Pockets in the gums - causes, symptoms, prevention.
Pockets in the gums are the first sign of periodontal disease, a disease that affects the tissue around the tooth (periodontal). Basically, this is a painless phenomenon that develops quite slowly. The gum tissue begins to turn pale, bleed, loosen, “settle”, a gap appears between the tooth and the gum - a pocket. With advanced periodontal disease, the necks of the teeth and even the roots are exposed, which is fraught with tooth loss. Often, pockets in the gums become infected, causing suppuration.
What causes periodontal disease is still not completely clear. Presumably, this is a combination of several factors, such as impaired blood supply to the gums, endocrine diseases(diabetes), nutritional disorders and gastrointestinal diseases, vitamin C hypovitaminosis, poor hygiene teeth.
To prevent the occurrence of periodontal disease, you must adhere to the following points.
1. Eat fiber-enriched plant foods (vegetables, fresh fruits).
2.Eat foods rich in vitamin C or take vitamin C supplements.
3.Do not chew hard food (nuts, bones).
4. Avoid alternately eating hot and cold food.
5.Massage your gums regularly.
6.Do not smoke or overeat sweets.
7.Use a rinse or a decoction of herbs (chamomile, calendula, oak bark, sage).
How to treat pockets in the gums using a folk method.
The following recipes can be used to treat periodontal disease.
1. Hydrogen peroxide. After caring for your teeth, rinse your mouth with 3% hydrogen peroxide. Two procedures a day will be enough. The course of treatment is 10 days. But if peroxide causes discomfort, which do not go away for a long time, this means that this method needs to be replaced by another.
2.Collection for periodontal disease. Oak bark, pine needles, St. John's wort, rose hips are taken equally. From the collection, a not very strong infusion is made, which is used as a rinse, and it is suitable for long-term daily use.
Using these recipes, I cured the pockets in my gums, and after several months I confidently say that periodontal disease has been defeated!
Helpful advice.
To prevent periodontal disease, you can do the following massage. After brushing your teeth, soak your toothbrush in saline solution(or sea buckthorn oil, nettle decoction, onion juice, onion peel decoction) and massage the gums with gentle movements in a circle.
Diseases of the gums and oral mucosa are far from uncommon these days. A signal of serious problems is a pocket in the gum between the teeth; we will look at how to treat it and where it came from in this article.
Pocket in the gum between the teeth - how to treat
First you need to have some idea of what periodontal disease is. Periodontium is all the tissue surrounding the tooth. This includes bone, ligaments, root cement, and gums. The root of each tooth is located in its designated hole inside jaw bone, to which it is attached using strong and elastic ligaments called periodontium. These ligaments prevent the tooth from falling out of the socket, as well as from rotating around its axis and tilting. They provide very little movement, called physiological mobility. This type of mobility is normal and almost unnoticeable. Everyday life. Periodontal ligaments also transfer chewing pressure from the tooth to the bone, acting as a shock absorber. In general, the function of these ligaments is extremely important.
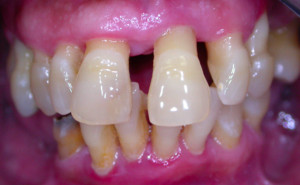
In advanced periodontal diseases, the gums become inflamed constant exposure microbes and begins to decrease, exposing the root. The periodontal ligaments are also destroyed. The process transfers to the bone, its height becomes less and less, the teeth become loose and fall out. So gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) turns into periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontium, accompanied by loss of bone tissue).

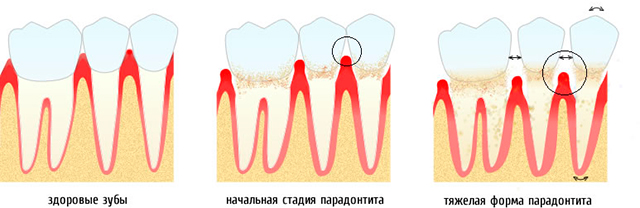
Classification of gum pockets
Normally, the gums fit tightly to the teeth throughout. In the area of the neck of the tooth, the gum lies somewhat looser, slightly behind the tooth, forming a normal gingival groove. Its depth should not be more than 3 mm. The depth is measured using a special instrument - a probe with a blunt end, which is carefully immersed in the space between the gum and tooth.

In the case when in the area of the neck of the tooth long time soft and hard plaque accumulates, harmful bacteria cause inflammation of the gums, which can subsequently lead to the formation of a pocket.
