Any disorder in the functional activity of the digestive tract indicates problems in the body. But when abdominal pain, diarrhea and heat, such a symptom complex should cause alarm. It indicates the development of an infectious process in the body - food poisoning, dysentery or another serious disease.
Both adults and children can be susceptible to this condition. In each case, immediate medical attention will be required; the severity of the pathology may increase in a matter of minutes.
Main signs of intestinal infection
To the beginning pathological process, developing inside the body, is preceded by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the intestines. Their spectrum is quite wide; their origin can be viral, fungal, but more often - bacterial.
Children suffer from the disease after pathogens enter through oral cavity from toys, contaminated fruits and vegetables, furniture, and animals. In adults, the pathological phenomenon is caused by eating low-quality (expired) foods and drinks, lack of proper processing of fruits and vegetables, and as a result of non-compliance with personal hygiene rules.
Depending on the nature of the infection, the pathogen, penetrating through the oral route, reaches the intestine and, settling on its mucous surface, begins to multiply and function, causing numerous symptoms. After a certain incubation period (the time period from the moment the microorganism enters the digestive tract until the first signs appear), the person begins to experience the first changes: he has a stomach ache accompanied by diarrhea and fever.
It is impossible to predict how pronounced the manifestations will be in the future, but the lack of treatment in some cases can cause fatal outcome. The degree of intoxication depends on several factors. Among them:
- General state of immunity.
- Presence of concomitant diseases.
- The number of pathogens that have entered the body.
- Individual characteristics of the microorganism.
- Patient's age. Pain and discomfort of the child are more intense.
 Diarrhea can be not only the human body’s reaction to attacks by intestinal pathogens, but also the result of uncontrolled use of certain medications: antibiotics, antifungal drugs, and medications made on a plant basis. But in this case, intestinal disorder is observed separately, without developing symptoms such as hyperthermia; noticeable abdominal cramps; nausea; vomiting of undigested food, bile or blood; dizziness; fainting.
Diarrhea can be not only the human body’s reaction to attacks by intestinal pathogens, but also the result of uncontrolled use of certain medications: antibiotics, antifungal drugs, and medications made on a plant basis. But in this case, intestinal disorder is observed separately, without developing symptoms such as hyperthermia; noticeable abdominal cramps; nausea; vomiting of undigested food, bile or blood; dizziness; fainting.
Types of intestinal diseases
If the patient has not previously been bothered by chronic diseases, for example, cholecystitis or peptic ulcers, and their exacerbation cannot be expected, then we are talking about intoxication, the cause of which can only be determined by a specialist.
The doctor interviews the patient to collect the most accurate anamnesis - information about the condition preceding the onset of the disease. He finds out what the patient ate, when he noticed the first deterioration in health, and how they manifested themselves. Characteristic symptoms- abdominal pain, diarrhea and fever - manifests itself wide range diseases.
Diarrhea
Acute diarrhea is a temporary condition that can be easily corrected if promptly addressed therapeutic measures by contacting your doctor. Typical bacteria can cause the disease. Then the patient needs to take drugs that strengthen the intestinal walls; means that normalize microflora; enterosorbents (the most famous of them is activated carbon).
It is necessary to maintain bed rest and normalize water balance. This will help avoid dehydration, especially if the disease is accompanied by excessive vomiting. It is important to observe symptoms. With a correct diagnosis and well-designed treatment, complications such as:
- admixture of pus in stool;
- increase in body temperature to high values;
- weakness;
- the presence of blood in the vomit.
If the loss of body fluid is not replenished, dehydration occurs over time, which is manifested by increased heart rate, decreased blood levels. blood pressure, dry mucous membranes.
Dysentery
The disease affects both adults and children. The infection is not transmitted by airborne droplets or contact, so it can be avoided. For the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to consume only purified water, process food efficiently, and pay attention to Special attention hygiene, hand care.
The pathological process is manifested not only by stomach pain and diarrhea. There is a steady increase in body temperature, there is vomiting, general malaise, and the stool becomes watery. The symptoms are not much different from those that develop during acute diarrhea, and therefore require differential diagnosis with the help of a specialist.
 Products can accumulate toxins as they expire. This process accelerates in warm time of the year. Warmth is beneficial for the active growth of bacteria. This is why there are more food poisoning cases in the summer.
Products can accumulate toxins as they expire. This process accelerates in warm time of the year. Warmth is beneficial for the active growth of bacteria. This is why there are more food poisoning cases in the summer.
The body's natural reaction to the ingestion of toxic substances is diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, weakness, active intestinal motility. Providing first aid involves gastric lavage, taking enterosorbents, and calling a doctor.
Regardless of the intensity of the manifestation of the infectious process, it is not recommended to take analgesics without permission, before the doctor arrives, since the abdominal cavity can also hurt in case of appendicitis. Install this life-threatening the condition will be more complicated if the attack is stopped.
Treatment
Therapy involves A complex approach. If the condition is caused by food poisoning, gastric lavage is performed, tonics and vitamins are prescribed, and the body is detoxified through saline infusion.
Bed rest is mandatory. Depending on the severity of the disease, it is possible that hospitalization will be required, especially if we are talking about a child.
Dehydration is corrected by normalizing the water balance and administering solutions intravenously.
A condition like acute diarrhea, are not treated with antibiotics. You will need to take products that have enveloping properties and adsorbents, as well as normalize your diet (fasting is not recommended).
