Whenever a person goes to the hospital, tests are taken to determine his blood sugar level. These indicators are the main ones for determining the patient’s health status. Thanks to glucose, the body's cells are saturated and receive all the necessary energy.
But it is worth remembering that the body is not able to process the sugar it receives on its own without a hormone such as insulin, which is produced by the pancreas. There is a group of foods that help maintain blood sugar levels in both adults and children. Signs of high blood sugar may not appear immediately, therefore, if you experience any discomfort in the body, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
Normal blood glucose level
Sugar levels in the body should not exceed the permissible level and, if we talk about numbers, the maximum permissible glucose level is 100 ml / 1 deciliter. With slight increases in the indicator, the patient may not feel any changes. But, if the level significantly exceeds the required norm, then the symptoms will be visible. Unfortunately, few people know what sugar levels are considered acceptable.
Both men and women have the same blood sugar levels. But an exception is the period of pregnancy. Over the course of 9 months of gestation, many changes occur in the body of the fairer sex, and sugar levels are no exception, which accordingly affects the development of the child.
It is worth considering that before donating blood for sugar testing, you must refuse food, as this affects the final result. Otherwise, you need to warn your doctor about the products you are using, this will help to correctly calculate the indicators. The normal blood glucose level is healthy person The level is considered to be within 3.9-5 mmol/1 liter. If a person consumed food or drinks shortly before taking the test, the readings may increase to 5.5 mmol. It is worth remembering that the indicators of capillary and venous blood are slightly different.
Blood sugar readings in men and women differ significantly from those in children, but the symptoms and causes of changes are the same.
Signs of high sugar levels
Both an increase and a decrease in blood sugar levels will not go unnoticed, and the body will immediately begin to respond to such changes. A sharp change in glucose levels can be detected independently. This can be done based on the following symptoms:
- There is a constant feeling of thirst. A person constantly drinks water, but the feeling of fullness still does not occur. This happens because glucose is a substance that attracts water. When the amount of sugar increases, the amount of water in the body decreases, which leads to constant thirst.
- Against the backdrop of the first sign, a desire to frequently visit the toilet appears. The body begins to actively get rid of excess fluid, the kidneys work in enhanced mode. If your kidneys malfunction, your blood pressure may rise. Even if these symptoms appear, you should visit a doctor.
- Itching occurs on the skin. In children, this phenomenon can lead to the formation of wounds on the skin.
- An increase in blood sugar can lead to inflammatory processes genitourinary system. Pain in the groin area in men and inflammation of the foreskin occur. Women may experience itching, burning in the labia area, and dry mucous membranes.
- High sugar levels lead to poor healing of various skin lesions. This happens because the cells lack energy and the tissues cannot recover quickly. A high glucose content is a favorable condition for the proliferation of various bacteria, which leads to inflammation and purulent processes.
- Changes occur in the body such as electrolyte imbalance. Such changes occur due to the fact that a person excretes a large amount of fluid, which removes all useful microelements; this is especially dangerous for the child and his development. This manifests itself in the form of muscle and calf cramp and disorders of the cardiovascular system.
- At the same time, a person may feel general constant fatigue, lethargy, and headaches. In children, this manifests itself in a constant desire to sleep and inattention.
- Another symptom of high blood sugar is a constant feeling of hunger. A person constantly wants to eat, the result is excess weight, which is quite difficult to get rid of.
- Too much sugar in the blood is manifested by the smell of acetone from the body and from the mouth of a person. This condition is quite dangerous, so if this symptom occurs, you should consult a doctor very quickly.
Without treatment, a person gradually develops more serious disorders in the body:
- Violation visual functions, vision gradually becomes worse, noted painful sensations In eyes.
- The gums begin to bleed and, as a result, the teeth become loose.
- The limbs may lose sensitivity, numbness, goosebumps, and tingling are felt.
- There are malfunctions in the functioning of the digestive tract, constipation alternates with diarrhea.
- Due to the constantly large amount of fluid in the body, swelling appears.
- Kidney function is impaired, and diseases of the urinary system are often observed.
- Diagnosed various diseases of cardio-vascular system.
- Problems with intelligence arise, memory impairment is noted.
If in adults the disease manifests itself more clearly, then in children it is difficult to identify it at the first signs and in order to detect high sugar levels it is necessary to take glucose tests.
Causes of increased glucose

