Content
The inability to breathe freely, headaches, and nasal discharge require a visit to an ENT doctor. Advanced disease causes serious complications. Why does rhinosinusitis occur, what are the symptoms? It is useful to get acquainted with the characteristics of various types of illness, diagnostic methods, methods of treatment with medications, surgery, and folk remedies.
What is rhinosinusitis
Inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses cause infections caused by bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Rhinosinusitis often begins in an acute form. When the disease develops:
- under the influence of infection, secretion and vascular permeability increase;
- the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity and sinuses swell and thicken;
- the anastomosis between them overlap, forming a closed space;
- accumulation of mucous purulent exudate occurs;
- severe and unpleasant symptoms occur.
The patient, feeling signs of illness, should consult a doctor. The disease in its acute form lasts up to a month. Untreated rhinosinusitis is dangerous due to its transition to chronic stage, the occurrence of complications such as:
- bronchial asthma;
- defeats optic nerves– visual impairment;
- abscess of soft tissues of the face;
- purulent inflammation of the middle ear;
- damage to the nervous system;
- brain abscess;
- transfer of infection to the lungs;
- purulent inflammation of the eye sockets;
- thrombosis of the cavernous sinus;
- sepsis – infection through the bloodstream;
- meningitis;
- risk of death.

Reasons for the development of rhinosinusitis
Emergence inflammatory process in the paranasal sinuses cause numerous diseases. The causes of the development of the disease are provoking factors of various etiologies. The reasons for the appearance of the disease are:
- taking medications for a long time;
- defects of nasal structures – acquired, congenital;
- hereditary factors;
- the habit of blowing your nose incorrectly - cleaning both nostrils at once;
- violation of the patency of the sinus anastomosis;
- weakened immunity;
- injuries.
The causes of the disease are:
- in adults – nasal polyposis;
- in children – adenoiditis;
- pathologies of nearby organs;
- allergic rhinitis;
- bronchial asthma;
- immunodeficiency states;
- endocrine diseases;
- fungal infections caused by pathogens of the genus Candida, Aspergillus, moldy fungi;
- bacterial pathologies caused by staphylococcus, streptococcus, intestinal, Haemophilus influenzae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- diseases associated with the activity of viral microorganisms - influenza, adenovirus, parainfluenza.
Symptoms of rhinosinusitis
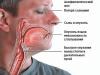
The disease can develop in various forms, each of which has its own characteristics. There are symptoms common to all types of illness. When rhinosinusitis appears, the following are observed:
- nasal congestion;
- swelling of the mucous membranes;
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- stuffy ears;
- hearing impairment;
- loss of smell;
- lacrimation;
- nasality;
- sneezing;
- problems with taste;
- mucous discharge with pus;
- toothache.
The disease causes intoxication of the body, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe headaches, localized near the sinuses;
- temperature above 39 degrees;
- weakness;
- malaise;
- runny nose;
- loss of appetite;
- dizziness;
- sore throat;
- irritability;
- sleep disorders;
- cardiopalmus;
- increased fatigue.

Types of rhinosinusitis
In medicine, it is customary to classify diseases. This helps in diagnosis, correct treatment, and selection of medications. Rhinosinusitis is systematized according to several parameters. Types of disease by etiology:
|
Pathogens |
Note |
|
|
Bacterial |
enterobacteria staphylococcus Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli streptococcus |
|
|
Viral |
rhinoviruses adenoviruses parainfluenza |
occurs in acute form |
|
Fungal |
mushrooms of the genus Candida, Aspergillus |
several microorganisms infect a cell at once |
|
Mixed |
begins with a bacterial infection, complicated by other types |
Inflammatory disease is classified according to several parameters. According to the nature of the course, acute, chronic, and recurrent forms are distinguished. Localization of the process can be one-sided or two-sided. The course of the disease varies in severity - mild, moderate, severe. The types of the disease are classified according to the location of the lesion:
- maxillary – sinusitis;
- ethmoidal - parts of the ethmoid sinuses are affected - ethmoiditis;
- frontal – frontal areas are affected – frontal sinusitis;
- sphenoidal – inflamed sphenoid sinuses – sphenoiditis.
Spicy
Diseases in this form begin rapidly and require urgent medical attention. The progression of the patient’s disease occurs over a week. Acute rhinosinusitis has a characteristic clinical picture:
- intoxication – fever, pressure in the ears, feeling of weakness, weakness, fever;
- decreased sense of smell;
- swelling of the face;
- paroxysmal headaches;
- nasality;
- labored breathing;
- bad smell from mouth;
- nasal congestion;
- mucous discharge;
- discomfort, squeezing in the sinus area.
If symptoms have not changed within a week, a bacterial infection cannot be ruled out. This condition requires hospitalization, antibacterial therapy. This will help prevent the development of the disease in chronic form, the occurrence of serious complications. Provoking factors for the occurrence of an acute inflammatory process in the nasal sinuses are:
- incorrect or incomplete treatment of sinusitis;
- disturbances in the discharge of mucous exudate;
- deviated nasal septum.