It is important to understand that self-medication is dangerous to health. Only a specialist can prescribe examination and therapy.
Very often, with diarrhea, abdominal pain appears and a high temperature rises (from 38 degrees and above). These symptoms are typical for gastrointestinal disorders. But diarrhea and abdominal pain can cause inflammatory processes in the stomach or intestines, in chest, pathologies of the kidneys and biliary tract, some abnormalities nervous system. The intensity of diarrhea and other symptoms depends on the location of the pathology. When making a diagnosis, all the patient’s complaints are taken into account. Accent diagnostic examination is done to clarify the development processes of all pathological sensations.
It is precisely the accurate transfer of their condition to patients that helps doctors diagnose accurate diagnosis, therefore, each of us must learn to clearly formulate our pain sensations, be able to explain where exactly the discomfort is felt in the abdomen, how often loose stools appear, when the temperature begins to rise.
The intensity of discomfort in the body may vary. The scale of manifestation depends on the reasons for its appearance. Any abdominal pain may be:
- Barely noticeable.
- Causing constant discomfort.
- Moderate.
- Expressed.
- As strong as possible.
Making a diagnosis is much easier if the patient gives the most full description discomfort in the abdomen, explains what it looks like and where it is located. The stomach always hurts in different ways. Sometimes with diarrhea, pain appears in the abdomen, discomfort can spread horizontally and go to the back. Wandering or moving pain in the stomach is considered dangerous. According to the nature of the severity, abdominal pain with diarrhea can be cramping, constant, dull, aching, bursting. Severe pain often literally burns the stomach and compresses all the insides.
Doctors divide stomach pain into:
- spicy;
- chronic.
It is not difficult to distinguish these symptoms from each other. Acute abdominal pain is intense, but not for long (no more than a day). Chronic abdominal pain bothers the patient for long period time (week, month, year), significantly worsening a person’s quality of life. When collecting anamnesis, doctors will definitely try to find out the time of occurrence of stomach pain. For some, they appear immediately after eating certain foods or after diarrhea; for others, during high physical activity, in still others, during long periods of hunger. It is important to note, if you have diarrhea at night, what it is accompanied by: high fever or severe pain.
Illnesses with diarrhea, abdominal pain and fever
When all these signs appear together, they can be harbingers of many diseases:
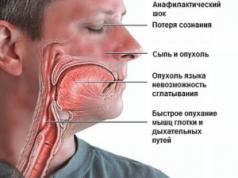
The source of the malaise can be recognized using differential diagnosis. The presence of an ulcer is indicated by the fact that discomfort begins half an hour after eating. With appendicitis, pain occurs in the right side, in its lower section, closer to the groin. It intensifies if you sharply press on the uncomfortable area and then release your hand. Please note that loose stools do not always occur with appendicitis, but nausea and high fever almost always accompany inflammation. Severe diarrhea is possible only in one case, when appendicitis begins against the background of a violation of the evacuation function of the intestine.
When does diarrhea, stomach pain and fever of 38° occur?
High temperature (38 degrees) with diarrhea is observed in the following cases:
If the patient complains of diarrhea and abdominal pain, and the malaise is accompanied by sharp increase fever and vomiting, if a person is constantly feeling sick, one can suspect food poisoning. There are several reasons for this:
- Pathogenic bacteria.
- Viruses.
- Fungi.
- Chemical reagents.
Each specific case has its own symptomatic complex. So, for example, when the cause of poisoning is bacteria and microbes, diarrhea and very severe nausea appear immediately, two hours later, after the contaminated product enters the stomach. Viral intoxication begins to manifest itself only after twelve hours. In case of poisoning caused by a chemical reagent, diarrhea and high fever, severe pain in the abdomen, as well as nausea and weakness that paralyzes movement appear 30 minutes after poisoning. Such knowledge helps you find your bearings in time and call an ambulance.
Fever, diarrhea and abdominal pain - probably each of us has encountered such ailments at least once in our lives. They greatly aggravate daily life and bring a lot of inconvenience and discomfort. Many people try to independently answer the question: why these conditions arise, and, therefore, begin to treat them according to their own understanding. In fact, there are many reasons and it is absolutely forbidden to self-medicate, because... you can start the disease.
In this article we will figure out what can cause such signals from the body.
Main reasons
The main reasons why the stomach hurts and diarrhea appears in an adult or child are diseases of an infectious or non-infectious nature. They are often accompanied elevated temperature and general malaise.
The problem of the 21st century is poor nutrition and, as a result, diseases of a non-infectious nature, i.e. disrupting the structure of the gastrointestinal tract and their functions. This is primarily due to quick snacks, which have become a part of everyday life.
No less terrible are diseases of an infectious nature that arise as a result of people’s lack of the habit of washing their hands after coming home, using the toilet, before eating and other basic hygiene rules against the backdrop of ever-increasing migration, with which new, hitherto unknown viruses are coming to countries.
Since each type of disease has many characteristics, they will be discussed in detail in this article.
Infectious diseases
All infectious diseases gastrointestinal tract arise due to the influence of an external pathogen. These are bacteria and viruses, which, when they enter the intestines, begin to actively multiply and poison the body with waste products. In rare cases, the microorganisms themselves cause ulcers, thinning of the intestinal walls and other changes.
All diseases of this nature have similar developmental features. These include:
- The incubation period differs significantly between bacterial and viral forms of the disease. If in the latter it can last up to two, in rare cases three days, then a bacterial infection can manifest itself within 1-2 hours after entering the intestines.