Table. Types of pathological pockets in the dental area.
| False pockets | True pockets |
|
|---|---|---|
| A false gum pocket is actually swollen gum. Increasing in volume and height due to inflammation or hypertrophy, it creates the illusion of a real pocket and when measured, an increase in the depth of the gingival sulcus is actually visible. However, the difference is that in a false pocket, the attachment of the gum to the tooth is not broken and it still fits tightly to the root along its entire length. | A periodontal, bone, or true pocket is formed when the ligaments that attach the tooth to the bone are destroyed. |
|
| Supraalvelar pockets (periosteal) appear when bone destruction occurs in a horizontal direction | Intraalveolar pockets (intraosseous) appear in the vertical direction of bone destruction |
|
Risk Factors for Gum Pocket Formation

Who can get a gum pocket?
Usually people do not pay too much attention to the condition of their gums until the disease becomes quite severe. Most often this occurs between the ages of 30-40 years. Men are more prone to periodontitis, which is, in particular, due to the predominance of men among smokers, as well as difficult working conditions. In adolescents, gum disease and false pocket formation are more common than bone loss. However, there are separate forms periodontal diseases that develop at a young age and are extremely severe, so when the first symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis. In general, gum disease can appear at any age if personal oral hygiene is not given due attention.
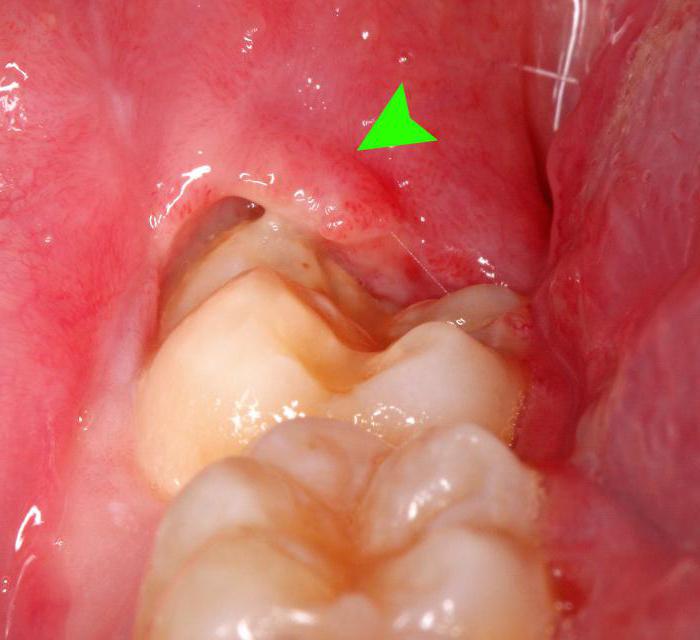
How can I tell if I have pockets in my gums?
There are a number of signs that may indicate the presence of pockets in the gums:
- bad breath that does not disappear despite the hygiene products used;
- red, swollen gums, sometimes of an unusual shape;
- sensitive and bleeding gums;
- pain when chewing and eating;
- mobile teeth;
- too much sensitive teeth, feeling of pain when eating cold or hot food or drinks;
- loss of gums, exposure of tooth roots.
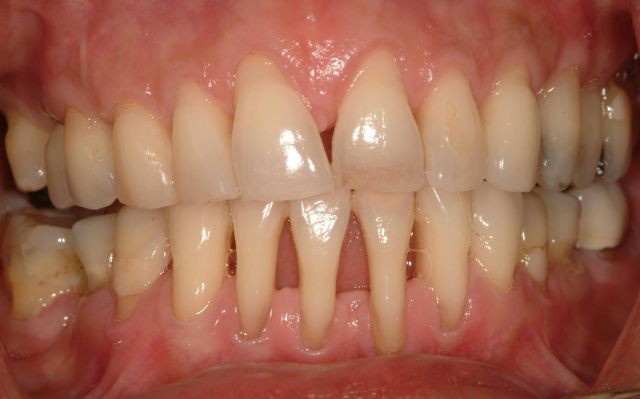
Each of these signs serves as a signal of serious problems in the oral cavity. If you experience any of the symptoms, you should consult a dentist to determine the cause. If periodontal disease is suspected, diagnosis usually consists of the following:
- asking the patient about the development of the disease, existing risk factors, and previous treatment;
- inspection and instrumental study teeth and gums to identify signs of inflammation;
- measuring the depth of the gum pockets with a thin probe with a rounded tip (most often painless);
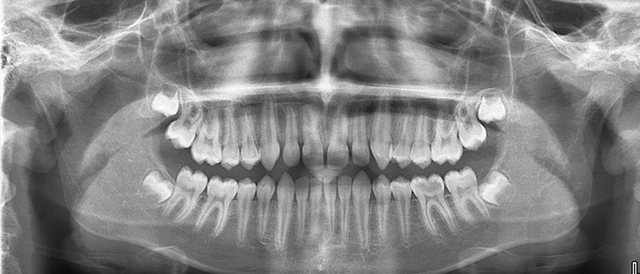
- performance x-ray upper/lower jaw to determine the presence of bone loss, its depth and extent.
