Hearing, vision, the oral cavity (these are especially connected by the trigeminal nerve), the brain and all other parts of the face and head are in close interconnection, and having captured one of them, pain can spread its nasty metastases to a neighbor.
If you have a toothache that radiates into your ear, this could mean the following:
- Acute inflammation of the pulp or inner part of the tooth, colloquially the “nerve.” With such a problem, if it (the nerve) is disturbed in some way, for example, by accidentally pressing on a tooth, or by drinking cold water, can be provoked sharp pain radiating to the ear area closer to the temple. If you do not go to the dentist and wait for the weather by the sea, then at the moment of death of the nerve the pain may go away, but most likely there will be complications such as osteomelitis, phlegmon or abscess.
- Wisdom tooth (figure eight). When this atavism begins to grow, the gums around it swell, causing the pain to be transmitted to the ear. In severe cases, pain occurs with any awkward movement of the jaw. Such teeth are usually removed.
- Pulpitis or pulpal abscess. This disease is accompanied by a sharp, throbbing pain radiating to the ear. No self-medication, go to the dentist immediately.
- Ordinary or . The pain radiates to the ears, neck joints, and temples.
- Trigeminal neuralgia. Sudden electric shock-like pain in the ear, lasting about two minutes. It also manifests itself as redness of the facial skin or reduction of facial and masticatory muscles. You should contact a neurologist for help.
- Otitis media. Manifested due to the presence of streptococci, can be characterized as childhood disease due to the special structure of the auditory tube, but sometimes occurs in adults. Pain extends to incisors ( chewing teeth), and in the area of the ears, slightly covering the back of the head. You need to contact an otolaryngologist.
- Dysfunctional functioning of the temporomandibular joint. The cause may be the appearance of adhesions, some forms of arthritis, mechanical injuries facial joints. It is diagnosed as severe pain and clicking in the area of the nodules, when trying to completely close or open the mouth, also when moving the jaw to the side. Depending on the degree of damage, the pain can be sharp or aching, and always gives the patient a feeling of toothache. It radiates into the ear and partially into the face area.
- Swelling of the temporomandibular joint. Occurs due to improper structure of teeth, defective bite. They manifest themselves as prolonged aching pain, radiating to the ear, and intensifying at the time of eating and opening the mouth wide.
- Sinusitis or maxillitis - inflammation of the lower sinus due to infectious diseases. The pain affects the areas of the teeth and ears.
This terrible, wandering pain sometimes arises for reasons completely unexpected at first glance:
- Diseases of the circulatory system (otherwise known as cardiovascular diseases).
- Nervous diseases.
- Problems with the spine and specifically the cervical vertebrae.
- Mental disorders.
What to do?

- If the pain is too unbearable, then it is not forbidden to try to save yourself with some painkiller. But even if this does not help, increasing the dose is unacceptable, as it is harmful.
- You can use regular special solutions, or evenly mixed decoctions, medicinal herbs, such as chamomile, golden mustache, sage, etc. You can also use healing propolis tinctures, sea salt, garlic, etc.
- Ear drops (if otitis is likely).
We will only conduct brief overview some of the drops, but after consulting with your doctor and familiarizing yourself with the topic in more detail ear drops On the Internet, everyone can find the most suitable drug for themselves:
Tsipromed

Instill 5-6 drops 3 times a day; if obvious symptoms disappear, you need to continue treatment for another two days. Prohibited for use during pregnancy, lactation, and children under 15 years of age. Sold by prescription.

The normal dosage for an adult is 4-5 drops, 2-4 times a day, for a child 2-3 drops, 3-4 times a day. Standard course treatment 7 days. Prohibited during pregnancy and lactation; children under one year of age should only take it under medical supervision.
Dispensed by prescription.
Otinum

Apply 3-4 drops, 3-4 times a day. Application period: 8-10 days. Not recommended for use when bronchial asthma, urticaria, acute rhinitis, and in the presence of damage to the eardrum. Sold without a prescription.
What can't you do?
Apply warm compresses, pick your teeth, touch your gums, take antibiotics yourself, drink any energy drinks for neuralgia, self-medicate, because... due to the specific influence of different medicines on the body, it will then be difficult for the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis (only moderate self-medication is acceptable in desperate circumstances).
Prevention

Action plan:
- Meet with the dentist at least once every six months, and if you discover caries, immediately make an appointment for an emergency appointment. Caries is known to be the cause of many kidney diseases, digestive tract, and even hearts.
