Among infectious diseases Scarlet fever occupies a special place in children. An adult can also get it, but children are more susceptible due to undeveloped immunity and poor resistance.
Just 10 years ago, this disease terrified parents and instilled fear in children, because the mortality rate from it was high. Today, this disease can be successfully treated and consequences can be avoided. However, for no disease there is nothing better than quality prevention.
Scarlet fever is an acute infectious disease caused by excessive susceptibility of the body's defense systems to the immune complexes of streptococcus. Mostly the skin is affected, but it is also often affected internal organs.
The human body is very susceptible to streptococci - bacterial pathogens of most diseases. Immunity to them is weak and not everyone develops; damage to internal organs can lead to its deficiency, and the bacterium itself develops resistance to new antibiotics.
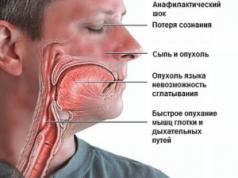
It is the characteristics of the pathogen that explain the danger of the disease. Streptococcus can infect the throat, but the “tail” of complications will damage the kidneys, heart, and liver. Scarlet fever in children is dangerous because an infection that is not completely cured can lead to damage to these organs in a matter of hours. Treatment of complications lasts for years, and does not always end in success. Fortunately, today such methods are available and effective. antibacterial agents, like flemoxin or azithromycin, to which the bacterium does not yet have immunity.
As mentioned earlier, children are more susceptible, but adults with immunodeficiency and pregnant women are also at risk. For the latter, scarlet fever is extremely dangerous and often serves as a reason for termination of pregnancy or a contraindication to natural childbirth.
Causes
The various causes and contributing factors are called etiology. What caused the disease determines how it manifests itself - in the form of inflammation, allergies, or is asymptomatic.
Scarlet fever is an infection caused by group A streptococcus. This is a particularly persistent and strong bacterium that produces a toxin that is carried throughout the body in the blood. 
What you need to know about the pathogen:
- streptococcus does not die at a temperature of 70°C, so the body cannot independently overcome the infection (be it a sore throat or scarlet fever);
- The danger is not so much the bacterium itself as the product of its vital activity - erythrotoxin, which spreads through the bloodstream to all organs and tissues (hence the rash);
- the bacterium is sensitive to antiseptics;
- the child’s body reacts sharply to streptococcus, producing an extremely aggressive immune response, which can damage organs that are not involved in the disease, such as the heart;
- It is very difficult to kill streptococcus; due to undertreatment, it often becomes a chronic inhabitant of the body, and a person becomes a carrier of the bacterium.
This is the direct cause of the disease.
In addition to this, there are also predisposing factors:
- chronic tonsillitis ( frequent illnesses throat and tonsils in particular);
- atopic dermatitis - autoimmune disease, which increases the body’s reactivity to streptococcus;
- diathesis and other immune skin pathologies- for the same reason;
- malnutrition, malnutrition, low body weight relative to the age norm and, as a consequence, poor resistance;
- any immunodeficiency conditions - AIDS, HIV, pregnancy, acclimatization;
- diabetes mellitus, other endocrine pathologies;
- pathology of the adrenal glands, hormonal instability;
- chronic pathological changes in the nasopharynx - pharyngitis, nasopharyngitis;
- regular use of immunosuppressants, such as steroid hormones, which are often prescribed for allergies, stenoses, and obstructions in children.
Each factor individually is predisposing, but if more than two coincide in one child’s body, this is a 90% probability of the disease. Despite so many factors contributing to the disease, prevention and immune support can reduce the risk many times over.
Development mechanism
How a disease develops, is transmitted, and causes symptoms is pathogenesis. His parents only need to know general outline in order to have an understanding of the stages of the onset of symptoms.
The source of infection is a sick person or carrier. This is important, because the majority of city residents are carriers of streptococcus - everyone suffering from a cough and runny nose. But not everyone will get sick. If the risk factors described above are present, contact with the carrier will cause the development of the disease. Without them, the child will get away with a mild cold.
Scarlet fever is transmitted by airborne droplets. Through the upper respiratory tract (the most accessible mucous membrane there), streptococcus enters the child's body. On their damp and warm surface, the bacterium multiplies, creating colonies and damaging the vulnerable mucous membrane. Among other things, it feeds and secretes metabolic products, which are absorbed into the blood and gradually distributed throughout the body.

Our blood, like a perfect environment, quickly reacts to enemy agents and activates specific cells - lymphocytes. This is called antibody function.
That is, the streptococcus bacterium and its toxin are an antigen, and lymphocytes produce antibodies. Together, this creates an immune complex “antigen-antibody”, the circulation of which causes dysfunction of internal organs and all associated symptoms scarlet fever in children.
While immune complexes are located in the upper respiratory tract, inflammation is localized in the throat. Later, a rash appears as a more systemic reaction. If the bacterium is killed, and immune complexes are still wandering through the child’s blood, consequences will be observed.
That's all parents need to understand so as not to stop the course of antibiotics halfway.
Clinical picture
Typical forms
Alas, sometimes even good prevention unable to prevent infection. Depending on the internal forces child's body, the disease may have different shapes and periods of occurrence.
The forms are as follows:
- mild, in which the symptoms are mild, the course is moderate, and complications often do not arise;
- moderate - signs of the disease are more than moderately expressed, but the course is uncomplicated and the prognosis is conditionally favorable, provided that treatment is timely;
- severe - manifests itself with complications, the symptoms are pronounced, difficult to correct, the prognosis is unfavorable (complications on internal organs, their insufficiency).
The severe form can also occur in different ways:
- toxic;
- septic;
- toxic-septic.
You need to know the stages of scarlet fever in order not to mistake the stage of the disease for recovery.
In total, there are 4 periods of the disease:
- Incubation.
- Elementary.
- Rash period.
- The period of convalescence.
Incubation, or latent period , is characterized by the fact that the pathogen is already in the body, but there are no open manifestations yet. During this period, parents of a sick child may notice a slight increase in temperature and fatigue, and mistake it for ARVI. About a week passes from the moment of contact with the “culprit” to the beginning of this period. And the incubation period itself can vary from several days to a week.
Initial period - this is the appearance of the first signs - one of the leading symptoms. It begins with a sore and sore throat, in the area of the root of the tongue and tonsils. On examination, the mucous membrane of the tonsils will reveal bright redness (hyperemia) and a characteristic rash - exanthema.
This rash looks like hives. At first, the rash is only in the throat. In order to detect a scarlet fever rash, you need to look at the boundaries - it should not extend beyond the tonsils and soft palate.
Already during this period, doctors prescribe an antibacterial drug - Flemoxin, Augmentin, Erythromycin.