There are many reasons why your blood sugar level may increase, but the main ones include the following:
- Heredity factor. Genetic predisposition may appear in early age in children. Most often, it is worth reviewing the diseases of immediate relatives to determine the level of risk.
- At autoimmune diseases. In this case, the body begins to reject its own organs, causing them harm.
- Excess body weight.
- Physical and psychological trauma. Often, severe stress causes disturbances in sugar levels. In a child, this may manifest itself in constant irritability and nervousness.
- Changes in the blood supply to the pancreas.
All of the above symptoms occur in case of illness, but there are also accompanying issues that can change glucose levels in a healthy person. The main reasons for changes in sugar include:
- eating foods containing large amounts of carbohydrates;
- if there is low physical activity;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol), very often this is the main reason for men.
Also at risk may be patients who experience complications such as:
- diseases endocrine system;
- liver diseases;
- pancreatic disorders.
It is worth noting that high blood sugar in children, the symptoms of which are the same as in an adult, manifests itself only slightly and to identify it, you should pay more attention to the baby’s well-being.
Restoring blood glucose levels
Before starting treatment and normalizing blood sugar levels, it is necessary to identify the causes of its imbalance. This can only be done after tests and consultation with a specialist.
Usually, sugar imbalance is a consequence of some disease, and only if it is detected and treated accordingly, it is possible to bring sugar back to normal. You can restore glucose levels not only with the help of medications, but also by using a certain diet, but only with the approval of your doctor.
If a patient is diagnosed with diabetes, the doctor prescribes a certain course of treatment that is the same for both men and women. At the same time, it is necessary to follow a certain diet, which involves reducing sugar consumption.
It is also necessary to add foods that help reduce glucose levels in the body. You need to discuss with your doctor what foods you can eat if you have diabetes. For children, sticking to such a diet is much more difficult, but if it is difficult for them to give up sweets, then such products can be replaced with sweeteners.
In any case, if there is the slightest deviation in health or a change in the well-being of a child or adult, you should visit a doctor and undergo full examination. After all, this can help in the timely identification of the disease and the initiation of treatment, which in many cases can even protect against the most dire consequences.
Glucose is the main supplier of energy needed by the brain, red blood cells, and the kidney medulla. To provide energy to the brain, it is even able to overcome the blood-brain barrier - a semi-permeable barrier between blood and nerve tissue that protects the central nervous system. However, human cells cannot metabolize glucose without insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas.
Blood glucose level is one of the most important medical indicators, showing whether everything is in order with carbohydrate metabolism.
Generally accepted standards
People suffering from diabetes, regardless of the duration of their illness, should take the following measures:
- Eat healthy and balanced, carefully choosing foods for your diet
- Take medications selected taking into account individual characteristics
- Move more and regularly engage in moderate exercise.
Some foods can slightly reduce the concentration of sugar in the body. The list of such products should be discussed with your doctor.
People with diabetes must constantly, that is, every day, monitor their blood sugar and blood sugar levels. It is especially important that these recommendations are followed by children with this diagnosis. If the patient is irresponsible towards symptoms sharp increase blood glucose levels he may be in serious danger dangerous condition- diabetic coma.
If there are noticeable signs of rising blood sugar, you should contact a specialized doctor as soon as possible.
Everyone knows what function sugar in the blood performs. But exceeding its permissible content is a reason to be wary.
This condition is called hyperglycemia, and it is fraught with a number of negative consequences.
The norm is how much, how to determine its boundaries
Sugar is the main source of energy for cells, supported by the interaction of the endocrine and nervous systems.
If this indicator corresponds normal level, this means there is nothing to worry about.
Normal blood sugar levels are 3.3-5.9 mmol per liter of blood fluid, depending on how it is determined.
A higher sugar level indicates deviations from the norm. This indicator is usually determined by taking a blood test on an empty stomach.
Factors for increasing indicators
Natural factors leading to increased sugar levels:
- After eating food, glucose levels may rise for several hours. This is normal because the body absorbs it;
- after stress and strong emotional experiences;
- due to a sedentary lifestyle;
- due to smoking and other bad habits;
- premenstrual syndrome can also provoke surges.
If blood glucose is constantly high, this may indicate the presence of serious diseases.