- Any cold, such as flu or sore throat, must be treated to the bitter end. Otherwise, you can get otitis media (ear inflammation).
- It is very difficult to predict neuralgia, because it often occurs as an appendage to another disease, and which one is also difficult to say, everything is individual. It could be some kind of infection or injury. Here we can advise you to spend less time in the cold.
- Dental treatment should only be done by dentists with a good reputation. Negligent treatment can have bad consequences.
Pain in the area of the teeth and ears can have many various reasons. Many of them are noted in our article. And yet, each individual person has his own, individual reaction to many things.
Therefore, even if as a result of self-medication, or the pain itself has gone away, it is still necessary to undergo examination by a doctor.
On my own toothache very painful. And if a tooth and ear hurt at the same time, then a person’s suffering is doubly intensified. Can ear pain be caused by dental problems? Or vice versa? Let's figure it out.
The reasons why the ear suffers can be different. Most often they are associated with upper jaw. Their roots are located in close proximity to the ear canal, so any inflammatory processes in the mouth can radiate there.
One of the most common causes of pain is the eruption of the eighth molar, or otherwise “wisdom tooth.” The fact is that the eighth molars erupt differently for each person. Some feel only slight discomfort, others experience all the “delights” of the process: the gums swell, not only the teething teeth hurt, but also the ear.
This happens when the “wisdom tooth” grows with pathologies, for example, they become inflamed facial muscles. In the case when painful sensations do not go away for a long time, and the symptoms only get worse day by day, you need to go to the dentist. The doctor must make sure that there is no purulent process or begin to urgently treat it.
One more common reason- soft tissue injuries. Pain behind the ear or in the ear can occur after tooth extraction or some other dental procedure, when, due to injury to the soft tissue or tooth root, swelling occurs and the tooth socket becomes inflamed. The pain in the ear most often has a pulsating character. In this case, a consultation with a dentist is also necessary.
The reason that toothache radiates to the ear may be a cyst. If the tooth was treated incorrectly, the problem area may swell and fester. It is important to stop the process as soon as possible, otherwise the ear canals may also suffer due to inflammation of the tooth. With advanced inflammation, the cyst grows to a sufficiently large sizes and the pain is not localized in one place, but spreads over the entire painful side of the face. In addition, a cyst can occur not only after unsuccessful treatment, but also when timely treatment absent.
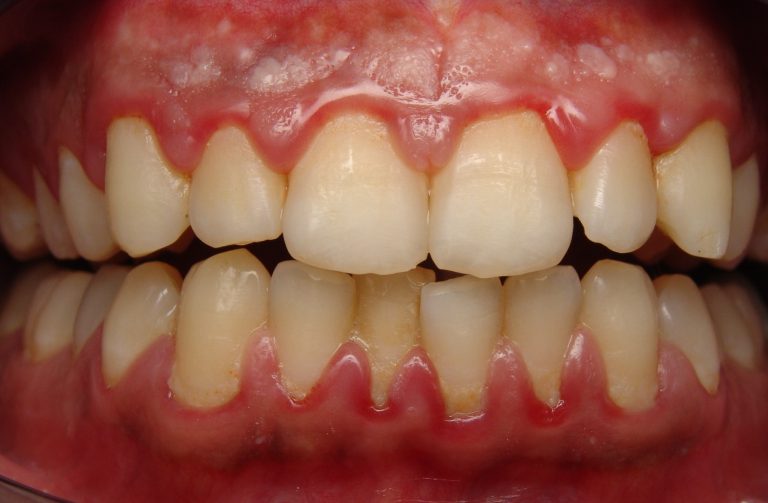
Gum inflammation
On initial stage development of gum inflammation is almost asymptomatic. Over time, blood begins to ooze from the gums, the temperature rises, and the tooth begins to loosen. In especially severe cases, a fistula may form, from which purulent contents flow. Pain from inflammation of the upper gum can radiate into the ear and cause severe pain. You should contact your dentist about this problem as soon as your gums become sore. You should not wait for the development of the inflammatory process and the appearance of pus.
When the pulp is inflamed, pain can occur both in the ears and in the temple. If the pain overtook you at a time when for some reason you cannot get to the dentist, then you should take painkillers and see a doctor as soon as possible. Inflamed nervous dental tissue should be treated as quickly as possible. Only a dentist can do this correctly, and folk remedies will only eliminate the symptom without affecting the cause of the disease. In advanced cases, pain in the ears, tooth and temple will no longer be relieved by painkillers, and the tooth will be destroyed and will have to be removed.