The baby’s skin at this stage is hard, rough and hot, but clean. This period lasts from several hours to 1-2 days. At the same stage, a changed tongue is observed - with hypertrophied papillae, bright red.
Period of rash begins one day after the throat is affected and lasts from the beginning of the first elements to five days after it. The nature of the rash is pinpoint, roseate.
The elements of the rash are located close to each other, but do not merge. Within a few hours, the rash spreads to the neck, top part torso in the area chest, gradually it covers the entire torso and flexor surfaces of the limbs.
On the first day, the rash is bright red and the skin resembles sandpaper. This can be explained by the fact that they increase in size hair follicles. By the third day, the color changes, the rash fades and becomes muted pink. At adequate treatment By the fifth day, the rash may disappear.
It is important to remember that for the entire period of the rash, plus five days after the rash disappears, the child is contagious, which means he must be quarantined. It is not advisable to bathe your baby at this time.
In addition to the rash, during this acute period the child will experience increasing signs of intoxication. The temperature can rise to 39 degrees, and it is difficult to respond to antipyretic measures. All this is naturally accompanied by nausea, vomiting and headache. So the body tries to remove the toxin, but to no avail, because the pathogen remains intact.
Convalescence period - this is the time when the symptoms gradually subside, but in no case should you stop treatment. This is a period of active circulation of immune complexes in the blood. It can last 5-7 days.
Atypical forms
In some cases, the clinical picture may look atypical for scarlet fever and cause difficulties in diagnosis.
Atypical scarlet fever can occur in three ways:
- Extrapharyngeal - intact (unaffected) tissues of the oropharynx and pharynx, but against this background regional lymphadenitis is pronounced.
- Subclinical (erased) form - with it, typical syndromes are absent or mildly expressed.
- The vestigial form lasts only 2-5 days.
Symptoms
To briefly describe what scarlet fever is typical for in children, the following symptoms can be identified:
- angina;
- hyperthermia;
- red tongue with hypertrophied papillae;
- intoxication phenomena;
- exanthema on the throat;
- roseola on the body.

