But often this condition is a manifestation of a disorder such as abulia.
Abulia is a mental disorder nervous system, from which it is impossible to get out on your own. So what is this disorder and how is it treated?
We say abulia, we mean lack of will
From the ancient Greek language, the term “abulia” means “lack of will.” In medicine, abulia is a condition in which a pathological lack of will manifests itself.
A person may experience constant bouts of laziness, he is overcome by a feeling of indecision, lack of will, and the desire to perform certain duties that require mandatory fulfillment may completely disappear.
This pathological disorder of the nervous system is a manifestation of apathy. It is not widespread, and the disorder itself is often confused with weakness of will. Abulia is easiest to identify in an adult patient; in children, this condition is usually accompanied by various associated problems.
Etiology and pathogenesis of the disorder
Typically, symptoms of abulia can manifest in people with weak mental health who are prone to various somatoform disorders.
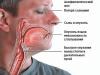
Abulic syndrome can manifest itself during disorders in the blood circulation of the right hemisphere of the brain in the frontal part. This usually occurs due to traumatic head injuries or some serious brain disease.
The pathogenesis of abulia is associated with a decrease in dopaminergic neurotransmission in the frontal lobes of the brain. These lobes are responsible for the purposeful motor functioning of the body, the ability to manifest initiative processes, systematic activity, which is aimed at performing certain functions and overcoming difficulties.
Typically, patients with disorders of the frontal part of the brain experience a state of inertia and inactivity.
Most doctors and specialists note that the main factor that provokes the manifestation of abulia is stress.
The presence of abulia leads to the deprivation of the main factor of a person’s full existence - he ceases to be a person. This is due to the fact that this disorder contributes to the disappearance of a person’s motivation, which provokes him to perform functions to achieve his cherished goal.
Such pathological spinelessness is especially dangerous in childhood. Many parents may simply not notice the presence of this disorder in their child and mistake it for a character trait - laziness, apathy, weakness of will.
The most difficult is considered to be hereditary abulia, which occurs in children from the moment of birth. Many parents are happy when their child is very calm, quiet, for a long time sits in one place instead of running and playing. And this condition should cause concern in parents and be the first factor for conducting an appropriate examination.
What can cause a violation
Abulia can manifest itself as a symptom of numerous disorders with a psychoneurological nature, among others the following:
Abulia often occurs in patients with schizophrenia. People with this pathological disorder Often, over time, their mental state deteriorates, volitional impulses weaken, passivity increases, and they often lack the desire to perform simple and necessary actions.
The short-term onset of abulia can manifest itself as a reaction to mental trauma. This condition may not last very long; it goes away after the situation that has a traumatic effect on the psyche is resolved.
During stupor with a depressive and apathetic character, as well as during catatonic stupor, the state of abulia can develop within 2-3 months, and can last for several years.
Combination of abulia with other syndromes
Forms of abulia can be mild and temporary, which are accompanied by minor deviations, reduced motivation, as well as more severe, up to complete suppression of will. In an extreme form of lack of will, there may be no desire to perform basic actions - get out of bed, wash, and so on.
Syndromes that accompany abulia:
- Depressive syndrome asthenic type, which is accompanied by elements of adynamia, neuroses, and psychopathic disorders. During this disorder there is a short absence volitional motives and decline in activity.
- Abulia of periodic type. This form often occurs in drug addicts, alcoholics, in patients with severe somatoform disorders, in patients with schizophrenia. Repeated periods of lack of will may occur, as well as psychoses of the manic-depressive type.
- Catatonic syndrome and stupor. This form is characteristic of schizophrenics, and also manifests itself in severe organic brain damage. In this condition, there is a constant lack of motivation and volitional impulses.
- Abulia can often be combined with mutism - a complete lack of desire to talk. Verbal contact with patients is disrupted, and it is impossible to get answers to questions from them.
- Apato-abulic syndrome. With this syndrome, emotional insufficiency and automaticity of movements occur. Patients experience complete withdrawal into themselves, they have a lack of desire to communicate, they show with their appearance complete indifference to the interlocutor, to close people, they have a complete loss of interest in their favorite activities and entertainment.
- Abulic-akinetic syndrome. With this disorder, there is a combination of lack of will with partial or complete immobility. This may often be accompanied by inhibition in the thinking process.
Clinical picture and symptoms
Psychotherapists and neurologists note that during abulia there often appears a pathological reluctance to show interest and effort in various, sometimes necessary actions or previously favorite activities, or a complete decrease in energy level volitional signs.
Other characteristic clinical symptoms abulia:
- the patient looks sloppy and untidy;
- movements are slow, inhibited and uncoordinated;
- there are problems with speech and emotional manifestations, speech is often slow;
- the patient has a complete lack of desire to communicate with other people, friends, close relatives, they experience social isolation;
- speech becomes scarce, facial expressions disappear;
- there is a closed state, lack of activity;
- a person cannot make a decision on his own;
- loss of interest in all activities and entertainment that were previously favorite;
- Before answering the question posed, a person can think for a long time and remain silent.
Establishing diagnosis
Abulia is not separate disease, usually this is a consequence-symptom of some neurological or psychological disorder.
The main methods used to make a diagnosis:
- to begin with, the doctor conducts a survey and tests the patient, due to this he compiles a general history and establishes the presence of various concomitant diseases;
- Magnetic resonance imaging is performed;
- computed tomography is prescribed;
- ultrasound examination is prescribed;
- electroencephalography of the brain is performed;
- You definitely need to take a general blood test.
Goals and methods of therapy
First of all, in case of abulia, treatment of the underlying disease that accompanies it should be prescribed. Therapeutic treatment should be carried out only under the full supervision of a doctor - neurologist, psychotherapist.
Features of treatment depending on the concomitant disease:
- if the syndrome has developed against the background of schizophrenia, then atypical antipsychotics are prescribed;
- against the background of depressive conditions, the use of antidepressant drugs is prescribed;
- if apato-abulic syndrome develops, the use of Frenolone is often recommended; it is prescribed from 5 to 10 mg three times a day;
- During the manifestation of apatico-abulsic syndrome in schizophrenics, the drug Triftazin is effective for therapy; it is started with 5 mg three times a day together with Piracetam, one capsule 2 times a day, the dosage is gradually increased every day by 5 mg and increases dosage per day.
When suppressing volitional impulses, the use of Sulpiride is prescribed. It is prescribed at 0.2-0.4 grams per day. The maximum dose per day should not be more than 0.8 grams;
Additionally, physiotherapy is prescribed to increase the activity of the nervous system, phototherapy, swimming, medicinal baths.
Abulia
The man is worried various states. Completely healthy people can go through stages when they are overcome by deep psychopathic states close to psychiatric ones. No one is immune from this harmful condition. Therefore, you should act very quickly here. A healthy person can easily get rid of abulia, unlike a sick person.
Abulia
One of the signs of apathy is considered to be abulia - lack of will, weak character, passivity. This state is characterized by a lack of volitional motivation, complete inaction even to satisfy basic needs, lack of initiative, and disinterest in anything. If previously a person could be interested in something, now even favorite activities and hobbies do not bring a joyful state.
Abulia is considered not just a pathological condition, but also a mental disorder, since sometimes it has completely physiological reasons for its occurrence. That is why, if necessary, you should seek the help of a psychiatrist on the website psymedcare.ru. If you notice the first signs of abulia or suffer from this state someone close to you, then you should solve the problem and not let it take its course.
Abulia must be distinguished from other conditions. Apathy is a depressed mood. If there is a combination of depressed mood and lack of will, inaction, then apathetic-abulsic syndrome occurs. The first signs appear on the first day. A person stops performing actions, his productivity drops sharply to zero. There is a lack of emotionality here. The person doesn’t feel anything, doesn’t want, doesn’t worry. Nothing worries him. This should be distinguished from the inability to feel or do anything. Abulia is the absence of desire, and impossibility is something else.
If a person stops performing any actions, that is, is completely immobilized under the influence of his condition, then we are talking about abulic-akinetic syndrome (catatonic stupor). When translated from ancient Greek, “abulia” means “there will be no action.” We are talking about a state when a person loses motivation and the will to act.
This disorder is dangerous at any age. It spares neither the young nor the elderly and can develop in anyone, even if mental pathologies have not been observed before.
Causes of abulia
For what reasons does abulia develop? Physiological and psychological factors are considered here:
- Traumatic brain injury that damages the functionality of the central nervous system.
- Brain disorders in the frontal region.
- Infectious diseases: meningitis, encephalitis, etc.
- Heredity.
- Circular psychosis.
- Stress.
- Oligophrenia.
- Borderline states: psychasthenia, psychoneurosis, hysteria.
- Stroke.
- Improper production of dopamine.
- Schizophrenia.
- Deep depression.
- Brain tumors.
- Neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease.
- Brain hemorrhages.
- Exposure to toxic substances, such as cyclosporine-A.
- Dementia.
- Affective insanity.
- Addiction.
- Excessive parental care, suppression of the child’s will.
- Constant failures in life.
Obviously, there are many reasons. Some of them depend on a person's genetics, and many can result from poor lifestyle choices. Here the psychological factor becomes important - the presence of motivating incentives. IN in this case Abulia often becomes a companion to apathy.
The condition itself is often found in the list of other diseases, for example, apathy, schizophrenia or Alzheimer's disease. However, psychologists have already noted the need to separate this condition from other diseases, even if it accompanies them. Thus, abulia can develop as an independent disease.