The rise in blood sugar in a woman is not a disease.- this is a state possible symptom a certain disease.
What does high blood sugar mean:
In pregnant women and after childbirth


At the first appearance in antenatal clinic The pregnant woman receives a referral for a series of tests. Her blood glucose levels will be determined.
If it is elevated, this can be explained natural causes. Under normal conditions, this indicator is regulated by insulin constantly produced by the pancreas.
It affects the sugar received with food, which enters the cells of the body and functions there. At the same time, the sugar level decreases.
During pregnancy the situation is different. Hormones for bearing a child are insulin antagonists. An increase in sugar levels during pregnancy is possible due to the fact that it is difficult for the pancreas to cope with the work under such conditions.
The pregnancy hormone provokes the release of glucose into the blood, but insulin, which binds excess sugar, is not enough.
Therefore, pregnancy diabetes may appear, the consequences of which can be very dangerous. But this situation does not arise for all expectant mothers.
There are factors that increase the likelihood of this problem.
These are excess weight, hereditary predisposition, a similar situation in previous pregnancies, age over 25 years, and polycystic ovary syndrome.
Sometimes an increase in sugar occurs characteristic symptoms and signs, and sometimes future mom and doesn't notice him at all.
Often pregnant women let the situation take its course, believing that after childbirth everything will return to normal.
But keep in mind that such a condition may have Negative influence to the fruit, therefore specialist supervision is required and implementation of all its recommendations.
In most cases, after childbirth, the sugar level in a woman’s venous blood actually returns to normal.
If it remains elevated or jumps even more, you need to consult a specialist.
About glucose levels during pregnancy in this video:
Alarming symptoms
An elevated glucose level can be determined by the following signs:

- constant thirst;
- feeling of dry mouth;
- itchy skin;
- frequent urination, increased volume of urine excreted (polyuria), urge to urinate at night (nocturia);
- weight loss for no reason;
- weakness and fatigue;
- deterioration of visual acuity;
- deterioration of the reparative function of the blood (wounds will heal slowly);
- frequent infectious diseases.
With such symptoms, hyperglycemia can be suspected. But only a doctor can make a specific diagnosis.
How strongly the symptoms are expressed is determined by the severity pathological condition. Acute hyperglycemia is more pronounced than chronic hyperglycemia.
What is the danger
Complications higher level there are sugars acute and late. Acute symptoms appear at a critical level and are characteristic of the first type of diabetes mellitus.
May develop coma with damage to the central nervous system. Possible extinction of the simplest reflexes, loss of consciousness.
In such conditions there is a risk fatal outcome, so you need to get help on time.
If no measures are taken, consequences such as inhibited reactions, muffled consciousness, and then coma are possible.
If sugar is elevated for a long time, symptoms appear late complications. Hyperglycemia negatively affects the functioning of all human organs and systems.
The most common dangerous consequences are the following:

- Diabetic retinopathy. This is damage to the retina of the eye, which can cause permanent blindness.
- Diabetic foot. Suggests damage to blood vessels and the peripheral nervous system. As a result, gangrene is possible.
- Diabetic nephropathy. In this case, irreversible destruction of the kidney filters occurs, resulting in chronic renal failure.
Necessary tests and studies
If there is a suspicion that a woman has elevated sugar levels, blood tests from a vein on an empty stomach are prescribed to determine the amount of sugar and deviations from the norm.
If it is confirmed that it is elevated, a consultation with an endocrinologist is necessary. He usually prescribes a diet to follow.
It is also important to monitor this indicator every day using a glucometer. The results must be recorded so that it is possible to track the dynamics of progression or extinction of the disease.
If indicators worsen, you should immediately consult a doctor to prevent coma.
The danger of diseases associated with the endocrine system is that they may not manifest themselves in the initial stages and develop.
Features of therapy
The specialist can prescribe an individually compiled therapeutic diet. Specials may also be shown drugs that lower glucose levels in blood fluid. Sometimes herbal preparations help.
Experts advise reconsidering your lifestyle. There must be a place in it physical activity and proper nutrition.
It is especially important to start correct treatment those who suffer from diabetes. Therapy must be strict, constant glucose monitoring is important.