Specific symptoms of scarlet fever:
- Filatov's symptom - pallor of the nasolabial triangle, bright crimson blush on the cheeks, bright crimson tongue;
- white dermographism - after passing a hard object over the skin, a persistent white mark remains that does not disappear within a few seconds;
- lamellar peeling and flaking on the plantar surface of the foot and palmar surface of the hands.
Streptococcal symptoms are a group of signs of damage to additional organs in the later stages (during the period of convalescence). These include:
- tachycardia;
- violation heart rate(arrhythmia);
- hypertension (reactive) in the first days;
- hypotension from the fourth day of illness;
- expansion of the percussion boundaries of the heart;
- systolic murmur at the apex of the heart;
- accents for splitting the second tone at the point of listening to the pulmonary artery.
In general, the full period of scarlet fever lasts 20-25 days. It is very important not to miss the moment when it begins in order to start treatment on time and avoid complications.
Diagnosis of the disease
The first thing to do if any of the symptoms appear is to consult a doctor. First, you should call a pediatrician who will examine, palpate and listen to the child to determine whether it is scarlet fever, measles or a regular viral infection.
When the diagnosis of scarlet fever is confirmed, the doctor may advise you to go to the infectious diseases hospital. You shouldn’t refuse, because they will take all the necessary tests and will be able to provide full assistance that cannot be provided at home.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor must interview the patient or his parents in detail, not only about the current disease, but also about all previous infections, whether they have been vaccinated, had contacts with patients, and the presence of HIV status. Based on this history, a guess can be made.
- clinical, aka general analysis blood;
- smear to determine the microflora of the pharynx - determine the pathogen and its number;
- analysis of venous peripheral blood to determine the titer of antibodies to group A streptococcus;
- sensitivity of streptococcus to the main drugs of therapy - Flemoxin, Azithromycin.
Laboratory diagnostics are most informative during the first days of the disease, while the concentration and activity of bacteria is maximum.
Parents do not need to know the decryption - if discovered, laboratory and clinic workers will definitely contact them. All these analyzes are monitored over time, that is, throughout the entire period of the disease.
In addition to laboratory methods, hardware methods may also be needed - ECG, ultrasound of the kidneys, heart. 
Features of the course in children of different ages
The course of the disease and its consequences largely depend on how well the immune system is developed, that is, on age.
In children under one year of age, scarlet fever is almost never diagnosed. However, in some cases this may be the case. In infants, scarlet fever will be very severe; such children are kept under 24-hour medical supervision. The stages are the same as for older children.
During kindergarten age, the incidence of scarlet fever is at its peak. The course is moderate, the prognosis is favorable. The periods of the disease are milder, but last longer.
At an older age (from 14 years old), scarlet fever can cause complications, since the course is more severe and resistance, oddly enough, decreases. The prognosis is favorable with timely therapeutic measures.
As for the difference in consequences in boys and girls, there is no clinical evidence of the influence of streptococcus on the development of the gonads.
Lifestyle of a child during illness
The infection weakens the baby, so he needs to be provided with bed rest, in a room without bright lights and loud sounds. Reduce stress levels as much as possible.
Despite the fact that in our society it is customary to feed sick children, in the case of scarlet fever it is better not to do this. It is necessary to give food little by little; all foods must be boiled and ground so that they are easy to swallow. Food should be warm, not hot. The diet excludes hot, salty and spicy foods that irritate the throat.
As for the drinking regime, you need to drink a lot. It is better if it is an alkaline warm drink. The baby should have access to it around the clock. Dehydration must not be allowed. You need to drink fractionally, that is, sip at a time, but often.
It is not advisable to bathe your baby during scarlet fever, at least for the first 5-7 days. Temperature changes and unnecessary irritation will only intensify the appearance of the rash. It is also not worth treating the rash with anything.
Treatment
Drug therapy for scarlet fever in mandatory should include antibiotics of the penicillin series. Streptococcus is not sensitive to the rest. Unfortunately, bacteria cannot be killed without antibacterial therapy. The course of treatment must be followed exactly as prescribed by the doctor, without unnecessary initiative. 
Used for treatment antibacterial drugs. The most frequently prescribed are Augmentin and Flemoxin. Less commonly prescribed are Erythromycin and Amoxiclav. All antibiotics can be supplied in any form - tablets, injections, suspensions.
Flemoxin is given in tablets, the children's dosage is 0.125 g once a day or 0.25 twice at the age of one to three, from three to six years, the dose is 0.25 g. Flemoxin is given for 10 days.
Augmentin has more options - syrups, drops, suspensions, tablets. You can choose the one that best suits your specific age. The dosage also depends on the form. The instructions are presented in detail on the Internet and should also be explained by the attending physician.
Along with a course of antibiotics, it is necessary to give a high-quality probiotic that will support the baby’s microflora. Flemoxin is more aggressive towards the intestines, but is more effective in terms of treatment. Augmentin is relatively gentle.
Paracetamol can be used to lower the temperature. Ibuprofen is best avoided if possible, as it has strong effects on the liver and kidneys.
Symptomatic therapy involves local anesthesia and sanitation of the throat (gargles, sprays and lozenges), treatment accompanying pathologies such as otitis or conjunctivitis.
It is also important to carry out adequate detoxification therapy - maintain the balance of fluids and salts.
Prevention
Not all children can get scarlet fever. Only three out of ten will become infected after contact with a sick peer. Prevention of scarlet fever infection involves stimulation of the immune system and timely treatment of ENT diseases; a cold should not be allowed to last for a long time.
For most dangerous infections Vaccination already exists, but a vaccine against scarlet fever has not yet been developed. And there is no particular need for development, because the immunity of most children is able to cope with the disease.
Useful video about scarlet fever
I like!
Body rash, sore throat, fever are symptoms of many childhood diseases, one of which is scarlet fever. The disease is common among children and can cause serious complications. Adults can also get it, but in childhood the pathology occurs more often due to undeveloped immunity and, as a result, poor resistance to infection. Scarlet fever in children has specific symptoms, so it can be suspected even when it appears primary signs, while on early stages the disease is easier to treat.
What is scarlet fever in children
The disease belongs to the category of infectious, caused by excessive susceptibility of the defense systems to the immune complexes of streptococcus. The disease mainly affects the skin, but internal organs are also often affected. Because the human body susceptible to streptococci (bacterial pathogens of many pathologies), the immunity to protect against them is weak. Damage to organs can lead to their failure, and the pathogen itself develops resistance to antibiotics.
How is it transmitted?
Type A streptococci are transmitted from sick/carriers to healthy children by airborne droplets. Through the top respiratory organs(where the most accessible mucous membrane) the infection enters the body. On a warm, damp surface, the bacterium multiplies, creates colonies and damages the delicate mucous membrane. In addition, the infectious disease spreads outward along with metabolic products. Gradually, the infection is transmitted to other organs and systems through the blood.
Blood is perfect environment, which quickly reacts to foreign bacteria and activates specific protective cells, which are lymphocytes. Thus, streptococcus and its toxin are an antigen, and lymphocytes produce antibodies, as a result of which an “antigen-antibody” immune complex is created. Its circulation stimulates organ dysfunction and accompanying symptoms of infection spreading throughout the child’s body.
A sick baby is a carrier of the infection from the moment the initial signs of streptococcal infection appear. The contagious period can vary in length for different children and last from several days to a couple of weeks. If the pathology proceeds without complications and therapy with antibacterial drugs was started in a timely manner, after 7-10 days the child ceases to be infectious to others. A dangerous infectious disease spreads by sneezing, coughing, or throat, so people around the patient are at greater risk.
Symptoms of scarlet fever in children
It is important for parents to know about specific symptoms in children, which indicates the development of an acute infection. The main signs of scarlet fever in a child:
- Symptoms of intoxication of the body with streptococcal toxins. The pathology is manifested by fever, aching joints/muscles, tachycardia, vomiting, and general malaise.
- A characteristic rash with scarlet fever in children appears on days 1-3 of the pathology. The rashes look like bright pink or red dots and are usually localized in the face, groin, flexion zones of the limbs, and on the sides of the torso. In this case, the clinical symptom has maximum intensity under the arms, on the bends of the elbows and knees: the rash forms dark red stripes. There are no skin rashes in the area of the nasolabial triangle, but the skin in these places looks pale.
- Severe sore throat is also characteristic symptom scarlet fever. When the pathogen comes into contact with the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, it begins to produce streptococcal toxins, which cause the development of purulent foci of infection and inflammation of the tonsils. The child's throat becomes bright red.
- Changing the color of the tongue. The crimson color can be seen on days 2-4 of the development of the pathology. The tongue shows graininess due to the increase in the size of the papillae.
- Characteristic peeling skin. The symptom develops 1-2 days after the initial signs of the disease (peeling is replaced by a specific rash). On the palms and feet the skin peels more strongly, on the body, neck, and ears - less. The symptom is especially pronounced on the hands: the epidermis is removed from the fingertips in large areas. There is no pigmentation left after the rash.

First signs
Scarlet fever in a child begins to appear approximately 3-7 days after the moment of infection - this time is called incubation stage diseases. In some cases, this period is reduced to 1 day or even several hours; even less often, the incubation of the disease is extended to 12 days. The initial signs of illness in a child are usually observed during the first few days. The occurrence of the disease can be guessed by the following signs:
- body temperature rises to 38-40 degrees;
- a sore throat and a white coating appear;
- Some babies have febrile seizures due to fever.
Causes
The infection is caused by group A streptococcus, a persistent bacterium that produces a toxin that subsequently spreads throughout the body through the bloodstream. This is the direct cause of the disease, but besides it there are other predisposing factors:
- atopic dermatitis – a disease that increases the child’s body’s reactivity to streptococcus;
- chronic tonsillitis (frequent tonsil lesions, throat diseases);
- undernutrition, malnutrition, low body weight relative to the child’s age forms low resistance to diseases, including scarlet fever;
- immune skin pathologies, including diathesis;
- diabetes mellitus, endocrine diseases;
- immunodeficiency conditions (HIV, AIDS, acclimatization);
- hormonal instability, pathologies of the adrenal glands;
- systematic use of immunosuppressants, for example, steroid hormones, which are often prescribed to children for stenosis, allergies, obstructions).
Features of the course in children of different ages
The length of time scarlet fever lasts and the severity of the disease are determined by the functioning of the child’s immune system. In babies under one year of age, pathology is diagnosed extremely rarely due to the protective properties that the newborn’s body acquires from the mother through milk. If the infection affects the infant, the pathology will be extremely difficult: such children are subjected to hospitalization with round-the-clock medical supervision. The stage of development of the disease in very small babies does not differ from older children.
In children of preschool age, the incidence of scarlet fever is at its peak. The course of the disease is moderate, and the prognosis is usually favorable. The periods of pathology are relatively mild, but have an increased duration. In adolescents from 14 years of age, the disease can cause complications, since its course is more severe, and the immune system is in a state of restructuring, and the body’s resistance to infections decreases. After suffering from scarlet fever, which was adequately treated, the prognosis for the teenager is favorable.