Chronic
If acute rhinosinusitis is not completely cured, it leads to the development chronic pathology. The disease can last up to six months. The provoking factors for the occurrence of this form of pathology are:
- allergic reactions;
- severe form of intoxication;
- facial injuries;
- smoking;
- constant inhalation of dusty, polluted air;
- acquired, congenital defects of the nasopharynx.
Chronic rhinosinusitis is characterized by the presence of mild symptoms. This type of disease is dangerous due to the development of complications. The narrowing of the anastomosis between the sinus and nose as a result of edema reduces the supply of oxygen, which intensifies the inflammatory process. The following clinical picture of the disease is observed:
- weakened sense of smell;
- hearing impairment;
- constant nasal congestion;
- lack of temperature;
- nasal voice;
- labored breathing;
- discharge from the nose of mucous secretion with pus;
- distension in the sinuses;
- irritation;
- weakness.
Polyposis
Advanced inflammation of the paranasal sinuses leads to the proliferation of mucous membranes. Chronic polypous rhinosinusitis develops against the background of a decrease in the concentration of immunoglobulin G. The provoking factor is exposure to aggressive chemical substances a, allergens, viruses, hereditary predisposition to allergies. The development of the disease occurs according to the following scheme:
- swelling of the mucous membranes occurs;
- the walls thicken and grow;
- outgrowths are formed - polyps;
- stagnation of purulent contents occurs in the sinuses.
The disease is dangerous due to its complications - meningitis, damage to the eyeballs. Required surgery– removal of polyps. The clinical picture is characterized by symptoms:
- nasal congestion;
- sensation of a foreign body inside;
- loss or decrease in taste and smell;
- swallowing problems – in advanced cases;
- sleep disturbance;
- tachycardia;
- stuffy ears;
- chronic fatigue;
- pain in the head, sinus area.
Purulent
Rhinosinusitis of this type is bacterial in nature. Often, the activation of pathogenic microorganisms on the mucous membranes of the nose and sinuses occurs due to injury. The disease is dangerous with complications, life-threatening– abscesses, empyema of the orbits, brain, meningitis, requires hospital treatment. The clinical symptoms of this pathology are clearly expressed:
- purulent nasal discharge;
- fever;
- toothache, headache;
- swelling of the face at the site of sinus lesions;
- sleep disturbance;
- lack of appetite;
- weakness;
- aching joints;
- muscle pain;
- heat.

Allergic
The provoking factors for the development of this type of disease are exposure to allergens. This could be food medications, plants, dust, fungal spores, animal hair. Allergic rhinosinusitis requires the exclusion of irritants that lead to the disease and the use of antihistamines. The disease is distinguished by clinical symptoms:
- redness eyeball;
- copious clear exudate from the nose;
- lacrimation;
- itching in the nasopharynx;
- irritability;
- malaise;
- headache;
- drowsiness;
- sneezing.
Catarrhal
A disease that occurs without purulent discharge, also called viral runny nose. Catarrhal rhinosinusitis is distinguished by abundant and transparent mucous exudate. The disease is provoked by:
- fungal, viral infections upper respiratory tract;
- neoplasms, polyps in the nasal cavity;
- weakened immunity;
- deviated nasal septum;
- hypothermia;
- dental infections;
- allergies.
The inflammatory process is dangerous with complications and requires timely treatment to exclude them. The disease has a clinical picture:
- elevated temperature;
- swelling of several sinuses;
- nasal congestion;
- inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eyes;
- loss of smell;
- dryness, burning sensation in the nasal cavity;
- hypothermia;
- headache;
- swelling;
- profuse lacrimation;
- lack of sleep.
Vasomotor
If there is a violation of the tone in the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity blood vessels swelling of the mucous membranes occurs. Vasomotor rhinosinusitis begins against the background colds, ARVI. Provoke the development of the disease:
- frequent use of nasal drops;
- stressful situations;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- smoking;
- changes in air temperature;
- hypothermia;
- alcohol consumption;
- chronic stomach diseases;
- anatomical pathologies of the nose;
- injuries.
Sudden dilation of blood vessels leads to the appearance of edema, while the clinical picture of the disease is characterized by constant nasal congestion, watery mucous discharge, which turns into green exudate as the disease progresses. Symptoms observed:
- nasal voice;
- sneezing;
- lacrimation;
- labored breathing;
- decreased sense of smell;
- headache;
- lack of appetite;
- sleep disorder;
- temperature increase.

Diagnostics
If symptoms of the disease appear, you should not self-medicate; you must contact a specialist. The otolaryngologist begins the diagnosis by interviewing the patient. During the visit:
- is assessed general state sick;
- complaints are heard;
- symptoms are clarified;
- The cheekbones and forehead are palpated to determine the area of pain and identify abnormalities in the nasal cavity.
To clarify the diagnosis, instrumental studies are carried out:
- rhinoscopy - examination of the mucous membranes of the nasal passages;
- endoscopy – violation of anatomy is revealed in detail, individual areas are studied;
- X-ray – examination of the frontal and sphenoid sinuses is performed;
- computed tomography - a feature is revealed anatomical structure nose;
- Ultrasound – inflammation of the frontal sinuses is diagnosed, cysts and polyps are identified;
- Magnetic resonance imaging - tumors and inflammation are detected.
They help determine the diagnosis with high accuracy laboratory research. As prescribed by the ENT doctor, the following is carried out:
- diagnostic puncture of the contents of the sinuses;
- smear for eosophils;
- microbiological examination of exudate from the sinuses, nasopharyngeal discharge, to identify the causative agent of rhinosinusitis, determine its sensitivity to antibiotics;
- blood analysis.
Treatment of rhinosinusitis
IN complex therapy For diseases, doctors prescribe medications for local use and oral administration, use sinus lavage, and physiotherapy. When treating rhinosinusitis, it is necessary to solve several problems:
- eliminate the cause of the inflammatory process;
- eliminate the outbreak;
- relieve painful symptoms;
- restore the body's defenses.
Antibacterial agents play an important role in this. Depending on the identified pathogen, antibiotics are prescribed - cephalosporins, tetracyclines, macrolides. The duration of the course of treatment is determined by the doctor. For topical use, sprays with antibacterial action are used - Isofra, Polydex. For rhinosinusitis, antibiotics are often used in the form of tablets, injections, suspensions for children:
- Clarithromycin;
- Augmentin;
- Azithromycin;
- Amoxicillin.
The course of therapy for the disease includes the use of:
- to relieve inflammation - corticosteroid Hydrocortisone, antihistamine Loratadine;
- in order to increase protective forces - immunomodulators - Ismigen, Imunorix, Immunal, to strengthen local immunity - IRS-19;
- for pain relief, fever relief – Paracetamol, Ibuprofen;
- combined topical sprays - Rinofluimucil, Vibracil.
To remove pathogenic contents from the sinuses, otolaryngologists recommend:
- mucolytics that promote liquefaction of sputum and its normal outflow - Sinupret, ACC;
- Aquamaris moisturizing spray;
- vasoconstrictor, decongestant drugs in the form of drops - Rinonorm, Tizin, Nazivin;
- rinsing solutions - Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin.
Rhinosinusitis in children, if the disease is not in an advanced form, is tried to be treated without the use of antibiotics. Doctors prescribe antiseptic drops Protargol, Bioparox, inhalation with a nebulizer using mineral water"Borjomi". Complex therapy for the disease in children and adults includes:
- rinsing the sinuses with a solution sea salt, decoctions medicinal herbs, saline;
- physiotherapy – electrophoresis, UHF, diadynamic currents;
- laser treatment;
- strengthening the immune system;
- dental sanitation;
- use of traditional medicine recipes.