At the same time, scientists indicate that the reasons for the development of abulia can influence the formation of other diseases. If we are talking about disorders or damage to the brain, then other diseases will certainly develop, for example, dementia.
Mild forms of the disease can develop due to low resistance to stress, as well as due to a tendency to somatoform disorders.
Symptoms of abulia
Abulia comes in different types. However, her symptoms change slightly. The following disorders of will are distinguished:
- Hyperbulia is marked by excessive activity and activity.
- Hypobulia is characterized by a sharp decrease in activity.
- Abulia is a loss of desire to perform actions effectively, to achieve goals and results.
- Parabulia is noted as a behavioral disorder.
Depending on the duration of the condition, its types are distinguished:
- Short-term is often observed in borderline states and depression. While a person is in a depressive decline, he experiences lack of will and inaction. He understands the need to perform some action, but is unable to muster the strength. Also this type Abulia manifests itself in psychopathy and neuroses, when drives are reduced, there is no motivation, and the ability to make a decision disappears.
- Constant.
- Periodic can be seen in psychological disorders and drug addiction. When an exacerbation occurs, symptoms of abulia appear.
go to top
What are the symptoms of abulia when it occurs in a person?
- Lethargy. Intellectual activity decreases.
- Insulation. The person experiences certain difficulties in social contacts.
- Difficulty in making decisions.
- Neglect of hygiene.
- Lack of will to take any action. A person lies on the sofa and is unable to bring himself to go to the toilet or kitchen.
- Decreased need to meet basic needs, such as sleeping or eating. Laziness is clearly manifested: you don’t want to wash your face, comb your hair, or get out of bed. There is complete indifference to one’s own appearance.
- Loss of interest in favorite activities, usual activities.
- Spontaneity or constraint of actions.
- Passivity.
- Mutism is speech passivity. A person may not answer questions and lose interest in live communication.
- Apathy is indifference and indifference. The person does not experience emotional experiences. Often fenced off from the world around him due to a lack of interest and desire to take any part in it.
- Adynamia is inhibition of motor or mental processes.
- Pessimism.
- Unreasonable fatigue.
- Social phobia.
- Inability to concentrate.
- Poor appetite. He can chew food for a long time without swallowing. May suddenly refuse food while it has already been chewed.
- Memory impairment.
- Insomnia.
If you look at the patient from the outside, it may seem that he is indifferent to absolutely everything (not only to those around him, but also to himself and his needs). Nothing interests him, he is passive and even motionless. His reaction to verbal cues is inhibited. He doesn't show initiative.
Diagnosis of abulia
Already by external manifestations which a person cannot hide, the first stage of diagnosing abulia is carried out. However, certain difficulties arise here. In many ways, abulia is similar in symptoms to other disorders and character traits. Also here it is necessary to exclude mental illnesses that may be hidden behind abulia. For example, psychologists rule out schizophrenia and dementia, which are in many ways similar to the behavior of a person with abulia.
The most the right way diagnosis is observation of the patient. Within a few days, you can collect the entire list of symptoms that appear in a person and make an accurate diagnosis. The localization of the disease is found by taking images on computer and magnetic resonance imaging, collecting blood tests and conducting neurological testing.
Differential diagnosis should exclude manifestations of weakness of will, which is a character trait, not a syndrome. Weakness is the result of upbringing. A person is active, has desires and interests, but is not able to defend them.
This is where avoiding laziness becomes important. The person may simply be lazy or unwilling to follow other people's instructions. However, this is not abulia. It becomes very difficult to recognize laziness when diagnosing children. They can fake their condition if they know what annoys their parents. Often children simply do not want to follow their parents’ instructions, which from the outside seems like a disorder. Here you cannot do without the help of a specialist, since parents may be mistaken in their suspicions.
It is also necessary to exclude apathy, which simply makes a person unemotional. Through observation, conversations with a psychologist and research using CT and MRI, a diagnosis can be made. If there are obvious disturbances in the functioning of the brain, as well as if all the symptoms are identified, we can talk about abulia.
Treatment of abulia
Depending on the causes of abulia, one or another course of treatment is prescribed. Specialists take a comprehensive approach to the problem when not only medication is needed, but also psychological help. If the cause is psychological, then it is eliminated. If the cause is a dysfunction of the brain, then medications are used.
You should get rid of abulia in a comprehensive manner:
- Find something interesting to do. Since a person has problems with interest, he must overcome this barrier.
- Lack of self-pity. Often abulia becomes a problem due to the fact that people cherish this condition within themselves. Support, sympathy, understanding - all this only harms the patient.
- Involvement in common activities or entertainment. You cannot get rid of abulia without the support of loved ones. The patient should be invited to joint feasts, entertainment activities. You should also ask him for help, emphasizing that without him you will not be able to do anything.
Often the patient may feel unwanted. This is often observed in older people. In this case, you should offer to take part in your life. Relatives, their attention and spending time together, can cure abulia.
In severe cases, you cannot do without medication. Here only specialists decide how to help the patient. In addition, psychotherapeutic and psychoanalytic work is carried out with the patient. Antidepressants are often prescribed antipsychotic drugs, atypical antipsychotics, and a rehabilitation program to stimulate parts of the brain.
If abulia is a consequence of a mental disorder or physiological disease, then treatment should be aimed at eliminating the cause. Abulia is a consequence that will go away if the cause is eliminated.
Prognosis for abulia
The prognosis for abulia is far from favorable. If abulia is an independent disease that developed against the background of a mental disorder, then much depends on the degree of recovery from a negative state. If we are talking about brain damage, heredity and serious mental illnesses, then the result will be disappointing.
Life expectancy depends entirely on the underlying disease. Abulia itself is not fatal. However, cases of its complete cure are becoming rare.
At the stage of abulia formation ( mild degree) it is possible to return a person to a social lifestyle, increase activity and resume normal existence. However, at a severe stage of the disease, cases of complete recovery become rare.
Scientists are trying new treatments for abulia. Cognitive behavioral psychotherapy, hypnosis, and medications that increase dopamine activity are used here. However, not yet positive results. Today, psychologists can only slow down or partially restore interest in life and volitional motivation. However, this process is difficult. If there are serious mental disorders The process of eliminating abulia becomes almost impossible.
The main task of specialists is to return a person to social life. If the patient can socialize and adapt, then the chances of his recovery are high. Not only psychologists, but also physiotherapists and speech therapists take an active part here. In rare cases, it is possible to recover from this condition on your own, since a person may not be able to cope with the contradictions that arise in him. At the same time, the patient must gradually understand responsibility for his life, which is ensured by shifting the responsibility to care for himself onto him.
Abulia - causes and treatments
Sometimes there is a desire to let everything take its course and not take part in the events that are happening. This condition is considered normal, but if it is observed constantly, then it makes sense to consult a doctor, since this symptom is a companion to a number of serious disorders.
What is abulia?
The name of the disease comes from a Greek word, its prefix “a” is equivalent to negation, the root “boile” means “will” and the suffix “ia”, which translates as “action”. It turns out that abulia is inaction, complete passivity in any area of relationships. This happens due to a lack of desire, motivation to move, and not due to a lack of opportunity.
Abulia – psychology
A lack of desire for decisive action does not always mean the presence pathological changes, but there is a disease that requires close attention. Abulia in psychology is a mental state characterized by constant apathy and inability to make volitional decisions. This is not just a loss of strength, but a complete absence of sudden desires, a strong decrease in interest in social life and favorite hobbies.
Experts cannot say what abulia in itself means; it necessarily accompanies some disease, that is, it is a sign of a mental disorder or trauma. Psychiatric interviews are used to diagnose the underlying cause. various ways brain studies, neurological testing and blood tests. Abulia is divided into the following types:
- hyperbulia– excessive manifestation of activity;
- parabulia– violation of behavior, an irresistible desire to commit unnatural acts.;
- hypobulia– decreased interest in any activity.
Abulia - symptoms
- Slowness of thinking.
- Problematic decision making.
- Passivity.
- Ignoring hygiene standards, sloppy appearance.
- Loss of motivation to work.
- Spontaneity or stiffness of movements.
- Neglect of natural human needs, even food and sleep.
- Reducing social contacts, sometimes to the point of voluntary isolation.
- Mutism is a reluctance to communicate and contact with others.
- The slightest load is not accepted, obstacles become insurmountable, excessive demands and laziness appear. At the same time, patients can often entertain themselves all day long and eat with pleasure.
Abulia is characterized by volitional inactivity, often complemented by emotional indifference and apathy. As a result, apatho-abulic syndrome is formed, which is manifested by isolation, indifference, a tendency to reduce contacts to a minimum and prolonged silence. The most severe course is a complete lack of movement, but the disease can also be expressed in the form of subtle inhibition of thought processes.
Causes of abulia
Mild manifestations of the disease are observed in persons with unstable psyche and a tendency to somatophoric disorders. Abulia and apathy occur when the blood supply to the right frontal region of the brain is disrupted due to injury or disease. Recent research suggests that this problem is related to improper production of dopamine. Abulia can develop against the background of the following disorders.
- Schizophrenia.
- Post-traumatic and post-stroke condition.
- Parkinson's, Pick's, Alzheimer's, Huntington's diseases.
- Congenital dementia.
- Intoxication with alcohol, drugs and drugs.
- Severe depression.
- Consequences of infectious diseases and hypoxia.
- Brain tumors.