How to treat gum pockets?
The main goal of periodontitis treatment is to eliminate the infection. The types and number of procedures vary greatly and are determined by the form and severity of the disease. In this case, not only the manipulations themselves and the doctor’s prescriptions are important, but also the careful implementation of all recommendations by the patient at home. The doctor will also advise you to get rid of bad habits and treat other diseases (for example, diabetes).

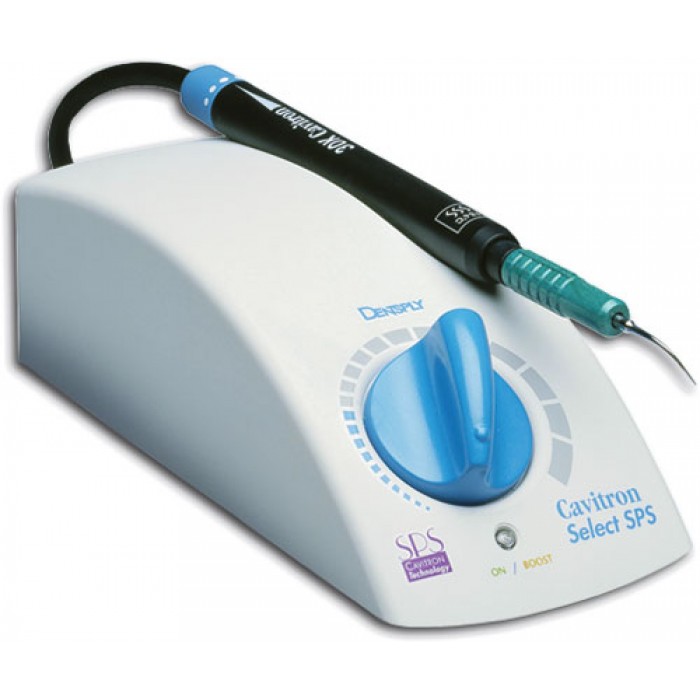
Professional teeth cleaning and closed curettage
The first procedure that is prescribed when gum pockets form is a thorough brushing of the teeth. dental office. Only a doctor can carry out such cleaning, as it is very different from home brushing with a toothbrush. Here, special methods are used to clean all tooth surfaces from soft and hard plaque; manual or ultrasonic scalers are used, as well as curettes that carefully scrape and separate accumulated tartar from the surface of the crown and root of the tooth. Despite all the aggressiveness of these instruments towards plaque, they do not damage the surface of the root itself.

After cleaning with scalers and curettes, the surface of the tooth is polished so that less plaque accumulates on it. This can be achieved using machines that supply polishing dispersion, either manually or using a laser.
Medicines for the treatment of gum pockets
After professional hygiene oral cavity in the presence of pockets in the gums, as a rule, medications are prescribed.

All these drugs only complement the main treatment and cannot be used without professional hygiene. They also will not replace surgical interventions prescribed for moderate and severe forms periodontitis.
Surgical methods for treating gum pockets
The first option surgical treatment periodontitis and gum pockets is open curettage. The objective of the method is to clean plaque and microbial residues, as well as affected tissues in the area of the roots of the teeth. In this case, a section of the gum limited in height is separated from the teeth and bone after making the incisions, and thus the doctor can visually monitor the progress of cleaning the teeth and tissues. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Once the cleaning is complete, the gums are sutured into place and an anti-inflammatory agent is applied to improve healing of the gums and reduce the risk of complications.

If there is significant bone loss, a flap operation is performed, which differs from open curettage in that the gum is peeled off from the bone completely along its entire length, before moving into the mucous membrane of the lips and cheeks. Often lost bone tissue is also replaced with grafts.
However, even such serious and labor-intensive operations cannot permanently prevent the re-development of periodontitis and its exacerbation. All therapeutic measures should be used in combination; the loss of at least one link significantly reduces the effectiveness of treatment in the future.
How to care for teeth and gums if there are already gum pockets?