ethnoscience
Use for natural treatment herbal remedies must be agreed with a doctor. Traditional medicine recipes become an addition to complex therapy, but do not replace it. Popular remedies for the treatment of rhinosinusitis:
- rinsing the nasopharynx with diluted and salted lemon juice, beetroot, sage decoction - a spoonful of herbs in a glass of boiling water;
- instillation of a mixture of equal parts of liquid honey, onion juice and potato into the nose;
- warming the nasal septum with hot salt in a linen bag - strictly as prescribed by the doctor, to avoid the spread of inflammation.
- Make compresses, nose drops, inhalations with a decoction of herbs - two spoons per half liter of boiling water. The composition of the collection includes equal parts of eucalyptus, sage, valerian, calendula, chamomile.
- Perform daily instillation of 2 drops of Kalanchoe juice into each nasal passage.
- Place turunda with a warm mixture of equal parts of vegetable oil for half an hour three times a day, baking soda, honey.
- Take half a teaspoon of a mixture of the juice of three lemons and grated horseradish root in the morning on an empty stomach.
Surgical intervention
If conservative treatment rhinosinusitis did not produce results, the likelihood of complications is high, doctors prescribe surgical intervention. There are several methods of surgical treatment. One of them is sinus puncture, during which:
- make a puncture with a needle in the thinnest place of the maxillary bone;
- remove pus by washing the sinus space with antiseptics;
- medications are administered.
An alternative method to puncture is the use of a YAMIK catheter. For complete cure Rhinosinusitis requires several procedures. While the session is running:
- a catheter with two rubber balloons is inserted into the nose;
- they swell and close the nasal cavity;
- purulent contents are removed with a syringe;
- An antiseptic is supplied through the catheter for flushing, and the medicine is administered.
Surgical methods for treating the disease include the following:
- Sinusotomy is the removal of part of the facial bone by opening it. It is characterized by long rehabilitation and many contraindications.
- Endoscopic removal of polyps. The instrument is inserted into the nasal passage, does not cause damage to healthy tissue, and the risk of recurrent rhinosinusitis is reduced.
The non-invasive cuckoo treatment technique is performed separately for each nostril. Features of the procedure:
- a syringe is inserted into one nasal passage, and a suction hose into the other;
- saline solution or antiseptic is supplied under pressure;
- the fluid passes through all the sinuses into the sinuses;
- the contents are sucked out at the same speed;
- During treatment, in order not to choke, the patient constantly says “ku-ku” - the glottis must be open.
Video
Found an error in the text?
Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we will fix everything!
Rhinosinusitis is a disease that affects the lining of the nasal passages and paranasal sinuses. Often pathological process occurs in adults aged forty to seventy years. Rhinosinusitis can also be found in childhood.
As the inflammatory process progresses, the mucous membranes in the nose become very swollen and thickened. As a result, the anastomosis between the tissues overlap and a closed cavity is formed. And purulent contents accumulate in it. The duration of this illness is acute period is about four weeks. In a chronic course, the disease does not leave the patient for three months.
Acute rhinosinusitis can occur as a result of several causes.
- Presence of bronchial asthma.
- Decreased immune strength of the body.
- Getting a viral or bacterial infection.
- Fungal infection.
- Long-term use of certain medications.
- Hereditary nature of the disease.
- Nose injury.
- Nasal polyposis in adults.
- Deformation of the side wall of the nose.
- Enlarged adenoids or formation of polyps.
- Allergic reactions.
- Unfavorable working and living conditions.
One of the above reasons may be the start for the development of rhinosinusitis. If the disease is left untreated for a long time or the wrong medications are taken, the disease becomes chronic.
Symptoms of rhinosinusitis
The inflammatory process in the form of rhinosinusitis is a common disease. Often the main factor is a viral infection. Occurs as a result of hypothermia in the cold season.
The main symptoms are generally considered to be the following.
- The presence of mucous secretions that flow down the back wall down the throat.
- Swelling of the mucous membrane.
- Pain in the paranasal sinuses.
- Painful feeling in the head.
- General malaise.
- Congestion of the nasal passages and ears.
- Increased body temperature.
- Manifestation of cough.
Concomitant symptoms directly depend on what form of the disease is observed in the patient.
Acute rhinosinusitis
Acute rhinosinusitis is usually called an inflammatory process that occurs in the mucous membranes with further spread to the paranasal sinuses. This illness manifests itself as a complication after a cold or flu after seven to ten days.
The main features are usually considered to be the following.
- The presence of discharge of a thick consistency and brownish, yellowish or greenish color.
- Painful feeling in the head.
- Nasal congestion.
- Increase in body temperature to 38 degrees.
- Nasality.
Acute rhinosinusitis in children is characterized by the following factors.
- Increased moodiness.
- Bad sleep.
- An increase in body temperature to 39 degrees.
- A cough that results in coughing up phlegm.
- Mucus running down the back wall.
- Lethargy and general malaise.
Also in medicine it is customary to distinguish two stages of the disease.
- Catarrhal rhinosinusitis. It is characterized by a slight increase in body temperature up to 37.5 degrees and a runny nose, which after two to three days passes into the paranasal sinuses. Swelling of the mucous membrane occurs, and the patient feels heaviness in the facial area. If acute catarrhal sinusitis is not treated, it turns into another form.
- Purulent sinusitis. In such a situation joins bacterial infection, as a result of which the anastomosis in the nasal cavity becomes blocked with purulent contents. There is an increase in body temperature to 38 degrees, painful sensations radiates into the ears and teeth. In this case, pain may radiate to the back of the head or eyes when bending forward. Acute purulent rhinosinusitis quickly becomes severe, which leads to the development of complications. The development of pathology can be determined using x-ray examination.
Acute purulent sinusitis is usually divided into several types.
- Sinusitis. A painful sensation occurs in the maxillary sinuses.
- Frontit. Purulent contents accumulate in the frontal part, as a result of which the pain can radiate to the eye sockets.
- Ethmoiditis. The inflammatory process develops in the ethmoid sinuses, resulting in nasal sounds.
- Sphenoiditis. The disease occurs in the sphenoid sinuses, and the disease is characterized by dull painful sensation in my head.

