wounds in oral cavity- a fairly common phenomenon. Sores on the mucous membrane are not only an unpleasant sight that causes discomfort when eating, but are also accompanied by pain.
Ulcers have different sizes, depths, colors, their appearance can be either single or multiple.
It is impossible to independently determine the exact cause of wounds in the oral cavity. This manifestation may be caused by a dangerous pathology.
Therefore, at the first appearance of ulcers, you need to contact a specialist - a dentist. The doctor will determine the cause and prescribe treatment. The main causes of mouth ulcers in adults are:
- Chronic disease aphthous stomatitis. It is characterized by periodic eruption of small ulcers (aphthae) throughout the oral cavity. The hard and soft palates, buccal mucosa, tongue, and lips are affected. The healing time for aphthae reaches 1.5-2 weeks.
- Injuries to the oral cavity. Such injuries can occur due to accidental tongue biting, improper brushing of teeth, dental treatment, taking some medicines. When the traumatic factor is eliminated, the wound heals within a week.
- Viral infection gingivostomatitis. The mucous membrane becomes covered with sores due to reduced immunity, chronic fatigue, hypothermia, with an allergic reaction, with sharp pains when eating food.
- Herpetic stomatitis. A disease accompanied by the appearance of small sores, the similarity of which is reminiscent of herpes. Such wounds are characterized by a gray color and are mainly located at the bottom of the oral cavity. Healing lasts for 10 days.
Among the causes of ulcers in children are:

- poor oral hygiene (as a result, Bednar's aphthae occurs, localized on the palate);
- diphtheria or “dirty hands disease” (bacteria enter the mucous membrane of the larynx and nose, causing redness and swelling);
- viral disease chickenpox (rashes are localized not only on the skin, but also in the oral cavity);
- acute infectious diseases (scarlet fever, measles) are also accompanied by the appearance of a specific rash in the mouth.
In young patients, the disease is diagnosed by a pediatrician. The presence of sores in a child’s mouth does not cause concern, but it causes a general deterioration in the patient’s condition; the child becomes capricious and refuses to eat.
Sores as a symptom of other diseases
The appearance of ulcers in the mouth can serve as a signal for full examination patient. Sometimes such ulcers occur as additional feature against the background of another disease.
|
Tuberculosis of the mucous membrane |
Typically this is secondary manifestation diseases when tubercles appear under the tongue, on the cheeks and tongue. Wounds with this disease are small in size and depth, have soft edges and are quite painful. Treatment should take place in special anti-tuberculosis institutions. |
|---|---|
|
Recurrent herpes |
People of any age who were previously infected with this disease are susceptible to pathology. The disease is characterized by the appearance of single rashes up to 5 mm in size. Prolonged exposure to the sun, sharp viral infections, stress, etc. Treatment takes up to 10 days. |
| At the initial stage of the disease, the rash does not cause pain. They are characterized by a round, ellipsoidal shape with a red or dark gray bottom. Around the wound, the mucous membrane swells, turns blue and rises slightly. The wounds heal within several months. It is possible that small scars will appear in their place. Treatment is carried out in venereology hospitals. | |
|
Dermatological pathologies |
Dermatological pathologies that affect skin, mucous membranes with small bubbles. Over time, they increase in size and unite through fusion. As a rule, the cause of such pathologies is a hereditary predisposition. |
|
Shingles |
Most often, people who have had the disease are susceptible to the disease. chickenpox. One-sided rashes appear on the mucous membrane, which, when touched, cause strong pain. Accompanied by itching and multiple herpetic rashes. |
These are not all diseases that can be the main ones when sores appear in the mouth. Therefore, at the first symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
The first symptoms include a slight tingling and mild burning sensation, followed by the formation of blisters, rashes, and a specific rash.
IN severe forms There is a general deterioration in the condition, possibly the manifestation of fever.
Treatment and precautions
How to treat yourself: white sore in the mouth, a sore in the corner of the mouth, in a child, and so on? Let's figure it out now. So, treatment can be carried out at home, using recipes traditional medicine, and by medication.
In any case, you first need to establish the cause of the sore, neutralize it, carefully treat the wound and sanitize the oral cavity.
 Sanitation involves a set of procedures that help detect dental diseases; it is recommended to carry them out twice a year.
Sanitation involves a set of procedures that help detect dental diseases; it is recommended to carry them out twice a year.
During treatment, irritation of the mucous membrane should be avoided. All spicy, salty and hard foods, as well as those foods that can cause allergic reaction.
Food that can injure the cavity is also excluded: nuts, citrus fruits, etc. The menu, for the period of treatment, contains only soft and pureed food. Carbonated drinks and hot tea are not recommended for consumption.
With strongly expressed pain apply special gel with analgesic effect.
How to treat a child
- If the sores are on the lips, the child sprays them thermal water, lubricate your lips with hygienic lipstick several times a day. Oils containing vitamin A are also used. Vaseline is used, sea buckthorn oil, rosehip, avocado and tea tree oil.
- The corners of the lips where wounds form are wiped with the juice of some plants. Juice can be squeezed from the stems and leaves. Lotions are also made from decoctions of medicinal herbs.
- Honey and butter will help soften the wounds.