It will return to normal only if the patient follows all medical prescriptions:
- eat properly and in accordance with the regime;
- Constantly monitor your sugar level;
- perform certain physical exercises;
- take insulin and other necessary medications.
If therapy is completed and symptoms of hyperglycemia ( high sugar in a woman’s blood) do not go away, you should consult your doctor.
Perhaps the treatment tactics in your case are completely different.
Diet
The diet prescribed for hyperglycemia is based on proteins, grains and plant foods.
You need to eat at the same time, drink at least 1.5 liters per day clean water. Daily calorie content, as a rule, should be 2300-2400 kcal.
Allowed to use lean meats, any vegetables except potatoes, mushrooms, fish and seafood, liver, low-fat dairy products, legumes, porridge with water and milk.
Acceptable to use up to 300 grams of baked goods made from unleavened dough, unsweetened fruits and berries, a small amount of honey, marmalade, marshmallows, marshmallows.
The specific menu is compiled individually.
What not to do

First of all, you need to eliminate from your diet foods that are prohibited if you have high sugar levels.
These are flaky and rich pastries, fish and meat broths, milk soups with cereals, fatty types of fish and meat, fish roe and canned food, smoked meats, cheeses, sweet dairy products, marinades, cream, pasta, sweet fruits, drinks with a high sugar content.
Lard, fatty and spicy sauces, sweets, chocolate, pastries, cakes and other harmful sweets are prohibited.
Besides it is important to eliminate stress, mental or physical stress - all this affects the body negatively.
Try to get more positive emotions, lead a healthy lifestyle and spend more time outdoors.
One of the most important substances that allows our body to function normally is glucose. It is easily processed by the gastrointestinal tract and serves as an indispensable source of energy for brain cells, muscle tissue, and blood. But if glucose levels rise above normal, it can pose a serious health threat.
Increased sugar levels (hyperglycemia) in women can occur when various states. It is not always caused by the presence of some disease. Mostly, pathological process associated with improper carbohydrate metabolism in the body. To find out the causes of high sugar, you need to see a doctor and undergo tests prescribed by a specialist.
Causes of high blood sugar in women

Every cell in the body needs glucose as an energy carrier. Physiological processes carbohydrate metabolism, balanced work of the central nervous system and endocrine system allow you to maintain metabolic processes fine. The normal blood sugar level for women is 3.3-5.5 mmol/l.
Pathological hyperglycemia can be caused by:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- infectious hepatitis;
- neuroendocrine disorders (obesity, Cushing's disease);
- adrenal dysfunction;
- tumor formations in the pancreas;
- hormone-producing neoplasms;
- suffered heart attacks, strokes, injuries.
In women with diabetes, sugar may rise due to non-compliance with the dosage or frequency of taking hypoglycemic drugs, as well as the wrong combination of drugs.
A temporary increase in sugar levels in women can occur with:
- pregnancy;
- excessive amounts of simple carbohydrates in the diet;
- stress;
- severe bleeding;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- carbon monoxide intoxication.
Glucose levels may rise after taking certain medications:
- glucocorticosteroids based on prednisolone;
- birth control pills;
- beta blockers;
- phenothiazines.
Important! If a woman has not previously suffered from diabetes, and the sugar level after meals often shows slight hyperglycemia, this may indicate high risk developing diabetes in the future.
Forms of hyperglycemia
Based on the etiology of the development of pathology in women, several forms of hyperglycemia are distinguished:

- Physiological- happens at healthy women, is not accompanied by disruption of the functionality of organs and systems. Neurogenic physiological hyperglycemia occurs against the background stressful situations, and nutritional - as a result of excessive intake of sweets and carbohydrates into the body.
- Pathological- develops under the influence of existing diseases.
Based on the concentration of glucose in the blood, there are several degrees of hyperglycemia:
- light- glucose level not more than 8.2 mmol/l;
- average- no more than 11 mmol/l;
- heavy- above 11 mmol/l.
Clinical manifestations of the pathological process
The main signs of high blood sugar are:
- strong thirst;
- itchy skin;
- increased diuresis;
- polyuria;
- weight loss or obesity;
- weakness and increased fatigue;
- ketonemia;
- blurred vision.
To confirm the diagnosis, you need to take a blood sugar test or test at home using a glucometer. The intensity of symptoms depends on the severity of the condition. With sudden hyperglycemia (due to, for example, overeating), the symptoms will manifest themselves more clearly than with chronic hyperglycemia.