Chronic rhinosinusitis
Chronic rhinosinusitis refers to an inflammatory process that periodically makes itself felt. In this case, the duration of one relapse can be about three months. The disease affects the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, resulting in severe swelling and lack of oxygen.
Chronic rhinosinusitis is manifested by the following symptoms.
- Presence of purulent discharge.
- Nasal congestion.
- Decreased olfactory function.
- The appearance of nasality in the voice.
- Heaviness in the facial area and throbbing.
- Painful feeling in the head.
- Increased tear production.
- Raising body temperature.
The pathological process can affect several sinuses at once and have several forms.
- Catarrhal sinusitis. This is a type of disease that is characterized by the formation of an inflammatory process in the nasal and paranasal sinuses, while there is no mucus discharge. The disease occurs as a result of a viral infection. The main symptoms of the disease include:
loss of smell;
tearfulness;
general intoxication of the body;
swelling of the paranasal sinuses;
burning sensation and dryness in the nasal cavity;
insomnia;
increased body temperature;
pain in the head;
loss of appetite.
Catarrhal rhinosinusitis can cause a number of complications such as meningitis, abscess, respiratory tract diseases and pharyngitis. - Purulent sinusitis. The main cause of this type of disease is considered to be a bacterial infection, which is located in epithelial tissues. In some situations, purulent sinusitis can occur due to injury, a deviated nasal septum, or allergies. However, bacterial rhinosinusitis is diagnosed only in ten percent of all cases. Despite this, doctors prescribe antibacterial drugs to all their patients. To put accurate diagnosis, you need to take a nasal swab for analysis. Another main criterion in determining the type of disease is the duration of the disease. It is worth noting that chronic purulent rhinosinusitis lasts more than ten days.
- Chronic polypous rhinosinusitis. This type of disease most often occurs in those people who have severely reduced immune function. When exposed to viruses, allergens and chemicals, the mucous membrane begins to swell. As a result, thickenings form and polyps grow. The main role in the development of this disease is played by allergic rhinosinusitis, obstructive bronchitis and asthma. If such rhinosinusitis occurs, treatment becomes very complicated, since the patient becomes intolerant to analgin and aspirin. Surgical treatment may cause suffocation. Therefore, the elimination of polyps occurs only after the cause is found and eliminated.

Other possible types of rhinosinusitis
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish several more types of rhinosinusitis. This includes.
- Allergic rhinosinusitis. This type of disease occurs due to exposure to irritants in the form of dust, pollen from flowering plants, medications, and pet hair.
Allergic rhinosinusitis manifests itself as symptoms:
appearance of a rash on skin;
the presence of clear discharge in the nasal passages;
redness of the eyes.The first step is to correctly differentiate acute catarrhal rhinosinusitis from allergic rhinitis. To do this, an examination is carried out, which includes skin tests.
- Vasomotor rhinosinusitis. The main reason for this type of disease is colds. The patient develops a runny nose with the release of mucus of a liquid consistency. After a few days, they begin to thicken, acquire a yellowish or greenish color and an unpleasant odor. Often this type of rhinosinusitis occurs in childhood due to frequent colds. The child experiences fever, general weakness and sleep disturbances. With severely weakened immune function, vasomotor rhinosinusitis becomes chronic and sinusitis.
If a patient develops rhinosusitis, symptoms and treatment should be determined as quickly as possible. This disease quickly flows from one form to another, so consultation with an experienced specialist is required.

Rhinosinusitis treatment process
Many patients ask how to treat rhinosinusitis. The first step is to visit a doctor. He will conduct an examination and listen to the patient's complaints. Based on this, a diagnosis is made. If the patient has acute purulent sinusitis, then it is prescribed additional examination to exclude complications and determine the pathogen. If purulent sinusitis is confirmed, then treatment includes surgical intervention in the form of a puncture. The patient's sinuses are pierced and the purulent contents are pumped out.
After this, drug therapy and physical treatment are prescribed.
- Taking broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Rinse the nasal passages with saline or furatsilin solution.
- Usage vasoconstrictor drops.
- The use of immunostimulating agents.
- Carrying out UV or UHF.
If rhinosinusitis occurs in children, treatment includes the following steps.
- Taking probiotics to normalize the digestive system.
- Carrying out the “cuckoo” procedure with the addition of saline solution.
- Carrying out a procedure for suctioning mucus with a special apparatus.
- Carrying out inhalations using a nebulizer.
- Taking vitamin complexes.
- Use of antihistamines.
Duration of treatment antibacterial agents is two weeks. Full recovery in acute rhinosinusitis it occurs within a month.
Treatment of rhinosinusitis with traditional methods
Treatment folk remedies used as complementary therapy. They can be used either topically in the form of rinsing the nasal passages or instilling drops, or taken orally.
To prepare medicinal drops, you need to take calendula, eucalyptus, valerian, and sage in equal proportions. Pour two tablespoons of boiled water and let it brew for thirty minutes. The infusion should be strained. After this, the drops should be instilled into each nasal passage, two or three drops up to three times a day.
Some experts advise preparing oil drops. To prepare them you will need olive oil and a small piece of propolis. Dissolve the ingredients in a water bath, mix well and let sit for an hour. You need to instill up to two times a day. The procedure should be carried out after rinsing the nasal passages or inhalations.
Compresses can be used as warming procedures. But carry out this procedure should only be done if the patient has a non-purulent form of rhinosinusitis. To carry out the manipulations, you need to finely grate the black radish. Give a little juice and wrap in gauze. Place a compress on the affected sinus and cover with a warm scarf. Leave the product on for fifteen minutes.
In childhood, sinuses are often warmed up using a bag of salt. But before the procedure you need to consult a doctor.
If the child does not have allergic reactions, then you can drop two drops of liquid linden honey into each nasal passage. This remedy will relieve swelling and eliminate the inflammatory process.
Inhalations are considered an irreplaceable and effective remedy. In childhood, you can use a nebulizer with the addition of saline solution and herbal decoctions. Adults can perform steam inhalations with the addition of essential oils.
Rhinosinusitis is a complex disease in which the paranasal sinuses and the nasal mucosa are simultaneously affected by infection or viruses. As usual, the inflammatory process starts in the maxillary sinus and later moves to the main mucous protective structures.
Signs and symptoms
The main symptoms of rhinosinusitis usually include significant difficulty in breathing. Regardless of the degree and severity of the disease, the patient is also observed with localization at the base of the nose, constant discharge of purulent secretion with its regular entry into the nasopharynx, as well as general swelling of the nasal mucosa.
The remaining symptoms determine the main type of this disease and its specific form.
Main types and forms of rhinosinusitis
Current and clinical pictures at different types the above diseases differ in particular cases:
Acute rhinosinusitis