Inflammation of the middle ear
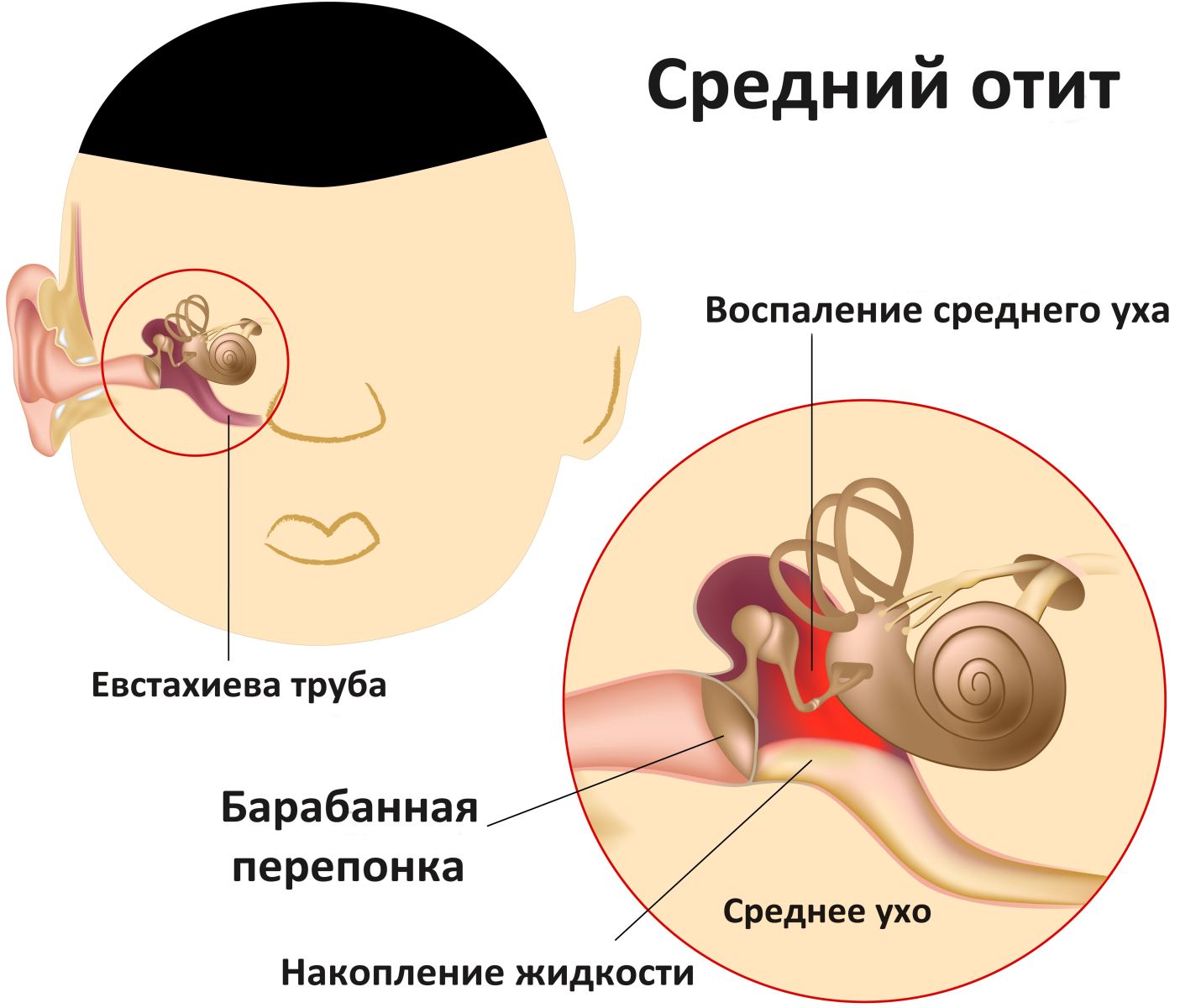
Teeth are not always the culprit for ear pain; the opposite situations also happen: teeth hurt because of a sore ear. This is possible, for example, with otitis media. Otitis is a disease that cannot be ignored. It should be treated only under the supervision of an otolaryngologist. Treatment is carried out medications, and as additional measures are used traditional methods. With otitis media there is a sharp and constant pain, which affects one tooth or the entire jaw at once.