The disease does not always have a permanent form; sometimes the body reacts this way to mental trauma. In this case, the condition does not last long and normalizes when the situation that had a negative impact is resolved. In some cases, symptoms appear in response to long-term medication use. With depressive, catatonic and apathetic stupor, the condition can last several months or years.
Abulia with depression
Heavy life circumstances can lead to depression. Depression, abulia and apathy can go in the same row. Restoration of normal functioning occurs when the underlying problem is solved. Therefore, to eliminate weakness of will, it is necessary to cope with the situation that led to depression. Treatment can be done through a combination of medications and talking to a doctor.
Abulia with neurosis
Disorders of this kind may be accompanied by a loss of volitional ability. In such circumstances, abulia disease is short-term and not always pronounced. A person can reduce demands on household amenities and himself, reduce the time of communication and any interaction with others, and slow down the performance of work that previously was not particularly difficult.
Abulia in schizophrenia
Symptoms of impaired will can appear in various mental illnesses. If a patient has schizophrenia, abulia accompanies its periods of exacerbation in most cases. It becomes difficult for patients to take care of themselves; in the absence of adequate therapy, they may lose the ability to self-care. Hypobulia can also become a companion - a perversion of the will that pushes an individual to commit actions that contradict generally accepted moral norms.
Abulia - treatment
The disease is truly terrible; as it progresses, the personality is lost, and instead only a shell remains. If the doctor has diagnosed abulia, he will also tell you what to do; independent choice of medications and dosage can lead to a worsening of the condition. Conversations with a specialist are also required to correct the condition. The following drugs are often used in practice.
- Frenolone is effective for apathy and schizophrenic-type disorders. Contraindicated for arrhythmia, kidney and liver problems. Possible side effects include tremors, swelling and loss of coordination.
- Cipralex for abulia is prescribed for depressive conditions. Side effects include decreased libido, nausea, weakness, increased sweating, sleep disorders.
- Triftazin is prescribed for abulia due to schizophrenia, recommended in old age. Cannot be used for kidney and heart problems.
- Solian helps suppress symptoms. Does not cause drowsiness, contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
- Sulpiride is prescribed for depression; it helps relieve apathy and inhibition of reactions. Can increase blood pressure, cause tremors, menstrual irregularities, galactorrhea outside lactation, and nausea.
Abulia - treatment with folk remedies
If abulia is diagnosed, not only pharmacology can tell you how to get rid of it. The following methods are capable of providing an auxiliary effect, some of which do not have official confirmation.
- Treatment at thermal springs.
- Yoga and cold showers.
- Rubbing vegetable oil, which had lain in the ground for a year.
- Homeopathic medicines.
- Decoctions of ginseng, angelica, zamanikha or knotweed.
Sindrom.guru
Sindrom.guru
The mental state associated with apathy and lack of will is called medical term abulia. It can occur at any age and is difficult to treat. This disease requires a thorough examination and immediate initiation of therapy. Why does it occur and what are the treatment methods? We'll find out.
What kind of disease is this?
Abulia is the name of a person’s mental state when apathy, indifference, and lack of will prevail in his feelings. Such conditions happen to every person from time to time. But mentally healthy people this feeling passes over time and is replaced by normal behavior. And with mental disorders, the patient experiences indifference to those things that previously evoked certain emotions in him and brought him satisfaction.
Abulia is a mental disorder of the nervous system from which it is impossible to get out on your own.
But not only these symptoms characterize apathetic-abulic syndrome. These include:
- absolute passivity;
- lack of interest in previously favorite activities;
- detachment from the real world;
- the person does not express any emotions.
Psychiatrists consider abulia to be a pathological condition associated with a decrease in the patient’s internal energy, with the fact that he does not have any aspirations or drives. When the patient begins to perform any actions, then at the very beginning mental modifications arise from the mere realization that something will need to be done.
Apatoabulic syndrome is associated with the lack of any desires, and this, in turn, causes great passivity and almost complete discord in emotional sphere. In other words, abulia is a condition caused not by the fact that there is no opportunity to do something, but by the fact that there is no desire to do something.
It can be concluded that abulia is a mental illness accompanied by a lack of the individual’s will to perform actions or motivations, which occurs due to various reasons.
How does abulia occur?
In most cases, the disorders that cause abulia do not occur on their own out of nowhere.
This pathological disorder of the nervous system is a manifestation of apathy
As a rule, there are some accompanying factors, which may include the following:
- a brain tumor;
- stroke disease;
- head injury;
- cerebral hemorrhages;
- influence of toxic substances;
- disruption of the normal level in the brain of the hormone responsible for joy and pleasure (dopamine).
Injuries that cause damage to specific areas of the brain, such as those responsible for motor activity or abstract mental activity, interfere with the individual’s ability to activate movement, speech activity or social interaction. These symptoms are associated with damage to both halves of the frontal region of the head, because this is where the brain centers responsible for movement, independence, and the ability to regulate one’s behavior are located.
Abulia can occur with existing mental disorders - schizophrenia or severe depression, as well as with Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases.
Symptoms of abulia
When looking at a person diagnosed with abulia, one immediately notices his complete detachment, apathy, and reluctance to participate in the conversation. Such a person seems quiet outwardly, his actions are slow, he is inert and indifferent to everything that happens around him.
Typically, symptoms of abulia can manifest in people with weak mental health who are prone to various somatoform disorders
Apathetic-abulic syndrome is the patient’s lack of desire to perform any actions, be proactive, be able to make decisions or resist anything. Patients with this diagnosis move slowly, talk slowly, their thinking slows down, and there are no emotions. During dialogue, answers to questions asked are drawn out over time. Such people become largely dependent on others. Patients lose interest in themselves; they are sloppy, uncombed, with dirty, uncut nails, and in wrinkled clothes.
This condition is characterized by loss of appetite, sleep disturbances, and memory impairment. A person feels constant fatigue and is pessimistic. Any way to stir them up fails. Such a person gradually ceases to feel like a person.
Abulia is not a separate disease; it occurs in combination with other mental disorders and is diagnosed depending on the underlying disease.
Diagnosis is carried out using various methods, namely, the doctor will help:
- ultrasonography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- computer research;
- electroencephalogram;
- psychiatric interviewing;
- blood analysis;
- neurological tests.
Magnetic resonance imaging is performed
Treatment methods
Treatment of abulia is not carried out separately on its own, but in combination with therapy for the underlying mental disorder. It consists of reducing symptoms and general rehabilitation of the patient. The bulk of therapy rests with doctors who specialize in psychiatric or neurological disorders of the body. Rehabilitation specialists, physiotherapists, speech therapists and some other specialists also take part in the recovery of a patient with abulia.
There are no specific treatments for abulic conditions. But patients suffering from depression are prescribed antidepressants. For patients who have suffered strokes, hemorrhages, or skull injuries, a rehabilitation program is prescribed that helps restore speech activity and physical activity.
Modern scientific developments are seeking methods of medicinal influence on the human body to activate brain activity. The recovery of a patient with apatoabulic syndrome is directly dependent on getting rid of the underlying type of disease.
Swimming, taking medicinal baths, and phototherapy have a beneficial effect on the body and mental state of those suffering from abulia. Physiotherapeutic methods show great effect when combined with a stay in a sanatorium. Mineral thermal baths and therapeutic mud give good results. It should be taken into account that for patients with depressive disorders The best climatic recreation area is considered to be warm southern regions, and for patients diagnosed with schizophrenia - high mountain areas.
Against the background of depression, the use of antidepressant drugs is prescribed
Sessions with a psychotherapist also have a positive effect. First they are conducted individually and then in small groups. The purpose of the classes is to regain communication skills, communication in everyday life, and interaction with other persons. The role of loved ones is very important here; the doctor helps resolve conflict situations in the family and establish trusting relationships.
Preventing the development of abulia
What is the prevention of apathetic-abulic syndrome? As you know, it can appear at any age.
Therefore, preventive measures are relevant in every age period:
- Elderly people need confidence in their relevance, need, and that they can be useful to their relatives. It is from such positions that the desire to do something, to provide assistance arises;
- For the younger generation and middle-aged people, interest in life will not disappear when they have activities to their liking and various hobbies.
Excessive care of relatives for the patient can only harm him. Often this consists of exclusion from participation in common events and joint work. Relatives try to predict and fulfill any desire. This imaginary concern will only provoke further progress of the disease. The tactics of relatives should be structured in such a way that the sick family member is as active as possible. life position. And it doesn’t matter what it will be connected with - rest or work. This is the only way to get out of the mental state.
Abulia
Abulia is a condition characterized by a pathological lack of will, spinelessness, lack of motivation to action, inability to make volitional decisions and perform any actions. Considered a psychotic disorder, it is a sign of apathy and a mandatory symptom of schizophrenia.
General information
The study of abulia has been carried out since 1838. Currently, experts consider abulia as a symptom of other diseases and mental disorders, although there are attempts to consider this condition as an independent nosological unit.
Abulia, in which the patient feels a partial or complete lack of desire for any activity, is between:
- apathy - a psychotic state, which is accompanied by a lack of desire for any activity, an indifferent and detached attitude to what is happening around;
- akinetic mutism - a rare condition in which the patient practically does not speak or move, although such a possibility exists from a physical point of view (understanding of the surrounding reality is preserved, the patient follows the people around him with his eyes and finds the sources of sounds).
Abulia is distinguished from weak-willedness and laziness by the awareness of the need for any actions and the inability to force oneself to perform them (laziness and weak-willedness can be fought with the help of training and self-discipline, but with abulia this is impossible).