Each symptom has its own development mechanisms. Increased thirst occurs due to the osmotic ability of glucose to attract water. When its level increases, fluid begins to be rapidly removed from the body. As compensation, the body reflexively tries to replenish water losses, which is expressed by intense thirst.
The attraction of many water molecules to 1 glucose molecule leads to increased excretion from the body through the kidneys. In this regard, there is another characteristic feature hyperglycemia - increased diuresis. The binding of water molecules by glucose molecules can lead to hypertension if the fluid does not have time to be eliminated from the body.
If the sugar concentration exceeds 10 mmol/l, it is detected in urine. This increases the symptoms of hyperglycemia.
Weight loss is observed if a woman has a catastrophic deficiency in insulin synthesis. Glucose cannot penetrate the cells, they experience constant energy hunger. As a result, weight loss occurs.
If a woman has excess weight tissues begin to experience a state of insulin resistance. Insulin is synthesized within normal limits, but the receptors that are supposed to bind it do not work correctly. As a result, glucose cannot enter the cells in the required quantity. But the primary excess of fat does not cover energy hunger. The body tries to obtain energy in another way, associated with lipid oxidation. This increases the content of ketone substances in the body (ketonemia). It is characterized by the release of the odor of acetone when breathing.
Treatment Options
How to lower blood sugar? Symptoms characteristic of elevated glucose levels require mandatory examination. To choose the right treatment, you need to find out what exactly caused hyperglycemia, whether this phenomenon is temporary or permanent.
Often, with short-term, moderate hyperglycemia, nutritional correction, avoidance of stress and moderate physical activity help stabilize sugar levels. If you have diabetes, you need to regularly monitor your glucose level and learn to take timely measures if it increases.

- follow a prescribed diet high sugar in blood;
- use a glucometer to constantly monitor blood sugar, recording the data in a notebook;
- perform a special course of exercises;
- If signs of elevated sugar levels appear, immediately seek help from a doctor;
- if necessary, adjust glucose levels with medications that lower blood sugar (as prescribed by a doctor).
Medications
If there is a stable increase in sugar levels, the doctor may decide to use medicines. These include:
- Insulin;
- Siofor - stabilizes the body's sensitivity to insulin;
- Actos - increases cellular sensitivity to insulin;
- Victoza - normalizes appetite.
Diet and nutritional habits
Proper nutrition is one of the main methods of normalizing blood sugar. You need to adhere to a gentle diet, which involves limiting the consumption of carbohydrate foods.
Diet rules for high blood sugar:
- steam, boil or bake food;
- avoid eating animal fats;
- increase intake of fermented milk products;
- exclude sweet fruits and sweets with sugar;
- drink plenty of fluids a day, better water, unsweetened compotes;
- exclude coffee, juices.