Elena Malysheva and her team talk in detail about otitis media and its manifestations in the following video:
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
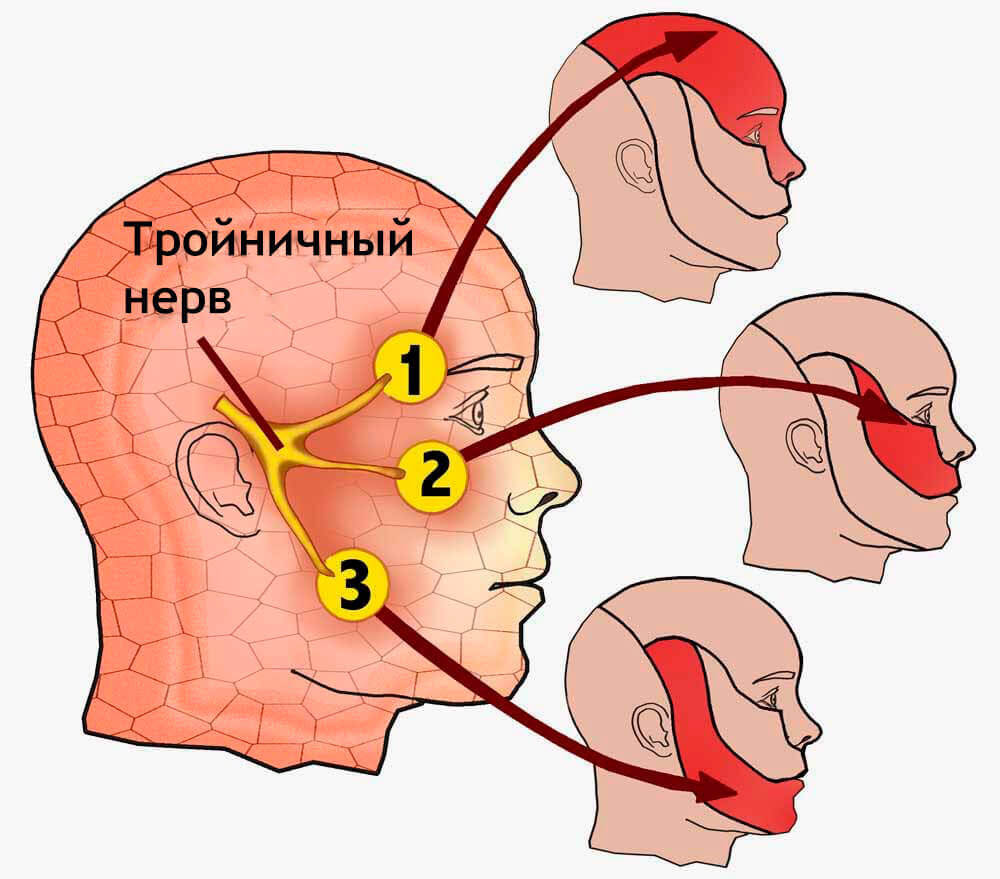
Teeth and ears do not always hurt due to dental problems or ear problems. Acute pain may occur due to an inflammatory process in the trigeminal nerve. Such pain appears sharply and suddenly, without any prerequisites or external stimuli. It continues for some time, then subsides and after a while returns again. The pain is so strong that patients describe it, comparing it to an electric shock. In some cases, the pain is not so severe, but constant and excruciating. One of the symptoms of inflammation trigeminal nerve are redness on one side of the face, difficulty chewing, cramps facial muscles. With such a problem, you need to contact a neurologist.
In the video, a neurologist examines the causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve in general, and the inflammation resulting from improper treatment in dentistry in particular:
Mechanical damage and other reasons
Painful symptoms in the ear and teeth can be caused by dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. This can happen as a result of a joint becoming dislodged after an impact or as a result of arthritis. In addition to unpleasant sensations, a person has problems opening and closing the jaw, and the pain itself can be either sharp and paroxysmal, or aching and constant. In this case, the person will have to be treated by two doctors at once - a dentist and an orthopedist. If drug treatment does not help within 2-3 days, the orthopedist will straighten the joint and apply a plaster cast.
Sometimes pain in the teeth and ear is not associated with either organ at all. This may be a symptom of completely different diseases. For example, mental disorders nervous system, cardiovascular system, at pathological processes in the brain, spine or problems in cervical vertebrae. For any pain, you should consult a doctor, because even minor and temporary discomfort can be a symptom of a serious illness.