The acute form of this type of disease is characterized by severe intoxication of the body, rapid and vivid manifestation of the symptoms described above. Within five to seven days after the onset of inflammatory processes, a person cannot conduct full life, his performance is significantly reduced, pain syndromes in the head become paroxysmal in nature.
At the same time, body temperature almost always rises, often exceeding 39 degrees Celsius. Swelling of the mucous membranes can extend beyond the organ and spread to the eyelids and upper facial tissues. Pathogenic microflora actively multiply and occupy increasingly larger spaces, affecting neighboring sinuses and causing complications.
Chronic rhinosinusitis
This kind of inflammatory process is less pronounced when compared with the previous form of rhinosinusitis, but it is longer lasting and can often occur in a sluggish form from twelve to thirty weeks. The main symptoms of this condition are normal temperature, significant weakening of hearing and smell, constant moderate swelling of the mucous membranes with severe blockage of the nasal passages, as well as a nasal voice and mucopurulent secretion discharged from the nose.
Pain syndromes in this case appear much less frequently, they are “smeared out” and, if they occur regularly, cause a feeling of weakness and irritation.
In the chronic form of rhinosinusitis, the likelihood of getting a complication is much higher than in the case of acute course diseases.
Polypous rhinosinusitis
Further progression of chronic rhinosinusitis usually leads to the formation of polyps - active growth and thickening of the walls of the mucous membranes, as a result of which the swelling significantly increases in size, and vasoconstrictor drugs do not help to temporarily restore normal breathing. This condition is quite often accompanied by stagnation in the sinuses, a large number of purulent masses, which further activate inflammatory processes in the body and form the basis for the development of associated complications, in particular fatal dangerous meningitis and tissue/eyeball lesions.
This type of rhinosinusitis can only be cured with surgical methods, mechanically removing polyps.
Allergic rhinosinusitis
The main cause of allergic rhinosinusitis and catarrhal, non-purulent course of the disease is the effect of allergens on the body. Such allergens can be plant pollen, wool, body reactions to certain medications, fungal spores, car smog and dust, etc.
The main symptom directly indicating allergic type diseases are considered to be side rashes on the skin, significant redness of the membranes of the eyeball, itching in the nasopharynx, copious clear discharge from the nose. Fighting allergic rhinosinusitis with antibiotics is useless; to effectively get rid of the problem, they use antihistamines and isolation of the person/environment from the allergen.
Treatment of rhinosinusitis
Treatment of rhinosinusitis in adults is a complex process that includes eliminating the cause that caused the reaction, eliminating the source of inflammation, reducing symptoms, and restoring natural immune defenses.
- Antibacterial therapy with broad-spectrum antibiotics - these are drugs or alternative Augmentin. The duration of such a course does not exceed ten days
- Maximum removal of pathogenic secretions from the nose and sinuses. For this, (Naphthyzin), moisturizing and mucolytic drugs (Aquamaris), as well as agents (saline solution) are used.
- Reducing inflammation. For this, an ENT doctor may recommend corticosteroids (hydrocortisone) and antihistamines (Loratadine).
- Strengthening the immune system. It can be carried out both at the local level using special homeopathic sprays (IRS 19), and general procedures, including normalization of nutrition, taking interferon, and regular exercise.
Treatment of the disease in children