- The clinical manifestation of the disease is accompanied by pain, diarrhea, and often vomiting. Peculiarity infectious diseases is that they are accompanied by a sharp increase in body temperature, reaching 38-40 degrees C.
- After the manifestation of clinical signs, an active fight against foreign organisms begins. But often strength immune system not enough, since the human intestine contains great amount nutrients for the causative agent of the disease. Therefore, at the first symptoms of an infectious gastrointestinal disease, you should consult a specialist.
- Recovery period. This event was marked by a decrease in temperature to normal indicators, cessation of abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea. However, after the symptoms disappear, there is a long recovery process ahead.
As you can see, all infectious diseases have a similar development pattern, but still, each of them has its own distinctive features that are unique to it.
Here are just a few common infectious diseases that you need to know in detail:
- Food poisoning
- Intestinal infection
- Dysentery
- Enteritis and colitis
Food poisoning
All poisonings are infectious in nature. However, they are divided into bacterial and viral. Distinctive feature bacterial form is a rapid manifestation clinical symptoms. This is due to the fact that toxins (the waste products of bacteria) are already present in large quantities in food. While viral poisoning manifests itself no less than 12 hours later (the virus needs to accumulate colonies in a person).
The external symptoms of both bacterial and viral poisoning are the same, the difference lies in the severity of the manifestations.
Acute poisoning is accompanied by vomiting, severe pain in the abdomen, as a rule, the right side hurts ilium, also frequent pain occurs in the colon (projected to left side lower back). Feces have light color, liquid consistency and characteristic pungent odor. Headaches and fever may occur. This condition is treated with rinsing, drinking plenty of fluids and diet.
There are also cases of mild poisoning, when a person does not experience pain or other ailments. The only thing that worries him is diarrhea, which is severe bad smell, but is not as frequent as with acute poisoning. Such cases occur quite often. They indicate the body’s ability to cope with infection on its own: with the help of diarrhea, pathogenic microorganisms are urgently eliminated. You can only help him by drinking plenty of fluids and abstaining from eating food for 1-2 days.
Intestinal infection
This concept includes many diseases of a viral nature. Rotaviruses, astroviruses, adenoviruses and many other viral forms can cause illness.
Infection most often occurs by airborne droplets, but it can spread through food. Since the virus has a capsid (a special protective shell), it can long time be outside the host's body.
A distinctive feature is the localization of the pathogen in the small intestine, less often in the large intestine. Since the stomach has natural protection - hydrochloric acid, the virus passes through it in an inactive form. After entering the place of its future breeding, at least 24 hours must pass for the population to increase in order for the organism to notice it. After this, the body temperature rises to 40 degrees, which indicates the beginning of the immune system’s struggle. This is accompanied by frequent diarrhea, as the body thus tries to wash the infection out of itself. Vomiting occurs less frequently with this disease. Pain occurs in the epigastric region. Also, pain can change its location throughout the gastrointestinal tract. This is due to intestinal spasms (where there is spasm, pain occurs). Feces have a characteristic liquid consistency, a pungent odor and are often light in color (comparable to the color of clay).
At the onset of an intestinal infection, it is best to consult a doctor who will take stool tests to rule out the possibility of a bacterial infection, and also prescribe a strict diet and medications to help the body cope with a viral infection, for example Enterofuril.
Everyone knows that diarrhea causes dehydration, so the sick person should increase the amount of fluid they drink. The best option in this case would be a simple boiled water or unsweetened tea. During the illness, it is better to refuse food, since it will give the pathogen “soil” for development and delay recovery. If there is no vomiting, you can use
or activated carbon.
Dysentery
A dangerous disease of infectious nature. The causative agent is the dysentery bacillus, hence the disease bacterial nature. Has such signs as: very frequent diarrhea, weakness, general malaise. At acute form the stomach begins to ache in a cramping manner (pain occurs in the iliac regions, along the white line of the abdomen and in the navel area), worsens general state, tachycardia occurs, body temperature rises to 40 degrees. Dysentery is marked by a very pungent, often putrid odor of feces. During long-term treatment, the person defecates with water containing the same odor.
The danger is that the bacteria takes some time to grow a colony, in other words incubation period lasts several days (usually 3-4 days, it all depends on the body’s immune system), and as a result, the disease takes a person by surprise, without previously visible signs. Dysentery is called the disease of dirty hands. From the name it is clear that the stick is transmitted through dirt on the hands. It is found much less frequently in contaminated food products.
If there are obvious signs of dysentery, you should call an ambulance. The disease has a pronounced infectious nature and is dangerous both for others and for the sick person. Therefore, it is treated in the infectious diseases department under the strict supervision of a doctor, in contrast to outpatient treatment of intestinal infections.
Enteritis and colitis
These diseases have much in common and differ only in localization: enteritis in the small intestine, colitis in the large intestine. Both diseases are accompanied by periodic pain, and in the acute form, constant pain. The reasons for this are the presence of bacterial or viral infection(typhoid, cholera), which disrupt intestinal function.
The secretion of the small and large intestines is disrupted due to inflammation of the mucous membrane. The ability to absorb nutrients is lost. It can also lead to disruption of intestinal motility. In this regard, a person suffers from light sand-colored diarrhea with a pungent odor. Each bowel movement is accompanied by acute pain in the lower abdomen, and when the disease degenerates into chronic form the pain becomes constant and dull.