Since abulia is not an independent disease, its prevalence has not been described. It is believed that this symptom is detected quite often, since the main risk factors for its occurrence include depression, a common condition in countries with high level life of the population.
Abulia can be:
- Congenital. Observed in severe mental retardation (oligophrenia). This intellectual disability is caused by brain pathology and is manifested by developmental delay or incomplete development of the psyche. Abulia is characteristic of torpid mental retardation (characterized by inhibited reactions).
- Acquired. May be temporarily present in cases of stupor (a movement disorder that can be catatonic, psychogenic and melancholic), stroke, or traumatic brain injury. Develops in schizophrenia, depression, borderline states, Parkinson's disease.
The combination of abulia and immobility is called abulic-akinetic syndrome, and when combined with apathy, apathetic-abulic syndrome is diagnosed.
Causes
Abulia develops when there is a lack of blood circulation or damage to the frontal area of the brain (affects the frontal lobe, basal ganglia, anterior cingulate cortex or capsular genu of the corpus callosum).
- traumatic brain injuries;
- brain tumors;
- encephalitis and meningitis;
- oligophrenia;
- borderline states (with circular and senile psychosis, psychoneurosis and hysteria);
- stroke;
- schizophrenia;
- severe depression;
- exposure to toxic substances.
Pathogenesis
Man's conscious organization of his activities and behavior is carried out through will. Abulia is accompanied by a violation of volitional processes.
The main points of the volitional process include:
- the emergence of motivation and goal setting;
- the stage of discussion and struggle of different motives;
- decision-making stage;
- execution of the decision.
The neurophysiological basis of volitional acts is a complex interaction of various brain structures, in which:
- cortical centers frontal lobes are responsible for the purposefulness of actions;
- regulation voluntary movements carried out by pyramidal cells;
- The energy supply to the cortical structures is carried out due to the reticular formation.
When one of these structures is damaged, disturbances in volitional processes are observed.
Symptoms
- inhibited state;
- decrease in intellectual activity;
- decreased social contacts and tendency to isolation;
- difficulty in making decisions;
- indifference to hygiene and one’s appearance;
- decreased need for food and sleep;
- loss of interest in usual activities;
- passivity and an unreasonable feeling of fatigue;
- indifference (no emotional experiences);
- stiffness or spontaneity of movements.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of abulia is made when the underlying disease is diagnosed. To diagnose the main mental illness use tests and questionnaires, and if organic damage is suspected, do the following:
When making a diagnosis, it is important to distinguish abulia and apatho-abulic syndrome from apathy, asthenopathic depression, asthenoanergic syndrome and other conditions with similar symptoms. It is also important to exclude manifestations of weakness of will, which is a character trait, not a disease.
Treatment
Abulia is a symptom of many pathological conditions, so treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease.
Drug treatment includes the use of:
- atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia;
- antidepressants for depression;
- correctors of blood circulation in the vessels of the brain during stroke and circulatory disorders;
- glucocorticoids for severe encephalitis, etc.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is also used to treat abulia, which may include:
- phototherapy;
- therapeutic swimming;
- medicinal baths;
- oxygen barotherapy, etc.
Physiotherapy methods are more effective in combination with sanatorium-resort treatment.
Treatment of abulia also requires individual and group sessions with a psychotherapist.
Abulia
Abulia is a pathological psychiatric symptom, symbolizing volitional absence. This condition is pathological in its manifestation and is very different from laziness or lack of desire; it is characterized by banal impossibility, the loss of all kinds of goals.
Apathy and abulia are a classic pathological condition that is characteristic of a number of disorders with pathological manifestations of lack of will and severe psychiatric diagnoses.
Every individual desires to have some drive and motivation, and it is in this order of life that there is happiness, in achieving some motivations or goals. But for an individual in an abulic state, this mechanism is significantly shifted and cannot be used, which is why it is difficult to treat this disorder with such patients.
What is abulia?
Abulia is a term that comes from Greece and has a simple meaning: “bulia” is will, volitional effort, and the particle “a” denotes a negative meaning. That is, abulia is lack of will.
Abulia is a pathological condition, complete lack of will. Lack of will is a condition that quickly affects all areas, since relatives will not be able to tolerate such a condition of a relative for a long time.
Abulia – serious symptom or pathology, since it cannot be corrected by behavioral methods and requires deeper approaches. Abulia is not ordinary lack of will, but pathological, and therefore irresistible.
Will is an important sphere that, together with the effector sphere, builds the human system of motivations, drives and desires. In its absence, life for the individual loses all its colors, turning into meaningless garbage.
Degrees of abulia are a type of classification and refer to a large number of characteristics. They are divided into light, which provides some opportunities for self-realization, and heavy, which completely deprives the possibility of organizing life.
In conjunction with apathy, there are several classic syndromes. In combination with akinesia, akinetic-abulic syndrome appears, which is clinically similar to catatonic stupor. Apathy and abulia are combined into the very iconic and severe apatoabulia syndrome.
Abulia is not the only pathological condition in volitional disorders. Among the disorders, there is also hyperbulia, as a volitional strengthening, parabulia is a perversion of volitional cravings, hypobulia is a decrease in volitional cravings, but unlike abulia, some volitional impulses remain, the motives are reduced, but not absent. Hyperbulia is a volitional strengthening, similar to the strengthening of motives; hyperactivity in actions quickly loses interest in the goal. Parabulia is manifested by a change or craving for violation of forms of behavioral motives.
The duration of volitional disorders in abulia varies. Short-term abulia is characterized by features characteristic of neuroses with periodic appearance. Periodic abulia is a symptom that occurs with a certain frequency and indicates a relatively severe disorder. Constant abulia is already a serious disorder, leading to pathologies on the psychiatric spectrum.
Abulia rarely manifests itself as a single symptom. This is usually a combination that can be included in many associated symptoms. For example, mutism includes abulia with a clear reluctance to speak and many symptoms that aggravate the outcome of the pathology.
Apathy and abulia are frequent combination, which takes away from the individual the opportunity to perceive the world happily, leaving only an automatic effect. In addition, this condition can worsen by the abulic-akinetic type with the same mutism and complete inaction even in formal terms.
Causes of abulia
Abulia has many causes and, in combination with the symptomatic picture, makes it possible to identify a specific disorder leading to life difficulties. Abulia, as a monosymptom in slightly expressed manifestations, accompanies individuals with a psyche prone to vulnerability. They often somatize some of their symptoms and think a lot about the situation, succumbing to melancholy.
Of the classical organic causes, the most common cause of abulia is a stroke condition with circulatory disorders such as thrombus formation. In this case, abulia is more pronounced when the right hemisphere is affected. If the frontal cortex is involved in the lesion, then there may be disinhibited behavior. The disorder can be triggered not only by a stroke, but also by an unfortunate injury and certain pathologies. Sometimes oncological processes provoke abulia.
The cause of the pathology is a disruption of dopamine neurotransmission, which is associated with a decrease in satisfaction, while initiative decreases. This deprives the individual of purposeful motor activity and the desire for action and initiative.
The main factor in abulic manifestations in the absence of organic disorders is stress, leading to nervous exhaustion and loss of personal qualities. Hereditary abulia, manifested in early age It is genetically determined, but it is difficult to diagnose due to the characteristics of childhood.
There are risk factors for abulia. In particular, these are intoxication or any other etiology of hypoxic conditions, which, due to lack of oxygen, destroy neuronal connections and harm the production of neurotransmitter factors. Dementias of all etiologies also push an individual to develop abulia. Congenital dementia can also often be combined with abulia.
Depressive states, especially those of severe endogenous origin, are also accompanied by powerful stupors with abulia. Although often exogenous depression provoked by a strong stressor can also cause abulic disorder with very negative symptoms.
Schizophrenia is certainly accompanied by an apatoabulic defect to one degree or another; it is an invariable companion of pathologies of the schizophrenia spectrum and is associated with the same dopaminergic system.
As a reaction to expressive psychotrauma, a psychogenic stupor can form, the structure of which also includes abulia (the condition in this case is temporary, but difficult to experience). It lasts until the traumatic situation is resolved, but abulia may remain as a somewhat longer-lasting symptom. It can also develop after somatic illnesses and when taking certain groups of drugs, in particular antipsychotics.
Violation of the functionality of the nervous system is a kind of preamble to abulia. Meningitis and encephalitis can serve as such a trigger; mental retardation and circular psychoses can have a similar structure. Many borderline personalities may also have similar symptoms. It occurs in psychasthenia, a condition of the nervous system, as well as in neuroses and hysterical people. Bad habits and addictive behavior also form abulia. Also, the development of this condition can be provoked by incorrect types of education that do not teach the child to act independently.
Symptoms of abulia
Perhaps the main symptom of abulia is lethargy. It manifests itself not only in movements, but also in actions, speech, conversation and even thoughts. They say about such people that they are like “cold tar.” But in the case of abulia, it is very difficult to control and somehow change.
Intellectual activity decreases, but not as with mental reasons, but simply manifests itself in the difficulty of consideration. Naturally, if abulia is provoked by oligophrenia, then signs of mnestic-intellectual decline will be obvious.
Another symptom of abulia is isolation. Its degree also depends on the pathology that will act on the formation of abulia. If in schizophrenia isolation reaches complete autization and isolation from the outside world, in psychopathy it will be much less pronounced. This social isolation complicates or eliminates social interaction, as if closing a vicious circle, taking away the opportunity to work and be in society.