When gum pockets appear, you will have to fight pathogenic bacteria at home, too. After treatment, strict adherence to all the dentist’s recommendations is required. Personal oral hygiene should be especially thorough and at least twice a day. It is advisable to periodically use antiseptic rinses, but strictly as prescribed by a doctor. The market also offers special pastes for people prone to gum and periodontal inflammation. It is highly recommended to purchase an irrigator - a special device that allows you to increase the degree of teeth cleansing. It also massages the gums, helps blood circulation, healing and regeneration after surgical interventions and curettage. The dentist will recommend using it as an irrigation liquid. medicinal solutions and decoctions of medicinal herbs.

How to prevent pockets in the gums?
- Follow personal hygiene teeth, massage the gums with a brush or irrigator.
- Don't forget about cleaning between your teeth.
- Visit your dentist at least once every six months or more often if necessary.
- Maintain the overall health of the body, do not trigger the course of major diseases.
- Give up bad habits - smoking, alcohol.
What happens if gum pockets are not treated?
With the further development of periodontitis, the depth of the gum pockets rapidly increases, plaque continues to accumulate, affecting an increasing number of tissues. Next, the ligament holding the tooth in place deteriorates to the point where it becomes loose, eventually leading to tooth loss. In addition, increasing inflammation will cause more and more discomfort, extremely bad breath will appear, gums will hurt and bleed more, preventing normal food intake.
In addition, microbes will continue to multiply in the thickness of the plaque, and their toxins will gradually enter the bloodstream. Ultimately this may lead to serious illnesses heart, when the harmful effects of bacteria spread beyond the oral cavity.
Therefore, treatment of periodontal diseases should not be delayed, and if you suspect the presence of gum pockets, consult a dentist.
Video - Periodontal pockets
17/10/2016
Gum disease is one of the most common phenomena in dentistry. The leading place among them is periodontitis or inflammation of the gum pocket.
In a healthy state, the gum fits tightly to the tooth. The permissible peeling depth is about three millimeters. This condition is not critical and is even normal; in this case, the pocket easily cleans itself of bacteria and small food particles. It is enough to brush your teeth in a timely manner. However, if the situation develops unfavorably, the pocket expands and becomes deeper. Plaque and food debris accumulate inside, and it becomes impossible to get rid of them with a toothbrush.
Sediments become a breeding ground for bacteria, which cause further development diseases.
You should be wary if you notice the following symptoms:
- Bleeding gums;
- Tissue swelling;
- Redness around the teeth;
- Pain when brushing teeth;
- Unpleasant smell from mouth;
- Tartar deposits and the appearance of soft plaque.
The formation of a gum pocket can lead to serious problems. On late stages exposure of the necks of the teeth develops. Pathogenic organisms penetrate deep into the tissues, affecting bone tissue and roots, which leads to their loss.
Causes of gum pockets
The main reason for the detachment of the gum from the tooth is poor oral hygiene. Incompletely cleaned plaque lingers on the enamel, hardens and forms a stone. This, as well as uncleaned food debris, contributes to the active proliferation of bacteria. They penetrate into the formed hood and gradually lead to an inflammatory process.
Some other factors may also influence the development of the disease:
- Unsuitable hygiene products (too hard Toothbrush, aggressive toothpaste);
- Smoking;
- Lack of vitamins;
- Excessive consumption of sweets;
- Availability of some chronic diseases.
Treatment of gum pocket inflammation
On early stages and with timely treatment, the disease is easily treatable. You should not try to cure yourself with the help of widely advertised toothpastes or mouth rinses. Only a specialist can prescribe adequate therapy after necessary research. As a rule, they include:
- Initial examination;
- Performing panoramic x-rays, in which all teeth are visible at once, as well as the depth of tissue damage. This will allow you to select The right way treatment.
- If necessary - comprehensive examination for the presence of chronic diseases;
- Making a diagnosis and developing a plan for further action.
As a rule, gum inflammation is treated in several stages. This is a process that requires not only the professionalism of a dental specialist, but also the active participation of the patient himself.
Stage 1. Removing dental plaque
It is plaque and tartar that are sources of bacteria. Therefore, they need to be removed first. This may require several procedures, depending on the extent of the damage to the teeth.
At this stage, special attention is paid to cleaning the gum pockets. It is very important to remove stone and plaque from this area, as it is the most difficult to clean at home. In addition, gum pockets “open” the way for bacteria to reach the deep tissues of the tooth.
Stage 2. Anti-inflammatory therapy
This stage is started only when dental plaque is completely removed. The dentist rinses the gum pockets with special antiseptic solutions and applies a gel that relieves inflammation.