Rhinosinusitis in children is treated in a more gentle way, excluding the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics and glucocorticosteroids. In this case, it is rational to use local steroids/antibiotics (Isofra, Bioparox, Protargol), rinse the sinuses more often salt solutions, do it using Borjomi, strengthen the child’s immunity.
Only in the most extreme case, with a very advanced form of the disease and in the event of a direct danger to the baby’s life, is there a need to use classical “adult” drugs that have strong side effects and causing serious harm to the liver, kidneys and heart of your child.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for rhinosinusitis, of course, are not a panacea for this disease, but they can really help you recover faster in the case of complex therapy with medications.
The most popular methods “from the people” are considered to be warming up the nasal septum using hot salt in a bag, inhalation and drops into the nose herbal infusions based on calendula, valerian, chamomile, eucalyptus and sage, as well as compresses based on tinctures of the same herbs. It should be understood that the above methods must be agreed with your doctor in order to prevent the condition from worsening and the occurrence of concomitant diseases.
Useful video
Have a quick recovery!
Nasal discharge is not always a symptom common runny nose, they may be a sign of more serious illnesses, for example, rhinosinusitis. This disease is characterized by inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nasal passages and sinuses., which brings a lot of unpleasant troubles to patients. How to treat rhinosinusitis? Which medicines will this be required?
Rhinosinusitis is a complex disease that develops as a result of the effects of viruses or bacteria on the nasal passages and sinuses. When the inflammatory process spreads to the inside of the nose, the mucosal tissues swell, thicken and block the anastomosis through which the pathological secretion should come out. Further, purulent contents begin to accumulate in the sinuses, which leads to the development of pathology.
Most often, the cause of this disease is an untreated acute viral infection. Pathology can develop against the background of influenza, ARVI, adenovirus and other infectious diseases. When rhinosinusitis occurs, the causes of inflammation are determined:
- fungal microorganisms;
- polyposis;
- allergic reactions;
- staphylococcus and streptococcus.
If the nose is injured, the nasal septum may become deviated and other defects may appear, which can also lead to narrowing of the sinuses and, as a result, to the accumulation of pus. If rhinosinusitis appears, then symptoms and treatment in adults and children require special attention. Depending on the type of this pathology, appropriate treatment is selected.
Classification
Modern medicine identifies many types of rhinosinusitis. They are classified according to the time and nature of the flow, location and many other criteria.
- According to the causative agent of infection: bacterial, viral, fungal and mixed.
- According to the location of the inflammatory process: right-sided, left-sided, bilateral.
- According to the type of disease: chronic, acute and recurrent.
- According to the type of inflamed sinus: sphenoiditis, sinusitis, ethmoiditis, frontal sinusitis.
- According to the severity of the course: severe, mild and moderate forms.
Depending on the type of disease and the severity of its course, the doctor selects the necessary course of therapy. At correct observance With all medical recommendations, coping with rhinosinusitis will not be difficult. How to suspect the development of this disease? What symptoms accompany this?

The first signs of rhinosinusitis and its symptoms
The very first sign of the development of the disease is considered to be impaired nasal breathing, which is accompanied by copious mucous or purulent discharge. In addition, symptoms of rhinosinusitis include:
- hyperthermia (increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees);
- runny nose;
- general weakness, increased fatigue;
- loss of appetite;
- headaches at rest and when tilting the head;
- change in voice timbre;
- stuffy ears;
- impaired sense of smell;
- lacrimation.
Depending on the type of pathogen that caused the disease, nasal discharge may differ in color and consistency. Sometimes, in addition to the listed conditions, a cough may develop.
Polypous rhinosinusitis
The mucous membrane of the nasal passages consists of soft tissues. With frequent inflammatory processes, it becomes thinner, and the body, having received a signal about this, begins to grow a new layer. Quite often these overgrown pieces appearance differ from the mucous membrane: they are shaped like a drop, and inside they are filled with infiltrate (accumulation of lymph and blood). This formation is called a polyp; it makes nasal breathing difficult and can lead to the development of many diseases.
Polypous growths can be quite large. At the same time, constant discomfort is felt, the sense of smell deteriorates, it seems as if there is something in the nose. foreign body. Polyps can also block the sinuses, allowing pus to accumulate in them. This is how polypous rhinosinusitis develops.

Purulent rhinosinusitis
The most common cause of the disease in this case is the common cold. When viruses enter the nasal passages, inflammation develops, which is accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane. As a result, the mucous contents of the sinuses come out with difficulty and a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms is formed in places where secretions accumulate.
The formation of pus in the sinuses is often accompanied by a rise in temperature to high levels. The patient suffers from headaches that worsen when bending over, weakness and general malaise appear. Nasal breathing is difficult due to congestion; a person tries to breathe through the mouth, which can lead to the development of a cough.
In especially severe cases, bad breath appears, cheeks and eyelids become swollen. A feeling of fullness is noted in the affected sinuses. On the background high temperature General intoxication of the body may develop.
Allergic rhinosinusitis
In this case, inflammation of the nasal sinuses develops when an allergen enters the human body. Due to swelling of the mucous membrane copious discharge they do not come out of the nasal cavities well, which results in the formation of pus. The cause of the disease can be:
- dust;
- plant pollen;
- pet hair;
- household chemicals;
- medications.
The main goal of treatment is to eliminate the provoking factor and reduce the body’s pathological reaction to the allergen. To do this, protect the patient from exposure to the allergen and prescribe antihistamine therapy.

Vasomotor rhinosinusitis
The development of vasomotor rhinosinusitis can also begin against the background of an acute viral infection. Its occurrence is associated with disruption of the functioning of nerve endings. When any irritant appears (cold, heat, strong odors), the nasal mucosa reacts quite violently: severe swelling appears, and the discharge becomes very abundant.
Vasomotor rhinosinusitis often develops in pregnant women. This occurs as a result of a sharp change in hormonal levels during pregnancy. Usually after childbirth everything returns to normal even without drug treatment.
Catarrhal rhinosinusitis
Catarrhal rhinosinusitis is one of the respiratory diseases in which the nasal mucosa becomes inflamed, as well as paranasal sinuses. Acute stage The disease is not dangerous and is very treatable. The symptoms of the pathology are in many ways similar to those of other types of rhinosinusitis:
- pain syndrome localized in the sinuses;
- swelling of the mucous membrane and its redness;
- increased body temperature, sometimes to very high levels;
- conjunctivitis;
- tearfulness;
- copious mucous discharge.
Complications of this disease occur extremely rarely. However, some patients may develop bacterial rhinosinusitis against the background of catarrhal disease. In this case, treatment is supplemented with antibiotics.

Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease, you need to contact an otolaryngologist. Based on the examination, medical history and examinations, the doctor will suggest the development of a diagnosis such as rhinosinusitis. Diagnostic measures may be as follows:
- urine and blood analysis;
- rhinoscopy (examination of the nose);
- radiography;
- CT scan;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- pharyngoscopy;
- examination of exudate for the presence of a pathogen and its sensitivity to drugs.
Rhinoscopy reveals swelling and redness of the tissues, as well as mucous exudate. After lubricating the nasal passages with a vasoconstrictor solution, pus is found in the area of the sinus anastomosis.

