol.
Nutrition
A well-known doctor works hard on the topic of treating atopic dermatitis in children. Komarovsky, who devoted many years to this issue. He recommends organizing meals when the child’s diagnosis is confirmed (see). This will speed up the healing process and prevent recurrence of the disease.

To do this, you should follow a few simple nutritional rules:

Also Komarovsky advises maintaining the room temperature no more than 20C. This will reduce the level of sweating in the child.
Folk remedies
If the disease was diagnosed in a child over 3 years old, then many parents use traditional medicine as therapy, which are in no way inferior in effectiveness to synthetic drugs. But before using them, you should definitely consult with your doctor.
Table. ethnoscience with atopic dermatitis in children.
| Product name | Application |
|---|---|
  | Pour 1 liter of boiling water over 3 tbsp. l. chamomile flowers and leave in a closed thermos for 2-3 hours. Use the finished product to wipe your baby's skin after bath procedures. |
  | Grind the currant shoots (necessarily young ones) and, placing them in a thermos, pour boiling water over them and leave for 2 hours. Strain the product through cheesecloth and give it to your child to drink throughout the day. |
  | A simple and at the same time effective anti-inflammatory agent used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Squeeze the juice from several potatoes and apply it to the affected areas of the skin. An hour after application, the juice should be washed off with warm water. |
  | Mix 4 tbsp in one bowl. l. butter and 1 tbsp. l. St. John's wort juice. Heat ingredients over low heat, stirring occasionally. Place the mixture in the refrigerator for storage. Apply the ointment to the affected areas 2 times a day. |
  | To prepare the decoction, pour 500 ml of boiling water into 3 tbsp. l. chopped plant and cook over low heat for 30 minutes. After this, the medicine should infuse for 2 hours. The finished decoction should be taken 1 tbsp. l. 3-4 times a day. The duration of the treatment course is 3 weeks. |
The use of homeopathic remedies helps normalize the gastrointestinal tract, and also restores the child’s immune and nervous system.
Many doctors recommend supplementing traditional treatment methods hyperbaric oxygen therapy, reflexology and phototherapy methods. This will speed up the recovery process, strengthen the child’s body and reduce the likelihood of re-development of the pathology.

Often, when diagnosing atopic dermatitis, children require the help of not only a dermatologist, but also a psychologist.
Possible complications
Incorrect or untimely treatment of atopic dermatitis in children can lead to the development of serious complications, which, in turn, are divided into systemic and local. TO systemic complications relate:

TO local complications atopic dermatitis in children include:
To avoid such complications, the disease must be treated in a timely manner, so at the first suspicious symptoms, the child should be shown to a doctor as soon as possible.
Prevention measures
To prevent your child from encountering unpleasant symptoms of atopic dermatitis in the future, the following recommendations should be followed:

Atopic dermatitis in children- This serious illness skin, requiring increased attention. The disease can periodically disappear and then appear again, so only timely therapy and preventive measures will get rid of dermatitis forever.
Video - 10 rules for treating atopic dermatitis in children
Atopic dermatitis in infants is a chronic immune inflammation of the child’s skin, characterized by a certain form of rashes and their staged appearance.
Childhood and infant atopic dermatitis significantly reduces the quality of life of the entire family due to the need for strict adherence to a special therapeutic diet and a hypoallergenic lifestyle.
Main risk factors and causes of atopic dermatitis
A risk factor for atopic disease is often a hereditary history of allergies and. Factors such as constitutional features, nutritional disorders, and insufficiently good care for the child are also unfavorable.
Understanding the pathogenesis of this allergic disease will help you understand what atopic dermatitis is and how to treat it.
Every year, scientists' knowledge about the immunopathological processes occurring in the body during atopic childhood is increasing.
During the course of the disease, the physiological skin barrier is disrupted, Th2 lymphocytes are activated, and immune defense is reduced.
Concept of the skin barrier
Dr. Komarovsky, in his articles popular among young parents, touches on the topic of the characteristics of children's skin.
Komarovsky highlights 3 main features that are important in breaking the skin barrier:
All these factors lead to a decrease in the protection of the baby’s skin.
Hereditary predisposition
Atopic dermatitis in infants can occur due to a filaggrin mutation, in which changes occur in the filaggrin protein, which ensures the structural integrity of the skin.
Atopic dermatitis develops in children under one year of age due to a decrease in the local immunity of the skin to the penetration of external allergens: the biosystem of washing powder, the epithelium and hair of pets, fragrances and preservatives contained in cosmetic products.

 Antigenic loads in the form of toxicosis in pregnant women, taking medications by a pregnant woman, occupational hazards, highly allergenic food - all this can provoke an exacerbation of an allergic disease in a newborn.
Antigenic loads in the form of toxicosis in pregnant women, taking medications by a pregnant woman, occupational hazards, highly allergenic food - all this can provoke an exacerbation of an allergic disease in a newborn.
Prevention of allergies in infants can be a natural, as long as possible, rational use medicines, treatment of diseases of the digestive system.
Classification of atopic dermatitis
Atopic eczema is divided according to age stages into three stages:
In newborns, the rash looks like redness with blisters. The bubbles break easily, forming a wet surface. The baby is bothered by itching. Children scratch out rashes.
Bloody purulent crusts form in places. Rashes often appear on the face, thighs, and legs. Doctors call this form of rash exudative.