Diagnosis occurs in several stages:
- First of all, the attending physician collects anamnesis and interviews the patient, percussion and auscultation.
- To confirm the primary diagnosis, a coprogram, an x-ray, endoscopic examination, functional study for dysbacteriosis and a biochemical blood test to determine the presence of malabsorption.
Inpatient treatment of the disease includes lavage and antibacterial or antiviral treatment. This happens in acute cases, when there is a risk of intestinal atrophy with subsequent infectious process leading to ulcers. At home treatment This means drinking plenty of fluids, taking medications that enhance intestinal motility, and eating any astringent foods.
Non-communicable diseases
There are enough diseases that are caused by external factors, not related to infection. Their occurrence is often associated with a person’s negligent attitude towards his own body - frequent snacks on the go, lack of adequate nutrition and timely examination by a specialist. Exacerbation chronic diseases accounts for about a third of all non-communicable diseases. At the same time, there are often cases when diseases of other organs not related to the digestive process are the causes of gastrointestinal disorders.
Abdominal form of myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction occurs due to myocardial vasospasm. Its abdominal form occurs with spasm from the diaphragm. Of course, the heart attack itself has many associated factors such as:
- Genetic predisposition
- Obesity
- Alcohol abuse
- Tobacco smoking
- Passive lifestyle
This form of heart attack is dangerous because it has clinical signs similar to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Accompanied by sharp, cutting pain in the stomach, spleen and liver. The reason for this is irritation vagus nerve, which can cause headaches, nausea and diarrhea (it's worth noting that the frequency of bowel movements will vary for each person). The stool has a liquid consistency and is lighter in color than normal. However, it does not have a sharp putrid smell, as in case of poisoning or other infectious diseases. The condition is also accompanied by increased blood pressure, tachycardia and bloating.
In order to diagnose abdominal myocardial infarction, it must be differentiated from diseases such as:
- Enteritis
- Cholecystitis
- Pancreatitis
This form of heart attack can be distinguished using the methods indicated below:
- Anamnesis is collected: patient complaints and cases of heart attack in the family. The latter plays a big role, since often, if close relatives have had a heart attack, the patient is immediately included in the risk group. First of all, this is done in elderly patients, since all of them, without exception, are at risk.
- The final diagnosis is made after an ECG, MSCT and coronary angiography. In rare cases, with an abdominal form of myocardial infarction, blood is taken for analysis.
A distinctive feature of the disease is that after some time (from 12 hours to 8 days), it flows into its usual form.
Myocardial infarction is treated in a hospital setting. The patient is placed in intensive care unit, where doctors stabilize his condition. Afterwards he is transferred to a regular ward. For the first three days, you must observe strict bed rest (you cannot sit down and it is undesirable to roll over). During 2 weeks of inpatient treatment, medications are prescribed: beta blockers, statins, nitrates, Aspirin, Clopidrogel. A doctor should prescribe supplements that strengthen the heart muscle. Required: magnesium, coenzyme Q10 and L-carnitine. The patient continues to take the medications selected in the hospital after being discharged home. In this case, it is necessary to follow a salt-free diet, give up fatty foods, alcohol and smoking, and limit physical activity.
Gastritis and ulcer
Today, gastritis, or rather its catarrhal form, and, as a consequence, gastric and duodenal ulcers are very common diseases. This is due to poor nutrition, namely the abuse of fatty and spicy foods. The disease is non-infectious and occurs due to thinning of the stomach walls and loss of their functions.
The first stage of the disease is gastritis, accompanied by periodic paroxysmal pain in the epigastrium. Any spicy, fried or fatty food increases these pains and provokes diarrhea, characteristic feature which is a lighter color and the presence of undigested foods. In the absence of treatment and non-compliance with the diet, an ulcer develops against the background of gastritis.
Essentially, an ulcer is a severe thinning of the wall of the stomach and intestines, followed by hemorrhage and loss of cell function. The advanced form is considered to be a perforating ulcer (a through hole in the stomach or intestines). This disease can cause very strong, burning, cutting pain, from which a person can lose consciousness. If an ulcer is detected, immediate hospitalization is required, followed by drug treatment and strict adherence to a diet excluding fatty and spicy foods, baked goods, alcoholic and carbonated drinks. Particularly severe cases - exacerbation (open ulcer) or perforation - require surgical intervention.
These diseases are diagnosed primarily by palpation. To confirm the disease, gastroscopy and FGDS (helps to distinguish an ulcer from gastritis), and x-rays are used. A biopsy is ordered for chemical analysis gastric juice.
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendage of the cecum has many causes. One of the most common is poor nutrition and, as a result, disruption of intestinal microflora and motility. In this regard, stool stagnates and accumulates in the cecum. Without proper treatment with microorganisms, they become dangerous to the human intestines. Since the appendix is a concentration of lymphoid nodes, it primarily responds to such accumulations with inflammation. This may subsequently be aggravated by an infectious process.
Appendicitis does not involve uncontrollable bowel movements or vomiting. A distinctive feature is severe pain in the area of the right ilium, projected to the groin area.
Inflammation can only be prevented by a balanced diet and taking care of your own health. Otherwise, appendicitis, which can only be treated surgically, that is, deletion cannot be avoided.
What to do?
In any case, even with mild pain or just regular diarrhea, it is best to consult a doctor. Since only a specialist will be able to understand the nature of the disease and prescribe proper treatment. Often behind chronic pain, to which a person gets used very quickly, there are dangerous diseases, having serious consequences.