A more accurate picture can be seen during endoscopic examination. Using a special probe with a camera at the end, the doctor identifies abnormalities in the anatomy of the mucous membrane that may interfere with normal nasal ventilation.
How to cure rhinosinusitis in adults?
Treatment of rhinosinusitis is carried out in outpatient setting. In particularly advanced cases, hospitalization may be required. At the initial stage, treatment is conservative, including drug therapy and rinsing the nasal cavities in order to eliminate pathological secretions and pathogens. It is also possible to supplement the main course with traditional methods of treatment.

Drug therapy
When choosing a treatment method and the necessary medications, the doctor is based on the severity of rhinosinusitis, taking into account the presence concomitant diseases. To facilitate nasal breathing and reduce swelling of the mucous membrane in all types of pathology, vasoconstrictors are prescribed in the form of drops and sprays. The following are considered the most effective:
- "Xylene";
- "Galazolin";
In addition, doctors recommend daily rinsing of the nasal passages with a solution of sodium chloride or special aerosols based on sea water. This procedure helps more rapid recovery inflamed mucous membrane.
Xylene
In advanced forms of rhinosinusitis, it is possible to prescribe antibacterial drugs. For treatment severe forms diseases use:
- "Ampicillin";
- "Azithromycin";
- "Ceftriaxone".

With the development of rhinosinusitis of viral etiology, the use of immunostimulating and immunomodulating agents will be required. They help fight viruses, restore protective functions body and speed up recovery. Most often prescribed:
- "Anaferon";
- "Viferon";
- "Kagocel".

The doctor will also select medications for symptomatic treatment. To thin the mucus you will need mucolytics: Rinofluimucil, Sinuforte. To relieve pain and reduce body temperature, use antipyretic drugs Paracetamol and Ibuprofen. For allergic rhinosinusitis, antihistamine therapy is also indicated. Help reduce the body's reaction to allergens:
- "Suprastin";
- "Zyrtec";
- "Cetirizine";
- "Zodak".

Rinofluimucil to thin mucus
To treat all types of rhinosinusitis, it is possible to use special combination sprays that contain antibacterial components, as well as hormonal agents. “Polydex” and “Isofra” have proven themselves well.
Treatment with folk remedies
Of course, rhinosinusitis cannot be cured using folk remedies alone, but they can be a good addition to the main course of therapy. For a disease that develops against the background of a viral infection, onion and garlic drops help well. They are very simple to make: the onion vegetable is peeled and finely chopped. Using gauze, squeeze out the juice from the resulting mass and dilute it clean water in a ratio of 1:5. Apply these drops 2-3 times a day. Home remedies from medicinal plants help quite well.
Recipe No. 1 - Cyclamen
This beautiful perennial flower is considered today one of the most effective remedies to help get rid of rhinosinusitis. It is used in many pharmaceutical preparations, since the plant has many medicinal properties. At home, you can prepare cyclamen drops, do it as follows:
- The root of the plant is washed well and crushed using the finest grater.
- The juice is squeezed out of the resulting mass.
- To prepare the drops, the juice is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:5 and left to infuse in the refrigerator.
- Apply the product once a day. Place two drops in each nostril.
The positive effect after such treatment is noticeable within 1-2 days. Nasal breathing becomes easier, swelling decreases, as does the amount of secretion.

Recipe No. 2 - Horseradish and lemon
For cooking effective remedy against rhinosinusitis you will need 3 lemons and horseradish root. Citrus juice is mixed with the root chopped in a meat grinder and put in the refrigerator. The resulting mixture is taken on an empty stomach, half a teaspoon. This remedy is quite effective in the chronic course of the disease. Accept home remedy possible within 1-2 months.
Recipe No. 3 - Aloe
Agave has long been famous for its positive properties. This home plant with elastic, fleshy leaves, it helps fight many diseases. For rhinosinusitis, prepare effective drops. To do this, one leaf is crushed and the juice is squeezed out of it. Instill the resulting product 3-4 times a day, 2-3 drops.
Rhinosinusitis during pregnancy
The development of this disease during pregnancy occurs quite often. Weakened by a heavy load, the mother's body quickly picks up viral infections, which become the cause of this condition. Since many medications cannot be used during pregnancy, the course of treatment should be limited to local therapy.

Only a doctor should treat rhinosinusitis during pregnancy. In particularly severe cases, antibiotic sprays may be prescribed. These drugs act locally directly on the pathology itself and are practically not absorbed into the systemic circulation.
Also nasal drops based on sea water are approved for use in pregnant women: “Quix”, “Aquamaris”. Such drugs help clear the nose of mucus, moisturize the tissues of the nasal passages, relieve swelling and make breathing easier. Sometimes it may be necessary to use vasoconstrictor drops: “Naphthyzin”, “Nazivin”, but it is better to take them in a child’s dosage. At allergic variety for rhinosinusitis: Suprastin and Loratadine are allowed.
If the disease does not respond complex treatment approved drugs, the otolaryngologist may prescribe a puncture of the sinus followed by the administration of an anti-inflammatory solution. This procedure will help significantly alleviate the patient’s condition without harming the unborn child.
Rhinosinusitis in children
In young patients, this disease is acute. Due to the characteristics of the baby’s body, the signs and symptoms of the pathology are more pronounced than in adults. What should you pay attention to when treating rhinosinusitis in a child?