- Antifungal drugs prescribed by a specialist. As a rule, a remedy is used to which the pathogen is very sensitive.
- Removing tartar helps get rid of ulcers.
- The child’s diet includes foods containing vitamins B2 and E.
Folk remedies
There are several traditional methods, the use of which will help get rid of sores in the mouth.

- Chop the garlic and add two tablespoons of yogurt (you can use yogurt). Sore spots are lubricated or the composition is taken into the mouth and kept for several minutes. Repeat 2-3 times a day.
- An infusion of calendula diluted with a glass of water is used as a mouth rinse. For the same procedure, use the juice of carrots, cabbage and baking soda. The product is good antiseptic and helps relieve redness and inflammation of the affected areas.
- Simple and accessible means is a raw potato. The peeled and washed slice is applied to the ulcer for 10-15 minutes. You can chop potatoes and use them as a compress.
- The use of propolis will help not only relieve inflammation and pain, but also eliminate bad smell, strengthen the gums. A bandage soaked in the product is placed under the tongue or next to the gum, depending on the position of the wound. Propolis is used to irrigate the oral cavity. Sores heal faster if you periodically chew the product.
Medications
Such treatment for sores in the mouth is prescribed by a doctor; it depends on the cause of the ulcers, the severity, and the frequency of relapses.
- As a rule, “Fluocinonide” gel is used, it helps to quickly relieve swelling, eliminates pain syndrome. Pregnant and lactating women need additional consultation specialist
- Cauterizing wounds in the mouth is considered an aggressive measure that must be used with great caution. Liquid for sanitation of the mouth "Chlorhexidine Gluconate" is suitable as a cure for such sores.
- Can be prescribed by a doctor antihistamines: “Loratodine”, “Tavegil”, “Suprastin”, etc. They are used to treat wounds on inside cheeks.
- Costeroid ointments and vitamin preparations promote rapid healing of wounds.
Ointments are applied after irrigation with solutions of the oral cavity to the mucous membrane, previously dried with a napkin.
Preventive measures
In the event that the appearance of ulcers is not additional symptom against the background of another disease, the following is recommended as prophylaxis:
- pay attention to the condition of the teeth;
- conduct proper cleaning teeth, for 3 minutes with a brush with soft bristles;
- refuse products causing allergies and provoking the appearance of sores;
- drink vitamins and mineral complexes once every six months;
- rest and sleep for the required amount of time.
To avoid infectious diseases try to prevent infection from entering the body. News healthy image life and strengthen the immune system. Children should wash their hands more often and not eat unwashed vegetables and fruits.
Only by knowing the cause of the disease and starting treatment on time can you get rid of such sores.
Compliance with preventive measures will contribute to proper hygiene oral cavity and long-term avoidance of ulcers. Look after yourself and your child. Be healthy!
Finally, we invite you to watch a video from Elena Malysheva’s program on the treatment of sores in the mouth:
One of the manifestations of the inflammatory process in the mouth is stomatitis on the cheek. As a result of the disease, a person experiences noticeable discomfort, ulcers form in the mouth, and the mucous membrane becomes covered with a white coating. With these manifestations, you need to think about further development events, not forgetting that any neglected condition can transform into a more complex disease, the elimination of which will be expensive and may not lead to any result at all. Thus, it is necessary in a timely manner, namely when primary signs, contact medical institution for examination, diagnosis and prescribing a course of medication. To begin with, you should determine a number of the main reasons for the manifestation of stomatitis on the cheek in order to, if possible, eliminate the risk of its formation.
- Sustaining an oral injury.
- Occurrence from allergies.
- Impact on nervous system, depression, stress.
- Incorrect installation of fillings, crowns, and corrective dental structures.
- Lack of the proper set of vitamins necessary for the body, especially zinc and iron.
- Incorrect operation digestive system and gastrointestinal disease.
- Using toothpaste that contains sodium lauryl sulfate.
Types of stomatitis
The disease has different reasons manifestations, and also differs in the course of the disease and symptoms. Depending on the characteristics, stomatitis is divided into the following types.
Allergic
Today there are many irritants that can instantly affect the human body. And this happens quite quickly. We are talking about various chemicals that are used in everyday life, plants, animals and even ordinary dust, surrounding a person everywhere. One of the main carriers is food, which in most cases contains many elements, additives and components that can cause an allergic reaction, including causing the formation of stomatitis on the cheek. As a rule, allergic stomatitis does not begin to appear at the first exposure negative factor on the body, but has a formation under investigation in case of leakage.
Signs of allergic stomatitis

The disease is accompanied by certain symptoms, through which a diagnosis can be made. Knowing the signs of illness is not only necessary medical workers, but also to the average person, which will allow timely determination of the presence of the disease. A patient with stomatitis on the cheeks feels dry mouth, chewing is accompanied by an unpleasant burning sensation and pain. Distinctive feature a metallic taste appears in the mouth. The surface is covered with white bubbles, which burst and turn into ulcers. The process is accompanied by pain, after which the mucous membrane becomes covered with a film. Upon visual examination, traces of hemorrhage are visible on the mucous membrane, redness and swelling in the mouth are noticeable. Allergic stomatitis can also cause inflammation lymph nodes and strong salivation.