Abulia also manifests itself in the difficulties of decision-making; the individual does not doubt something, but simply cannot think and decide, due to a change in the course of thinking due to the peculiarities of the abulia influence.
A sign of abulia, which is especially characteristic of schizophrenics, is non-compliance with hygiene rules, reluctance to any hygiene procedures. This is not because of sloppiness, but because of abulia, in which the individual does not want to do anything or work on anything at all. This is not only related to hygiene, there is not enough willpower for any actions associated with minimal volitional effort. Such an individual can simply do nothing at all for months and not worry about it due to the formation of a defect. This leads to the impossibility of self-care and forced hospitalization due to this. An individual with abulia does not perform completely basic actions that everyone should do. At the same time, even basic needs and aspirations for their satisfaction are muffled. From the outside it looks like very strong laziness, but in reality such individuals do not want to, they simply physically cannot.
Lack of excitement about not wanting to do anything is another sign of abulia. This will worry the relatives, they will try to find ways out, but not the patient, he is completely indifferent to this. This is the insidiousness of this disease, since the patient is indifferent not only to himself and his needs, indifference is manifested both in the family and in work, and to people whom the person previously loved dearly. There is no longer joy due to joyful events and sadness due to sorrows.
Spontaneous actions disappear, stiffness appears, and in speech there is often the same reluctance, up to mutism - a complete absence of speech while maintaining the speech apparatus. Often this manifests itself in completely formal contact, with a loss of interest in the conversation and a reluctance to participate in any way.
The world around us does not attract and does not cause pleasure, forcing us to take refuge in our “shell”. At the same time, a lot of thoughts appear or, conversely, the head is empty. Pessimism and causeless fatigue are a constant companion to this phenomenon.
Treatment of abulia
Relief of abulic manifestations varies greatly depending on the pathology that caused it. If abulia is mild and provoked by a personality type or stress, then you can try to change the situation. A change in climate or travel helps a lot. This allows you to look at your life from the outside and give a normal self-assessment of your actions.
If abulia is provoked by certain human factors, then it is worth trying to abstain from this communication or use the services of a psychoanalyst to understand this condition.
Abulia due to mental pathology requires intervention from neurosurgeons and correct corrective treatment. Mental retardation, in turn, is treated using cognitive techniques and proper education with an impact on all cognitive areas.
Interest and work are relevant, but all this is only in the case of pathology of a certain spectrum. In case of stressors, it is important to exclude them and turn off the relevance of the traumatic situation.
In case of pathology of the psychiatric spectrum, it is impossible to do without correctly selected medications and consultation with a psychiatrist. It is very important to use atypical antipsychotics that have an effect on the apatoabulic defect in schizophrenia: Sonapax, Rispaxol, Solian, Rispolept, Risperidone, Queteron. In case of depression, apathy and abulia are relieved by antidepressants: Fluoxetine, Paroctetine. If there is accompanying insomnia, it is worth using Imovan, Zolpidem, Sonovan, Zolpiclone.
However, you should not abuse artificial stimulants so as not to completely destroy the dopaminergic systems with the response apparatus.
If a person is passive and has no desire to achieve goals or satisfy needs, then people mistakenly assume that he is lazy. With various mental and physical disorders, we can talk about abulia, whose symptoms resemble a person’s lack of will and indifference in anything. The reasons are often various disorders who are difficult to undergo treatment without the participation of a doctor.
In the life of any person there comes a period of a kind of abulia, when you don’t want to do anything, even get out of bed. However, this condition differs from a painful one, when a person is not temporarily, but permanently in a state of lack of will. The online magazine site examines a painful condition that may outwardly resemble a normal one.
What is abulia?
What is abulia? This is a pathological condition defined by lack of will, lack of desire, spinelessness, inability to make decisions and carry out actions, and lack of motivation to act. Roughly speaking, a person can lie on the bed and not want to do anything, even satisfy his natural needs.

Apathetic-abulic syndrome is diagnosed when it is combined with, and does not simply act as a symptom of it. Abulic-akinetic syndrome occurs when a person is immobilized.
Abulia should not be confused with weakness of will. Abulia can only be eliminated by medical means, while weakness of will can be eliminated by education, self-education and training.
Abulia has no age. It can occur in both young and elderly people. It manifests itself as a lack of volitional motivation to perform any activity. A person can lie on the bed for days without feeling any desire or interest in taking action, even if it is related to satisfying needs.
Abulic syndrome is remarkable and differs from laziness and weakness of will in that it cannot be overcome by training or self-education. It is often accompanied by organic disorders, which provoke this condition. With abulia, a person does not move not because he is lazy, but because he lacks motives, desires, and interests.
It is quite difficult for scientists to determine whether abulia is an independent disease or always a consequence of another disease. Its manifestations are so extensive and similar to other characteristics that people often confuse it with laziness, weakness, lack of will, etc.
Causes of abulia
There are many chances to encounter abulia yourself, since the reasons for its development and appearance are quite extensive. According to statistics, abulia manifests itself in people in large cities, since one of the causes of its occurrence is depression. And this condition is familiar to many.
If we list all the causes of abulia, we can identify the following:
- Head injuries.
- Infections or tumors.
- Tendency to somatoform disorders.
- Mental vulnerability.
- As a consequence of illness or head injury, which disrupts blood circulation in the right hemisphere of the frontal zone.
- Meningitis or encephalitis.
- Heredity.
- Circular psychosis.
- As a consequence of borderline states: hysteria, psychasthenia or psychoneurosis.
The main symptom of abulia is loss of identity. A person loses motives and desires to do and achieve anything. This turns it into a vegetable.
Abulia in childhood is especially dangerous, because parents may mistakenly perceive it as a child’s weakness or laziness, although in fact he needs help.

The most dangerous is abulia based on heredity. Such a child shows all the symptoms from birth. He is inactive, calm, and not loud. Parents should not be happy about this, but worried, since the disease will not go away on its own, and late diagnosis will give unfavorable prognosis for treatment.
Abulia accompanies many diseases of the body, especially those related to the brain. The risk group includes people with the following painful conditions:
- Post-traumatic and post-stroke conditions.
- Hypoxia.
- Infectious diseases.
- Parkinson's, Pick's, Huntington's diseases.
- Consequences of intoxication.
- Congenital dementia.
- Brain tumors.
- Drug or alcohol abuse.
- Schizophrenia.
- Long-term use of antipsychotic medications.
Temporary abulia may occur, which is a reaction to a certain traumatic situation (psychogenic stupor). This condition passes as soon as the situation is resolved or leaves the person.
Symptoms of abulia
Abulia develops gradually. At first, it may be mistakenly perceived as another condition. However, as the symptoms progress, you can understand that we are talking about abulia.

The first sign is indifference to one’s own appearance. A person stops washing, shaving, washing clothes, changing underwear, and taking care of himself.
The following symptoms of abulia include:
- Passivity.
- Sudden unexplained movement.
- Protracted response to a question (the answer does not arrive for a long time).
- Loss of interest in simple activities, games (in children) or activities (in adults).
- Loss of appetite.
- Decreased social contacts.
- Difficulty in taking targeted actions.
- Lack of impulse to take action.
- Violation of will.
- General lethargy.
- Slowness of mental and speech activity.
- Uncoordinated movements.
- Impoverishment of facial expressions, gestures, speech.
- Loss of interest in hobbies - previously interesting activities.
- Inability to make a decision.
- Inability to bear minimal loads.
- Refusal of the plan when any obstacle arises.
- Demandingness, impatience, laziness, inertia.
- Resistance to any attempts to move the patient.
- Avoiding leaving the house, getting out of bed, and maintaining basic hygiene.
- The decline of conscientiousness, modesty, compassion, and the ability to love in apathetic-abulic syndrome.
- The transition from “I don’t want” to “I can’t.”
The patient may even feel a desire to perform some action, but the activity is never carried out. This is explained by the fact that a person cannot find the energy in himself to move from desire to action.
Weakness differs from abulia in that it is a character trait that develops as a result of improper upbringing. It can be eliminated by re-education, external influences society, self-education or training.
Abulia can manifest itself in various forms and symptoms. It can be either mild, when a person is able to motivate himself to take action, or severe, when he does not even have the strength to get out of bed and feed himself.
There are 4 main volitional disorders:
- Hyperbulia is hyperactivity.
- Parabulia is a deviation of behavior from social norms.
- Hypobulia – decreased motivation to act.
- Abulia is the complete absence of any motives in committing actions.
Depending on the duration of abulia, it can be:
- Constant. It is observed in manic-depressive psychosis, severe brain damage, and catatonic schizophrenia.
- Periodic. It is noted in somatoform disorders and drug addiction.
- Short-term. Often observed in adynamic depression, neurosis, psychopathy, which manifests itself in the form of an inability to make a decision and take action.
Abulia can be combined with:
- Mutism – reluctance to speak. The patient avoids conversations and takes a long time to answer questions.
- Apathy is emotional impoverishment and automaticity of actions. The person shows indifference and indifference, avoids contact with people, and becomes withdrawn.
- Adynamia - complete or partial immobility, slowing down of thought processes.
Diagnosis of abulia
Abulia is accompanied by other mental disorders that doctors can think of. This is why diagnosis becomes difficult. The main technique that allows you to identify abulia is observing the patient and his behavior. CT and MRI, ultrasound, electroencephalography of the brain and lab tests blood to confirm the diagnosis.