Features of the pathology
Full formation maxillary sinuses in children it occurs by age 7. The problem arises due to the fact that the transition points between the nasal cavity and the sinus are very narrow, and even with a slight swelling of the mucous membrane, this opening will close. As a result, pathological secretion accumulates in the sinuses, which leads to inflammation and the appearance of pus.
The clinical signs of this condition are quite typical. Developing rhinosinusitis in a child is characterized by symptoms that are very similar to those respiratory infections. Therefore, in order to exclude the development of complications, it is necessary to show the baby to the doctor as soon as possible. Rhinosinusitis in children of preschool and kindergarten age most often causes damage to the frontal sinuses and the ethmoid labyrinth, located on both sides of the bridge of the nose; when a similar pathology develops in adults, all sinuses are affected.
Treatment of rhinosinusitis in a child
The main goal of disease therapy is to suppress pathogens and increase the body's defenses. For this purpose, special techniques are selected that provide a complex effect on the body. The result of treatment is complete elimination of the infection and normalization of nasal breathing.
The list of drugs used to treat rhinosinusitis in children is almost the same as in adults, adjusted for the required dosage. Only a doctor should prescribe a course of treatment. Independent intervention in the process can only worsen the baby’s condition.
Most often, doctors recommend vasoconstrictors, for example “Nazol baby” or children’s “Nazivin”. They help relieve congestion and make breathing easier. In addition, funds will be required to strengthen immune system: “Reaferon-Lipint”, “Likopid”, “Amiksin”. The decision about the need to use antibiotics is made only by a doctor. In most cases, outpatient treatment does not require antibiotic therapy.

In most cases, treatment of rhinosinusitis in children occurs fairly quickly. If you follow all medical recommendations, recovery occurs in 1-2 weeks. Complications requiring more aggressive therapy or even surgical intervention, occur quite rarely. However, without proper treatment, rhinosinusitis can lead to life-threatening pathologies.
If rhinosinusitis occurs, the symptoms and treatment in adults require careful study. After all, in order to start treatment, you need to have a detailed understanding of it. So, rhinosinusitis is a disease characterized by chronic inflammation nasal mucosa and paranasal sinuses. Inflammation usually begins in the area of the maxillary sinus and then spreads to other parts of the mucosa.
The main symptoms of this disease include difficulty breathing as a result of nasal congestion. With rhinosinusitis, the appearance of frequent headaches is a common symptom that makes itself felt regardless of the severity of the disease. In this case, general swelling and purulent discharge from the sinuses are observed.
At this stage, there are 2 main forms of the disease:
- spicy;
- chronic.
The acute form of rhinosinusitis is characterized by severe intoxication of the body. For a week after active inflammatory processes, such patients feel quite unwell. Their quality of life is significantly reduced, affecting their ability to work; constant headaches are paroxysmal in nature. As for body temperature, in this situation it almost always rises. The disease is often accompanied by swelling of the entire mucous membrane, which spreads across the face, involving the eyelids. Active reproduction pathogenic microflora provokes various complications with damage to neighboring sinuses.
 In the chronic form of sinusitis, the inflammatory process is sluggish and not too clearly expressed. But compared to acute form the course of the disease has more a long period, which varies from 2.5 to 7 months. Among the signs of the disease are weakened auditory perceptions, deterioration of the sense of smell, swelling of the nasal mucosa. Such patients have a nasal voice, and periodic discharge of mucous purulent secretion from the nose is observed. In these cases, pain occurs much less frequently, and the body temperature remains mostly normal.
In the chronic form of sinusitis, the inflammatory process is sluggish and not too clearly expressed. But compared to acute form the course of the disease has more a long period, which varies from 2.5 to 7 months. Among the signs of the disease are weakened auditory perceptions, deterioration of the sense of smell, swelling of the nasal mucosa. Such patients have a nasal voice, and periodic discharge of mucous purulent secretion from the nose is observed. In these cases, pain occurs much less frequently, and the body temperature remains mostly normal.
But as for complications, in the chronic form the risk of developing them is much higher than in the acute course of the disease. There are quite a few types of chronic sinusitis. The most common of them are:
- polyposis;
- allergic.
The name of the first variety speaks for itself. This means that the progression of the disease is usually characterized by the formation of polyps on the walls of the nasal mucosa, which significantly expand and enlarge. Such phenomena often lead to stagnation of pus in the sinuses, which contributes to an even greater activation of inflammatory processes. Thus, the formation of a basis for further consequences and complications, which can sometimes be quite serious, is inevitable. For example, a disease such as meningitis may develop, which is deadly to human life and health. In severe cases of this type of sinusitis, recovery is possible only with surgical intervention.
 The cause of allergic rhinosinusitis is exposure to certain irritants on the nasal mucosa. Moreover, allergens can be both external and internal. The reaction may occur due to:
The cause of allergic rhinosinusitis is exposure to certain irritants on the nasal mucosa. Moreover, allergens can be both external and internal. The reaction may occur due to:
- bloom;
- pet hair;
- dust;
- cosmetics;
- Food;
- household chemicals;
- synthetic and woolen fabrics;
- some medications, especially if the dose is exceeded.
Among side effects resulting from exposure may include a skin rash, redness of the eyeball, severe itching and burning in the nose and nasopharynx, the presence of copious clear nasal discharge.
Return to contents
Diagnosis of the disease
Rhinosinusitis, like any other disease, should be treated with a diagnosis, which is reproduced by questioning the patient and his detailed examination. When palpating and tapping the cheeks and forehead, the sensation may be painful. But swelling in the area of the eyes and cheeks indicates the presence of complications. A visual examination allows you to see redness of the membrane in the nasal passages and determine the presence of purulent discharge.
 With the help of endoscopic examination, it is possible to more clearly examine the affected areas and detect anatomical changes in the nose that may act as obstacles that interfere with normal nasal ventilation. Radiography makes it possible to trace the pathological process in frontal lobes and maxillary sinuses. By the size and type of darkening it is possible to distinguish the presence of catarrhal sinusitis from purulent one.
With the help of endoscopic examination, it is possible to more clearly examine the affected areas and detect anatomical changes in the nose that may act as obstacles that interfere with normal nasal ventilation. Radiography makes it possible to trace the pathological process in frontal lobes and maxillary sinuses. By the size and type of darkening it is possible to distinguish the presence of catarrhal sinusitis from purulent one.
Applying the method computed tomography The extent of the inflammatory process is determined. In very rare cases, they resort to punctures of the maxillary sinuses, which are performed under local anesthesia. The procedure involves puncturing the maxillary sinus at its thinnest point. After this, the liquid or purulent contents are sucked out with a syringe. If necessary, the sinus is washed out by injecting a special medicine.