In some cases, there are no signs of weeping. The rash looks like spots with slight peeling. The scalp and face are most often affected.
At the age of 2, sick children's skin is characterized by increased dryness and cracks appear. The rashes are localized in the knee and elbow pits, on the hands.
This form of the disease has the scientific name “erythematous-squamous form with lichenification.” In the lichenoid form, peeling is observed, mainly in the folds and elbow bends.
Facial skin lesions appear at older ages and are called “atopic face.” Pigmentation of the eyelids and peeling of the skin of the eyelids are observed.
Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in children
There are criteria for atopic dermatitis, thanks to which the correct diagnosis can be made.
Main criteria:
Additional criteria:
Laboratory diagnostic measures for severe atopic dermatitis, they are prescribed by a doctor after examination.
Complications of atopic dermatitis in children
Frequent complications in children include various types of infections. The open wound surface becomes a gateway for Candida fungi.
Prevention of infectious complications consists of following the recommendations of an allergist regarding the specific use of emollients (moisturizers).
List of possible complications of atopic dermatitis:
Traditional treatment of atopic dermatitis
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in children begins with the development of a special hypoallergenic diet.
An allergist prepares a special elimination diet for a mother with atopic dermatitis in her baby. This diet will help you maintain breastfeeding for as long as possible.
An approximate hypoallergenic elimination diet for children under one year of age with atopic dermatitis.

Menu:
The menu for a child, and especially for a child with atopic dermatitis, should not contain spicy, fried, salty foods, seasonings, canned food, fermented cheeses, chocolate, or carbonated drinks. On the menu for children with allergic symptoms limit semolina, cottage cheese, sweets, yoghurts with preservatives, chicken, bananas, onions, garlic.
Mixtures based on it will also help in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in a child.
If you are hypersensitive to cow's milk proteins, the World Allergy Organization strongly recommends against using products based on non-hydrolyzed protein. goat milk, since these peptides have a similar antigenic composition.
Vitamin therapy
Patients with atopic dermatitis are not prescribed multivitamin preparations, which are dangerous from the point of view of the development of allergic reactions. Therefore, it is preferable to use single preparations of vitamins - pyridoxine hydrochloride, calcium pathotenate, retinol.
Immunomodulators in the treatment of allergic dermatoses
Immunomodulators that affect the phagocytic component of immunity have proven themselves in the treatment of allergic dermatoses:
Hormonal creams and ointments for atopic dermatitis in children
It is not possible to treat severe atopic dermatitis in children without the use of local anti-inflammatory glucocorticosteroid therapy.
For atopic eczema in children, both hormonal creams and various shapes ointments.
 Below are basic recommendations for the use of hormonal ointments in children:
Below are basic recommendations for the use of hormonal ointments in children:
Calcineurin blockers
An alternative to hormonal ointments. Can be used on the face and natural folds. The drugs Pimecrolimus and Tacrolimus (Elidel, Protopic) are recommended to be used in a thin layer on the rash.
These drugs should not be used in immunodeficiency states.
The course of treatment is long.
Products with antifungal and antibacterial activity
For infectious uncontrolled complications, it is necessary to use creams containing antifungal and antibacterial components - Triderm, Pimafucort.
The previously used and successful zinc ointment was replaced by a new, more effective analogue- activated zinc pyrithione, or Skin-cap. The drug can be used in one year old child in the treatment of rashes with infectious complications.
For severe weeping, an aerosol is used.
 Dr. Komarovsky writes in his articles that there is no more formidable enemy for a child’s skin than dryness.
Dr. Komarovsky writes in his articles that there is no more formidable enemy for a child’s skin than dryness.
Komarovsky advises using moisturizers (emollients) to moisturize the skin and restore the skin barrier.
The Mustela program for children with atopic dermatitis offers a moisturizer in the form of a cream-emulsion.
The Lipikar program of the La Roche-Posay laboratory includes Lipikar balm, which can be applied after hormonal ointments to prevent dry skin.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis with folk remedies
How to cure atopic dermatitis permanently? This is a question that scientists and doctors around the world are asking themselves. The answer to this question has not yet been found. Therefore, many patients are increasingly resorting to homeopathy and traditional methods traditional medicine.
Treatment with folk remedies sometimes brings good results, but it is better if this method of treatment is combined with traditional therapeutic measures.
When the skin gets wet during a severe exacerbation of allergic dermatosis, folk remedies in the form of a lotion with a decoction of string or oak bark help well. To prepare the decoction, you can purchase a series in filter bags at the pharmacy. Brew in 100 ml of boiled water. Use the resulting decoction to apply lotions to the rash areas three times during the day.
Spa treatment
Most Popular sanatoriums for children with manifestations of atopic dermatitis:
What follows Avoid for atopic dermatitis: