Mycosis is a fungal disease that affects the skin, internal organs and bone tissue(nails, etc.). Foot fungus is one of the most common forms of this disease. According to statistics, every fifth person is a carrier of pathogenic microorganisms.
Forms of mycosis of the feet
The causative agents of this disease are saprophytes, molds, candida and other pathogenic microorganisms.
Main typespathogens:

Mycologists highlight four types of mycosis which can be caused by various foot fungi:
- Intertriginous or interdigital- the most common. Most often, the primary lesion begins with a fold of the large and index finger, further spreading along the foot. Possible causes of occurrence are contact with an infected person (surface), injury and failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- Squamous–hyperkeratotic. An advanced form of this foot fungus can cause deep cracks and damage to the tissue of the leg up to the ankle. It is noteworthy that at the initial stage of the disease there are no external manifestations. The sole does not itch or hurt; small cracks occasionally appear;
- Dyshidrotic or vesicular form– mycosis, which provokes the appearance of rashes and local erosions on the epidermis. It is transmitted exclusively from the patient and is extremely rarely diagnosed on the skin of the legs. It is believed that this fungus prefers the hands and palms. In the absence of proper treatment, mycotic eczema occurs due to exposure to pathogenic microorganisms;
- Erased form- the easiest of all described. It is characterized by slight itching between the fingers and slight peeling of the skin. The cause is the saprophyte Candida. Its incubation period is 2 weeks. Most often, patients simply do not notice signs of infection and spread the fungus. Even without treatment, the disease goes away on its own.
Symptoms and signs of foot fungus
Foot fungus is accompanied by onychomycosis - damage to bone tissue. It’s quite easy to “see” the symptoms on your own, so if you have the slightest suspicion of the presence of a fungus, you should immediately consult a doctor.

What symptoms indicate foot fungus infection:

It is important to pay attention to accompanying symptoms. First of all, this elevated temperature arms or legs. Mycosis significantly affects the nails: they become brittle, fragile, change their thickness and color.

How to treat foot fungus
Any organism, pathogenic or not, dies only if it is exposed to negative factors. To ensure quick recovery It is important to act comprehensively, using baths, ointments and tablets. Let's consider inexpensive and effective drugs for the treatment of foot fungus.
Medicines – ointments, creams and oils
Spray Domix Green Stop Fungus– varnish for the treatment of mycosis of nails and feet. It has a strong antifungal effect and helps disinfect shoes and clothes. Can be used to treat palms, nails and other affected areas.

– cream with the strongest fungicidal effect. The composition includes Terbinafine - active substance, to which dermatophytes and molds are sensitive. The product will help against chronic foot and toe fungus, as well as strengthen the nails and protect them from onychomycosis. Provides a preventive effect.

– a cream for foot fungus, will help to quickly get rid of old mycoses caused by yeast-like fungi. In addition, it treats excessive sweating and eliminates unpleasant odor.

Instructions on how to treat foot fungus with Bifosin:

The average duration of such treatment is 7 days, provided that the procedures are performed regularly.
- the cheapest ointment for foot fungus. The composition includes birch tar, castor oil and creroform. The product is used to treat mycosis on the heels, palms, nails and other parts of the body. Thanks to natural ingredients, it is used to treat skin diseases during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It has a pronounced irritating effect and may cause some discomfort when used: itching and burning.

– the best remedy for foot fungus. Its active components are Farnesol, Climbazole and oil. peppermint. The product is characterized by a powerful fungicidal and antimicrobial effect. In addition, it has a deodorizing effect, restores the nail plate, and helps relieve itching and burning.

Contains essential oil tea tree. Helps with local fever, scabies, pain. This product is rather a preventive component of treatment than the main one. They are recommended to treat the skin of their feet and hands when visiting swimming pools, saunas and gyms.

is a popular bactericidal ointment that is used at home to treat foot fungus, nail fungus and some types of lichen (red and ringworm). The product allows you to quickly heal microcracks, resume regenerative processes and normalize the functioning of the sweat glands.

– an antiseptic drug for the treatment of superficial mycoses of the feet, palms and nails. This is a solution that needs to be applied to the affected areas twice a day. Can be used during lactation, but is prohibited for use in children under 3 years of age. The composition contains powerful components, so the product is characterized by an aggressive effect. After application, a burning sensation or increased temperature may be felt on the epidermis. An analogue of the solution is Okomistin drops.

Stop active oil for foot and nail fungus– an effective medicine for the treatment of interdigital and through forms of the disease. Consists of completely natural ingredients: mumiyo and beaver musk. Sold in pharmacies and company stores. It has a softening and restorative effect, quickly relieves itching and swelling. But it is important to understand that this is rather a prevention of fungus than its main treatment.

– combined medical drug with antiseptic and antifungal properties. The solution is sold exclusively in pharmacies and has no analogues. Able to relieve itching and swelling after the first use. You need to take baths with it, a course once a day for a week. Previously, they used potassium permanganate instead, because it has a similar effect.

– a certified drug for the treatment various forms mycosis. Available in the form of drops and ointments. Contains naftifine hydrochloride. Included in the ranking of the most popular means for treating fungi in the CIS (data for 2016). Used to treat diseases on initial stages, as well as running forms.

- an ointment that provides complex action. It is used for the treatment of various mycoses (including lichen, thrush and onychomycosis). In addition to the cream, the dermatologist may prescribe Clotrimazole tablets to be taken orally.

– formaldehyde solution. The aggressive composition of the product destroys spores and prevents the development of fungi. Has an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect. The drug should not be used for cracks or other damage to the skin of the foot.

– iodine solution for skin disinfection. Used as additional measures in the treatment of fungal diseases. Necessary for cleansing the skin before applying the cream. It is successfully replaced by the more affordable Chlorhexidine.

– a popular remedy for the treatment of hydroperhidrosis. It includes boric acid, zinc, formaldehyde, glycerin and some other aggressive substances. To treat mycoses, the product should be applied to the epidermis twice a day in a thin layer.

– a good gel for mycosis. Contains bifonazole. This is a rather aggressive drug for fighting fungi. Approved for use during pregnancy and lactation, but only if there are appropriate instructions from a doctor. It has a locally disinfecting effect and quickly relieves symptoms of infection by pathogenic microorganisms.

Antifungal tablets
In addition to external medications, for effective treatment you need to take tablets for foot and nail fungus. They normalize work immune system and will allow you to destroy the mycelium from the inside.
– an active drug for the treatment of fungus. The composition includes Guanidine, which destroys spores and fungal microorganisms. The tablets can be used during pregnancy, but only after consulting a doctor. The course is a week.

– often used in folk medicine to treat sweaty feet, but it can also be used to remove fungus. Take 2 tablets per 1 liter of water, the procedure lasts 30 minutes. Repeat every day until symptoms disappear completely.

– antifungal tablets that block the ability of pathogenic microorganisms to reproduce. They are used to treat thrush, mycoses, lichen, and also as a preventive measure. The dosage regimen depends on the form of the disease. For sporotrichosis or mycosis of the feet, it is prescribed to take two tablets per day for a week. For thrush and other diseases caused by fungi - from 1 to 4 capsules.

Effective folk remedies
You can cure fungus at home without visiting a doctor or getting tested. Although, this requires serious effort and time. In addition, you need to understand that different organisms may react differently to the chosen method of combating them. In some cases, home remedies will only contribute to the localization of saprophytes.

Successful treatment with folk remedies is a combination of proper cleansing of the integument, destruction of pathogenic microorganisms and restoration of the epidermis. To cleanse and disinfect the skin, we recommend taking baths and wiping your feet and palms with antiseptic agents several times a day.

The list of bath cleansers includes:
- Boric acid;
- Apple cider vinegar;
- Hydrogen peroxide.
For 1 liter boiled water 20 grams of the selected component are taken. Rinse your feet in this solution for 20 to 40 minutes. Repeat baths every day.
To get rid of itching and slow down the rate of spore development, you need to wipe your feet with a mixture of baking soda and salt. To prepare an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory scrub, you need to take an equal amount of minerals and any antibacterial essential oil (celandine, tea tree, wormwood). The components are connected to each other, after which the areas between the toes, heels, feet, and palms are treated with the mass.

Helps against any mycoses tar soap. It contains birch tar, which has strong antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. The easiest way to get rid of fungus with it is to treat the affected areas with soap foam and leave for 5 minutes. Afterwards, rinse and moisturize the skin surface with cream or zinc ointment. The course of treatment is 14 days.

Good way remove flex from the skin of the feet - a compress with oil and garlic. You need to mix the components in equal parts and apply the mixture to the infected parts of the body. To prevent the mixture from smearing on clothes, the legs are additionally covered with polyethylene. It is best to do the mask at night. The duration of the course is until the symptoms disappear completely.

Regular sour cream will help cure foot, hand and nail fungus. It contains lactic acid, which burns the mycelium. You just need to spread it on the skin and leave until completely absorbed. It is important to ensure that the compress has a secure hold; a sock and a plastic bag are suitable for this. This method can be used for diabetes, pregnancy and cracked heels - it is absolutely safe.

Tips on how to speed up the treatment of fungus and prevent its further occurrence:

We have already thrown off the boots that have become boring over the winter and happily put on low shoes, shoes and sneakers. Soon, very soon, the time for sandals and flip-flops will come, and then... What happened, why does the skin of the foot constantly become keratinized and peel off, painful cracks appear on the heels and big toes, and the nails have changed color in some places or seem to have become thicker? Not only is it ugly and unpleasant: everything listed signs may be characteristic of fungal infections of the skin of the feet and nails. And it’s not at all necessary that we were inattentive, messed something up or made an annoying mistake this winter: fungal diseases of the feet often “die out” in the cold season, but worsen with the arrival of warmer weather.
According to various sources, from 10 to 30% of the planet's population suffers from fungal diseases of the skin and toenails. The general name for fungal skin lesions is ringworm, nails – onychomycosis. Many of these diseases are highly contagious: you can get this “bonus” when visiting swimming pool, sauna, hotel shower, if the staff is not very concerned about disinfection issues, or when doing pedicure in case of poor disinfection of instruments in the salon. You can become infected through "guest" slippers, having bought a pair shoes in a second-hand store or even trying on shoes in a store after a sick person. Fungal infections are easily transmitted through bath accessories ( washcloths, sponges, pumice stones, towels), and also through mats and another sports equipment(there is even a definition "athlete's foot" ). And this is not only a cosmetic problem: in the process of life, toxins are released, which are carried throughout the body by the flow of blood and lymph. These substances can negatively affect all organs and systems and significantly reduce immunity.
Factors that contribute to fungal infection are considered to be:
- general condition of the body (presence of chronic infectious or somatic diseases);
- stress and neurological diseases;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- long-term use antibiotics;
- decreased immunity due to the above or other reasons;
- age;
- excessive sweating of the skin of the feet;
- disturbance of peripheral circulation;
- , congenital deformity feet.
Children have thinner skin, their defense mechanisms are not yet fully developed - therefore, they are more likely to contract fungal infections, but in practice, dermatomycosis is more common in adults, especially men. A decrease in immunity can lead not only to infection by fungi from the outside, but also to the activation of opportunistic fungal microorganisms, which are normally present on the skin of any person. Warmth and humidity are ideal conditions for fungi to bloom in full bloom, so constantly wet feet in shoes are an ideal breeding ground. Uncomfortable shoes injure the skin of the feet, opening the entrance “gate” for infection.
Doctors distinguish three types of tinea pedis depending on the causative agent of the disease:
- athlete's foot(causative agent - Epidermophyton floccosum) , causes damage to the skin of the feet and nails;
- trichophytosis (rubromycosis, pathogens - Trichophyton interdigitale, Trichophyton rubrum ) also affects the skin of the feet and nails;
- candidiasis (or candidomycosis, pathogen - Candida albicans ); This well-known opportunistic fungus, under proper conditions, can affect many organs and systems, including causing mycosis of the skin of the feet and nails.
First two ringworm have similar clinical signs and are usually treated with the same drugs, so they are often combined common name "mycoses of the feet".
According to the form of the disease, the following classification is accepted:
- squamous form, sometimes also called scaly. Many patients with this form of mycosis of the feet do not initially experience any discomfort, do not suspect that they are sick and, accordingly, do not consult a doctor. However, such a patient is contagious and poses a danger to others. There is a reddened area on the skin of one foot, then it begins to peel off, but there may be no itching at all. Gradually, the entire skin of the foot becomes extremely dry, quickly becomes keratinized, and cracks appear on the heel or the outer lateral surface of the big toe. Over time, the disease spreads to the other foot and can develop into dyshidrotic form;
- dyshidrotic form. On the lateral surfaces of the foot and its arch there are vesicular rashes with a diameter of individual vesicles of 2-8 mm, which subsequently merge and burst to form erosive ulcers, the patient complains of their pain and itching; after the ulcers heal, the skin begins to peel off and the dyshidrotic form turns back into the squamous form; this process of transition from one form to another can occur repeatedly, however, at any moment, dyshidrotic fungal infection can be complicated by bacterial infection - then the liquid in the blisters becomes cloudy, over time the discharge becomes purulent, which is accompanied by edema, severe pain, increased body temperature;
- intertriginous form. Of all the forms, it is the most common; as a rule, cracks appear between the 4th and 5th toes (rarely between the 3rd and 4th), bordered by a convex rim of dead epidermis, the skin between the toes becomes wet, the patient complains of burning and itching; later the cracks are replaced by painful areas of erosion; this form is chronic, with partial winter remission and exacerbation in the warm season; gradually the skin on the affected areas becomes loose, its protective functions are already sharply reduced, and these are excellent conditions for infection with streptococci - purulent inflammation skin with erythema, pain, swelling and a general increase in temperature.
Candidiasis on the skin of the feet it surprisingly resembles in appearance intertriginous form of mycosis: the same erosions between the 4th and 5th or 3rd and 4th toes with a whitish rim, itching and burning are also possible, but the difference is in the nearby small pustular rashes.
All of the above forms of mycosis of the feet And candidiasis may further complicate onychomycosis, damage to the toenails. Onychomycosis happens hypertrophic When the nail plate thickens and crumbles, under the affected nail there is also thickened skin with signs of peeling. It is possible that the nail may grow ingrown and cavities with tiny contents may form along its edges. It also occurs atrophic onychomycosis when the nail plate becomes thin and can peel off completely, and in its place there is keratinized skin.
Onychomycosis is also known when the nail plate is affected. mold fungi , however, most often this is a secondary infection from other fungal nail infections. At the same time, the nail changes color from yellow-green to brown-black, it is possible paronychia– purulent inflammatory process in the nail bed.
Both candidiasis and mycoses of the feet are treated long and tediously, with possible relapses diseases. This is explained primarily by the fact that the very development of fungal infections occurs against the background, they also additionally “nail” the immune system. As for onychomycosis, let’s be realistic, no matter what the manufacturers of medicinal varnishes, films, drops, sprays and creams promise, final recovery will not occur until the affected nail plate is completely removed. According to the doctor's indications, this is done either surgically, or independently, using agents that destroy the nail and further filing it down.
For the treatment of mycoses of the feet, drugs based on terbinafine(also effective against candidiasis), itraconazole(can also be used for all types of fungal infections), natamycin(all fungal diseases), econazole(foot mycoses and molds), naftifine hydrochloride(besides wide range action, also has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. Unfortunately, clotrimazole Today it is ineffective, since it can only be used topically. For successful treatment, doctors recommend using potent drugs in loading doses in short courses, with long breaks between them, and a mandatory combination of systemic antifungal drugs with local ones.
From traditional medicine, after consultation with a doctor and in the absence of an allergy to iodine, you can use salt baths followed by treatment of feet and nails iodine. This is done like this: add 2 tbsp per liter of hot (70 C) water. l. salt and 1 tbsp. l. baking soda and steam your feet in the resulting solution for 30 minutes. Then the feet are thoroughly cleaned with a pumice stone or an abrasive grater, the nails are trimmed and filed down as much as possible, all procedures are best done with gloves. After the bath, your feet should be washed with soap, dried and iodine applied to the entire surface of the foot, between the toes, on the filed nail and under the nail folds. After drying, iodine is applied to the affected areas three times, and also to filed nails. In between treatments during the day, be sure to use a softening foot cream. This treatment is continued daily for a month.