Herpetic
The name speaks for itself; the disease occurs due to infection by the herpes fungus. Stomatitis is well established on the cheeks and oral mucosa. It appears initially in the form of small white bubbles, which are most often grouped. Next, the bubbles with clear liquid open and turn into painful erosions and ulcers. When touching the affected mucous membrane, the patient experiences discomfort, as well as the pain that is in different stages its course has its own strength of sensations.
Stomatitis occurs in mild form, the oral mucosa is painful for several days. During the treatment, the ulcerative formations will heal, and then disappear completely, without leaving even traces in the form of scars. Herpetic stomatitis can cause complications in newborns and children under one year of age. Therefore, you should pay close attention to the child’s oral mucosa and immediately consult a doctor to avoid more serious complications.
Signs of herpetic stomatitis
The disease is expressed in addition to foreign formations on the mucous membranes of the mouth, tongue, cheeks and other characteristic features. A patient with the herpetic form experiences weakness in the body, the need for food disappears or decreases, or rather the desire to eat it. Increased salivation occurs, and nausea may occasionally occur. Upon palpation, inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck and under the jaw will be clearly expressed.
Aphthous
One of the types of stomatitis, which is not typical for affecting the cheeks. More often it forms in the form of ulcers on the mucous membrane of the lips and the surface of the tongue on the sides. The causes of the appearance are ARVI, influenza, other viral diseases, as well as caries. The patient suffers from a slight fever, and if the condition is neglected, infection and spread of stomatitis to other areas of the mucous membrane in the mouth and the lip area may develop. The disease lasts from 2 weeks to a month, during which the ulcerative formations heal.
Candida
A characteristic type of stomatitis that appears on the cheeks in the oral cavity. The disease affects people with weak immunity, sick chronic diseases Therefore, older people and children under 3 years of age are more likely to suffer. Elderly people have many diseases due to the years they have lived; as a rule, they take antibiotics, as a result of which the body weakens significantly. Children, on the contrary, due to their small age, have not yet acquired strong immunity and an organism that can fight bacteria, infection, etc.
Children often develop small ulcers in their mouths white. They are not always dangerous. If there is only one such formation on the gum, it is enough to properly care for the oral cavity. If there are many ulcers and they cause discomfort to the baby, serious treatment is required.
Causes
Oral diseases
- Aphthous stomatitis. The development of such a disease can be triggered by several factors. These include weakened immunity, impaired functioning endocrine system, viral infections. Ulcers caused by aphthous stomatitis are seen on the gums, palate and cheeks. These are white or white-yellow sores that cause discomfort when touched. IN in this case rinsing the mouth with a decoction of calendula is recommended.
- Viral stomatitis. With this disease, there are many small white sores in the mouth. They are located on the back of the cheeks and pharynx, as well as on the gums. To treat sores, a light pink solution of potassium permanganate is used. It is necessary to understand that viral stomatitis is a contagious disease, so it is necessary to adhere to safety measures. So, the dishes of a sick child should be stored separately. It should be thoroughly washed and scalded with boiling water each time. Food should be unsalted and non-spicy. You need to feed your baby in small portions, because severe pain occurs when eating food.
- Herpes. With this disease, many ulcers form in the child’s mouth. Herpes does not always appear. This requires favorable conditions such as weakened immunity or cold weather. First, several bubbles form on the mucous membrane. Over time, they burst, leaving behind small ulcers with a grayish film. In this case, severe pain, fever, increased salivation and an unpleasant odor are observed. Special ointments and rinses are used for treatment.
The formation of ulcers in children often occurs due to a lack of various vitamins.
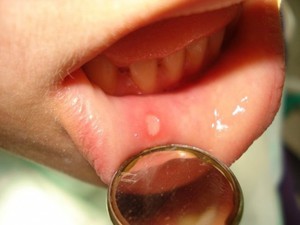
Other reasons
- Frequent consumption of sweets.
- Predominance acidic foods in the diet.
- Constant biting of the cheeks, which leads to injury to the mucous membrane and subsequent formation of ulcers.
- Illiterate use of an electric brush.
- Injury to the oral mucosa by the sharp edges of a filling or denture.
Treatment
Choosing a treatment method for white sores depends on the form of the disease and degree of damage.
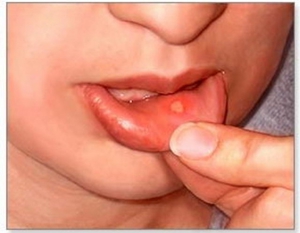
It is necessary to understand that a single formation of a white ulcer is not a reason to immediately run to the doctor. It is enough to rinse the baby’s mouth with a solution of potassium permanganate or chamomile decoction. Urgent consultation with a doctor will be required if many ailments on the gum or other alarming symptoms are observed.