In addition, home therapy is prescribed: rinsing with antiseptics and special gels. The patient performs this treatment independently twice a day for the time specified by the doctor.
Without the patient's compliance with this point, a successfully treated disease may develop again. At this stage, the dentist should tell you which toothbrush and what teeth cleaning products you can use, as well as explain the rules of dental care.
Brushing your teeth is done with short and gentle rotating movements. Try to reach even hard-to-reach areas. It is convenient to carry out the procedure in the following sequence:
- Cleaning the outside of teeth, both front and molars. The top and bottom rows are cleaned separately.
- Cleaning inside teeth. Special attention Focus on the outermost molars in the top and bottom rows.
- Cleaning chewing surfaces.
- Cleansing the tongue, including at the root. This is where it accumulates great amount bacteria that can easily migrate to the gums and teeth. Plus, cleaning your tongue keeps your breath fresh.
Prevention of gum pocket inflammation
- Use of specialized therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes. Due to their special composition, they ensure hygienic cleanliness of teeth and protection of gums from inflammation. Asepta Sensitive toothpaste has this effect. It contains calendula extract and protects teeth well from bacteria. In combination with it, it is recommended to use Asepta gum gel. It contains propolis, known for its healing properties.
- Carefully monitor oral hygiene. It's not enough to just brush your teeth. You should also use mouthwash regularly. Good effect has
Improper oral care leads to the appearance of plaque and tartar. As a result of pathological processes, inflammation begins. At first, its symptoms are quite harmless. There is slight swelling and sometimes pain. It gradually increases, and a purulent secretion may appear. At this stage they are already talking about advanced periodontitis. To treat this disease, curettage of the periodontal pocket is used. What is this procedure? What other methods are used to combat the disease? You will find answers to these questions in today's article.
Brief description of the problem
Against the background of the inflammatory process, bone tissue is gradually destroyed and replaced by granulation tissue. The latter consists mainly of osteoclasts and microbial elements. Day by day they spread to more and more areas, leading to even greater atrophy of the alveolar bone. A free area appears where there is no attachment of the gum to the surface of the tooth root.
As a result of the described changes, a periodontal pocket is formed. This is a space equal in size to the area of the destroyed bone. Its contents are granulation tissue, food debris and purulent secretion. The size of the gap formed is used to judge the degree of tissue deformation. U healthy person The depth of the periodontal pockets is no more than 3 mm, making it possible to freely clean the cavity from food debris. If this value exceeds the specified size, certain difficulties arise when caring for the oral cavity. The probability increases several times, which leads to the appearance of stone and plaque. The result of active tissue destruction can be tooth loss.
Diagnosis of pathology is carried out using x-ray examination or periodontal probe. Lack of quality treatment leads to deepening of the pocket over time. The consequence of this process is the movement of the teeth into a “fan” position.
Causes of pocket formation
The main reason for the formation of a periodontal canal is poor oral hygiene. Incorrect or lack thereof leads to the accumulation of bacterial deposits in the crown area. Microbes form a thin invisible film over the entire surface of the tooth enamel and begin to secrete products of their own vital activity. This is how inflammation of the periodontal pocket occurs.
Risk group
Among the factors that provoke the growth and reproduction of pathogenic flora, the following can be noted:
- improper diet, consisting mainly of carbohydrate foods;
- poor oral hygiene;
- bad habits;
- disturbances at the hormonal level;
- immunodeficiency;
- dental diseases;
- malocclusion;
- poor quality filling installation.
Symptoms of inflammation
The formation of a periodontal pocket can be asymptomatic for a long time. With the development of the inflammatory process, a characteristic clinical picture appears:
- discomfort in the gum area;
- bad breath;
- swelling, bleeding and redness of the gums;
- upon palpation, purulent secretion may be released;
- expansion of interdental spaces;
- deterioration of general condition.
If these problems occur, you should contact your dentist. A doctor's help is required even if the inflammatory process affects only one tooth. Every day the situation will only get worse, which can lead to the progression of the disease. 
Treatment methods
Before starting therapy, a diagnosis is carried out, with the help of which the doctor determines the degree of neglect of the disease. If the periodontal pocket does not exceed 0.15 mm and there are no signs of inflammation, apply therapeutic methods. The following procedures are commonly used:
- Hygienic cleaning using ultrasound. During the removal of stone and plaque, the gums are not damaged.