Why is scarlet fever dangerous?
The danger of the disease is explained by the characteristics of the bacterium (causative agent). A streptococcal infection can affect the throat, and complications that arise can lead to kidney, liver or heart failure. The disease in children is dangerous because an incompletely cured infection can affect the listed organs in a matter of hours. Treatment of complications takes years and does not give a positive result in all cases.
Complications
Doctors deny that the disease is more dangerous for boys than for girls. The only difference in the course of their disease is that the former have a higher risk of complications manifested by glomerulonephritis. Early negative consequences of scarlet fever, which develop as a result of the spread of infection to internal organs/tissues, are:
- otitis;
- lymphadenitis;
- sinusitis.
A common complication of the pathology is malnutrition, which occurs due to severe pain in the larynx and difficulty swallowing. Late allergic complications and other negative consequences of the disease are observed, as a rule, in children who were treated incorrectly. These include:
- arthritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- rheumatism;
- carditis.
Diagnostics
An important condition for preventing complications is to consult a doctor if you suspect scarlet fever. The pediatrician will examine and listen to the baby to determine the specifics of the pathology. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor may advise visiting the infectious diseases hospital, where the baby will be given full assistance, tests will be taken, etc. The doctor will definitely question the baby and parents not only about the current disease, but also find out whether it was a re-infection or a primary one, what infections there were previously the child, whether he was vaccinated, whether there were any contacts with sick people.
After collecting anamnesis, the following tests are prescribed:
- smear on the microflora of the throat (to determine the pathogen and the number of bacteria);
- general blood analysis;
- analysis of the sensitivity of streptococcus to basic drugs (Azithromycin, Flemoxin);
- analysis of venous peripheral blood to determine the titer of antibodies to type A streptococcus.
Laboratory diagnostics are more informative during the first day of pathology, while the activity and concentration of bacteria is maximum. Parents do not need to know the interpretation of test results: if an infection is detected, laboratory/clinic workers must contact them. All tests, as a rule, are monitored over the dynamics of the disease (during the entire period of its development). Diagnostic methods, except laboratory research, can serve as ultrasound of the heart, kidneys, ECG.
Treatment of scarlet fever in children
Therapy is carried out at home, and hospitalization is required only in severe cases of the disease, in case of complications, or if there are other children under 10 years of age in the family who have not previously had scarlet fever. An acute infection must be treated with an antibiotic, any medications prescribed by a doctor. While the temperature lasts, the baby is advised to rest in bed. Who is this, during the acute phase of the disease it is important to strengthen the drinking regime and adhere to the diet.
It is better to give food to the patient in liquid or semi-liquid form (light soups, various cereals, vegetable stews, etc.), and limit protein foods. The baby should drink a lot, but it is better to give him warm drinks - tea, herbal decoctions. How to treat scarlet fever in children at home:
- The baby is given separate dishes and household items for the duration of treatment;
- It is highly advisable to isolate the patient in a separate room;
- The premises should be cleaned daily using disinfectants;
- The baby must adhere to bed rest for at least 7-10 days.

Drug treatment
For a speedy clinical recovery, the doctor prescribes penicillin antibiotics. Streptococcus is not sensitive to other types of antibacterial drugs. It is important to strictly follow the course of treatment prescribed by the doctor, otherwise there is a high risk of complications. For the treatment of scarlet fever, the following are often used:
- Flemoxin. Basics active substance The medicine is amoxicillin, thanks to which the drug provides a wide spectrum of action. For children 1-3 years old, the daily dosage is 0.25 mg of the drug twice a day; for patients 3-6 years old, the antibiotic is taken once. The course of treatment lasts 10 days. The advantage of Flemoxin is its speed of action: active ingredient is absorbed immediately after entering the stomach, and the maximum concentration of amoxicillin in the blood is reached after an hour. The downside of the medication is its ability to disrupt the digestion process.
- Augmentin. The remedy for scarlet fever in children is available in the form of tablets, drops, syrup and suspension. The advantage of Augmentin is the ability to choose the most appropriate type of medication, which will be easier for the baby to take. The dosage depends on the form of the drug, so you should follow the one prescribed by your doctor. The disadvantage of Augmentin is that even with a slight overdose it can cause many side effects.
- Erythromycin. An antibiotic from the macrolide group is prescribed somewhat less frequently than the drugs described above. Its advantage is the variety of release forms: for the smallest babies they are optimal rectal suppositories, for older patients, a suspension or tablets are suitable. The downside of this product is its ability to cause allergic reactions and digestive disorders.
In addition to antibacterial therapy, babies need to be given probiotics that will support the intestinal microflora. To reduce the temperature, it is allowed to give paracetamol, and the use of Ibuprofen should be avoided, if possible, since it has a strong effect on the kidneys and liver. In addition, symptomatic therapy is carried out, which involves local anesthesia and treatment of the throat (scarlet fever is always accompanied by a sore throat, due to which a purulent plaque develops on the mucous membrane of the throat) with sprays, gargling solutions, etc.
Consequences
The impact of childhood infection on girls and boys is approximately the same. The causative agent of scarlet fever does not have a negative effect on the reproductive system. Purulent-inflammatory processes characteristic of the disease are caused by lymphogenous and hematogenous dissemination of streptococcus, while the clinical manifestations of the pathology are diverse and depend on the foci of inflammation. Possible consequences of scarlet fever include:
- phlegmon;
- boils;
- abscesses.
The maximum danger of pathology for girls and boys is a late allergic complication, complete cure which is not always possible. The most common negative consequences after scarlet fever are:
- Rheumatic changes. They are observed in large joints - wrist, knee, elbow. In this case, the baby experiences a change in configuration, swelling, and a decrease in the range of movements. With prolonged scarlet fever and lack of treatment, the joints lose mobility.
- Heart valve damage, organ failure. In extreme cases, this complication can lead to death.
- Glomerulonephritis. After an illness, chronic renal failure, which poses a danger to the baby’s life.
- Chorea Sidengami. The complication does not pose a threat to the child’s life, however, its clinical manifestations in the form of tremor, changes in character and gait greatly affect the development of the baby and the quality of life of the parents.
Prevention
Not all children can become infected with scarlet fever: only 3 out of 10 people are susceptible to pathology after contact with a carrier of the infection. Vaccinations from of this disease does not exist, but there is no need for such a vaccination, since children's body able to cope with the infection on its own. Prevention of scarlet fever in children involves timely treatment of any ENT diseases and stimulation of the immune system.
If a child becomes infected with an infection, he is not allowed to attend classes; he is hospitalized or isolated at home. During quarantine caused by an epidemic, wards with children are filled simultaneously within 1-2 days, and contacts of those recovering with patients in the acute period are excluded. The first ones are discharged from the hospital on the 10th day of treatment in the absence of complications.
The child is admitted to school or preschool groups on the second day after recovery. Children who have been in contact with a sick person and have not previously had scarlet fever can be allowed to attend classes only after a week of isolation at home. This rule applies exclusively to children up to school age, as well as first and second grade students.
Photo of scarlet fever rash