First aid
If the pain began suddenly and at night, and you can only get to see a doctor in the morning, then you are allowed to:
- take painkillers;
- rinse your teeth with soda solution;
- for chronic otitis, put the ear drops that you usually use into your ear.
If a tooth hurts and radiates into the ear, it is forbidden to self-medicate. Under no circumstances should you:
- press and touch the inflamed gum;
- pick at the sore tooth with toothpicks;
- apply warm compresses;
- drink energy drinks.
There can be many reasons why a tooth and ear hurt at the same time. Therefore, only a specialist can diagnose the disease. It is strictly forbidden to independently diagnose yourself and prescribe treatment, since after taking the wrong medications and remedies it will be much more difficult for the doctor to determine the disease.
There are several folk remedies that help relieve pain, but they should only be used after consulting a doctor.
Folk remedies for ear pain
- Wrap an aloe leaf in gauze, lightly knead it and insert it into the ear canal.
- Place a few drops of onion juice in each ear.
- Place warm olive oil in your ear.
- Severe pain can be relieved by rolling up a geranium leaf, which must be inserted into the ear canal.
- You can prepare a decoction of lingonberries. Pour 2 cups of boiling water over a handful of berries and drink 2 cups 30 minutes before meals.
- If otitis is your frequent problem, then you can prepare a celandine tincture in advance. It helps with severe pain. 20 g of celandine should be poured into 100 g of vodka and left in a dark, cool place for 10 days. Then strain and store in the refrigerator. A tampon is moistened with this infusion and placed in the ear.
Aloe leaf is inserted into the ear canal Onion juice can be instilled inside auricle Olive oil also instilled inside Geranium leaf helps relieve pain Decoction of lingonberries is taken 30 minutes before meals Celandine tincture helps get rid of otitis media
Folk remedies for toothache
- Chamomile or sage decoction: pour 5 tablespoons of boiling water over a glass, put on water bath for half an hour. Then strain the broth and cool until warm state. Rinse your mouth with the resulting product.
- Plantain can be used in 2 ways. Make an infusion from it or squeeze the fresh juice of the plant. To prepare the infusion you will need a spoon of raw materials and a glass of boiling water. Leave for half an hour and rinse. If you squeeze the juice from a fresh plant, then you need to wipe the gum in the area of the sore tooth with it.
- Famous folk remedy for toothache - garlic on the wrist. A clove of garlic should be finely chopped and applied to the wrist with inside, on the hand opposite to the sore spot. Tie with a bandage. Traditional healers We are sure that this method is similar to acupuncture; garlic stimulates points on the wrist, the impact of which reduces toothache. But if the skin under the bandage begins to burn or become very red, then you should wash your hand and abandon this method of treatment.
- Agave is famous for its pain-relieving properties. If you have this plant at home, you can cut off a piece of its leaf, rinse it under water and make a longitudinal cut on it. With this cut, the sheet is applied to the gum in the area of the diseased tooth. Keep the compress for 5 minutes. This product should be used with caution. Agave is a poisonous plant, and many people can experience severe allergic reactions to its juice.
Preventive measures
Regular visits to the dentist - good habit, which will help avoid most causes of tooth pain. The specialist will notice the problem on early stages and will eliminate it in a timely manner.
– almost everyone and, as a rule, more than once in a lifetime. The reasons for this phenomenon huge amount: from occurrence serious problems with teeth requiring long-term treatment, to the point of banal reluctance to treat ordinary caries.
Why have we combined these two types of pain? It's simple, many people complain about the occurrence of such painful sensations at the same time. That's why next we'll talk about whether a tooth can hurt your ear and why this happens?
The answer to this question is unequivocal - yes, it can.. Our body is complex system, in which all organs are in interaction with each other. Therefore, our teeth are closely interconnected with the ears, nasopharynx and even eyes.
Toothache can cause discomfort in the ears
And if a person exhibits painful sensations in one of these areas, this does not always mean that their source is located there.
Reference. Toothache from untreated caries except ear pain, can also provoke headache and create a feeling of pain in all teeth.
Let's look at the main reasons why toothache can cause pain in the ear:
- pulp inflammation- that's what it's called soft fabric tooth, inflammation of which is provoked by bacteria that have penetrated as a result of caries. This deviation can cause sudden severe pain, which intensifies when pressure is applied to the affected molar or when food that is too cold or hot comes into contact with it. In addition, such pain in the tooth radiates to the temporal region;
Reference. In no case should you postpone visiting a doctor if such symptoms are detected, since complications may develop in the form of an abscess, osteomyelitis or phlegmon.