If any sharp pains in a stomach,
and/or high temperature - you must call an ambulance.
Until she arrives, the patient needs to be provided with rest, a cold compress on the head, and if there is a high temperature, drink plenty of fluids.
Under no circumstances should you:
- take no medications on your own, incl. analgesics, as this may worsen the situation;
- apply a warm compress to sore spot, because it can increase inflammation;
- eat food so as not to increase the load on the gastrointestinal tract.
Prevention
It is best not to bring your body to a painful state due to the fact that any disease has far-reaching consequences for the body and can remind itself in old age.
The following preventive measures will help avoid the above-mentioned diseases:
- Eat right, i.e. limit fatty and spicy foods in your diet; fiber should be a priority;
- To live an active lifestyle;
- Do not abuse alcohol and tobacco;
- Avoid fast food;
- Eat only in proven places to avoid poisoning;
- Observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- Avoid contact with a sick person or do this only when absolutely necessary, taking precautions;
- Check the quality of food products;
- Check your health regularly with specialists.
By observing these simple rules, you can avoid serious diseases, which often become chronic. Any of the above diseases imposes dietary restrictions for the rest of your life. Therefore, it is better to regularly take care of your health than to sit on it all your life. therapeutic diet, limiting yourself in everyday foods.
If the disease does occur, then you should follow all the instructions of your doctor. This will allow you to recover as early as possible, undergo rehabilitation many times faster and return to a full life. Moreover, a responsible approach to treatment reduces the chance of relapse to a minimum.
The presence of symptoms such as:
- Stomach ache
- smell from the mouth
- heartburn
- diarrhea
- constipation
- belching
- increased gas formation (flatulence)
If you have at least 2 of these symptoms, then this indicates a developing
gastritis or ulcer.
These diseases are dangerous due to the development of serious complications (penetration, stomach bleeding etc.), many of which can lead to
outcome. Treatment needs to start now.
Read the article about how a woman got rid of these symptoms by defeating their main cause using a natural method. Read the material…
The appearance of diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain is a set of alarming signs that make patients worry about their health and experience quite severe discomfort.
It should be noted that such phenomena can be symptoms of many diseases, and therefore, before starting treatment, it is necessary to first determine the cause of abdominal pain, diarrhea and fever. Sometimes nausea and vomiting are added to this list. When determining a diagnosis, it is important to take into account all aspects and signs of illness.
If a patient complains of abdominal pain and diarrhea, then most likely he is developing a disease of the digestive tract. The cause of such symptoms can be a number of pathologies:
- Peptic ulcer stomach or duodenum. In this case, abdominal pain and diarrhea appear after eating food, after about two hours or less. The signs are especially pronounced if you have eaten sour or spicy foods.
- Pathological process in the intestines. There is also diarrhea with periodic pain that has the nature of contractions.
- Appendicitis. Most a clear sign such a disease – pain with right side lower abdomen. Stool disorders are observed quite rarely, only if there is an inflammatory process in the cecum.
Advice! Before a specialist arrives, you can use painkillers to relieve symptoms, as well as a warm heating pad or, conversely, cold objects. These remedies will help alleviate the general condition of the body and reduce pain.
What do abdominal pain, diarrhea and fever mean?
If an adult or child experiences symptoms such as fever, diarrhea and stomach pain, you should immediately consult a doctor. High body temperature in itself is alarm signal, and in combination with diarrhea is a sign of an intestinal infection. Of course, there are other factors that can have an impact, however, in any case, you need to check with a specialist.
Particular attention should be paid if the child has a stomach ache and a high temperature. These signs may indicate the following pathologies:
- Infectious bowel disease. This pathology caused by entering the body pathogenic microflora, viruses, rotaviruses, astroviruses, enteroviruses and so on. In addition to diarrhea and abdominal pain, other symptoms may also occur. associated symptoms, for example, nausea, vomiting, general weakness and high fever. If such symptoms are detected, it is recommended to immediately call a doctor, or go to an appointment yourself, if possible. Until an accurate diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed, you need to stop eating and drinking. more water to prevent dehydration. If observed frequent vomiting, you can also connect a solution of Regidron or salt with soda. In addition, you can use activated carbon or Smecta to remove toxic substances from the body.
- Dysentery. For of this disease characterized by pain in the stomach or abdomen, which is accompanied by fever and general malaise. In addition, there is diarrhea and a headache. Since dysentery is an infectious disease, the patient is treated under the strict supervision of a doctor in a hospital. Therefore, if such signs are detected, it is necessary to urgently call a doctor.
Important! You need to react especially quickly if a child has abdominal pain, which is accompanied by diarrhea and high fever. A child's body is more difficult to resist infections, so help must be provided as quickly as possible.
What to do if you have abdominal pain, diarrhea and vomiting?
If abdominal pain in a child or adult is accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea, it is likely that the cause of the symptoms lies in the following diseases:
- Enteritis. This disease is an inflammatory process concentrated in the small intestine. In addition to these signs, patients may also experience dehydration and intoxication. The cause of inflammation is poor nutrition, exposure to medicines intolerable by the body, hypothermia, infectious diseases, insufficient intake of protein and vitamins, which leads to disorder of the small intestine and the inability to perform a number of functions in this part of the digestive tract.