Video
Many people mistakenly consider scarlet fever to be a childhood infectious disease that goes away without a trace. This is true only for mild cases of the disease; if scarlet fever is severe, then the risk of serious complications is very high. Not only children, but also adults who have reduced immunity can get sick. Moreover, adults always get sick much more seriously. The causative agent of the disease has Negative influence to all internal organs. Complications of scarlet fever in children can be of different nature– allergic, infectious or toxic.
Forms of complications
Complications after scarlet fever in children can be early or late. Early complications are manifested by various infectious diseases that are provoked by streptococcus. Most often, the following diseases are associated with scarlet fever:
- tonsillitis;
- otitis;
- pharyngitis;
- sinusitis.
If the infectious disease is very severe, then after a certain time problems begin with the lungs, heart, kidneys and liver.
A week after complete recovery, the child should be examined to rule out various complications.
Why Scarlet Fever Causes Additional Health Problems
Complications arise due to the fact that bacteria in the process of life produce toxins that are dangerous to humans, which negatively affect all important organs. The heart, liver and kidneys are most often affected, since these are the organs through which the most blood passes.. Two weeks after scarlet fever, such a serious complication as toxic heart may occur; this condition does not last long, but poses a great danger to human health. After toxic damage heart, this organ noticeably increases in size, the pulse becomes less frequent and steadily decreases arterial pressure.
 The first signs of a toxic heart are:
The first signs of a toxic heart are:
- soreness in the sternum;
- causeless anxiety;
- lack of coordination, most often slowing down all movements;
- dyspnea;
- abnormal fatigue that cannot be explained.
If complications of scarlet fever in children manifest themselves in the form of allergies, then there may be short-term disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys and fragility of the blood vessels. If the walls of blood vessels are damaged, bleeding in various internal organs is possible. The most dangerous thing is a cerebral hemorrhage, which can lead to partial or complete paralysis.
Late complications mainly come from allergies. It is because of this that any streptococcal infections occur in a more severe form. Such pathogenic microorganisms lead to hypersensitivity, due to which the body aggressively acts on its own cells, gradually destroying them.
During any infectious diseases, it is very important to strengthen the child’s immune system. To do this, you need to include a lot of vegetables and fruits, as well as vitamin supplements, in your diet.
What complications can occur after scarlet fever?
Various complications can occur with scarlet fever. It is very important not to miss them and start proper treatment on time.
Rheumatism of the joints
This disease occurs two weeks after scarlet fever complicated by streptococcal sore throat. It can develop in both boys and girls equally. The main signs of rheumatism of the joints are the following conditions:
- aching pain in the extremities, mainly knees and elbows, in the evening painful sensations are intensifying;
- Sometimes the joints of the hands are affected, in which case it is difficult to move the hands;
- the pain can be either localized or move from one area to another;
- at the site of inflammation of the joints, the skin turns red and becomes hot.
To treat this disease, antibacterial drugs are prescribed, most often of the penicillin group.. If the child’s condition is not severely impaired, then the use of antibiotics is allowed wide range actions in tablets. Rheumatism in children is treated quickly and does not cause consequences.
Before starting to use antibiotics of the penicillin group in children, a test must be performed. Many children cannot tolerate these drugs.
Heart valve damage
 This disease is quite severe and is considered irreversible; such a complication after scarlet fever can only be eliminated with the help of surgical intervention
. Those valves that are affected by bacteria become dense and rupture. In such places, circulatory impairment occurs, resulting in heart failure. This disease is a dangerous consequence for the heart of boys. Children who have had scarlet fever are fully examined after recovery. At the same time, they must undergo tests and do a cardiogram.
This disease is quite severe and is considered irreversible; such a complication after scarlet fever can only be eliminated with the help of surgical intervention
. Those valves that are affected by bacteria become dense and rupture. In such places, circulatory impairment occurs, resulting in heart failure. This disease is a dangerous consequence for the heart of boys. Children who have had scarlet fever are fully examined after recovery. At the same time, they must undergo tests and do a cardiogram.
The main signs of damage to the heart valves are the following health problems:
- heart rhythm is disturbed;
- headaches and severe dizziness often occur;
- blood stagnates in the lungs; when listening, the doctor notices a violation;
- the child feels a feeling of pressure in the chest, it is difficult for him to breathe, and painful shortness of breath appears;
- constantly present unreasonable fear and a feeling of anxiety.
If such a problem is diagnosed, the attending physician prescribes antibiotics and blood replacement drugs.. In severe conditions it is indicated surgery, which should not be abandoned. If the child is not treated in time, acute heart failure develops.
When the first signs of such a complication appear, the baby must be examined urgently. The earlier treatment is started, the higher the chance of complete recovery.
Glomerulonephritis
 Bacterial glomerulonephritis is another dangerous consequence scarlet fever. This disease can be suspected if the child, after recovery, has a fever again. heat, lower back pain occurred and urine volume decreased. Experts consider this disease to be reversible; with timely treatment, the kidneys fully restore their functions. If therapy is started at the wrong time or the medications are chosen incorrectly, the result will be kidney failure.
Bacterial glomerulonephritis is another dangerous consequence scarlet fever. This disease can be suspected if the child, after recovery, has a fever again. heat, lower back pain occurred and urine volume decreased. Experts consider this disease to be reversible; with timely treatment, the kidneys fully restore their functions. If therapy is started at the wrong time or the medications are chosen incorrectly, the result will be kidney failure.
Glomerulonephritis is treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics, antiallergic drugs and vitamins. During the treatment of glomerulonephritis, diet is indicated. The diet should not contain spicy and salty foods, as well as harmful products nutrition.
The treatment of glomerulonephritis must be taken very seriously, as it can become chronic.
Chorea
 This disease affects the brain and usually develops two weeks after scarlet fever.. The main symptoms of this disease are:
This disease affects the brain and usually develops two weeks after scarlet fever.. The main symptoms of this disease are:
- sleep disturbance;
- memory impairment and absent-mindedness. Such children cannot remember even the simplest information;
- sudden change in mood;
- an unreasonable feeling of fear and anxiety.
The most important symptom This disease involves uncontrolled movements of the limbs. Such movements are non-rhythmic, characterized by large amplitude and randomness. With severe brain damage, speech and coordination of all movements are impaired.
With Sydenham's chorea it can be like full recovery, and dangerous irreversible consequences. If treatment is started on time, then all symptoms gradually disappear without a trace and the child becomes the same as before. If the disease is severe, the baby remains in this condition for the rest of his life..
What danger does scarlet fever pose for boys?
It is widely believed that scarlet fever is more dangerous for boys than for girls. Really, due to the structural features genitourinary system boys are more likely to suffer from glomerulonephritis than girls.
Some doctors argue that scarlet fever in boys at any age can lead to a decrease in potency, resulting in infertility. It is worth noting that extensive medical research no research has been carried out on this matter, so this statement is not substantiated in any way.
Another infectious disease that poses a danger to boys is mumps. If treatment is started at the wrong time, the genitals are affected, and as a result, infertility may occur.
What other consequences could there be?
 Regardless of the severity of scarlet fever, this infectious disease always leads to a decrease in immunity. Often, after such an illness, children often begin to suffer from respiratory diseases, sore throat and bronchitis..
Regardless of the severity of scarlet fever, this infectious disease always leads to a decrease in immunity. Often, after such an illness, children often begin to suffer from respiratory diseases, sore throat and bronchitis..
To minimize the risk of complications, it is necessary to diagnose the disease in time and follow all the recommendations of the attending physician. Most often, complications are the result of self-medication or medications chosen incorrectly by a doctor. Parents should carefully monitor their children, and if any suspicious symptoms appear, go to the hospital immediately.
Prevention of scarlet fever has no effect, only in some cases, at weak immunity in a child, he is prescribed antibiotics or gamma globulin in advance. These medications are indicated immediately after contact with a person with scarlet fever.
There are many diseases of an infectious nature that provoke the appearance of a rash on the skin of a child. One of them is with carlatina in children. Symptoms and treatment, prevention, photos signs of the disease - these are the points that will be discussed in detail in this article.
Scarlet fever: what is it?
Many parents wonder what is scarlet fever. Scarlet fever - infection bacterial nature, which is caused by beta-hemolytic group A streptococcus. This microorganism synthesizes and secretes erythrotoxic substances that provoke hemolysis. To understand what kind of disease - Scarlet fever, how is it transmitted? and in what ways it can be cured, the causes and mechanisms of the pathogenesis of the disease should be studied in more detail.
Scarlet fever, like many infectious diseases (, mumps, chickenpox), is transmitted by airborne droplets, although each of the listed pathologies is viral infection, and scarlet fever is bacterial. This disease is very contagious and has a number of other routes of infection - nutritional, contact and water - but they are extremely rare.
Pathogenic streptococcus provokes not only scarlet fever, but also a number of other pathologies, namely: pyoderma, sore throat, intestinal infections, erysipelas. Scarlet fever when infected with streptococcus develops in the absence of immunity to erythrotoxic substances produced by the microorganism. Most people in adolescence such immunity has already been formed due to other streptococcal pathologies, and immunity is also transmitted transplacentally from mother to fetus, and after birth it persists for up to 2 years. According to these data, the risk of developing scarlet fever is highest in children aged 3 to 10 years.
The features of such a disease as pathology will be discussed in detail below.