It is quite difficult to distinguish abulia from laziness, especially when it comes to children. Parents can sometimes be too impatient in their children fulfilling their requests, which is mistakenly perceived as abulia. However, if a child spends a long time reading one page of a book, for example, this indicates the possible development of a disorder.
Treatment of abulia
Treatment of abulia is complex, since it involves methods of eliminating the root cause and abulia as a consequence. The root cause is treated with various medications:
- Schizophrenia is treated with atypical antipsychotics.
- Depression is treated with antidepressants.
Elderly people need attention from their relatives. Middle-aged people are encouraged to actively engage in various activities and hobbies. As for children, their treatment should be handled by a specialist. Parents themselves often nurture and groom their child’s abulous state, which is why he gets used to it, taking it for granted.

The main directions in the treatment of abulia are:
- Involvement in work when there is a reference to the fact that without the patient nothing will happen.
- Introducing it in the company of relatives and friends.
- Visiting interesting, diverse places.
Separately, we consider senile (age-related) abulia, which can develop against the background of thoughts that no one needs a person, everyone has abandoned him. Various events will help here, where relatives will attract an elderly person. He should feel needed, significant, responsible, which will create a desire to take action.
Additionally, physiotherapeutic measures are used:
- Therapeutic swimming.
- Phototherapy.
- Oxygen barotherapy.
- Therapeutic baths.
- Mineral waters of thermal springs.
- Spa treatment.
- Highlands.
- Rest in places south of your place of residence.
Homeopathy offers the following medications to eliminate abulia:
- Carbo vegetabilis.
- Kali phosphoricum.
- Glonoinum.
- Gelsemium.
Bottom line
The result of abulia is the complete absence of any opportunities to bring a person back to life. There is definitely no way to do this without drug treatment. Before the development and during the treatment of abulia, the environment in which a person lives remains important:
- Older people need to feel needed.
- Adults and teenagers should take part in activities and do things they love.
- Children should not be protected from problems and difficulties, nor should their whims be indulged. Otherwise, their condition will only develop.
The study of abulia has been carried out since 1838. Currently, experts consider abulia as a symptom of other diseases and mental disorders, although there are attempts to consider this condition as an independent nosological unit.
Abulia, in which the patient feels a partial or complete lack of desire for any activity, is between:
- apathy - a psychotic state, which is accompanied by a lack of desire for any activity, an indifferent and detached attitude to what is happening around;
- akinetic mutism - a rare condition in which the patient practically does not speak or move, although such a possibility exists from a physical point of view (understanding of the surrounding reality is preserved, the patient follows the people around him with his eyes and finds the sources of sounds).
Abulia is distinguished from weak-willedness and laziness by the awareness of the need for any actions and the inability to force oneself to perform them (laziness and weak-willedness can be fought with the help of training and self-discipline, but with abulia this is impossible).
Since abulia is not an independent disease, its prevalence has not been described. It is believed that this symptom is detected quite often, since the main risk factors for its occurrence include depression, a common condition in countries with a high standard of living.
Kinds
Abulia can be:
- Congenital. Observed in severe mental retardation (oligophrenia). This intellectual disability is caused by brain pathology and is manifested by developmental delay or incomplete development of the psyche. Abulia is characteristic of torpid mental retardation (characterized by inhibited reactions).
- Acquired. May be temporarily present in cases of stupor (a movement disorder that can be catatonic, psychogenic and melancholic), stroke, or traumatic brain injury. Develops in schizophrenia, depression, borderline states, Parkinson's disease.
The combination of abulia and immobility is called abulic-akinetic syndrome, and when combined with apathy, apathetic-abulic syndrome is diagnosed.
Causes
Abulia develops when there is a lack of blood circulation or damage to the frontal area of the brain (affects the frontal lobe, basal ganglia, anterior cingulate cortex or capsular genu of the corpus callosum).
Observed when:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- brain tumors;
- encephalitis and meningitis;
- oligophrenia;
- borderline states (with circular and senile psychosis, psychoneurosis and hysteria);
- stroke;
- schizophrenia;
- severe depression;
- exposure to toxic substances.
Pathogenesis
Man's conscious organization of his activities and behavior is carried out through will. Abulia is accompanied by a violation of volitional processes.
The main points of the volitional process include:
- the emergence of motivation and goal setting;
- the stage of discussion and struggle of different motives;
- decision-making stage;
- execution of the decision.
The neurophysiological basis of volitional acts is a complex interaction of various brain structures, in which:
- the cortical centers of the frontal lobes are responsible for the purposefulness of actions;
- regulation of voluntary movements is carried out by pyramidal cells;
- The energy supply to the cortical structures is carried out due to the reticular formation.
When one of these structures is damaged, disturbances in volitional processes are observed.
Symptoms
Abulia manifests itself:
- inhibited state;
- decrease in intellectual activity;
- decreased social contacts and tendency to isolation;
- difficulty in making decisions;
- indifference to hygiene and one’s appearance;
- decreased need for food and sleep;
- loss of interest in usual activities;
- passivity and an unreasonable feeling of fatigue;
- indifference (no emotional experiences);
- stiffness or spontaneity of movements.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of abulia is made when the underlying disease is diagnosed. To diagnose the underlying mental illness, tests and questionnaires are used; if an organic lesion is suspected, the following are done:
- CT and MRI;
- laboratory blood tests.
When making a diagnosis, it is important to distinguish abulia and apatho-abulic syndrome from apathy, asthenopathic depression, asthenoanergic syndrome and other conditions with similar symptoms. It is also important to exclude manifestations of weakness of will, which is a character trait, not a disease.
Treatment
Abulia is a symptom of many pathological conditions, so treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease.
Drug treatment includes the use of:
- atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia;
- antidepressants for depression;
- correctors of blood circulation in the vessels of the brain during stroke and circulatory disorders;
- glucocorticoids for severe encephalitis, etc.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is also used to treat abulia, which may include:
- phototherapy;
- therapeutic swimming;
- medicinal baths;
- oxygen barotherapy, etc.
Physiotherapy methods are more effective in combination with sanatorium-resort treatment.
Treatment of abulia also requires individual and group sessions with a psychotherapist.
Clinical manifestations of the syndrome and its types
Will is a special regulatory factor, a planned ability for productive activity aimed at results. Violation of volitional processes is often associated with pathology of activity, motivation and behavior. Disorders of will are of the following types:
- hyperbulia,
- hypobulia,
- abulia,
- parabulia.
Hyperbulia is an excessive manifestation of activity, and hypobulia is its opposite, a decrease in the function that motivates activity. Parabulia appears directly as a behavioral disorder. Lack of will is characterized by a loss of desire for productive activity and a lack of motivation to achieve results. According to duration, abulia is divided into the following subtypes:
- short-term,
- periodic,
- constant.
A short-term course of the disease is observed in adynamic depression, borderline states (neuroses, asthenia). Patients with depressive disorders are often deprived of active activity, their motivational and volitional sphere is in decline. A person who is in the stage of depression understands the need for volitional direction, but cannot always muster the strength to begin to act. Also, short-term lack of will can be observed in neurosis, psychopathy and manifest itself in the form of an inability to make a decision, decreased motivation and lack of motivation.
Periodic lack of will occurs in drug addiction and advanced somatoform disorders. The recurrent nature of the decline in volitional processes often coincides with the stages of exacerbation in schizophrenia. Recurrent violations of will are often present in the clinical picture of manic-depressive psychosis. A constant lack of motivational base and volitional impulses is a characteristic sign of catatonic schizophrenia and severe brain damage. Lack of will in combination with immobilization in schizophrenia can turn into a catatonic stupor. It is the apato-abulic syndrome in the clinical picture of schizophrenia that is the most severe manifestation of impaired will.
Among the main symptoms of the disease are:
- slowness of thought processes,
- difficulties in making decisions,
- reduction in social contacts, up to isolation,
- lack of motivation to take action,
- neglect of hygiene,
- reducing the need for basic human needs (food, sleep),
- loss of interest in usual activities,
- passivity,
- stiffness or spontaneity of movements.
Abulia can occur in combination with mutism, apathy and adynamia. Mutism is understood as speech passivity, which manifests itself in the absence of a verbal speech component. Patients do not answer questions, showing with all their appearance their reluctance to come into contact with others. The French psychiatrist Florenville believed that the “involuntary manifestation of mutism” is combined with lack of will and passivity of motor activity.
Apathy, which is emotional indifference and indifference, is often combined with a lack of volitional activity, forming apatho-abulic syndrome. The clinical picture of this condition occurs in the form of emotional impoverishment and automated actions. Patients become withdrawn, often remain silent for long periods of time, and try to avoid contact with others. This condition is characteristic of schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder.
Adynamia, manifested in the inertia of the incentive function to action, can occur both in the form of inhibition of thought processes and in the complete absence of movements. According to the German psychiatrist K. Kleist, this phenomenon is characteristic of lesions of the frontal parts of the brain. The scientist called this specific combination of lack of will and inertia of movements “broken feather syndrome.”
Causes of the disease
The causes of this psychopathological syndrome are injuries and brain tumors, hereditary predisposition to schizophrenia and other mental disorders, and dementia. Mild manifestations of the disease can be observed with low stress resistance and a tendency to somatoform disorders. This psychopathological syndrome is observed in the following diseases:
- schizophrenia,
- lesions of the frontal parts of the brain,
- borderline states,
- depression,
- dementia.