White ulcers in the mouth, how stomatitis is treated
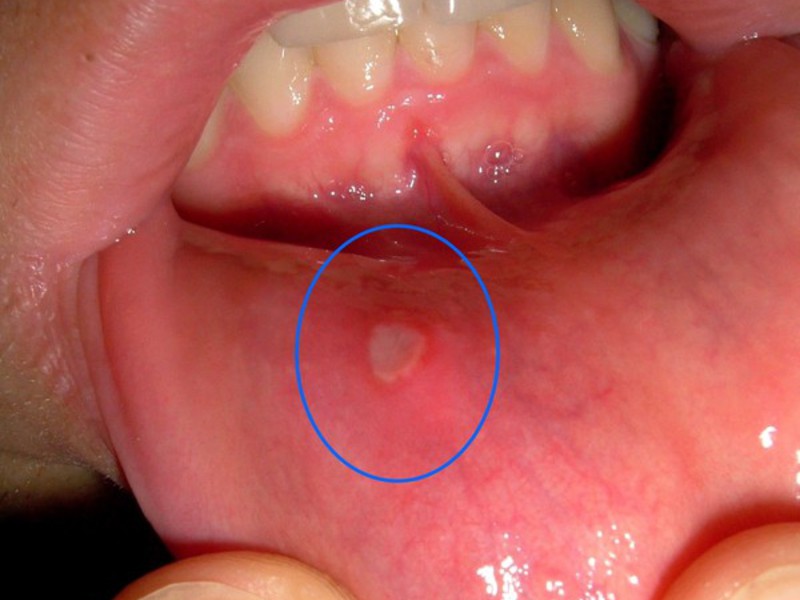

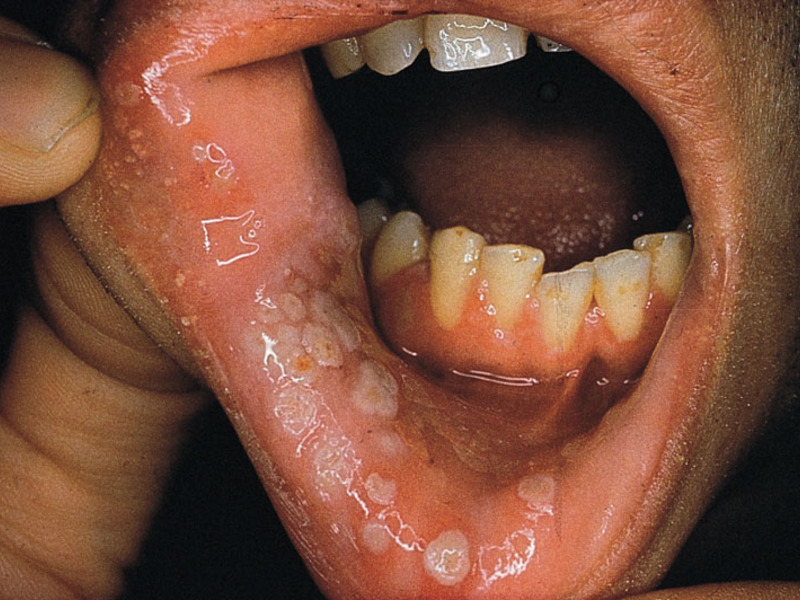
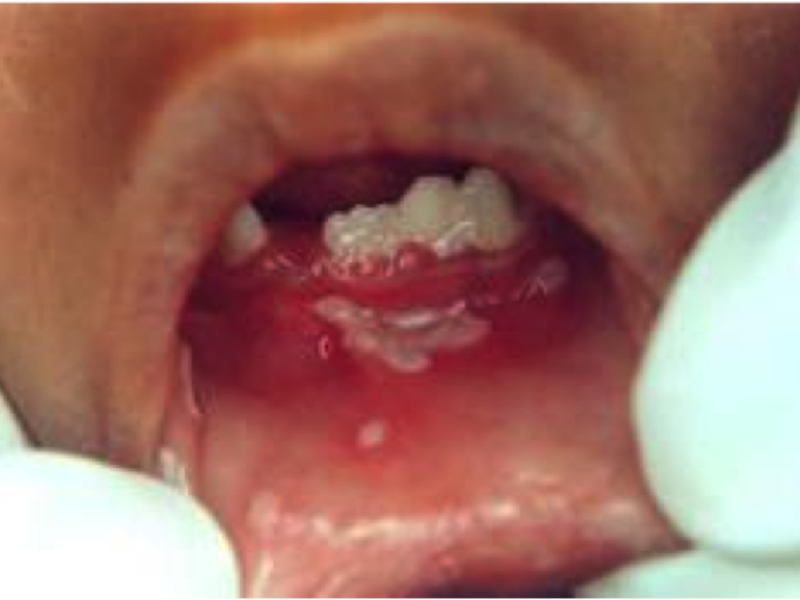

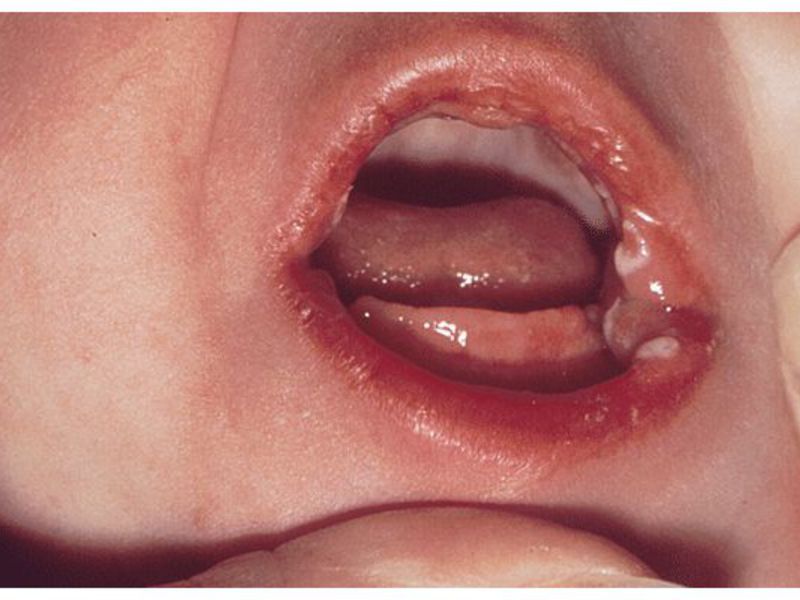
![]()
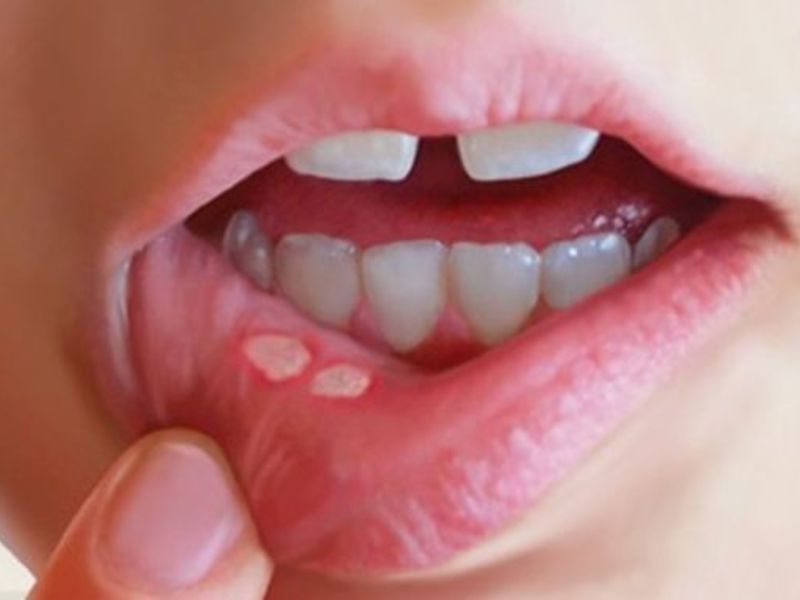
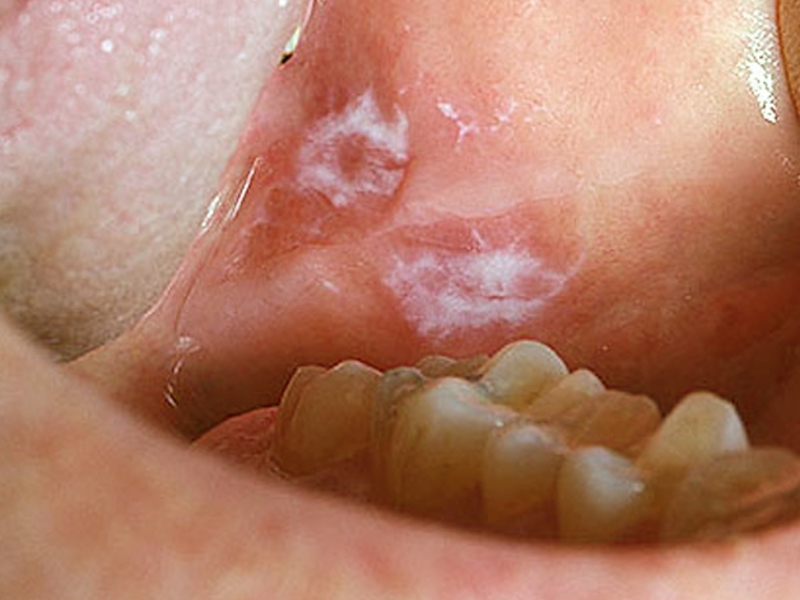

A fairly common oral disease today is stomatitis. This pathology is observed in every fifth inhabitant of the planet, and the disease can progress in different ways. In dentistry, stomatitis is usually referred to as the development of an inflammatory process on the oral mucosa and the inside of the cheeks. An illness is a reaction of the human body to an external stimulus. Previously, this disease was diagnosed, as a rule, in children, but today stomatitis on the cheeks is increasingly observed in adults. We will look at what causes this disease and how it progresses in this article.
Description
Have you ever encountered a similar phenomenon and don’t know what stomatitis looks like on the cheek? The photos used as illustrations for the article will help you form your own opinion about all the “beauty” of the disease. It’s not pleasant, I must say.
The disease manifests itself in the form of ulcers in the mouth, on the inside of the cheeks. It lasts up to fourteen days, after which it usually passes without leaving any traces. It is noteworthy that if the disease makes itself felt at least once, there is a high probability of relapses, the frequency of which is very variable. According to statistics, people turn to specialists with similar complaints three or four times a year. Some people are concerned chronic stomatitis(in the mouth on the cheek, on the mucous membrane of the lips), in which new ulcers appear when the old ones have not yet had time to heal. This disease is considered to be contagious, although it all depends on the causes of its occurrence.