Infection with scarlet fever is possible not only from those who are directly sick with it. Sources of infections can be patients with various forms of streptococcal infections, if the bacterial strain is a toxin-producing one. Infection is possible from patients with diseases such as:
- scarlet fever;
- angina;
- erysipelas;
- streptococcal pyoderma;
- intestinal infections;
- pyelonephritis;
- pneumonia;
- nasopharyngitis;
- otitis.
In very rare cases, infection may occur through contact with carriers of streptococcus.
Incubation period of scarlet fever in children and adults lasts from 2 days to 1 week, less often - up to 10 days. Most often it lasts 3-4 days. The incubation period is the period of time from the moment of infection to the moment the first signs of the disease appear. The patient becomes contagious most often the day before the onset of symptoms. When cases of scarlet fever are detected in kindergarten must be announced quarantine.

Scarlet fever is characterized by an acute, sudden onset - symptoms develop literally over the course of several hours. So, how it manifests itself This is a childhood disease in boys and girls? There are three main groups clinical manifestations which has scarlet fever - signs intoxication, sore throat and rashes.
- this is what can be found in this and subsequent sections of the article.
Intoxication
Among its manifestations are the following:
- temperature rise above 39 degrees;
- drowsiness and lethargy;
- constant nausea, periodic vomiting;
- abdominal pain;
- headache.
Angina
Scarlet fever causes symptoms of involvement respiratory tract in the infectious and inflammatory process. At first, the manifestations are catarrhal in nature - there is no plaque on the tonsils.
An important symptom of this disease is the so-called “flaming pharynx”: when examining the patient’s throat, a bright, limited hyperemia of the soft palate, tonsils, uvula and palatine arches is noted. These structural formations become deep red. Such symptoms occur in children,photo clinical manifestations reflect the severity of the inflammatory process.

The child may complain of pain in the throat area, and pain syndrome may have varying intensity - from mild soreness to severe pain. Children find it difficult to swallow and often refuse to eat.
With further progression of the process, especially if treatment measures are neglected, catarrhal manifestations are replaced by lacunar (plaque appears on the tonsils), follicular (formation purulent plugs and vesicles), necrotic (formation of foci of necrosis with plaque of varying shades).

Also, as the disease progresses, regional inflammation develops. lymph nodes, changes are observed in the tissues of the tongue. The surface of the tongue is covered with a whitish coating, and enlarged papillae of a bright pink hue are visible through it.

2 days after the onset of symptoms, the tongue becomes bright red,

this sign is also called “raspberry tongue.”