Most often, lack of will manifests itself in schizophrenia and organic lesions of the frontal parts of the brain. According to the German scientist E. Bleuler, lack of will, as one of the symptoms of schizophrenia, manifests itself as a kind of “loss of energy potential.” “The need against and despite,” according to the psychiatrist, was main feature patients with schizophrenia due to the simultaneous presence of desire and lack of strength to realize it.
Back in the 50s of the twentieth century. Soviet psychiatrist M. O. Gurevich proved that the frontal part of the brain performs the function of controlling impulses and volitional processes. Patients with lesions of the frontal regions are very inert in their judgments, often unable to make a simple effort to perform primitive actions. When the brain is damaged, the disease occurs in the form of motor inhibition combined with a weakening of thought processes.
Treatment of abulia

First of all, it is necessary to treat the main disease, within which the lack of will manifests itself. If the lack of volitional effort occurs on the basis of schizophrenia, atypical antipsychotics are widely used as medications. If the cause of abulic syndrome is depression, antidepressants are used. The treatment regimen is determined exclusively by a psychiatrist, who relies on anamnesis and diagnostic criteria.
The prognosis for the treatment of apatho-abulic disorder in combination with schizophrenia is often unfavorable. IN psychiatric practice with long-term therapy of the disease, only partial remission was observed, and cases of transformation of schizophrenia into progressive stages were noted. In the best cases, there were improvements in social interaction and communication with others.
Psychotherapy is widely used in the treatment of abulia, especially in short-term, mild forms of the disease. The use of psychotherapeutic methods for the treatment of lack of will within schizophrenia is controversial issue. However, many doctors practice using hypnosis and cognitive behavioral psychotherapy to reduce signs of the syndrome. The main goal of the psychotherapeutic approach is to establish social adaptation and form a strong-willed and motivational base.
Forms of the disorder
Unlike ordinary weakness of will, which is caused by improper upbringing, apraxia and abulia are directly associated with a lack of willpower, spinelessness, laziness and lack of will by lesions of the brain structure. With lesions of the frontal lobe, apraxia occurs.
There are several forms and types of abulia that make it possible to classify this disease. Psychological analysis identifies two main stages of abulia severity.
- Easy. There are slight deviations from normal behavior, a slight lack of will and motivation. At the same time, a person experiences a state when it is possible to involve him in activities.
- Heavy. This condition is accompanied by a complete refusal of any action and suppression of volitional impulses. The pathology is characterized by the fact that the patient is unable to perform even the most basic tasks, such as standing up, washing his face or eating.
Apathetic-abulic syndromes are a violation of the will associated with a decrease in initiative, lack of will or desire to overcome obstacles and achieve results. The condition is accompanied by the patient’s deviations from observing norms of social behavior.

There are several types of volitional disorder:
- hyperbulia;
- parabulia;
- hypobulia;
- abulia.
It represents a significant change in the number of motives required to perform a particular action. Hypobulia is a condition in which it is extremely difficult for a person to find the strength within himself and force him to complete a particular task.
Hyperbulia, in contrast to this type of volitional disorder such as hypobulia, has a basic characteristic symptom. Hyperbulia is characterized by the fact that it involves increased activity or hyperactivity, but the person very quickly loses interest in the goal.
Represents behavioral deviations directed against existing norms of behavior.
As for abulia, it is defined as a state of pathological lack of will to commit actions. Weakness or impairment volitional sphere, if you like.
Duration of volitional disorder
An important issue in the treatment prescribed for abulia is the duration of the volitional disorder. The disease is divided into three types depending on duration.
- Short-term. Her characteristic features there may be periodic neuroses, asthenic and depressive syndromes, as well as psychopathic type disorders.
- Periodic. With periodic abulia, symptoms usually accompany drug addicts and patients with severe forms of schizophrenia or somatoform disorder.
- Constant. With constant abulia, there is a high probability of developing the symptom of catatonic stupor. This form of abulia is often formed in schizotypal personality disorder, schizophrenia, or organic brain damage.
Combination with other diseases
Abulia can often be combined with other diseases, forming modified or complicated ailments:
- Mutism. In combination with mutism, that is, a reluctance to talk, serious disturbances occur in verbal contacts with patients. It is extremely difficult to get any response from the patient; the painful syndrome is accompanied by almost constant silence.
- Apathy. The formation of apathetic-abulic syndrome occurs. A distinctive feature of apathetic-abulic syndrome is a deficit in the expression of emotions and the performance of a number of actions “automatically.” The patient may simply withdraw into himself, actively avoid society, clearly show indifference to his interlocutors, and even ignore loved ones. The syndrome is also characterized by the fact that a person loses all interest in his once favorite hobbies or activities.
- There is a syndrome of abulic-akinetic type. It combines a lack of will as well as immobility. Moreover, mobility can be partial or complete. Thoughts are slow, a person cannot form his answer or thought for a long time.
Reasons for lack of motivation
Abulia is not a spontaneously occurring disease. This psychological disorder is characterized by the presence of certain factors or causes that shape the development of weakness of will. Moreover, unlike many other psychological personality disorders, abulia is caused by physiological reasons, such as brain damage or predisposition.

Abulia can occur against the background of:
- brain damage due to trauma;
- tumors in the brain;
- hereditary factor;
- predisposition to schizophrenia;
- dementia;
- depression;
- borderline state.
Most often, the patient experiences weakness of will when the frontal parts of the brain are affected or signs of schizophrenia develop.
Symptoms
To identify problems and begin treatment, you must first learn to identify the presence of a problem with motivation and will. For these purposes, a certain list of the main symptoms that appear in people with abulia is provided:
- The person has difficulty forming thoughts, the thought process is slow and does not allow active conversations or reasoning.
- It is very difficult for the patient to make any decision. Moreover, this can even apply to basic little things, such as buying bread or choosing socks.
- A person actively tries to isolate himself from the surrounding society. Some people simply try to communicate less with their surroundings, while others drive themselves into a state of complete isolation from the outside world.
- Patients with abulia cannot find the motivation to perform a number of actions. Any volitional decision is made with enormous effort and often ends in a quick abandonment of the planned actions.
- People with abulia partially or completely neglect basic hygiene rules, stop taking care of themselves and cannot even just wash their face in the morning. Any such action is accompanied by irresistible bouts of laziness.
- A person diagnosed with abulia gradually reduces his need for basic things and actions necessary for a person. For example, he stops eating normally, often refuses food or sleeps little.
- The patient may completely lose interest in his usual or even favorite activities. At some point, even his life's passion ceases to be interesting.
- There is passivity in all matters, actions, communication and decision making.
- A person tries to avoid any responsibility. He abstracts himself from those around him.
- Actions can be constrained and spontaneous. And sometimes they alternate with each other.
Features of treatment

The essence of treatment for abulia is the need to first overcome the disease against which it develops. volitional disorder. That is, it is not the abulia itself that needs to be treated, but the illness that provoked it:
- If abulia occurs against the background of schizophrenia, the specialist prescribes antipsychotics.
- Abulia associated with depression is usually treated with antidepressants.
- Any appointment is determined only by a psychiatrist.
- The choice of medications and treatment methods for abulia is made only after observation, history and diagnosis of the patient.
- For the purpose of treatment and prevention, the patient is often recommended phototherapy, swimming, medicinal baths and oxygen therapy.
Concerning medicines, then for the treatment of abulia the most common means of drug therapy are:
- Frenol.
- Triftazin.
- Solian.
- Sulpiride.
Unfortunately, the experience of psychologists shows that apato-abulic syndrome is predominantly accompanied by an unfavorable prognosis. Usually treatment ends with only minor disappearance of symptoms. Most often this concerns the patient’s partial or complete return to social contacts. At the same time, the absence of any measures aimed at combating abulia significantly worsens the person’s condition. Therefore, treatment is required at a minimum to prevent complications.
In psychology, will is considered one of the important mental processes. Will allows us to make decisions and move according to the decisions we make. Moreover, it is with the help of will that we can regulate our actions consciously, overcoming difficulties that arise along the way.
And, of course, disorders associated with the dysfunction of this process can cause a lot of inconvenience. Abulia is a disorder of the will, or rather the inability to perform volitional actions against the background of general emotional and physical apathy. In short, it is weakness of will. This state is associated with a lack of desires, aspirations and a reduced emotional background, as well as a lack of energy.
It is important to understand that periodic laziness or lack of desire to do anything, and even periodic lack of will, is not pathological and is inherent in every person. But abulia is a persistent condition that requires treatment.
How to determine?
This disorder has a number of signs that make it possible to understand that the patient has abulic syndrome. It is also worth paying attention to the fact that abulia is not an independent disorder, it is a consequence of other, more serious diseases.
How does abulia manifest itself, its main symptoms:
1. A person loses interest in his appearance. If in ordinary life in most cases we try to look good, then with abulia the patient does not care, he does not have the strength, desire and motivation to somehow maintain a good appearance. appearance. A person may wear dirty clothes, not wash his face, not comb his hair, and be completely indifferent to the recommendations of others about the need to change clothes.
2. Patients are characterized by slow speech, with long pauses, and a detached gaze; also, the person does not ask questions, does not show himself in the conversation. There is a feeling that the person does not have the strength to speak, or that he thinks about each phrase for a long time. In fact, this is due to apathy and an internal lack of energy even for conversation.