Types of stomatitis
Both children and adults can be diagnosed different types such a disease. Stomatitis on the cheek is very common (photos demonstrating the main manifestations of the disease are attached). Depending on the etiology, the following are distinguished:
1. Bacterial - develops due to the presence of streptococci and staphylococci in the human oral cavity, which enter there through wounds on the cheek.
2. Traumatic - develops with repeated injuries to the mucous membrane, as well as in the presence of a diseased tooth, fragments of teeth or malocclusion, constant presence of tobacco smoke.
3. Herpetic stomatitis - occurs when weakening immune system person. Moreover, the herpes virus continues to remain in the body even after a full course of treatment.
4. Candidal stomatitis on the cheek inside the oral cavity most often develops in childhood. The cause is yeast-like fungi, which are formed as a result of long-term use of antibiotics, as well as when human immunity decreases.
5. Allergic - develops as a reaction of the body to various allergens.
6. Aphthous - develops due to exposure to the mouth foreign body and represents the body's reaction to this stimulus.
7. Gangrenous stomatitis - develops most often in people who use narcotic drugs, as well as due to vitamin deficiency, infection of the oral cavity.
Reasons for appearance
Today, experts name a large number of factors that can contribute to the development of stomatitis. Wherein main reason The development of the disease is considered to be the entry of various bacteria into the human body, leading to inflammation in the oral cavity, resulting in the formation of ulcers in its various parts. As you know, there are always a lot of bacteria present in the mouth, but in order for inflammation to begin, additional factors are required. Stomatitis on the inside of the cheek can develop due to poor nutrition, lack of beneficial microelements in the human body, oral injuries, exposure to various chemical substances to the mucous membrane.
Quite often, the disease occurs as a result of habitual things and non-compliance with hygiene rules or violation of safety rules:
Trauma to the oral cavity as a result of biting the cheek, eating hard food, scratching the cheek with a deformed tooth or crown, denture;
Getting alkalis and acids into the oral cavity, leading to chemical burns;
Poor hygiene leading to ingestion pathogenic microbes and infections;
Drinking alcohol and smoking.
In some cases, stomatitis on the cheeks in the oral cavity may appear as a result of the presence of any infection in the body, oncology, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, or as a result of treatment malignant neoplasms(chemotherapy, radiation, etc.). Stomatitis often worries pregnant women, since during this period the body undergoes hormonal changes and its protective functions are reduced. Some illnesses accompanied by fever, severe blood loss and dehydration can also cause ulcers on the mucous membrane.
Thus, stomatitis on the cheek (inside the mouth) can be perceived as a signal from the body, indicating the presence of health problems. This may be the progression of chronic diseases or a decrease in the body’s protective functions. Of course, it is not recommended to ignore these “bells” (even if unpleasant symptoms will go away on its own in a couple of weeks) - contact your doctor in time! He will appoint competent effective treatment and will select medications that are right for you.
Symptoms and signs
The interesting thing is that different kinds Stomatitis can manifest itself in different ways, have different symptoms and signs. If it develops, ulcers and aphthae appear on the cheeks. Aphthae are round ulcers with plaque on top gray. They are not painful and do not cause discomfort, but if they reappear, scars may form that take quite a long time to heal, and the cheek may become deformed. Often with stomatitis, the mucous membrane turns red and a white coating appears.
At aphthous stomatitis the appearance of aphthae and ulcers is observed different sizes, which cause very painful sensations, the lymph nodes increase in size, weakness and irritability appear. 
Herpes stomatitis (most often appears on the cheek of a child) is characterized by an increase in body temperature, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, and is accompanied by weakness and malaise. This disease is infectious and is caused by the herpes virus.
With allergic stomatitis, there is swelling of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, which makes it difficult for a person to swallow, while the tongue increases in size and often does not fit in the mouth. Also, bubbles appear in the patient’s mouth, which burst after some time and turn into ulcers. Ulcers can merge, forming a large lesion.
Bacterial stomatitis on the cheeks and palate is characterized by swelling and the appearance of deep ulcers (down to the bone). If the disease is not treated, it leads to tissue necrosis.
In the case of traumatic stomatitis, erosions, ulcers, ulcers or wounds with a white coating appear on the affected area. Gradually, the area begins to swell, redness and swelling appear. In some cases, tissue necrosis may occur, usually after severe trauma. Often stomatitis on the inside of the cheek (photos illustrating the manifestations of this disease are, to put it mildly, unpleasant) of the oral cavity is accompanied by a fungal infection.
With gangrenous stomatitis, the patient has pain all over the mouth, as there are necrotic areas there. Blood clotting worsens, the patient stops eating and drinking, erosions and rashes appear, body temperature rises, fistulas form on the gums, cheeks, jaw and tongue. Tissue necrosis gradually develops, encephalitis and even blood poisoning are possible.
Diagnostics
It would seem that diagnosing stomatitis is a simple task. But the disease can be caused by many pathogens and provoked various factors that need to be determined by the attending physician. Therefore, the specialist must definitely appoint clinical analysis blood, test the blood for glucose, and also conduct PCR and bacterial culture from the oral cavity. Questioning and examining the patient also helps to identify the nature of the disease. Before making a diagnosis, the form of the disease is determined, taking into account the results of tests, tests and medical history. 