Skin rashes
Rash in a child appears a few hours after completion incubation period. Appears first ,



The brightest and most extensive rashes appear on the most delicate skin - inguinal, popliteal, axillary, elbow folds, skin on the neck and pubic area. The rashes are thickest in these areas. With scarlet fever, pinkish or bright red in color, finely spotted.

A hemorrhagic rash occurs less frequently, and is more often observed in the form of brown or purple dots. Hemorrhagic rashes often coalesce, forming streaks that persist even after the rash goes away.

Skin with rashes becomes dry and rough. The child's face is characterized by puffiness, red cheeks, cherry lips, and a pale nasolabial triangle.

Rashes on the face, body and limbs in some cases disappear after hours, but more often persist for several days. After the rash subsides, the skin peels off - on the body it is pityriasis-like, and on the limbs it is large-platelike.

The answer to the question whether scarlet fever itches or not is positive. Itching is characterized by moderate intensity.

Of course, scarlet fever most often develops in childhood, but this disease can also affect an adult. Scarlet fever in children, symptoms and treatment, prevention, photo pathology is extremely important, but even in adult patients a rather severe course of the disease is possible. Clinical symptoms are expressed implicitly, since the immune system fights the infectious agent, and a person may not distinguish scarlet fever from the usual ARVI. In some cases, scarlet fever in adults has more severe symptoms, initial stage characterized by a severe course.

There are a number of clinical manifestations of the disease in adult patients:
- Mild form: slight hyperemia of the pharynx, which can be noted on photo of throat, pain, symptoms of intoxication. Appears pale rash, but not in all cases. Thus, the answer to the question whether scarlet fever occurs without a rash is affirmative.
- Severe form: fever, chills, increased heart rate. Symptoms of intoxication are characteristic: nausea and vomiting. appears in the first days of illness, simultaneously with pain and redness in the throat. reflects the severity of the severe form of the disease. As it progresses, complications are possible in the form of otitis media, abscesses in the pharyngeal region, and hemorrhages in various internal organs. At a later time, rheumatism, myocarditis, and glomerulonephritis are possible.
Scarlet fever in adults also provokes dryness and flaking of the skin. Treatment of this disease will be discussed in more detail below.

Occurs quite often scarlet fever in children, symptoms and treatment, prevention, photo- This is something that the doctor should familiarize parents with. Therapeutic correction measures for scarlet fever will be prescribed by a specialist only after examining the patient. In severe cases, hospital treatment is possible, but usually scarlet fever is quite fast treated at home.
During treatment, it is important to observe the following measures:
- Proper care for the patient. Bed rest and restriction of activity are necessary even after the first manifestations of the disease have subsided. The premises should be regularly ventilated and wet cleaned. It is necessary to change both bed and underwear in a timely manner, giving advantages to natural materials.
- Diet correction. Assumes drinking plenty of fluids, you can give the patient tea, warm milk, compotes, fruit drinks, mineral water. If your appetite decreases, you should not insist on eating: such a reaction is a reflection of intoxication of the body. Gradually, soups, purees, cereals, and stewed vegetables can be introduced into the diet. All foods should be easily digestible and nutritious. Due to sore throat, it is recommended to serve food in semi-solid or liquid form to make it easier for the patient to swallow. Need to limit salty, spicy foods. Additionally, vitamin and mineral complexes can be administered.
- Medication correction with antibiotics. It is impossible to cure scarlet fever without antibiotics, some others tablets or ways. Antibacterial therapy is a mandatory measure. Antibiotic drugs are prescribed by a doctor; during treatment, you must strictly adhere to his recommendations regarding dosage, frequency of administration and duration of course therapy. Amoxicillin-based drugs are most often prescribed ( Flemoxin-solutab, Amoxiclav, Ampisid and a number of others). It is possible to prescribe macrolides ( azithromycin, macropen, josamycin). Cephalosporin antibiotics are relatively rarely prescribed.
- Antipyretics. For children under 12 years of age, medications such as Calpol, Panadol, Nurofen for children. Treatment is provided for patients of senior school age nimesulide, aspirin. The most effective use of antipyretic medications in the form of suppositories; after a period of intoxication, it is possible to give children syrups or tablets. You can bring down the temperature using other methods: drinking plenty of tea with raspberries, cranberry or currant juice, wiping.
- Medicines for throat treatment. Local antiseptics are well suited for this purpose, but age restrictions must be taken into account before use. The most effective drugs: Hexoral, Ingalipt, Stop-angin, Tantum-verde, Kameton. Gargling is also helpful. herbal decoctions, furatsilin solution. It is possible to eliminate symptoms with the help of lozenges.

By the end of the first week of pathology, both children and adults are no longer contagious to others. But still, discharge is possible only 21 days after the start of the active phase of the disease. This duration of home mode is explained high risk complications for an organism weakened after scarlet fever. If the child ends up in kindergarten earlier, then after contact with children, a secondary infection may occur and a significant deterioration in the baby’s condition.
No specific measures have been developed to prevent scarlet fever infection, that is, there are no vaccines for vaccination. To prevent infection, it is important to limit contact with patients who have a streptococcal infection. You should also strengthen your immune system, harden yourself, and take immunomodulators.
When treating and preventing scarlet fever, it is important to strictly follow the doctor’s prescriptions and recommendations, and comply with all prescriptions and dosages of medications. You should not self-medicate: this can aggravate the condition and provoke very serious complications that affect all body systems. The price for the health of both a child and an adult is very high, and you should not once again expose yourself to such a great risk.