- Drug treatment. Appointed immediately after ultrasonic cleaning. At mild degree pathological process, aseptic treatment is used (baths, irrigation, rinsing). During the procedures, “Chlorhexidine” or “Miramistin” is used. In particularly serious cases, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics. The following drugs are characterized by the greatest effectiveness: Amoxicillin, Lincomycin and Azithromycin.
The listed procedures are ineffective if the pocket depth is more than 2 mm. The doctor will not be able to completely remove the accumulated stone. In addition, the likelihood of additional periodontal trauma increases. As a result of the manipulations, the inflammatory process and tissue destruction begin to progress.
In case of complicated course of the disease, it is recommended surgical intervention. This method treatment involves mechanical impact with dental instruments on the subgingival areas. Currently the most effective procedure This type is considered to be curettage of the periodontal pocket. What it is? There are several types of manipulations: closed, open and patch surgery. The procedure itself allows you to get rid of all the problems caused by periodontitis. Let's consider each of its options in more detail. 
Open curettage
Such an intervention requires high professionalism from the doctor. Therefore, this service is not provided in all medical institutions. The duration of the procedure is about 2.5 hours. It consists of the following stages:
- Cleaning teeth from tartar and plaque.
- Use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Splinting of mobile teeth.
- Dissection of the gingival flap with a scalpel.
- Removal of granulations and stones using ultrasound.
- Antiseptic treatment of tooth roots.
- Planting synthetic tissue into the pocket to enhance natural bone growth.
- Apply sutures and cover the damaged area with a gum bandage.
After about 1.5 weeks, the sutures are removed. After a few more months, the damaged tissues are completely restored. Gingival papillae can completely cover the spaces between teeth. In some cases, open curettage of periodontal pockets leads to exposure of the roots. Therefore, it is recommended to avoid eating hot, sour and cold foods for some time. 
Closed curettage
The operation is effective when the pocket depth is 3-5 mm. The intervention is not complicated. It consists of the following steps:
- Examination of gums.
- Administration of local anesthesia.
- Treatment of periodontal pockets without cutting the gums.
- Tooth root polishing.
The intervention can simultaneously affect 2-3 teeth. Wound healing takes place within one week, but final recovery takes about a month. How much time is needed to form connective tissue and attachment of the gum to the tooth. The main disadvantage of the procedure is that the doctor at the time of the manipulation does not see whether all pathological formations have been removed.
If the pocket depth is more than 5 mm, closed curettage will only halt the progression of periodontitis. Partial removal of deposits and granulations allows for a temporary respite, but in almost all cases the disease resumes its development.
Flap surgery
This surgical procedure involves cutting the gums to gain access to the periodontal pocket. Recommended if its dimensions do not exceed 4 mm.
First, the doctor makes two small incisions with a scalpel and peels off the mucoperiosteal flap. Then standard mechanical cleaning of the pocket and polishing of the tooth surface is carried out. After completing the treatment of hard surfaces, they proceed to the preparation of soft tissues. The flaps are placed in place. At the end of the procedure, an osteogenic medicine is applied to the affected area, and the gum itself is sutured. The entire operation lasts no more than 40 minutes, but involves the use of local anesthesia.
Some patients are additionally prescribed for external use (for example, Furacilin). It is also recommended to use ointments to stimulate the process of gum epithelization (Actovegin, Solcoseryl). 
Vacuum curettage
In the presence of purulent abscesses and deep pockets (more than 5-7 mm), vacuum curettage is used. Cleaning is carried out using anesthetics. During this procedure, the doctor first scrapes off the tartar deposits and then polishes the tooth structure. After this, the specialist begins to remove granulations and damaged epithelium from the internal walls. The periodontal pocket is cleaned using a vacuum device, which sucks out necrotic masses along with stone fragments from the bottom of the cavity. At the final stage, rinsing with antiseptic preparations is mandatory.
Vacuum curettage is characterized by high efficiency. With the help of the procedure, lymph flow in the tissues is restored, the depth of the gum pockets is reduced and all inflammatory processes are eliminated.
Postoperative period
In order not to open periodontal pockets, it is recommended to refrain from eating and drinking for 10 hours after all manipulations. For getting desired result You should brush your teeth carefully, using a brush with soft bristles. The problem area must be avoided. After a week, you can start rinsing. To do this you need to use a weak brine or "Chlorhexidine". 
Regarding nutritional issues, preference should first be given to soft or pureed foods. Drinking cold or excessively hot drinks is strictly prohibited. For a week after curettage of periodontal pockets, it is recommended to avoid physical activity, playing sports, visiting the sauna. IN postoperative period It is important to monitor the condition of the oral cavity. You can use hygiene products intended for sensitive teeth. If necessary, you should contact your dentist. The specialist will select procedures to reduce the sensitivity of the necks of the teeth.