Diagnosis of pregnant women
Diagnosis of this disease in pregnant women is not much different from standard procedure. The difference is that the disease lasts longer in expectant mothers, sometimes throughout pregnancy. This is due to the fact that the immune system of pregnant women is weakened and the hormonal levels change.
Prevention
It is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it. Preventive measures to prevent the development of this disease include the following actions:
Hygiene of the oral cavity, hands;
Quitting alcohol, smoking, drugs;
Timely visits to the dentist and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases;
Prevention of injury to the oral cavity;
Limit any contact with patients with stomatitis.
Preventive measures should be carried out immediately after the child is born. Then stomatitis on the child’s cheeks (photos of children suffering from the disease evoke sincere pity and compassion) will not appear. It is important to take care of the oral cavity and follow the child’s feeding regimen. In preschool and school age children are most susceptible this disease Therefore, parents should explain hygiene rules to their children. 
Stomatitis on the cheek: treatment
Cure stomatitis alone folk remedies It’s unlikely to succeed, it’s necessary here medical supplies, which eliminate pathogenic bacteria, heal wounds, restore the acidity and microflora of the oral mucosa. Usually antibiotics, antiseptics, and vitamins are used as medications. The treatment regimen for stomatitis depends on its etiology and type. Let's consider this issue in more detail.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis
This type of disease is presented in the mildest form, so treatment can last only a few days. To recover, you just need to rinse your mouth with special disinfecting solutions. It could be potassium permanganate, herbal infusions and decoctions, hydrogen peroxide, "Chlorhexidine", "Iodinol", "Furacilin" and so on. It is also recommended to take medications to enhance immunity.
Treatment of herpes stomatitis
First of all, immunostimulating and antiviral drugs. This could be Zovirax, Anaferon and others. To eliminate ulcers, Lugol, brilliant green, and "Cholisal" are used - they need to be applied to the damaged areas several times a day using a tampon. Antifungal ointments are also used: oxolinic, interferon and others. After eating, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with calendula decoction. 
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
If a child gets sick, he is given antipyretics, painkillers and antiseptics. Furacilin solution and gramicidin paste are good in this case. After eating, you need to rinse your mouth with herbal infusions (chamomile, sage, oak bark). Adults are prescribed medications aimed at relieving intoxication and improving the condition of the immune system. Amiksin, Diflucan, Claritin, vitamins and immunostimulants are often prescribed. In any case, the doctor must prescribe antibiotics and antiseptics. A tannin solution is used to heal ulcers. It is very important to follow a special diet during treatment.
Treatment of allergic stomatitis
Treatment allergic stomatitis must be comprehensive. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate exposure to the allergen. The patient is prescribed a diet and is excluded from the diet mineral water. To treat this type of illness, they use antihistamines(“Suprastin”, “Clarotadine”, etc.) and vitamins B, C and PP. You also need to take folic acid. It is recommended to treat areas that are inflamed in the same way as when treating other types of stomatitis.
Treatment of traumatic stomatitis
Depending on the nature of the lesion in the oral cavity, a course of therapy is prescribed. Treatment should begin with eliminating the cause of the disease. This is followed by treatment of the oral cavity. To do this, use a solution based on hydrogen peroxide or a solution of furatsilin. The patient may also be prescribed medications to fight infection and relieve inflammation. The same means are used here as in the treatment of other types of stomatitis. Painkillers are often used.
Treatment of bacterial stomatitis
If stomatitis causes ulcers in the mouth, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. In principle, the treatment regimen is the same as for other types of disease. If tissue necrosis occurs, surgical intervention is necessary, after which the doctor prescribes necessary treatment. Immunostimulants play an important role - they help cope with the disease much faster. 
Treatment of gangrenous stomatitis
Treatment of this type of disease is carried out only in a hospital. The patient is given a blood transfusion, the affected areas are eliminated by surgical intervention. The doctor prescribes a complex of vitamins, recommends enhanced nutrition, the oral cavity is washed with potassium permanganate, and antibiotics are necessarily prescribed. It is quite difficult to cure gangrenous stomatitis; people often die from this disease, so it is better to avoid complications and treat the disease in a timely manner.
The best treatment regimen
As already noted, treatment depends on the etiology, type and form of the disease, as well as on the characteristics of the patient. After research and laboratory tests After making a diagnosis, the attending physician selects a treatment regimen aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease, as well as preventing relapses. The course of treatment involves the use of drugs of various effects:
Painkillers;
Anti-inflammatory;
Antihistamines;
Antiviral;
Immunomodulators;
Vitamin therapy.
The attending physician individually selects a set of measures aimed at eliminating the disease. 
Stomatitis today is not so terrible disease, but quite unpleasant. Its development can be prevented, and correct and timely treatment makes it possible to completely restore the body and not give the disease a chance to bother you again.
One of the most common forms of damage to the mucous membrane (in addition to the development of infection on the tongue, directly in the mouth, and other things) is stomatitis on the cheek. The disease has several primary symptoms, one of which is the formation of ulcers, white plaque on the mucous membrane and the occurrence of discomfort and pain in the immediate localization of inflammation.