We considered a disease such as scarlet fever in children. Symptoms and treatment, prevention, photos. Have you observed this? Leave your opinion or feedback for everyone on the forum.
Scarlet fever occupies a special place among typical childhood infectious diseases. If chickenpox and rubella in the vast majority of cases pass without a trace and leave no consequences, then scarlet fever in children, despite modern methods treatment, can remind about itself even after years. Therefore, it is important to recognize the disease in time and begin treatment as early as possible. How does scarlet fever occur in children? How dangerous is scarlet fever and how does it manifest?
Scarlet fever is an anthroponotic disease and can only be carried by humans. The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets (mainly) or through household contact. The causative agent of scarlet fever is one of the types of group A streptococcus. Once on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx, microbes penetrate the skin, begin to actively multiply and damage the integument. At the same time, a large amount of exotoxin, a waste product of bacteria, enters the blood, which causes intoxication of the body and associated poor health.
The degree of spread of streptococcus, the severity of the disease, the duration of the disease and the likelihood of complications depend on the body’s resistance and, to a large extent, on the time of initiation of treatment and its compliance with modern regulations for the fight against scarlet fever and its consequences.
Scarlet fever in children: symptoms and treatment
An experienced attending physician is unlikely to confuse scarlet fever with other diseases childhood. It has not only symptoms that are partially similar to, and, but also clear differences from these diseases.
According to the classical scheme of development of infectious diseases, scarlet fever is as follows.
Incubation period of scarlet fever. The time from contact with the pathogen to the first manifestation of the disease lasts from 5 to 7 days. During this period, the number of microorganisms accumulates.
Prodrome of scarlet fever. When a critical mass is reached, bacteria spread throughout the body, settling in the surface layers of the skin. They begin to actively release waste products into the blood. At this time, the temperature rises, signs of sore throat appear (redness of the throat and soreness), and health worsens. This stage of the disease rarely lasts more than a day, most often from 12 to 24 hours.
The height of the disease. At this time, a rash appears. It consists of small pinpoint phenomena (enlarged skin papillae) of a deep red color, which are located throughout the body. Especially often, an intense rash appears in places of folds (popliteal area, elbows, groin), along the side surfaces of the body, on the face. The only place where there is never a rash with scarlet fever is the nasolabial triangle. At the height of the disease, it stands out on the face and serves as a serious diagnostic indicator.
During this period, other symptoms of scarlet fever in a child are present:
- Scarlet fever rash in children is accompanied by high fever;
- Characteristic changes in the oral mucosa are bright red tonsils (“flaming pharynx”), on which plaque may appear after some time;
- The plaque on the surface of the tongue at the beginning of the disease soon disappears, the inflamed papillae become clearly visible on it, the tongue becomes characteristic bright color(“raspberry tongue”);
- From the first hours of illness, the child experiences headache, muscle pain and aches in the bones of the limbs;
- In case of severe intoxication, neurological signs appear - dizziness, trembling, convulsions, and sometimes loss of consciousness.
The acute period lasts from 4 to 7 days, depending on the severity of the infection. IN Lately mild forms of the disease predominate; sometimes there is a moderate course. Severe scarlet fever is now a rarity.
Exodus. Simultaneously with pallor (from 4–5 days) and the reverse development of the rash, the temperature decreases, and other symptoms of scarlet fever disappear. The patient feels weak. At the site of the rash, after 1 to 2 weeks, peeling of the skin is observed, lamellar in folds and pityriasis-like on open surfaces.
How does scarlet fever manifest in children? Symptoms photo

Photo of a tongue with scarlet fever in a child (“Crimson tongue”)

Photo of a rash on the body due to scarlet fever in a child

Scarlet fever rash in children. White nasolabial triangle.
Distinctive signs of scarlet fever in children
The differences between diseases manifested by a rash are given in the table:
| Disease | Incubation period | How does a skin rash appear and look like? | Condition of mucous membranes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scarlet fever | 5-7 days | Bright, appears in 1-2 days, on any area except the nasolabial triangle, creates roughness of the skin, leaves flaking. | Excessively bright coloring of the tonsils and tongue. |
| Rubella | 16-20 days | Pale red, not prone to fusion, leaves no traces. | Catarrhal phenomena in the nasopharynx. |
| Measles | 9-17 days | It begins to appear on the 3rd - 5th day of the disease, appears in stages (face - torso - limbs), disappears in reverse order, leaves pigmentation. | During the prodrome, whitish spots appear on the gums and inner surface of the cheeks. |
| Chickenpox | 11-21 days | A rash in the form of vesicles (pustules) does not appear all at once. | Sometimes red spots on the mucous membranes of the mouth. |
Treatment of scarlet fever in children
Unlike other childhood diseases with rash (symptomatic therapy), scarlet fever in children is treated according to developed regimens using antibiotics. Streptomycin-type drugs have not been used for these purposes for a long time, because they caused serious complications (hearing loss) in children. Today they are used antimicrobials in various combinations. With timely initiation of treatment, the disease is mild and leaves no side effects.
Important! Great importance has compliance with medical prescriptions regarding the frequency and duration of medication use. Deviations from the developed schemes can cause complications.
Except drug therapy changes in the patient's lifestyle are provided:
- For the first 5–7 days of illness, the child is prescribed bed rest;
- A mandatory component of treatment - drinking plenty of fluids - helps remove toxic elements from the body and prevents dehydration due to elevated temperature;
- Hygienic rules - separate room, dishes, linen, ventilation and wet cleaning;
- Limiting contacts - to avoid the addition of concomitant infections;
- Calm environment good nutrition(feed only if desired), dim lighting.
Organization correct content a child during illness is no less important than the use of medicine. These activities help avoid the consequences of scarlet fever.
Complications of scarlet fever in children
Streptococcus, which causes scarlet fever, can not only cause a temporary deterioration in health and a rash on the body. Its insidiousness and danger lies in its pathological effect on internal organs. The most common complications observed:
- On the heart - myocarditis, rheumatism;
- IN excretory system – renal pathology(glomerulonephritis);
- In the ENT organs - sinusitis (inflammation paranasal sinuses nose), otitis;
- Purulent phenomena - phlegmon, abscesses;
- General intoxication – blood poisoning.
Important! With timely initiation of treatment, excessive spread of streptococcus does not occur; by the seventh day of illness, the microbe ceases to be active. This prevents toxic effects on organs and systems and reduces the likelihood of severe complications.
Prevention of scarlet fever in children
There is no specific vaccine against scarlet fever, effective vaccination against scarlet fever and other diseases caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, has not yet been created by scientists. Since the spread and transmission of the bacterial component occurs by airborne droplets, the main preventive method is to avoid contact with sick people. However, this is a difficult task: scarlet fever mainly affects children of preschool and primary school age, when children spend a significant part of their time in a group of peers.
Quarantine measures do not have much effect; if there has been contact with a sick person, then most likely the child will get sick. But there is also a positive aspect to this: a child who has not been ill in childhood risks contracting scarlet fever at an older age, and in adults the disease is much more severe, despite adequate therapy. And the likelihood of complications is much higher.
Thus, scarlet fever in children is one of the few childhood diseases for which specific treatment regimens have been developed. The task of parents is to consult a doctor as early as possible. Then the prognosis of the disease will be extremely favorable.
Remember that only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis; do not self-medicate without consultation and diagnosis. qualified doctor. Be healthy!