Periodontitis is a pathological process in the tissues surrounding the tooth. The disease is characterized by inflammation of the periodontium, resulting in the destruction of the periodontal junction and the bone tissue of the jaw on which the teeth are located (alveolar processes of the jaw). Inflammatory process negatively affects the functioning of the oral cavity and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
As a result of pain when chewing, food is not crushed finely enough, which provokes injury to the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach. Untimely treatment of periodontitis contributes to increased bleeding of the mucous membrane and subsequent loss of the affected tooth.
Causes of periodontitis
The causes of the occurrence and development of periodontitis are:
Symptoms of periodontitis

Signals of the development of an inflammatory process in the oral cavity include the appearance of viscous salivary fluid with a foul odor and an increase in regional lymph nodes. There is a feeling of pulsation in the gums.
TO specific symptoms lesions of the oral cavity by periodontitis include the following:
- increased bleeding of gums;
- appearance yellow plaque on tooth enamel;
- severe swelling and redness of the mucous membrane;
- the appearance of periodontal pockets;
- there is increased mobility of teeth, subsequently their loss;
- tooth sensitivity to hot and cold foods increases.
Stages of the disease
For appointment effective treatment periodontitis, a specialist determines the degree of development of the disease. So, what are the stages of periodontitis:
- initial stage;
- development stage;
- stage of stabilization or remission.
The disease affects individual areas of the periodontium, and symmetrical inflammation is often noted. In the absence of treatment for periodontitis with folk or medications, the lesion becomes generalized and covers the entire surface of the periodontium.
At the initial stage of the disease, periodontitis is characterized by the absence of pain. The patient experiences increased bleeding of the gums when eating or brushing teeth, a burning sensation and numbness in the gums. Only a dentist can diagnose incipient periodontitis during oral sanitation. This stage can be treated with folk remedies.
At the stage of progression of periodontitis, swelling of the mucous membrane is noted. The gums begin to separate from the teeth, forming small pockets (5-6 mm), visually lengthening the surface of the tooth. Subgingival deposits are observed, which penetrates into the gums, affecting the root of the tooth. The space between the teeth increases, which leads to increased tooth mobility. The advanced stage of the disease should not be treated at home.
The last stage of progression of periodontitis is characterized by displacement and loss of teeth, as a result of expansion of periodontal pockets. Purulent formations begin to emerge from the damaged surface of the gums. The process is accompanied by the appearance of a strong unpleasant odor from mouth.
The stabilization stage occurs as a result complex treatment periodontal disease. The inflammatory process is reduced, there is a decrease in tooth mobility as a result surgical removal periodontal pockets. The stages of progression of the pathological process in adults and children can be seen in the photo.
Is it possible to get rid of periodontitis at home?
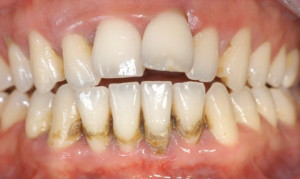 Periodontitis is treatable self-treatment at home on initial stage disease, which is characterized by the absence pathological changes in the gums. The maximum permissible depth of the periodontal canal at home treatment can reach 4 mm. With the progression of periodontitis, folk remedies may not have the desired impact. To cure progressive tissue inflammation, you should immediately consult a dentist for prompt removal of plaque and cleaning of the gum cavity.
Periodontitis is treatable self-treatment at home on initial stage disease, which is characterized by the absence pathological changes in the gums. The maximum permissible depth of the periodontal canal at home treatment can reach 4 mm. With the progression of periodontitis, folk remedies may not have the desired impact. To cure progressive tissue inflammation, you should immediately consult a dentist for prompt removal of plaque and cleaning of the gum cavity.
Comprehensive treatment of periodontitis is aimed at suppressing the development of pathogenic microorganisms that negatively affect tissues and mucous membranes in the oral cavity. Pharmacological agents are used for this purpose. medicines, affecting pathogenic flora, reducing swelling and painful sensations, restoring microcirculation in the affected tissues, provoking accelerated regeneration of inflamed areas.
Self-treatment of periodontitis involves the use of medications:
- antibacterial agents with wide range effects on the body (drink as prescribed by a doctor);
- drugs, NSAID groups;
- vitamin complexes;
- immunomodulators.