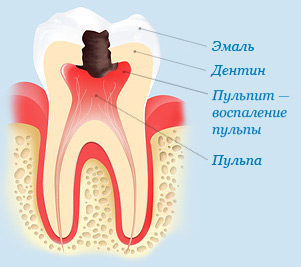
The cause of pulpitis is often caries
- acute pulpitis- quite often there is a purulent-diffuse appearance, accompanied by throbbing pain that spreads to the ears and temporal region;
- caries chewing teeth – the most common dental disease, familiar to everyone. If the extreme molars are in an advanced carious state, then pain in the ear is a completely natural phenomenon that will intensify in the evening;
- wisdom tooth growth– usually such molars do not erupt without problems, since they grow after the body has formed. Therefore, quite often they simply do not have enough space in the dentition. “Eights” erupt painfully, with an increase in temperature, and the pain can radiate to the ear, throat, even under the eye. General weakness may occur;
Important! With such signs, it is imperative to consult a doctor in order to avoid complications in the form of a purulent process, which can progress to bone tissue and nerve fibers.

If a “wisdom tooth” erupts, then painful sensations will definitely be observed.
- after dental operations– if the ear hurts after treatment of a tooth or it, then this may indicate the failure of the manipulations and the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the oral cavity;
- injury to teeth and soft tissues– if such traumatization occurs, then the formation of swelling in this place may be observed. The patient will feel a throbbing pain that will radiate through the ear cavity;
- dental cyst– can also cause ear pain due to a tooth. Because of improper therapy such pathologies may appear alarming symptoms– swelling and suppuration at the location of the tumor. If you start treating such a process at the right time, the ear canals can suffer quite significantly.
In addition to the above factors that provoke the occurrence of pain in the ears, there are a number of other situations associated with the appearance of such phenomena. Let's look at them in more detail.
Minor Factors
If a tooth and ear hurt at the same time, this may not always indicate dental problems. In such situations, a rather unpleasant pain spreads almost the entire half of the face and is characterized by a wavy character, and the patient is not able to determine what is the cause of this phenomenon and what is the consequence.
So, in addition to the main factors, there are also the following culprits of this disease:
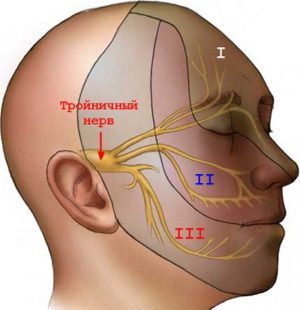
Trigeminal nerve inflammation is a common cause of tooth and ear pain.
- Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve — pain syndrome occurs suddenly, and is felt simultaneously in both the tooth and the ear. Such inflammation can be determined by the nature of the pain, since it lasts several minutes and is similar to an electric shock. In addition, redness of the face may be observed, as well as spasms of the masticatory and facial muscles. With such symptoms, you need to visit a neurologist.
- TMJ dysfunction– this deviation develops mainly due to injury or arthritis. It is characterized aching pain in the oral cavity and ear, and it is also impossible to fully open the mouth.
- Inflammation of the temporomandibular joint- appears due to malocclusion or chewing on one side. Soreness is constantly felt in the teeth and ear, and it intensifies during meals.
As we see, there are plenty of reasons for the development of such a process. But how can you tell if your tooth or ear hurts? It is very difficult to do this on your own, and is it really worth the guesswork? It is better to trust a competent specialist who will not only determine the cause, but also prescribe appropriate therapy.
What to do with this type of pain

Rinsing a sore tooth with baking soda will help relieve pain for a while.
What to do if your ear and tooth hurt at the same time? It is definitely necessary to visit a doctor immediately - this is the only right decision in this situation.
No self-medication or selection of medications, much less use various recipes folk medicinethere is no question.
Such actions without the consent of a doctor, except possible harm, can make it difficult for a specialist to make a diagnosis and determine the direction of treatment.
If there is no way to visit a doctor in the near future, then you can take first aid measures at home. To do this, you need to perform the following manipulations:
- take a painkiller;
- rinse your mouth with a soda solution;
- drop special drops into the ear.

You need to know what not to do at home with this type of pain
It is also worth paying attention to what absolutely cannot be done with such a pathology:
- Place warm.