The appearance of wounds in the oral cavity can provoke the development of ulcers and develop into more dangerous infectious pathologies.- Inflammatory process in the mouth, caused by the penetration of infections/viruses. Pathogenic environment provokes the development of ulcerative formations on the mucous membrane.
- Mechanical damage to the oral cavity.
- Permanent exposure to chemical pathogenic substances (acids/alkali) on the oral mucosa.
- Malocclusion.
- Sharp edges of teeth that can damage the mucous membrane. Damage (wound or scratch) from a tooth becomes vulnerable to the influence of unfavorable microorganisms. Stomatitis can be caused by improperly installed dentures (or low-quality dentures).
- Incorrectly selected diet. Lack of conscious consumption. Lack of certain substances in human body. The predominance of hard, dry food, which can cause mechanical damage to mucous tissue.
- Failure to comply with basic personal hygiene rules.
- Uncontrolled consumption of alcohol.
- Excessive use of tobacco products.
- Stomatitis may be a manifestation serious illnesses gastrointestinal tract.
- A weakening of the protective function of the immune system during pregnancy can provoke the development of pathology. An additional effect is exerted by changes in hormonal levels.
Classification
- Traumatic. Reason for development: mechanical damage (both single and permanent). Additional reasons developments are: improperly formed bite/excessive use of tobacco products (has a constant irritating effect on the tissue)/mechanical damage to the teeth.
- Candida. . Reason for development: an increase in the number of yeast-like fungi Candida in the mouth. An abnormal amount of fungi in a child’s body can be caused by a decrease in the protective function of the immune system (for example, after prolonged use strong antibiotics, hypothermia, worsening conditions external environment and other things).
- Aphthous. Reason for development: penetration of a foreign object into the oral cavity.
- Herpetic. Reason for development: weakening general level immunity, which is fraught with the development of the herpes virus on the mucous membranes of the mouth. A single manifestation (or any herpetic manifestation) indicates the presence of an incurable virus in the body. A person can only suppress the symptoms of the virus once. With a subsequent deterioration in health, herpes will appear again.
- Allergic. Cause of development: any type of allergen that has an adverse effect on an individual organism.
- Bacterial. Reason: development of staphylococcus and streptococcus in scratches and wounds in the mouth.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease may vary depending on individual characteristics the patient’s body, the degree of damage to the mucous membrane, types of stomatitis.
- Formation of ulcerative formations.
- White (grayish) coating around the ulcer.
- Slight swelling of the cheek. Swelling and redness may occur.
- Formation of a red halo around the ulcer. Formation of a white film inside the inflammation.
- Discomfort, painful sensations in the mouth. Difficulty chewing.
- Characteristic unpleasant odor from the oral cavity.
- Bleeding gums.
- A sharp increase in body temperature. Enlarged lymph nodes. General deterioration state of the body. Decreased performance.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of an adult and child's body is identical. After a thorough review of the medical history and general examination of the patient, the doctor begins a visual examination of the mouth. Special tests or laboratory research for does not exist. The process consists solely of visually determining the stage of the disease and determining possible reason its development.
Based on the symptoms indicated by the patient, the location of the ulcer formation, its size and shape, the specialist forms a medical opinion.
Therapy
Conservative therapy
Therapy consists of several blocks:
- drug treatment (administration of oral medications);
- local treatment (use of gels, ointments, powders, rinses against stomatitis);
- laser treatment (optional, most often used for adult patients).
The drug course of treatment consists of taking the following drugs:
- antiviral;
- painkillers (as needed);
- antifungal;
- antibacterial;
- immunomodulatory + vitamin complexes.
The exact name, dosage, and therapeutic course of administration can only be prescribed by the attending doctor, based on individual data about the patient. The time frame of the therapeutic course depends on individual indicators organism and type of disease. On average, treatment for stomatitis that forms in the mouth lasts 1-2 weeks.
ethnoscience
In some cases, qualified specialists recommend stopping using medications for minor forms and manifestations of stomatitis. This is done so as not to have an unnecessary inhibitory effect on the internal microflora and the level of immunity. Alternative conservative treatment- comprehensive home therapy. Home therapy consists of:
- rinsing with solutions and decoctions from medicinal herbs, berries, fruits, vegetables;
- rubbing the mouth with oils;
- special compresses that are applied directly to the inflammatory focus;
- applications medicinal herbs, vegetables, fruits to the source of inflammation;
- reception vitamin complexes and biologically active additives to stabilize body systems.
What happens if there is no treatment?
Lack of treatment can cause irreparable harm to the body in the following cases:
- too much damage to internal tissues;
- pronounced symptoms of the disease, which blocks the normal functioning of the body;
- severe cases of stomatitis, which can provoke the development of additional pathologies. This is fraught sharp decline immunity, its vulnerability.
In mild forms of the disease, provoked, for example, by non-compliance with basic hygiene standards, stomatitis can “heal” on its own. The main rule: if you decide not to treat stomatitis pharmaceutical products, try to limit re-exposure to the primary pathogen as much as possible. In the absence of an irritant, the wound will begin to heal, the microflora of the body will return to normal, protective function immunity will be restored. At the same time, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle in order to supply the body with everything necessary to independently fight the infection.