3. There is a loss of appetite and interest in the process of eating something. Interest does not come even if a person is offered his favorite dish.
4. A person moves slowly, tries to remain motionless more. Gets up and moves only when absolutely necessary (for example, to go to the restroom); the rest of the time he can simply lie down or sit without moving.
5. The patient cuts social contacts, tries not to communicate with people, does not answer calls or messages in social networks. Does not show interest in meetings, does not come to the door if someone comes to visit.
6. Abulia can also manifest itself in sleep disturbances (usually insomnia). Due to the fact that a person does not expend energy, he cannot fall asleep and remains awake for a long time, but at the same time feels tired.
7. Problems arise with thinking, it becomes viscous, and it is difficult for a person to concentrate on something for a long time. Functions such as memory, especially short-term memory, are also affected.
All of these symptoms are accompanied by general pessimism, lack of desire to take action, and resist circumstances. Therefore, abulia often leads to dependence on the people with whom the patient lives.
As mentioned above, abulia is a disorder that accompanies various diseases, mainly associated with brain dysfunction. These can be either brain injuries (especially the frontal lobes), or the consequences of a stroke, tumors or Parkinson's syndrome. Therefore, when signs of abulia appear, it is important to do full examination to find out all the reasons.
Abulia is a syndrome that also often occurs in older people, usually due to senile diseases. But people of all ages can be susceptible to it, although the risk group mainly includes the elderly and children (younger and adolescents).
Diagnosis and treatment
The main way to diagnose abulia is observation, as it manifests itself this disorder maybe just in behavior. With this disorder, the clinical interview method will not bring serious success, since the patient will answer slowly and will not be able to remember everything. Therefore, to collect reliable data, they often conduct a conversation with the patient’s family or close friends.
It is also important to study the medical history, as this can also help in identifying the causes. Among the medical methods, tomography is distinguished; it allows you to “see” disturbances in the functioning of the brain.
It is most difficult to diagnose this disorder at an early age, since many may mistake a child’s resistance to a parent’s requests for a lack of energy. Here it is important to observe the child for a long time, to pay attention to whether he shows interest in games, sweets, spending time with friends, how much time it takes him to perform this or that action. All these data should be compared with the typical behavior of the child, and not with the behavior of other children.
If we talk about treatment, then it would be natural to treat the underlying disease, the consequence of which is abulia. It could be like drug treatment, and complex psychotherapy.
Of the psychotherapeutic methods and techniques, most specialists offer the following:
1. Motivation of a person to act, based on his past experience. Here, in order to “remember” past motives and needs, both journaling and a hypnotic state are used.
2. Gradual introduction of a person into an active life. There are two main mistakes that parents make when faced with symptoms of abulia in their child:
- Parents indulge the child, do not touch him, allow him to remain in apathy and do nothing. This behavior will be a positive stimulus (the child will feel that his apathy is something right and natural) and will accelerate the development of the disease.
- Parents, on the contrary, sharply pull the child back, force him to do something through force and scold him for laziness. In addition to the fact that the child’s disorder will progress, a guilt complex will also form.
Thus, a gentle introduction of a person, a child, into life will be most optimal. Also, it is important not to forget about positive motivation, praise, and so on.
3. In some cases, in the early stages of the development of the disease, “immersion” methods are used, when a person is immersed in some active activity or event. It is important that at this moment the specialist is close to the patient. But this method should not be used at the beginning of treatment as it may create unnecessary resistance.
It is worth remembering that any disorder can be treated much easier, faster and more effectively with early stages. Therefore, it is extremely important to seek help when signs of the disorder become apparent. Author: Daria Potykan
In psychiatry and neurology abulia is understood as a painful lack of will, a psychopathological syndrome, a person’s lack of initiative. At the same time, there is no desire to act, no motivation for any action is detected, although the need for specific actions is fully realized. Basically, abulia makes itself felt in the middle period of life, and is one of the most striking manifestations of apathy. It is typical that the patient himself cannot make even minor decisions. The condition of abulia can manifest itself in mild degree, or it almost completely suppresses a person.
This disease is often called astasia, abasia, and is regarded as a violation of the volitional regulation of behavior. Currently, there is no consensus among neurologists and psychiatrists about whether abulia should be considered a symptom of another disease, or whether it is still an independent disease with its own signs and characteristics, for example, like, because its clinical manifestations are varied. Scientists conducted a study of motivation that extends to emotional states and connections biological processes. In the course of this work, an explanation was obtained for the purposefulness of human behavior.
A significant number of violations are explained by a lack of will and motivation, and a decline in the role of incentives. It is necessary to make a precise distinction between abulia and apathy. Abulia should not be mistaken for weakness of will, which can be overcome through self-education and will training.
Symptoms of abulia
 In medicine, the study of abulia has been going on for a long time; doctors became interested in the characteristics of the disease back in 1838, and therefore its symptoms have now been defined. Although, experts had to deal with descriptions that sometimes contradict each other. This disease is described as loss of speech and behavior, accompanied by decreased initiative, prolonged speech delay, and spontaneity of the thought process. In addition, signs that are considered clinical for abulia are highlighted.
In medicine, the study of abulia has been going on for a long time; doctors became interested in the characteristics of the disease back in 1838, and therefore its symptoms have now been defined. Although, experts had to deal with descriptions that sometimes contradict each other. This disease is described as loss of speech and behavior, accompanied by decreased initiative, prolonged speech delay, and spontaneity of the thought process. In addition, signs that are considered clinical for abulia are highlighted.
In particular, the patient makes spontaneous movements, difficulties in maintaining movements of a certain direction, passivity. In addition, with abulia, a person thinks for a longer time before answering a question, emotional response decreases, and interest in matters that previously seemed paramount disappears.
In some cases, you may notice that a person suffering from abulia chews food for a long time without swallowing, or, after starting to eat, he quickly loses his appetite and refuses to eat. Such symptoms should be checked several times to make sure that the person still needs food and is hungry. To ensure the necessary interest in food and good nutrition Experts recommend using sweet foods and seasonings.
It is important that with abulia, a person is well aware that certain actions are required of him in this situation, but he cannot force himself to do the right thing. Sometimes it happens that a person is not even able to move. A sign of abulia can also be considered the phenomenon of indifference to one’s own appearance. The patient is too lazy to wash his face, wash his hair, he doesn’t want to brush his teeth, change his underwear, etc.
Causes of the disease
 Different experts have different approaches to this issue, but everyone is unanimous that the main cause should be considered a frontal lesion of the brain, but not the cerebellum or its stem. closely related to dopamine dysfunction. Also among the reasons, not least in place are head injuries, leading to a number of personality changes, strokes, affecting right hemisphere. In some cases, abulia is congenital, it is caused by oligophrenia - mental illness. Schizophrenia can also cause abulia, and lead the patient into a depressive state.
Different experts have different approaches to this issue, but everyone is unanimous that the main cause should be considered a frontal lesion of the brain, but not the cerebellum or its stem. closely related to dopamine dysfunction. Also among the reasons, not least in place are head injuries, leading to a number of personality changes, strokes, affecting right hemisphere. In some cases, abulia is congenital, it is caused by oligophrenia - mental illness. Schizophrenia can also cause abulia, and lead the patient into a depressive state.
A person's ability to move, talk, perform social action, is due to the functions of the frontal lobes. If there are injuries in this area, they negatively affect these processes. The development of the disease is influenced by the withdrawal of amphetamine, and rehabilitation after a stroke is complicated. The patient does not want to do even the exercises that are available to him, such as walking. The provoking factor is not only the presence of injuries, but also infectious diseases and heredity. At the same time, it should be emphasized that many doctors consider stress to be the main culprit of abulia. In addition, addiction to alcohol can have a significant impact.
Essentially, due to abulia, a person loses the ability to be an individual, and here excessive parental care and suppression of the child’s will can play a role. Abulia often develops due to the fact that a person is haunted by failures, and he has complexes about any reason, and feels to a certain extent defective.
Treatment of abulia
 If abulia is a consequence of stress, at first loved ones treat the person with sympathy, allowing him to be in a state of apathy. But it is not recommended to do this, since the disease begins to develop, the patient gets used to this state of affairs, so it is difficult to remove him from this state. Elderly patients often suffer from abulia, and in this case the disease is considered age-related, mainly caused by psychological reason. The patient may feel that he has been forgotten by everyone and is no longer interesting to anyone. To prevent abulia from occurring in an elderly relative, visit him more often, show attention, and ask his opinion on various matters.
If abulia is a consequence of stress, at first loved ones treat the person with sympathy, allowing him to be in a state of apathy. But it is not recommended to do this, since the disease begins to develop, the patient gets used to this state of affairs, so it is difficult to remove him from this state. Elderly patients often suffer from abulia, and in this case the disease is considered age-related, mainly caused by psychological reason. The patient may feel that he has been forgotten by everyone and is no longer interesting to anyone. To prevent abulia from occurring in an elderly relative, visit him more often, show attention, and ask his opinion on various matters.
If a person of working age suffers from abulia, then in this case, those around them should help. You can throw parties, invite you for walks, interesting events. In addition, try to start renovations in the apartment and tell him that you need help and you won’t be able to do it without him. When a person feels that he is needed, it is much easier to overcome the state of abulia. At the same time, if the disease progresses and has gone far, you need to consult a doctor who will prescribe the optimal psychotherapeutic method and, if necessary, add drug therapy, which will certainly provide excellent results, and the person will be freed from abulia.