And of course, when treating fungal infections of the feet and nails, one cannot do without disinfecting shoes 1% chlorhexidine solution, 25% formalin solution or 40% solution acetic acid . It is recommended to boil the patient’s socks and iron them thoroughly. To reduce the risk of infecting family members, the patient’s linen is washed separately, he must wear closed slippers, use his own washcloth and towels, and thoroughly wash and disinfect the bathroom after himself.
Fungal diseases are easier to prevent than to cure, follow simple preventive measures: wear only your own shoes, take a change of shoes (including slippers) with you, do not walk barefoot in the sauna or pool, do a pedicure with your own set of tools, do not use other people’s towels and washcloths.
Good health to everyone!
Mycoses- a group of skin diseases caused by various fungi. The diseases have many similarities, although there are differences in the routes of infection and the symptoms that these diseases manifest. The principles of treating all fungal diseases are the same.
Fungal diseases of the skin and nails belong to a class of human infectious diseases that are caused by pathogenic fungi. Fungal infections (mycoses) come in different forms, but skin and nail infections are among the most common mycoses. This - infectious disease, which is transmitted from person to person.
Fungi reproduce in neutral or weak alkaline environment. The most suitable pH value for them is 6 - 6.7. It should be emphasized that skin pH healthy person is 5.5 (an acidic environment is not favorable for fungi), which is one of the factors protecting human skin from fungal infections. Increased sweating is precisely a risk factor for fungi, precisely in closed areas of the skin, where the evaporation of sweat is very difficult, and this is where some fungal diseases develop, accompanied by a shift in the pH of the skin to the alkaline side.
Fungi easily survive low temperatures. They do not die and retain the ability to provoke the development of the disease even after freezing. Elevated temperatures, on the contrary, have a detrimental effect on fungi. Humidified heat at 75 degrees provokes their death within 15 minutes. When boiling, the fungi die within 3–5 minutes. Therefore, elevated temperatures can be used for fungal diseases as a method of disinfection, and therefore, to prevent relapses of the disease, during and after full antifungal treatment, doctors strongly recommend boiling and ironing the patient’s underwear and clothes that have been in contact with the skin with a hot iron.
Fungi require a moist environment to reproduce and grow. That is why increased sweating and wet shoes are predisposing factors in the formation of fungal diseases, and the main way of infection with foot fungi is in swimming pools, baths and showers, on the damp floor of which fungi find very good conditions for their existence. Fungi, causative agents of human mycoses, survive drying well. It does not kill them, but only delays or stops their growth and development for some time. In dry hair and scales that the patient loses from the surface of the lesions, fungi remain viable for years (for example, on the floor or in carpets, in clothes or shoes). Subsequently finding themselves in suitable conditions (for example, on human skin), they again acquire the ability to grow and reproduce and can cause the formation of a disease.
In a 1% formaldehyde solution, fungi die within 15–20 minutes (it is used to disinfect shoes). In a chloramine solution, the death of mushrooms occurs in 30–40 minutes (used to disinfect objects).
Infection with fungi occurs through contact directly from a sick person or animal (direct route of infection through consumption by the sick person, or infected scales or hairs of sick animals (indirect route). The most significant factor in the formation of fungal skin diseases is age. It has been established that microsporia, known more widely population called " ringworm» infects mainly preschool and younger children school age and extremely rarely develops in adults.
Another group of fungal diseases - mycoses of the feet and nail fungus, on the contrary, infects mainly adults and is extremely rare in children, which also has its justification and is associated with age-related changes Skin pH, thickness and structure of the stratum corneum of the epidermis, weakness immune defense and skin resistance against the background of diseases that develop with age. Very great value for the formation of a fungal disease has a change in metabolism, which is associated with obesity, other endocrine disorders, and primarily with diabetes mellitus, diseases of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by changes in digestion and absorption of nutrients.
Nail fungus
Nail fungus (onychomycosis) is caused by fungal infections that are easily transmitted from person to person. Often, infection of nail fungus occurs in the family - through shared shoes, but sometimes through other household items. Infection occurs with equal frequency in public places: in bathhouses, showers, gyms, gyms, and swimming pools.
Nail fungus is an extremely resilient infection, and over time it damages all parts of the nail, destroys it, and spreads to other nails or skin. Nail fungus causes infection in other parts of the body. Even if all foci of nail fungus are cured, re-infection will occur from one unnoticeable foci of infection in the nails.
External signs Nail fungus consists of a change in the color of the nails, their hardening, and subsequent crumbling or destruction. Nail fungus turns nails white, gray, yellow, brown, sometimes black or green. The nail plate becomes cloudy because the fungi themselves are located between it and the base of the nail.
Compaction with nail fungus is caused by increased keratinization of the nail bed, this is a reaction to the invasion of the fungus. Horny masses in the nail grow over time and interfere effective treatment.
Untreated nail fungus leads over time to the penetration of the fungus into the entire thickness of the nail plate and to its delamination. Destruction of the nail plate from the free edge is observed at the same time as thickening. External changes caused by nail fungus are confirmed by mandatory laboratory examination of skin flakes or nail pieces.
Foot fungus
Many people find out about foot fungus when a medical certificate is needed, or aesthetic and physical torment has already begun. But such a frivolous attitude is unjustified, because foot fungus, like any advanced disease, threatens with more serious problems. For example, many types of foot fungi synthesize toxic substances, which means that toxins will accumulate in the body.
You can only become infected with foot fungus from an already infected person, who is a source of infection for others, and, firstly, for his family - through pedicure and manicure accessories, towels, shoes, socks. And then in public places - swimming pools, gyms, locker rooms, saunas, where infected scales from the floor easily stick to the wet skin of the feet.
To diagnose the presence of foot fungus, you need a dermatologist. There are many types of fungal damage, and only he can determine which fungus has affected the skin and nails. In addition, the diagnosis of foot fungus necessarily includes a laboratory examination of skin scales.
Treatment of nail and foot fungus
Treatment for nail fungus not so long ago consisted only of eliminating the nail plate. The problem was that the new nail often grew with fungus. Now operative method Treatment of nail fungus can be prescribed for some forms of severe onychomycosis.
Also, complex medicinal compositions for the treatment of nail fungus have long been preserved, which contained acids (salicylic, lactic), dyes (blue, brilliant green), iodine, vinegar and sulfur. All this was used in the form of various solutions, liquid ointments, plasters, peel-offs and varnishes. The treatment lasted a year, or even more.
But all of the above cannot be compared in effectiveness with modern antifungal drugs that kill the fungus, and sometimes with additional methods that help improve the condition of the nail itself. True, the effectiveness of treatment for nail fungus varies significantly even today, depending on the competence of doctors and their use of the latest advances, as well as on the phase in which patients contact the doctor, compliance with the treatment regimen, sometimes quite long, and compliance with precautions after the cure has occurred.
The newest antifungal drugs not only actively affect the fungus, stopping the development of mycosis, but also remain in the nails for a long time, which allows reducing the treatment period. Modern antifungal drugs are usually taken for 2-4 months (instead of 6-12), and in the most progressive regimens (pulse therapy) - several weeks.
Medications for nail fungus come in the form of oral preparations - capsules and tablets, and local forms- nail polishes and peel-off patches.
Antifungal varnishes for topical treatment of nail fungus are applied only 1–2 times a week. For severe forms, new external forms are combined with treatment with capsules or tablets. Combination preparations have emerged where antifungal components are combined with components that soften the horny masses. This makes it possible to combat nail compaction. Recently developed devices for hardware processing - modified drills with special cutters for nails - can also cope with this task. The doctor selects a specific treatment regimen individually each time.
A serious problem during and after treatment of nail fungus is the disinfection of everything that the fungus has come into contact with - floors, walls, equipment in baths, showers, bathrooms, as well as personal items: underwear, shoes, skin and nail care items.
And yet, the most effective way to combat nail fungus is primary prevention. To avoid nail fungus infection in the family, you must follow simple hygiene rules and use only your own shoes. You should not go without shoes in public places. There to warn probable illness, you can use antifungal drugs - sprays and aerosols, with which it is convenient to treat the skin of the sole and interdigital folds. But the main thing is to always monitor the health of your feet, wearing comfortable shoes that are not tight and do not provoke a lot of sweating, and regularly care for the skin of your feet and nails, at least at home.
The main thing in treating foot fungus is to consult a doctor in a timely manner - in the early stages, treatment is easier and faster. Modern medicines for the treatment of foot fungus they promise to get rid of it in the shortest possible time and in the most effective methods. The action of most of them is directed against several of the most common types of mushrooms. Side effects of new drugs are minimal. The choice of medications for the treatment of foot fungus is quite wide, and consists of systemic and local antifungal drugs. Local remedies for the treatment of foot fungus include creams, sprays, lotions, aerosols, and powders. They are easily applied to hard-to-reach spaces between the fingers and skin folds. Often, especially in advanced cases, the treatment regimen includes the prescription of both local forms and tablets.
Actinomycosis of the skin
called various types actinomycete fungi. In nature, fungi live mainly on cereals, their spores for a long time are stored in hay, so the risk of disease is high for people working with grain and hay. Fungal spores can enter the respiratory and digestive system. Depending on how the infection penetrates the skin, primary and secondary actinomycosis are distinguished. In primary actinomycosis, infection occurs through damaged skin; in secondary actinomycosis, the pathogen is introduced into the skin from other affected organs through the lymphatic system. Most often, actinomycosis affects the submandibular and sacrogluteal areas, and can appear on the face. Deep, painless lumps form in the thickness of the skin, which over time acquire a bluish-red color; after their opening, fistulas form. Over time, they scar, but new ones form nearby. Sometimes ulcers appear that have soft bluish edges and an uneven bottom with plaque. The disease is dangerous due to its complications - meningitis, damage to the liver, lungs, and intestines.
Candidiasis
caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. Decreased immunity, chronic diseases, predispose to the disease, long-term treatment antibiotics. The fungus can affect large folds of skin, especially under the mammary glands, inguinal-femoral, intergluteal, anus, navel, post-auricular folds, vagina, glans, foreskin of the penis. In obese people, the folds of the abdomen may be affected. Interdigital erosion on the hands occurs almost exclusively in women, which is associated with working conditions. Large areas appear first white, which quite quickly turn into weeping red erosions with a whitish peeling border around the edges. Painful cracks are visible in the depths of the folds, itching and burning are disturbing. Candidiasis on the mucous membranes looks like small plaques or whitish deposits.
Pityriasis versicolor
Microsporia (ringworm)
A fungal disease of the skin and hair that mainly affects children. The main source of infection is cats (especially kittens), and less commonly dogs. It is transmitted through contact with an animal or through objects contaminated with hair or scales containing fungus. Infection from a sick person is rare. Spots, small nodules and blisters appear on the skin, covered with scales and crusts. Large, rounded areas of baldness are noticeable on the head. All hairs are broken off at a level of 4-8 mm, and it seems as if they have been trimmed, which is why this disease is called ringworm.
Rubrophytia
The most common fungal foot disease. Infection occurs from a sick person through direct contact and through common objects. May affect the hands. The soles of the feet and palms become dry, rough, and the skin becomes keratinized. Feels itchy. If the skin outside the feet and hands is affected, spots of rounded outlines, with sharp boundaries, bluish-pink color with a brownish tint and peeling are visible.
Favus (scab)
Fungal disease of the skin, hair and nails. The source is a sick person. Weakening of the body as a result predisposes to illness chronic diseases, various kinds of poisoning, malnutrition and insufficient nutrition. Occurs at any age.
The affected hair becomes thin, dry, dull and dusty, but it retains its length. A peculiar yellow-gray crust with raised edges is formed, which gives it a resemblance to a saucer; hair grows from the center. A “mouse” (“barn”) smell emanating from patients is characteristic.
Athlete's foot
Fungal skin disease. Distinguish athlete's foot inguinal and athlete's foot.
Inguinal athlete's foot is usually transmitted through care items: bedpans, washcloths, sponges, oilcloths and others. The disease affects large folds, especially the inguinal-femoral and intergluteal folds, and may affect other areas of the skin and nails of the feet. Spots of round shape, red-brown in color appear, usually located symmetrically, clearly demarcated from the surrounding skin by an edematous ridge covered with small bubbles, crusts and scales. Itching, burning, and pain are felt, especially when walking.
Athlete's foot affects the skin and nails of the feet only, often accompanied by allergic rashes. Adults usually get sick. The disease begins with small cracks in the skin of the interdigital folds of the feet and peeling; blisters may form, sometimes merging into large multi-chamber blisters on the soles, especially in the area of the arches.
Erythrasma
A skin disease that mainly affects the legs. Most often, the source of infection is a sick person, but infection from the soil while walking barefoot is also possible. Predisposing factor - increased sweating. It is usually observed in adults, more often in men. It usually affects large folds, especially the inguinal-femoral folds. Large brick-red spots of rounded outline appear, sharply demarcated from the surrounding skin. Their surface is smooth, sometimes covered with small, scanty scales.
Treatment of mycoses.
The basis for the treatment of skin mycoses are antifungal drugs and antimicrobial agents. Personal hygiene is required ( You cannot use shared household items - towels, bed linen, slippers). Vitamin preparations are prescribed.
MEDICINES USED IN THE TREATMENT OF MYCOSES (AS PRESCRIPTED AND UNDER DOCTOR SUPERVISION)
Antifungal drugs
Amphotericin B (Amphostat, Fungilin, Fundizon, Saramycytin, Vencidin) Ketoconazole (Nizoral, Oronazole) Clotrimazole Levorin Mycoheptin Nystatin (Anticandin, Fungicidin, Fungistatin, Micostatin, Nystafungin) Fluconazole (Diflazon, Diflucan, Medoflucan, Myco-
max, Mikosist, Fluzol, Flucosan, Flucostat, Forkan, Fungolon, Tsiskan)
Ointments and solutions for external use
Griseofulvin Levorin ointment Mycozolon Nystatin ointment Triderm
Infection with fungi occurs either from a sick person or animal, or through objects that were used by patients. The skin is affected, usually the feet, palms, nails, and hair.
When skin fungi infect the skin, vesicles the size of a pea first appear, and gradually they expand, sometimes covering the entire surface of the foot or palm. Most patients experience itching. When nails are infected with fungi, a yellow spot or stripe appears at the free edge of the nail. Then the nail plate thickens, acquires a gray-yellow color, and crumbles easily. If the disease lasts for a long time, the nails can practically collapse. When the hair is damaged, flaky lesions appear on the head and the hair becomes brittle.
For mycoses, antifungal drugs are prescribed internally and externally.
Non-traditional and folk recipes for the treatment of mycoses
Home remedies for mycoses
Lubricate the affected areas with a 20-30% alcohol solution of propolis.
Wipe fungus-affected areas with onion juice.
Crush several onions and apply this paste to the fungus-affected areas.
For mycosis of the feet, mix 1 tablespoon of carrot juice and vinegar essence and lubricate the affected areas with cotton wool wrapped on a wooden stick and moistened with this mixture.
Mix equal parts garlic juice and 90-degree alcohol, add distilled water. The mixture is very strong antiseptic, it is useful to use as an external remedy against persistent infectious and fungal skin lesions that are not sensitive to drugs.
Garlic compresses treat fungal diseases, which are generally very difficult to treat. In addition to external treatment with garlic, you should also take garlic preparations internally. Garlic tea, garlic infusion and garlic tincture help. The result for mycoses is in 3-4 days.
If you have mycosis of the feet, you should wash your feet well and immerse your feet in strong wine vinegar. Go to bed wearing socks soaked in vinegar.
For fungi on the feet, corns, calluses and others skin rashes on your feet, running barefoot through the morning dew for at least 20-30 minutes is considered a very good folk remedy. After running, they do not wipe their feet, but wait until they dry themselves. Additionally, at night, it is recommended to massage the affected areas with freshly prepared potato juice or at least a slice of raw potato. The course of treatment for mycosis is 1 month, noticeable improvement occurs after 10 days.
Herbs and mixtures for the treatment of mycoses
Grind peppermint leaves along with table salt. Place the mixture between your toes for about 1 hour. Repeat the procedure until the fungus disappears.
Pour a bunch of milkweed grass (the whole plant) with 2-3 liters of boiling water, leave for 1-2 hours, wrapping it in a warm blanket. Keep feet affected by fungus in hot infused water for 30-40 minutes. Trim well-steamed nails with scissors. Repeat baths every 2 days until the fungus completely disappears.
Pour 10 g of common lilac flowers with 0.5 cups of alcohol. Leave for 10-15 days. Apply the resulting tincture to the areas affected by the fungus.
Grind the leaves of the common cocklebur and squeeze the juice out of the pulp. Apply juice to areas affected by fungus.
Mix 3 parts of oak bark, 2 parts of verbena herb, blackberry fruits, calendula inflorescences, horsetail herb. Pour 3 tablespoons of the mixture with 1 glass of water, boil for 15 minutes, strain. Warm decoction is used for rinsing lotions for mycoses.
For fungal diseases of the feet, mix equal parts of blackberry leaf, calendula flowers, horsetail herb, verbena herb and oak bark. Pour 10 g of this mixture with 1 glass of water, boil for 15 minutes, stand for 2 hours and strain. Make compresses and lotions, and also take 1 tablespoon orally 4 times a day
Vanga's recipes for fungus of hands, feet and nails
Fungus on hands
- Brew strong coffee (do not throw away the sediment), hold your hands in the coffee several times. You can also use this recipe to treat fungal infections of the feet, as well as to remove thick, flaky skin on the heels and for pain in the feet and ankles.
- Lubricate the sore spots with milk of any type of milkweed. The juice of this plant is used in the treatment and removal of warts, moles, non-healing ulcers, nail fungus, and lichen.
- Take a hot pepper, first cut off the bottom with the tail, remove the seeds and fill with strong rakia (Bulgarian vodka). Place the sore finger in there, and try not to let the brandy spill out, then bandage the finger. It is best to leave the bandage on overnight, but since this procedure is very painful, you need to keep it on as long as the patient can tolerate. Recovery occurs very quickly.
- Onion juice: grate the onion on a fine grater or pass through a meat grinder, squeeze out the juice and mix with honey in a 1:1 ratio. Store in a glass container with a ground stopper. Lubricate sore spots.
- Decoction of Veronica pilosa: pour 100 grams of Veronica pilosa herb into one liter of boiling water, boil for 15 minutes in an enamel bowl, let cool. Store for no more than two days. Use for baths, compresses and lotions.
- Mix grated garlic with fresh butter in a 1:1 ratio. Apply the mixture to the sore spot and change once a day until recovery.
- Birch tar – 25 g, protein chicken egg– 1 pc., sulfur – 1 teaspoon, honey – 25 g. Mix everything – use the ointment for eczema and fungal infections of the skin.
Fungus on feet
- Dip well-washed feet in strong wine vinegar. It is recommended to wear socks soaked in vinegar at night.
- Garden milkweed decoction: pour 100 grams of milkweed herb into one liter of boiling water, cover with a lid, and simmer for 10 minutes over low heat. Then cool for 20 minutes and strain. Pour the warm broth into a basin and steam your feet.
- Infusion of garden milkweed: put one kilogram of garden milkweed along with the roots in an enamel bucket, add hot water, boil, wrap the bucket warmly, leave for 25 minutes. Soak your feet with warm infusion.
- Grind the mint in a mortar with salt and place this paste between your fingers for about an hour. Repeat this procedure until the fungus disappears.
- Rub lemon juice on the sore spot.
- The juice from several cloves of garlic should be squeezed out using a manual juicer. Add an equal amount of 90% alcohol and 10 times the amount of distilled water. This is a very powerful remedy.
- One of the best means is walking barefoot in the morning dew for 10 to 14 days.
- It is very useful to take cool foot baths. Add one tablespoon to water baking soda and salt. Keep your feet in the water until completely cool, then rinse them with clean water.
Fungus on the skin of the feet is a very common infection. Fungus on the feet is distinguished by its vitality and ease of development. Based on statistics, 20% of the planet's population suffers from fungus.
What is skin fungus?
Can't deal with fungus?
Nail fungus, like all other fungal diseases, is contagious. The disease can manifest itself even in those who healthy image life.
At the first symptoms of nail fungus, you should immediately begin treatment. If the disease starts, the nail peels off, changes color, shape, crumbles and noticeably thickens.
It has the following properties:
- Penetrates freely under the nail and inter-nail spaces
- Has an antibacterial effect. Relieves itching and inflammation in 1 application
- Removes cracks and itching between fingers thanks to propolis
- Destroys spores due to poultry alkaloids
- Golden mustache restores healthy nails
 Stories from our readers!
Stories from our readers!
"For a long time I experienced discomfort from dandruff and hair loss. Standard shampoos helped, but the effect was short-term. But this complex was recommended by a friend who used it herself. An excellent product!
The skin stopped itching, the hair combed well and was not so greasy. The loss stopped fairly quickly. I couldn’t even dream of such an effect! I recommend."
Treatment
Treatment of a fungal disease should be started only after full diagnostics a specialist who must prescribe various drugs for treatment of this disease. Treatment of foot fungus can involve several methods.
These methods include:
- Systemic therapy.
- Local therapy.
- Folk remedies.
It's worth taking a closer look at each of them.
Systemic therapy
Systemic therapy means taking various antifungal drugs. Such medicines penetrate the blood and kill the fungal infection. Such products are also able to penetrate the nail plates, which can remain there for several weeks, gradually killing the fungus.
Effective remedies for foot fungus
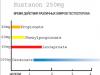
Effective means of combating fungus are considered terbinafine and itraconazole. These systemic drugs can cure a patient in two weeks.
Dosage of these drugs:
- Inraconazole – 2 tablets of 100 mg per day for 7 days.
- Terbinafine – 250 mg every day for 10-20 days.
It is important to note that systemic therapy is not prescribed to the following persons:
- Pregnant women.
- For nursing mothers.
- Persons suffering from liver diseases.
- Elderly people with concomitant diseases.
Ointments and creams
Systemic treatment of fungal diseases is recommended to be combined with local therapy. TO this method Treatments include various creams and ointments that can also have an antifungal effect. However, it is worth paying attention to the fact that if creams and ointments are used without systemic drugs, then treatment may be ineffective.
Local medicines to combat fungal infections are divided into 20 forms. In addition to creams and ointments, various sprays, gels, foams and varnishes are also used to treat foot fungus.
So, the following remedies are most often prescribed:
- Terbinafine ointment has gained leadership among other topical drugs. This product can kill mycoses of any type. The use of terbinafine provides a lower percentage of the likelihood of disease relapse. Terbinafine may have a toxic effect on the human body, but it will be minimal.
- The drug "Lamisil" ranks second in popularity and effectiveness and has minor side effects.
- For interdigital fungus, sprays and gels are usually used, which are applied to clean skin no more than once a day for a week. Sometimes treatment of interdigital mycosis is extended for the same period.
- To treat the erased form, creams, ointments and foams are prescribed, which are capable of creating a protective layer for the whole day.
When using local treatment for fungus, it is worth remembering that after applying any product to the skin, you do not need to wash your feet for 24 hours.
Other drugs that are prescribed for the treatment of foot fungus:
- Itraconazole
- Mifungar.
- Mikoket.
- Clotrimazole.
- Bifonazole.
- Oxiconazole.
- Miconazole.
- Econazole
Folk remedies
You can also cure foot skin fungus using folk remedies. To do this, you need to familiarize yourself with them in more detail.
Folk remedies for the treatment of nail fungus:
- A piece is applied at night kombucha to the affected nails.
- Attach a cut Kalanchoe leaf to your nails overnight.
Folk remedies for treating fungus between the toes:

Folk remedies for the treatment of foot skin fungus:
- Lubricate the affected areas of the skin with juice at night. onions A.
- Make a compress at night from propolis tincture 20%.
Folk remedies for the treatment of foot fungus:
- Make sea salt foot baths twice a day.
- Three times a day, take foot baths made from a decoction of chamomile, oak bark and calendula.
Prevention
Foot fungus most often causes sweating. Even in the cold season, the causative agent of the fungal disease is well preserved. But high temperature can kill the infection, so one of the methods of prevention is boiling. Another prevention method is disinfecting shoes with formaldehyde. With this action, the fungus dies within 20 minutes.
The fungus only creates discomfort. However, you should not ignore this infection. If the disease becomes severe, it may lead to pain and the development of other infections.
Foot fungus (mycosis, dermatomycosis) is an infectious disease that affects the skin of the foot and the areas between the toes. Often the pathology is combined with nail damage - onychomycosis. Mycosis is caused by microscopic fungi, dermatophytes, molds and yeast strains.
If left untreated, the fungus spreads from the foot to the entire limb. This increases the risk of developing erysipelas, formation of warts and increased frequency allergic reactions from the skin and mucous membranes. The body stops accepting antibacterial drugs, which complicates the treatment of other diseases.
Causes of foot fungus
Infectious foot fungus is usually caused by dermatophyte ascomycete fungi. Some strains cause rubrophytia and rubromycosis, accounting for more than 70% of mycosis diagnoses. About 10% of the entire population of the planet suffers from athlete's foot, the causative agent of which is Trichophyton mentagrophytes.
Molds and yeast-like fungi affect the extremities less frequently, accounting for up to 1.5% of cases.
What are the reasons for foot fungus infection?
- Somatic pathologies.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Hypothermia of the legs.
- Diabetes mellitus with diabetic foot symptom.
- Dermatological diseases - psoriasis, neurodermatitis, eczema.
- Hallux valgus and other pathologies of the foot.
- Visiting public places where you have to walk barefoot (saunas, swimming pools, fitness centers).
- Increased sweating of the skin of the feet (congenital hyperhidrosis or caused by other diseases).
- Decreased immunity in children and the elderly. In the 2nd group of patients, men are more likely to encounter the fungus if their toenails are already affected by onychomycosis.
- Abuse of funds antibacterial therapy, glucocorticoids, cytostatics, immunosuppressants. The factor has a detrimental effect on the immune system and increases the incidence of mycotic infection.
- The occupational factor in the development of mycosis means the possibility of infection of workers in bathhouses, swimming pools, the metallurgical and coal mining industries, athletes, and military personnel.
- Injury to the skin of the feet, leading to the appearance of calluses, cracks, and corns.
Favorite places on the foot for fungus with the subsequent formation of warts are areas of callus and hyperkeratosis. Localization is explained by the deterioration of local immunity, which has lost control over the development of human papillomavirus infection.
Clinical forms of foot fungus
The external symptoms of foot fungus depend on the type of strain causing the infection and the extent of involvement of the skin, nails and hair on the feet. Athlete's foot and rubromycosis have a similar course, so doctors combine them into “mycoses of the feet.”

Dermatologists distinguish the following types of foot fungus:
Let us describe what foot fungus looks like in the squamous form. At the initial stage, redness and peeling of the skin are observed. The modified areas have different areas. Itching does not occur in all patients.

Most patients do not notice any signs of mycosis at all. They do not go to the clinic, and this gives the pathology the opportunity to change its scaly form to a dyshidrotic one.
For dyshidrotic foot fungus visible symptoms There will be multiple bubbles with a diameter of 2 - 8 mm. They merge into large foci, open up and form erosions.

From the arch of the foot, the fungus spreads to the outer and inner lateral parts. In addition to extensive erosion, diaper rash forms at the site of burst blisters. Patients complain of soreness and itching and notice flaking.
If left untreated, a fungal infection becomes complicated by a bacterial one. Signs of secondary infection are clouding of the contents of the blisters with transformation into a purulent mass, increased body temperature, swelling and significant redness of the skin.
Intertriginous mycosis of the feet is considered the most common. It develops independently or against the background of a squamous form. Affects the skin between the 4th and 5th toes, less commonly develops in the interdigital space of the 3rd and 4th toes.

The main symptoms of intertriginous foot fungus:
- Itching and burning.
- Cracks in the skin in a whitish rim (the border is formed from exfoliating epidermis).
- Wetting between the toes of the affected limb.
- Replacement of cracks with erosions with severe pain in the area.
- Loosening of the skin with a subsequent decrease in local immunity. Streptococci penetrate into the loose structure and cause pustular inflammation of the skin. The tissues swell, turn red, and pain increases. The patient's general condition worsens.
Symptoms of candidiasis of the feet are interdigital erosions formed due to the activity of the fungus of the genus Candida. Changed lesions are visible between the 3rd and 4th or 4th and 5th fingers of the lower extremities.

The diseased skin becomes swollen. It is separated from healthy tissue by a “belt” of exfoliated epidermis. The problematic neighborhood consists of pustules and blistering rashes.
If the fungus affects, the patient is diagnosed with onychomycosis. At the initial stage of the pathology, yellow stripes and spots are visible on the free edge of the big toe nail. Hypertrophic onychomycosis is characterized by thickening and fragility of the plate, under which flaky skin is visible.

With atrophic onychomycosis, the nail structure is destroyed. Hardened skin is exposed under the modified plate. If onychomycosis develops as a result of infection of the foot by mold fungi, the nail plate becomes brown, black, green or yellow. The process is accompanied by paronychia - purulent inflammation of the nail bed.
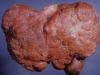
A selection of photos (above) with different forms of foot fungus will help determine the diagnosis.
Diagnosis and treatment of mycosis of the feet
In order for the treatment of foot fungus to be as effective as possible, you must visit a doctor as early as the first signs of the disease. Since the manifestations of mycosis are nonspecific and coincide with the clinical picture of other dermatological diseases, a specialist must differentiate it from dermatitis, keratoderma, dyshidrotic eczema and systemic lupus erythematosus.
To identify the pathogen and determine whether it belongs to any class of fungi, the patient undergoes:
- Nail scraping.
- Microscopy.
- Cultural research.
- DNA diagnostics of material.
When deciding how to treat foot fungus or the interdigital space and nails, the dermatologist considers the advisability of systemic and combination therapy.

But without fail, the patient receives prescriptions regarding external treatment. The basis of antifungal therapy is the use of antifungal drugs with diverse effects and medications to improve local blood circulation and eliminate concomitant pathologies.
For prevention reinfection The patient is recommended to disinfect personal belongings and common household items.
Systemic treatment of foot fungus
Systemic drugs in tablets and ampoules for mycosis are indicated for moderate and severe cases of the process. Due to the many side effects, their use is carried out under strict medical supervision.
To remove fungus from the foot, antimycotics of two groups are prescribed:
Most effective means Itraconazole and Terbinafine are considered for foot fungus. Their active ingredients quickly penetrate the affected skin and remain active for a long time.
Fungicidal antimycotics:
- Zalain.
- Fetimin.
- Natamycin.
- Exoderil.
- Sertaconazole.
- Griseofulvin.
- Clotrimazole.
Local antimycotics
When considering methods of treating foot fungus, it is worth mentioning separately the effectiveness of using topical medications. Ease of processing skin provides many dosage forms antimycotics. These are ointments, lotions, sprays, creams, drops and powder against fungus on the feet.

For swelling and weeping of the skin, antifungal drugs containing corticosteroids are used:
Fungicidal external agents are indicated when acute inflammation, provoked by the activity of fungal flora, subsides:
- Miconazole.
- Econazole
- Bifonazole.
- Isoconazole
- Lamisil (cream and gel).
- Lamisil Uno (solution).
If the nail is completely damaged, its removal is prescribed. The purpose of the operation is to remove colonies of fungi that have spoiled the plate and to increase the effectiveness of the use of antifungal ointments. Removal is carried out either surgically under sterile conditions, or using onycholytic patches and ointments that can destroy the affected nail.
Antifungal traditional medicine
According to dermatologists, it is permissible to use it without pharmaceutical medications in the early stages of mycosis, when there are no pronounced symptoms. In other cases traditional medicine can only complement basic medical prescriptions. Integrated approach guarantees the patient rapid extinguishing of foci of inflammation and support of local immunity.
Recipes home treatment mycosis of the feet using folk remedies:
- Rinse with herbal decoction. Oak bark, dry blackberries, verbena herb and calendula flowers are mixed in equal quantities. 3 tbsp. l. Boil the herbal mixture over low heat in 200 ml of water. After 20 minutes, the composition is filtered and used warm to wash problem areas and apply compresses.
- Wood ash ointment. Sifted wood ash is combined with pork fat until a thick ointment-like mass is formed. The product is applied to the feet in the morning and evening after hygiene procedures.
- ointment from copper sulfate and yellow sulfur. The medicine is prepared in pork fat by mixing the ingredients in equal quantities. The mass is brought to a boil, then taken to a dark room and waited to cool. Treatment of feet with sulfur-sulfate ointment is carried out several times a day.
- Baths with milkweed. An armful of fresh grass is poured with 2–3 liters of boiling water and the container is wrapped in an old blanket. After 3-4 hours of infusion, the herbal medicine is filtered and used for foot baths. Session time is 45 minutes. Baths are given every 2 to 3 days until the mycosis recedes completely.
- Coffee baths. If you are looking for a simple recipe on “how to treat foot fungus at home,” instant coffee will come to the rescue. The drink is brewed strongly in the required amount of water, poured into a basin and feet are steamed. Number of procedures – 1 – 2 per day. The task is to destroy pathogenic flora and eliminate the unpleasant odor emitted by the affected feet.
- Baths with wine vinegar. Before going to bed, wash your feet with warm water and place them in a basin with a strong solution of wine vinegar. After 3–5 minutes, wipe the feet and put on socks soaked in this solution. The procedure gives an antiseptic effect.