- Food poisoning. When the body is intoxicated due to the consumption of low-quality products, the patient, as a rule, notes that he has a stomach ache and diarrhea. The process may also be accompanied by vomiting and aching pain in the abdominal area. Poisoning can be not only food, but also viral and chemical. With the latter option, dizziness, severe headaches and even loss of consciousness may occur.
- Colitis– a disease that most often affects children. As a rule, a child has a stomach ache with this pathology. The stomach area may also hurt as harmful bacteria enter it. Over time, the child’s temperature rises, and bloody inclusions and mucus are noted in loose stools.
It is simply impossible to determine the nature of the disease on your own, since this requires a series of laboratory research. That is why experts always recommend that if you detect the slightest signs of infectious diseases in the intestines, seek help from a doctor. This is especially true for cases accompanied by high body temperature.
The closest attention should be paid to the child if he has vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain and fever. IN children's body Dehydration sets in faster, and it is much more difficult for him to fight viruses and bacteria. Self-medication is strictly prohibited in such cases.
Doctors state that they are most often called in connection with complaints of severe abdominal pain with a significant increase in temperature. Often such sensations are concentrated at the bottom or in the center abdominal cavity, so it is not always easy for a specialist to immediately make a diagnosis. Sometimes dyspepsia, diarrhea or constipation, severe flatulence, and lightheadedness are noted.
The doctor must fully analyze the entire set of symptoms. Observed pathological signs may indicate both the presence of infection and the development of severe inflammatory diseases. Therefore, the specialist needs to decide whether to hospitalize the patient and, possibly, prescribe an emergency operation. This is a very responsible task that requires a lot of experience and knowledge.
Diseases digestive system are quite difficult. They are accompanied by a certain set of symptoms, from which we can immediately say that the problem lies in damage to some organ of the gastrointestinal tract. Usually in such cases urgent treatment is required.
Most often, abdominal pain, high temperature (38-39), nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, etc. are observed.
Most often, such symptoms accompany:
- Acute appendicitis;
- stomach ulcer;
- acute cholecystitis;
- hepatitis;
- acute pancreatitis;
- duodenitis;
- peritonitis.
With these diseases, pain in the abdominal cavity is observed, localized in the side or spread throughout the abdomen, belching, vomiting, and fever. These symptoms do not go away and even worsen over time.
In this case, there may be blood in the vomit, urine, or other secretions. Therefore, the patient requires a complete diagnostic examination.
When the stomach hurts and the temperature is 38-39, then severe gastritis, poisoning or peptic ulcer can manifest itself. It should be borne in mind that discomfort can spread to the entire abdominal area.
Therefore, it is better to contact a gastroenterologist, especially if the pathology has already been diagnosed earlier. You shouldn’t wait for everything to pass or hope for the so-called “ folk remedies" Exacerbation threatens perforation of the stomach ulcer and further development of peritonitis. These conditions already threaten the patient's life.
If the intensity of the symptoms is high and the person cannot get to the clinic, it is necessary to call an ambulance. The arriving team of specialists will assess his condition and take him to the emergency hospital. There, a gastoenterologist or surgeon will conduct an examination, make a diagnosis and decide on further hospitalization. Perhaps in in this case surgery will be required.
Emergency conditions
If the stomach hurts and the temperature is 38 in an adult, these symptoms should be alarming in any case. Under no circumstances should such manifestations be ignored.
Even if the discomfort is not too pronounced, the fever has appeared only recently, but other symptoms are present warning signs, you cannot postpone calling a doctor. In the absence of timely medical care, everything can end in the death of the patient.
This becomes especially important when there are emergency conditions. Typically they include unbearable pain in a stomach, strong increase fever and vomiting.
In such cases, there should be no self-medication or self-diagnosis. An ambulance should be called immediately after such symptoms occur.
Most often, such severe conditions develop with the following dangerous diseases.
Acute appendicitis
Pain occurs in the abdominal cavity, continues for quite a long time, then concentrates in the right hypochondrium. Sometimes the pain is diffuse and can appear in a variety of places.
However, most often the patient has pain in the lower abdomen and a temperature of 38-39, there is severe vomiting, nausea and lightheadedness, and sometimes fainting occurs.
Fever indicates the development of a strong inflammatory process. Such a serious condition can progress very quickly, leading to the appearance of an abscess, and then peritonitis.In this case, it is advisable for the patient’s relatives to remember in detail what preceded the attack in order to correctly explain everything to the visiting team of specialists.
The human condition is usually quite severe. He lies bent over and may vomit. Sometimes he remains unconscious. The doctor examines him, palpates the abdominal cavity, prescribes clinical analysis blood.
In this case, pronounced leukocytosis and significant increase in ESR. Then urgent surgical intervention, which is a necessity.Peritonitis
It is characterized by a complication of an inflammatory or purulent process in the abdominal cavity and may be a consequence
- Appendicitis;
- intestinal abscess;
- injuries;
- thrombosis;
- rupture of the gallbladder or cyst;
- malignant neoplasm;
- complications of peptic ulcer or urolithiasis;
- acute pancreatitis;
- violation of asepsis rules in the postoperative period.
Peritonitis is characterized by severe pain in the abdominal cavity, high fever, pale skin, a sharp drop in blood pressure, and confusion. One of his most characteristic features there is a strong tension in the abdominal muscles, so that they practically become stiff. It is impossible to palpate the patient's abdomen in this condition.