Local preparations
For effective treatment of periodontitis use local drugs, the action of which is aimed directly at the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and gums. Drugs with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects are available in the form of sprays, lozenges and dental gels.
| Name of the drug | Release form | Compound | pharmachologic effect |
| Dologel ST | Dental gel |
| It has a pronounced analgesic, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect. |
| Kamistad | Dental gel |
| Shows local anesthetic effect. Due to chamomile flower extract, it has an antimicrobial effect. |
| Metrogil Denta | Dental gel |
| It has an antiseptic, antimicrobial effect against most gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. |
| Holisal | Dental gel |
| Destroys pathogenic microflora, has an anesthetic property. |
| Hexasprey | Spray |
| It has an anti-inflammatory effect and is active against streptococcal and staphylococcal infections. |
| Oralcept | Spray |
| Reduces swelling of the gums, eliminating the inflammatory process. |
| Tantum Verde | Rinse solution, spray, lozenges. |
| Shows antimicrobial, antiseptic effects on pathogenic microflora. Has an analgesic effect. |
Mouth rinses
An effective way to combat microorganisms and their metabolic products is to rinse the mouth. pharmaceuticals or herbal decoctions. Among the wide range of pharmaceutical medicinal rinses, the most effective are the following drugs:

A solution of sea salt. Prepare salt rinse simple - you need to dissolve a teaspoon of fine sea salt in a glass of boiled warm water. It is recommended to rinse your mouth at least three times a day, and the duration of therapy depends on the speed of healing of the wound surface.
To relieve inflammation and promote healing of the periodontal pocket, you should rinse your mouth with a decoction of oak bark. To prepare the decoction you will need carefully crushed raw materials and water. Cold water in an amount of 500 ml. you should pour two tablespoons of raw material and simmer over low heat for 30 minutes.

Important! Before using the decoction, it must be filtered through a thick layer of gauze to avoid particles of oak bark getting into the inflamed areas.
A decoction of St. John's wort herb has an astringent and disinfecting effect. To prepare the decoction, you need to pour two tablespoons of crushed raw materials into boiling water (500 ml). There is no need to boil the mixture. To obtain pharmacologically active home remedy, the mixture must be tightly closed with a lid and allowed to brew for a quarter of an hour.
Herbal tinctures
Often, when the initial stage of pathology occurs, experts prescribe rinsing the mouth with tinctures. The effectiveness of these products is explained by the interaction of ethyl alcohol (as an antiseptic) and herbal raw materials on the affected areas of the tooth and gums.
The most prescribed tinctures for periodontitis, which can be prepared at home, are:
- Calendula tincture - dissolve a teaspoon of tincture in a glass of warm water. The minimum number of rinses per day is 3 times.
- Eucalyptus tincture – add 15 drops of tincture to a glass of warm water. Rinse oral cavity twice a day.
- Honey tincture - dissolve a tablespoon of honey in 300 ml of vodka or alcohol. The tincture is infused for at least a week. To prepare the solution, add a teaspoon of honey tincture to a glass of water. Rinse your mouth twice a day.
Therapeutic compresses
A significant role in the treatment of periodontitis is played by therapeutic compresses applied to the affected area. Contact biologically active substances with inflamed gums, it delicately affects the cause of periodontitis and helps reduce bleeding gums.

other methods
To get rid of microorganisms and prevent the formation of pus in periodontal pockets, you can restore the mucous membrane using high-quality essential oils from the following raw materials:
- carnation;
- tea tree;
- eucalyptus;
- mint;
- immortelle;
- lavender.
Essential oils can be used in pure form. To do this, you need to drop a few drops under your tongue before going to bed. Essential oils can also be added to toothpaste or moisten dental floss with them. With a progressive degree of periodontal damage, a cotton swab soaked essential oil, apply to the gum for 30 minutes.
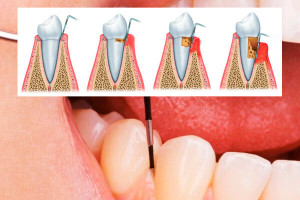
Treatment of periodontal pockets at the dentist
To treat periodontitis, dentists perform a procedure called periodontal pocket curettage. The following types of procedure are distinguished:
Preventive measures
To avoid the development of periodontal disease, gum inflammation, caries and other diseases should be treated promptly. pathological processes in the oral cavity. The following rules must also be observed:
- clean regularly tooth surface from dental plaque;
- clean interdental spaces daily with dental floss;
- perform finger massage of the gums;
- rinse the mouth with water at a contrasting temperature;
- include fresh fruits and vegetables, lactic acid products in the diet.