Prevention measures
To prevent high blood sugar, you need to take measures to prevent the causes of this condition.
Prevention of hyperglycemia includes:
- weight normalization;
- maintaining proper nutrition;
- exclusion of alcohol;
- moderate physical activity;
- control of blood glucose concentration;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the endocrine system.
Increased sugar levels in women are not always a sign of diabetes. The presence of signs of hyperglycemia is an alarm bell that cannot be ignored. If high blood sugar becomes chronic, it becomes very dangerous for the body. You need to be examined in time and immediately take the necessary measures to eliminate the problem.
From the following video you can learn how to lower blood sugar at home if your blood sugar levels are elevated:
Diabetes mellitus is a disease that comes in two types – first and second. In type 1 diabetes, too little insulin is produced, which causes glucose to leave the blood and go into the tissues. In type 2 diabetes, enough insulin is produced, but the tissues are resistant to it. All clinical manifestations These types of disease, including the picture of complications, arise from the fact that there is elevated blood sugar - hyperglycemia syndrome. How does it manifest itself?
Of course, if your fly is unzipped and a bee is flying nearby, then this is an obvious sign of glucosuria and diabetes. But this only happens in medical jokes. In fact, the symptoms of diabetes are quite varied. But they all stem from hyperglycemia syndrome. Normally, between the ages of 14 and 60 years, the blood sugar level should not exceed 5.9 mmol/liter. There is no gender difference in glucose levels between men and women.
Levels of hyperglycemia vary. At mild form the blood plasma glucose level does not exceed 10 mmol/l, with an average level it does not exceed 16.5 mmol/l. Before listing the signs of hyperglycemia, you need to say a few words about the causes of its occurrence. Certainly, main reason Its increase is caused by such a disease as diabetes - both in women and men, and even in children. But to come to this conclusion, it is necessary to exclude other causes of increased glucose levels. These include:
- Physiological hyperglycemia. All conditions in which the counter-insular hormone, glucagon, is released, and glucose is released from liver glycogen into the blood, can be classified in this group. It's stressful, it's intense. emotional overstrain, high exercise stress, smoking and even the release of adrenaline at the time of taking a blood sugar test.
- Other endocrine diseases: pheochromocytoma, Cushing's syndrome, acromegaly and thyrotoxicosis.
- Pancreatic diseases such as acute pancreatitis and exacerbation chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, and tumors of the pancreatic zone.
- Antibodies to insulin receptors.
- Vascular accidents, such as hemorrhagic stroke.
- Myocardial infarction.
- In case of taking thiazide diuretics, estrogens (in women), corticosteroid hormones.
- Taking large amounts of glucose.
If all causes and options are excluded, then the search for diabetes mellitus begins, since simply an increase in glucose levels has long ceased to be a diagnostic criterion. For example, you need to study the level of glycosylated hemoglobin. But in addition to the above reasons, there is also gestational diabetes, or diabetes during pregnancy. As a rule, with timely detection and treatment, it goes away completely. It develops because the placenta secretes its own hormones, which have a counter-insular (that is, opposite) effect in relation to insulin. Thus, placental hormones increase blood sugar levels.

Symptoms of hyperglycemia
Signs of high blood sugar are:
- Thirst, synonym – polydipsia. This is "transient" water and should dilute the plasma glucose concentration as the blood becomes thicker.
- Dry mouth, which may occur immediately after quenching thirst.
- Polyuria is excessive urination. It should not be confused with frequent urination, which is often the cause inflammatory diseases urinary system. Nocturia also occurs, in which the patient visits the toilet several times during the night.
If a child develops diabetes, it is polyuria that attracts the attention of parents. Its manifestation resembles normal bedwetting. That child who has just learned to control his bladder, suddenly loses this ability again and becomes unkempt.
- Muscular and general weakness occurs, and loss of performance appears.
- Skin itching and scratching appear. The itching is especially painful in the genital area.
- Abrasions, wounds and all kinds of scratches on the skin do not heal well.
- Drowsiness appears, including during the day.
- The skin becomes dry, its turgor decreases.
- Despite obesity, sometimes pronounced, patients have a constantly increased appetite.
- Sometimes severe hyperglycemia is manifested by significant loss of body weight - up to 15 - 20 kg in a short period of time.
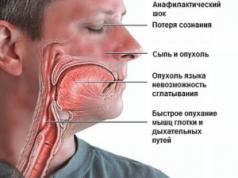
If a person does not pay attention to his condition, he may experience a further increase in blood glucose levels. After reaching the level of 16.5 mmol/l, a precomatous state occurs, and then, with exceptionally high glucose levels (more than 50 mmol/l), a coma occurs, which is called hyperosmolar, or diabetic.
This coma develops slowly and gradually. The precomatose period lasts about 10 days. At the same time, increasingly worsening carbohydrate metabolism disorders occur. All of the listed complaints intensify, sometimes patients become lethargic, indifferent and inactive - adynamic. The skin is very dry, facial features are sunken, eyeballs also become sunken and soft.
Then neurological disorders and manifestations of convulsive syndrome may occur. Arterial pressure falls, tachycardia occurs. We can say that dehydration develops, but not due to loss of water, but due to “too sweet” and thick blood. Edema may develop despite constant thirst. The cause of these edemas will be venous thrombosis.
The most important step in the treatment of this coma will be rehydration and a decrease in the level of osmolarity of the blood plasma (that is, diluting it with a hypotonic solution of sodium chloride). Therefore, you need to carefully monitor the slightest signs increased blood sugar because severe complications arise unnoticed, against the background of depression of consciousness.