Before the ambulance arrives, it is necessary to lay him on his back, provide him with the opportunity to freely separate the vomit, and place an ice pack on the painful area. In this case, immediate surgery to save the patient's life.Acute pancreatitis
With this disease, the pain is diffuse at first, and then localized in the left side or has a girdling character. Very often she gives it to the back. The patient is severely nauseous and vomits.
Body temperature is significantly increased. Symptoms become most intense three days after the onset of the disease. She requires urgent hospitalization in a surgical hospital.
Acute jade
Its main manifestations are severe abdominal pain and high fever. Differential diagnosis can be made by tapping the kidney area. Such touches result in severe discomfort in the lower back.
With this disease, the patient complains of urine retention, darkening, and unpleasant odor. It threatens severe intoxication of the body and the development of uremia.
Very rarely, such symptoms can hide a harmless condition. High temperature, severe and aching pain themselves indicate a sharp disadvantage. Therefore, the patient should not be given any medications.
They will not only complicate the diagnosis, but can even lead to death.
Abdominal pain and a temperature of 38 may indicate very serious conditions requiring emergency care. At the slightest suspicion of the development of the listed pathologies, one cannot wait further development events. An ambulance should be called as soon as possible.
Infectious diseases
Most often, pain in the abdominal cavity combined with fever occurs with infections of the digestive system. This is explained by the rapid proliferation of pathogenic microflora with the simultaneous release of toxins and decay products of their vital activity into the blood. Therefore, such pathologies affect the entire human body.
Abdominal pain, vomiting and temperature 38-39 are manifestations of almost all infectious diseases and poisonings. In this case, you should also not self-medicate.
This is how they most often manifest themselves:
- Salmonellosis;
- hepatitis;
- dysentery;
- food poisoning;
- infection with staphylococcus;
- rotavirus infection;
- botulism;
- cholera.
 When they occur, most often the patient complains that he has pain in the lower abdomen and a temperature of 38-38.5. These infections are characterized by general intoxication of the body, severe diarrhea, headache.
When they occur, most often the patient complains that he has pain in the lower abdomen and a temperature of 38-38.5. These infections are characterized by general intoxication of the body, severe diarrhea, headache.
A person's stomach tightens so much that he is unable to bear it. After visiting the toilet, the pain goes away a little, but soon returns. The stool is usually loose, with mucus, pus, or even blood.
In this case, the patient needs urgent help doctor Most often, he needs urgent hospitalization not only to preserve his health and life, but also to stay in quarantine. These diseases are often extremely contagious. Most often they affect people with reduced body defenses.
In this case, you also cannot wait for a possible improvement; you should urgently call an ambulance.
While waiting for her, it is necessary to remember what the person ate or drank the day before, whether he swam in questionable bodies of water or visited places that did not meet sanitary requirements.
In such cases, it is necessary to take the patient’s stool for analysis, including culture to determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
It is after this that it is possible to assign the most effective drugs. The person must remain in hospital until complete absence in the results of studies of any colonies of pathogenic microorganisms in order to exclude cases of possible carriage.
Helminthiasis
Often severe pain in the abdominal cavity with a significant increase in temperature is caused by helminthic infestations. The most common among them are:
- ascariasis;
- giardiasis;
- opisthorchiasis;
- echinococcosis;
- hookworm disease.
 Helminth infections are characterized by severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. In addition, the patient may experience yellowing of the skin, chills, and sudden changes in mood.
Helminth infections are characterized by severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. In addition, the patient may experience yellowing of the skin, chills, and sudden changes in mood.
Danger helminthic infestations is that they may not show themselves for quite a long time.
The symptoms are mild, and the pain is rarely severe. The threat is development dangerous complications in the absence of medical care for an extended period.
Therefore, you need to consult a doctor even during the period when symptoms subside. At this time, helminths do not disappear from the body, continuing to suck the juices out of a person, destroying his tissues and releasing their waste products into the blood.
Differential diagnosis is usually carried out by analyzing stool for helminth eggs and protozoan cysts.
If pain in the lower abdomen and temperature are observed, then a clinical blood test is usually also prescribed for the presence of eosinophils and PCR reactions to individual helminths.
Sometimes radiography is required and ultrasonography to determine damage to the liver, gallbladder and pancreas.
Pathology of other organs and systems
Abdominal pain, accompanied by a significant rise in temperature, often occurs with other diseases. These include:
- Renal colic;
- ovarian rupture;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- gynecological diseases;
- urolithiasis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- acute pyelonephritis;
- radiculitis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- myocardial infarction.
These diseases cause severe pain in the abdominal cavity, a sharp rise in temperature, significant intoxication of the body, bloody issues and so on. However, patients may complain of difficulty urinating, blood and mucus in the urine.
An attack can be especially dangerous for the patient renal colic. In this condition, severe pain occurs suddenly and becomes so unbearable that the patient is unable to bear it. This is very dangerous condition, threatening the development of anuria, or rupture of the ureter.
In such cases, it should be especially alarming that simultaneously with severe abdominal pain, there is also heaviness in the lower back, a feeling of pressure in the chest, and numbness in the limbs.
This suggests that other organs are affected. They provoke circumstances when unpleasant sensations are transferred to other areas. Very often this happens with kidney disease, female genitalia or intervertebral hernia.
For a specialist precise definition source pain is the main task. Therefore, he must examine the entire human body. If their most intense focus is felt in the abdominal cavity, then the patient may not pay attention to the pressure in the lower back, chest or back.
This is especially dangerous if he, on his own initiative, took analgesics and antipyretic drugs before the doctor arrived. In this case, immediate hospitalization is required full examination patient. You will also be interested in:When is urgent medical attention needed?