- Touch and press with your fingers on the inflamed gum.
- Use toothpicks.
- Take the special ones yourself before visiting a doctor.
- Drink energy drinks, strong tea and coffee (for trigeminal neuralgia).
After providing first aid, you should as soon as possible visit the dentist, since only a doctor can eliminate the cause of the pain.
Our body is designed very cunningly, so we are not always able to find the cause of discomfort, since it may be hidden in a completely different place.
That is why you should not look for medical talents in yourself, but it is better to immediately trust the doctors. Wasted precious time trying to independently identify and treat the disease can result in irreversible consequences for health.
If a patient is diagnosed with otitis media and the teeth hurt unbearably, this indicates that the disease has progressed to a more severe form. severe form. Otitis is a fairly common ailment, which often causes severe toothache. In this case, it is sometimes difficult to understand which organ should be treated - the ear or the tooth. The patient is often confused which specialist to contact first. An ambiguous situation also arises when teething in babies, since the symptoms are similar to otitis media, and the cause of ear pain is completely different.
How to recognize the disease?
Otitis - inflammatory process, occurring in the ear, accompanied by severe pain, weakness, insomnia and loss of appetite. If not properly treated, this disease can lead to negative consequences up to fatal outcome. Therefore, upon detection characteristic symptoms(ears begin to hurt), you must immediately contact an otolaryngologist, who will prescribe effective medications and prescribe procedures to help overcome the disease.
Usually the disease begins with inflammation of the outer ear, but if the process is not treated, it goes deeper, causing the so-called otitis media. The disease may be accompanied by severe toothache and headache. The discomfort radiates to the temple, back of the head or jaw, so the patient feels as if his tooth hurts or his ear hurts. The pain can be continuous or throbbing, pulling or shooting.
A similar inflammatory process usually develops in acute otitis media. It is caused by an infection that enters the middle ear through the auditory tube due to diseases of the nasopharynx. This is typical for persons with reduced immunity, a deviated nasal septum, chronic rhinitis, and sinusitis. IN auditory tube the free flow of air is disrupted, which leads to deterioration of blood flow in eardrum, fluid accumulates in the ear.
Otitis media in its course goes through 3 main stages. Aching or throbbing pain in the jaw is most often observed at the first stage of development of the disease. It can be combined with elevated temperature body and worsen when swallowing, coughing, sneezing. If the disease is not treated at this stage, it will progress to the second stage, characterized by a decrease in ear pain, the release of pus from the ear canal and the formation of cracks in the eardrum. Hearing may deteriorate without further recovery, so contacting an ENT specialist is necessary. At the third stage, pus ceases to be secreted, and the perforation on the eardrum is closed by a scar. Patients complain mainly of ear congestion and hearing loss.
In the treatment of otitis, warm compresses with alcohol solution, physiotherapeutic procedures. In the most severe cases, painkillers, antibiotics, antipyretics and sulfonamides may be prescribed. Also ear canal washed with a solution of furatsilin or boric acid.
What to do if your baby is suffering?
 If a child who is not yet able to speak screams continuously, refuses to eat, and frequently rubs his ears and cheeks, parents should be very careful to understand the reason for this behavior. Otitis media is often diagnosed in children under 3 years of age. During this same period, baby teeth erupt. Irritability, refusal to eat, throbbing pain in the ears - all this is typical for both the first and second cases.
If a child who is not yet able to speak screams continuously, refuses to eat, and frequently rubs his ears and cheeks, parents should be very careful to understand the reason for this behavior. Otitis media is often diagnosed in children under 3 years of age. During this same period, baby teeth erupt. Irritability, refusal to eat, throbbing pain in the ears - all this is typical for both the first and second cases.
Despite the fact that pain in the ears is characteristic mainly of infectious diseases, the appearance of discomfort during teething is due to the close location of the ear nerves and jaw muscles. Therefore, the child cannot always understand where and what exactly hurts him.
There are a number of differences between these processes. When teething, the child is capricious from time to time, has swollen gums, increased salivation. Otitis media occurs, as a rule, after a runny nose; the baby may cry and scream for a long time without stopping. In any case, you should contact your pediatrician to determine the cause of your baby’s anxiety and take appropriate measures.
Thus, an adult or a small patient may have pain in the ears and teeth at the same time, but only a competent specialist will help determine the factor that caused the pain and prescribe competent treatment.