 In any case, when an adult has a stomach ache and a temperature of 38, it is better not to delay calling an ambulance.
In any case, when an adult has a stomach ache and a temperature of 38, it is better not to delay calling an ambulance.
Only a doctor can say with certainty which disease is the root cause. Usually, even a specialist requires not only an examination of the person and anamnesis, but also laboratory and instrumental tests in order to accurately make a diagnosis.
Therefore, you cannot take any action on your own, so as not to complicate further treatment.
Abdominal pain with fever is enough alarming symptom in order to treat it lightly. Therefore, before the specialist arrives, it is necessary to provide first aid to the patient and, if he is in serious condition or lies unconscious, prepare detailed story about the development of the disease for the doctor.
In general, it is best to make it a rule to contact a therapist or gastroenterologist in every case when you feel pain in the abdominal cavity, accompanied by fever. Even if the patient’s condition is satisfactory, it can quickly and sharply deteriorate. In contact with
Abdominal pain occurs for various reasons; in addition, diarrhea, fever and vomiting may accompany the pain.
Therefore, before starting treatment, it is worth determining which disease is causing certain symptoms.
Diarrhea and pain in the lower abdomen
So, pain in the lower abdomen and diarrhea can be the cause of a number of diseases:
1. Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
In this case, these symptoms appear after 30 minutes. – 2 hours after eating. Symptoms are especially pronounced if the food was spicy or sour.
2. Intestinal diseases.
The pain is usually cramping, and loose stools are also observed intermittently.
3. Appendicitis.
The pain is concentrated in the right lower abdomen; when pressing in the appendix area, the pain increases. Usually, with appendicitis, normal stool is observed, but in case of inflammation of the cecum, diarrhea is observed.
What to do:
1. Take painkillers;
2. Put warm heating pad(or cold) on the lower abdomen;
It is necessary to remember that the above procedures will be effective and safe if you consult a doctor and find out the exact causes of these symptoms. Otherwise incorrect treatment may be fraught with consequences.
Stomach pain, diarrhea and fever
1. Intestinal infection ( stomach flu, rotavirus infection, etc.)
Typically, such symptoms are observed in acute intestinal diseases. Viruses (rotaviruses, enteroviruses (noroviruses), astroviruses, adenoviruses) that enter the stomach additionally cause nausea, headaches, aches, and the body is weakened throughout.
What to do:
Until a definitive diagnosis is established, you should refrain from eating;
Not worth taking various medications(activated carbon, smecta);
You should drink more fluids;
When frequent vomiting and diarrhea are present, it is permissible to use saline solutions;
If there is no vomiting, it is allowed to use smecta, activated carbon or enterosgel.
2. Dysentery.
With this disease, diarrhea usually occurs, as well as cramping pain; with a significant exacerbation, an increased body temperature of up to 38-40 ° C is observed. The disease is also accompanied by general malaise, weakness, tachycardia and pallor.
If there are obvious signs of dysentery, you should urgently call an ambulance; the disease is infectious and therefore treatment takes place in a hospital, in the infectious diseases department under the strict supervision of a doctor.
Stomach pain, diarrhea and vomiting
1. Enteritis.
Enteritis is an inflammatory disease of the small intestine, clear signs of which the above symptoms are. In acute enteritis, dehydration, intoxication and cardiovascular disorders are also observed.
The cause of the disease is the absence or lack of the required amount of protein and vitamins in food. The absorption of food elements is impaired, resulting in a disorder in the secretory and motor functions of the small intestine.
What to do:
For this disease (if diagnosed) it is recommended:
Application of a cleansing enema;
Drink plenty of fluids;
Taking astringent drugs;
Regular, proper nutrition.
All of the above symptoms can occur with diseases such as food poisoning and colitis.
Food poisoning occurs due to consumption of stale or poor-quality food. Such food or drinks contain toxic substances of bacterial or animal origin. Poisoning, in addition to abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting and/or fever, is accompanied by nausea and general malaise.
1. Bacterial poisoning.
Diarrhea, abdominal cramps, vomiting are observed an hour after eating food;
2. Viral poisoning.
Characterized by abdominal pain and headaches, fever and chills, vomiting and diarrhea 12 to 48 hours after eating contaminated food.
3. Chemical poisoning.
The disease is accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea, increased sweating, dizziness, increased salivation. Abdominal pain begins half an hour after eating low-quality food
In this case, gastric lavage, an enema and plenty of fluids are necessary. Depending on the type of poisoning, the doctor prescribes a specific treatment.
Colitis. The disease is characterized by cramping stomach pain and diarrhea, and is also accompanied by general malaise. Acute colitis, which occurs as a result of bacteria entering the stomach, is accompanied by elevated body temperature. Loose stool often with mucus and mixed with blood.
Also, acute colitis often becomes chronic. Dull and spasmodic pain in the abdomen is observed, which often intensifies before or after bowel movement, and lack of appetite, nausea and general malaise are also characteristic. The stool is usually loose or constipated.
It is also necessary to understand that all of the listed symptoms can occur not only due to a direct disease of the gastrointestinal tract. Such symptoms may be associated with hepatitis, cystitis, various diseases female organs and etc.
In any case, you need to understand that self-medication is dangerous; it is best to contact doctors who will identify the causes of the disease and prescribe necessary medications. And only after this can we begin treatment of the disease and its immediate prevention.